DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39757
辉钼精矿的氧化焙烧
王 璐1, 4,李梦超1,阙标华1,薛正良2,张国华3,蓝文韬4
(1. 武汉科技大学 钢铁冶金新工艺湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430081;
2. 武汉科技大学 省部共建耐火材料与冶金国家重点实验室,武汉 430081;
3. 北京科技大学 钢铁冶金新技术国家重点实验室,北京100083;
4. 佛山(华南)新材料研究院,佛山 528200)
摘 要:纯氧条件下对辉钼精矿的氧化焙烧行为展开基础研究,并结合最佳模型拟合法、TG-DTA、SEM-EDS和热力学软件FactSage 7.3等方法和手段对实验结果进行分析。结果表明:精矿在723 K和773 K下不能完全氧化,然而当温度升至873 K时,精矿能完全氧化生成三氧化钼(MoO3)。在较高温度下,如873 K和773 K时,精矿的氧化焙烧过程由界面化学反应控速;然而在较低温度下,如723 K时界面化学反应和形核长大模型共同发挥作用。反应过程中,产物由初始颗粒形态逐渐转变成具有层状结构的片状形貌,并且在晶面指数(020)、(040)、(060)和(0100)等晶面上衍射峰强度显著增加,表明生成的MoO3具有一定的各向异性和择优长大倾向。辉钼精矿的氧化焙烧过程符合挥发-冷凝机理,期间伴随着少量中间产物二氧化钼(MoO2)的生成。焙烧过程中产生的烧结现象是局部温度的升高和低熔点共晶体的形成共同作用所致。结合热力学数据本文还理论分析了主要杂质元素在焙烧过程中的演变规律及其对烧结行为的影响机制,并提出有效降低烧结现象发生的可行方案。
关键词:辉钼精矿;氧化焙烧;三氧化钼;烧结现象
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-07-1952-13 中图分类号:TF841 文献标志码:A
引文格式:王 璐, 李梦超, 阙标华, 等. 辉钼精矿的氧化焙烧[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(7): 1952-1964. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39757
WANG Lu, LI Meng-chao, QUE Biao-hua, et al. Oxidation roasting of molybdenite concentrate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(7): 1952-1964. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39757
辉钼精矿是三氧化钼(MoO3)制备及后续钼产品深加工的重要原材料[1],实际工业生产中一般采用多膛炉或回转窑炉对其进行氧化焙烧[2],如陕西省西安市金堆城钼业股份有限公司采用8~12级的焙烧多膛炉[3]。空气是现阶段焙烧辉钼精矿的主要原料,焙烧过程中,精矿原料在上层阶段主要发生
氧化反应生成二氧化钼(MoO2),在下层阶段MoO2将继续氧化生成MoO3,整个焙烧过程耗时一般较长。具体焙烧过程大致可描述成式(1)和(2)所示[4]:
MoS2+3O2=MoO2+2SO2 (1)
MoO2+0.5O2=MoO3 (2)
钢铁行业方面,富氧或者纯氧技术已在高炉炼铁当中得到了广泛应用,冶炼效率大幅提高[5-6]。鉴于此,探索一种新的焙烧工艺,使辉钼精矿在富氧或纯氧条件下快速氧化焙烧成MoO3受到了钼冶金领域专家的广泛关注,相关研究也有文献进行了报道[7-9]。在前期工作中[10],本文作者同样对纯氧条件下辉钼精矿的氧化焙烧行为展开了研究,然而对于某些问题的解释,当时未能给出足够的证据。本文是在进一步的文献调研和深入探讨之后,结合带有能谱功能的扫描电子显微镜与热力学数据,理论分析了杂质组元在焙烧过程中的演变规律及其对烧结现象产生的影响机制,是对前期工作[10]内容的一些补充和所得结论的佐证。
1 实验
1.1 实验原料
论文所用实验原料为来自陕西省西安市金堆城钼业股份有限公司的辉钼精矿,其化学元素组成如下(质量分数):Mo,54.89%;S,33.27%;Si,1.83%;Fe,1.12%;Ca,0.28%;Al,0.19%;K,0.14%;Ti,0.04%;Pb,0.08%;Cu,0.07%;C,0.17%;P,0.01%,其他杂质组元还包括Na和Mg等。原料物相经XRD衍射分析确定其主要成分为二硫化钼(MoS2),形貌经扫描电子显微镜观察呈无规则形态,颗粒粗大且分布不均匀[10]。
1.2 实验步骤
辉钼精矿在纯氧条件下氧化焙烧的实验步骤在前期工作[10]中已有过详细描述,鉴于此,本文对其进行简要概述。原料经383 K烘箱烘干12 h后,称取3 g左右样品放入尺寸大小为 50 mm×25 mm×20 mm(长×宽×高)的氧化铝坩埚中,厚度约为5 mm。此后将装有样品的坩埚放入石英管内,密封完好并通氩气以排尽管内空气。然后将石英管缓慢送入事先升至指定反应温度的Si-C电炉的恒温区,待温度稳定后将氩气切成氧气开始反应。一段时间后,将氧气切回氩气进行保护并将石英管取出炉外冷却。当样品冷却至室温时关闭氩气并取出样品进行称量。根据实验结果,本文在不同温度下设定不同的反应时间进行分析,研究温度为723 K、773 K和873 K。实验结束之后,收集样品将其进行物相检测和横切截面结构观察与能谱分析,并对反应过程中的动力学行为和发生的烧结现象进行深入剖析。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 动力学分析
本文对723K、773K和873 K下辉钼精矿在不同反应时间反应前后的质量分别进行了称量,按式(3)对其质量损失率进行计算,得出不同反应条件下辉钼精矿的质量损失率曲线,结果如图1(a)所示[10]。
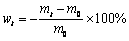 (3)
(3)
式中:mt和m0分别为精矿反应时间t后的质量和初始质量,初始质量为3 g。从图1(a)可以看出,精矿的质量损失率随着反应时间的延长不断增大,温度越高,增加速率越快。在反应时间接近20 min(723 K下约为25 min)时,精矿的最终质量损失率均达平台,温度越高,平台值越大,如温度为723 K、773 K和873 K时,精矿最终质量损失率的平均值分别为9.8375%、10.5865%和11.4330%。根据论文作者前期工作[10] XRD衍射分析结果可知(具体分析数据见文献[10]):精矿在723 K和773 K时,未能完全氧化,产物为MoO3和部分未被完全氧化的MoS2;在873 K时,则完全氧化,产物为MoO3;氧化焙烧过程中,其他杂质组元及MoO2未能测出,这可能是由其含量过少以致超出XRD检测限度所致[10]。
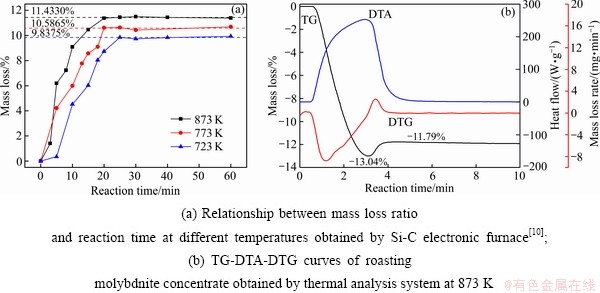
图1 氧气气氛下辉钼精矿的氧化焙烧动力学曲线
Fig. 1 Kinetic curves of roasting molybdenite concentrate in oxygen atmosphere
为进一步分析辉钼精矿氧化焙烧过程中的吸放热情况,本文以873 K为例补充了辉钼精矿氧气气氛中的氧化焙烧动力学实验,结果如图1(b)所示。由Mo(54.89%)和S(33.27%)的元素化学成分可推知,倘若Mo和S按摩尔比1:2进行化合形成MoS2,则S含量略显不足,Mo含量则有所过剩。为便于分析,本文假设S全以MoS2形式存在(与实际情况可能不符,因为其他金属杂质元素也有可能形成相应的硫化物),因此,由S含量推测的辉钼精矿的精度(MoS2的含量)约为82.17%,过量的Mo以其他钼矿形式存在。假定辉钼精矿中的其他杂质组分不参与氧化反应,则氧化产物全为MoO3时质量损失率约为8.2%,氧化产物全为MoO2时质量损失率约为16.4%。根据图1(b)中TG曲线(黑色实线)可知,随着反应时间的不断延长,反应物的质量损失率逐渐增加,当时间约为3.15 min时质量损失率达到最大,为13.04%。此后随着反应时间的继续延长,质量损失率开始逐渐减小,在质量损失率约为11.79%时达到平台。热重曲线结果表明,辉钼精矿达到平台时的质量损失率与图1(a)中Si-C电炉取样分析达到平台时的质量损失率数值相符。虽然11.79%或11.43%相比辉钼精矿完全氧化成MoO3时的质量损失率数值(8.2%)明显偏大,然而最终产物组成却为MoO3,这表明辉钼精矿中还含有其他较易挥发的杂质组分。此时,11.79%可认为是当前精矿原料完全氧化时的理论质量损失率。而图1(a)中773 K和723 K温度下原料的最终质量损失率值均低于此数值,这也说明了773 K和723 K下辉钼精矿未能完全氧化。由图1(b)还可看出,最大质量损失率(13.04%)介于完全氧化成MoO2和MoO3所需质量损失率之间,说明此时产物既含有MoO2,又含有MoO3。据此可以推知,后续质量损失率开始逐渐减小是部分MoO2的氧化增量所致。因此,辉钼精矿完全氧化成MoO3(如反应式(4)所示)可认为由两段反应组成,首先MoS2发生部分氧化生成MoO2,如方程式(1)所示;随后生成的MoO2快速氧化生成MoO3,如方程式(2)所示,两者几乎同时进行。MoO2是辉钼精矿氧化焙烧过程的中间产物。当反应时间为3.15 min左右时,质量损失率达到最大,此时可认为MoO2的生成反应基本结束,此后MoO2的氧化反应占据主导。另外,根据图1(b)中的DTA曲线(蓝色实线)可知,整个氧化焙烧过程均为放热反应,在反应后期放热效应更为明显且达到最大,说明MoO2的氧化反应比MoO2的生成反应放热效应更为显著,放出的热量更多,该热量能够促使焙烧过程中的局部反应温度迅速提升。DTG结果(红色实线)表明,辉钼精矿原料的质量损失速率随着反应时间的推移逐渐加快,在时间约为1.12 min时达到最快,随后质量损失速率缓慢减小直至为0(时间约为3.15 min);此后,MoO2的氧化反应占据主导样品的质量开始增大,且其质量增加速率同样是先增加后减小直至为0。
MoS2+3.5O2=MoO3+2SO2 (4)
上述结果在论文作者前期工作[10]及其他参考研究[4]中有过体现,然而均缺乏对其反应动力学的系统分析。本文将Si-C电炉分段取样法获取各个温度下的平均质量损失率假定成各自温度下精矿完全氧化时的最大质量损失率,采用归一化处理方法对其动力学进行分析,其中反应进度可表示成一定时间内精矿的实际质量损失率与最大质量损失率之比,如式(5)所示。
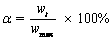 (5)
(5)
式中:wmax为各个温度下精矿完全氧化时的最大质量损失率,本文以达平台时的平均质量损失率进行表示。
通过式(5),原料的反应进度与反应时间的关系可表示成图2(a)所示。采用不同的反应模型对图 2(a)中的数据进行多次拟合,结果发现化学反应模型(见式(6))能够很好地对实验数据进行表达,结果如图2(b)~(d)所示。
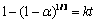 (6)
(6)
式中:k为反应速率常数。从图2(b)~(d)可以看出,在较高温度下,如873 K和773 K,模型拟合结果与实验所得数据具有良好的线性关系,表明此时化学反应模型具有一定的合理性,即873 K和773 K下精矿的氧化焙烧过程由界面化学反应控速。然而在较低温度下,如723 K,模型处理结果与实验所得数据的线性关系并不可观,多数实验数据点分布在拟合直线下方,尤其是反应初始阶段(见图2(b)),表明该温度下氧化反应并不由或不单由化学反应控速。事实上,在较低温度下的化学反应,产物的形核与长大过程占据很大一部分主导作用;当核心数量足够多和尺寸足够大时,控速环节才有可能发生改变。即在723 K下,精矿的氧化焙烧前期过程很有可能由三氧化钼的形核与长大控速,之后再逐渐转变成精矿与氧气之间的化学反应控速,即此时成核与长大和化学反应共同发挥作用。在实际工业多膛炉或回转窑炉内的氧化焙烧过程中,反应温度通常维持在873 K或者更高,从动力学角度分析化学反应控速占据主导。对于辉钼矿的氧化焙烧动力学,已有研究曾采用热重分析技术对其进行研究,结果表明该过程由三维界面化学反应控速,与本文结果相符[11]。
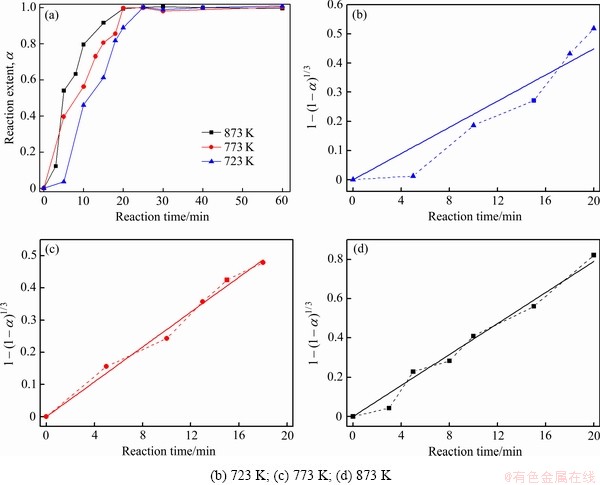
图2 不同温度下反应进度与反应时间的关系图及不同温度下1-(1-α)1/3与反应时间的关系图
Fig. 2 Relationship between reaction extent with reaction time at different temperatures(a) and relationship between value of 1-(1-α)1/3 and reaction time at different temperatures((b)-(d))
2.2 反应机理分析
本文作者[10]曾根据样品的粉末形貌特征分析其反应机理,结果发现随着反应时间的延长,样品由颗粒状逐渐转变成细长的薄片状,部分粗大的片状三氧化钼会逐渐从团聚体当中脱落下来形成单个晶体,长度可达1 mm,肉眼清晰可见。本文在前期工作[10]基础上,结合样品的横切截面结构图和热力学数据继续对其焙烧行为展开分析以期完善和更深入理解其反应机理。
样品经镶样、打磨和抛光后,采用扫描电子显微镜进行观察,结果如图3所示。焙烧5 min后,样品横截断面出现大量细小孔洞(见图3(a)),这在前期工作[10]的粉末形貌特征图中未曾发现,此时表面孔洞是由大量产物气体SO2的逸出所致。10 min后,产物由大量针状物相互交织在一起,形成一个近似网状结构的横切截面(见图3(b))。当磨样不均匀时,一些奇特的现象清晰可见,产物表面有大量片状凸起形成,凸起与凸起之间相互交错(见图3(c)),这些片状凸起是从底部基质当中挥发出来而后冷凝所成。从图3(c)还可发现,大量细小的小凸起与底部基质结合紧密,有逐渐长成大凸起的趋势。对这些细小凸起进行能谱分析(见图3(d)点1),结果发现其主要元素组成为Mo和O,且摩尔比接近3:1,表明凸起物质主要成分为MoO3。基质能谱分析结果表明其成分较为复杂,既包含Mo和O,还包括S和Al等元素,Al可能来源于原料中的杂质组分,S来源于未被完全氧化的辉钼精矿。这些未挥发成凸起的基质还可能是由杂质组元的存在形成的高熔点钼酸盐。40 min后,精矿已完全氧化(见图1(a)中所示质量损失率曲线和文献[10]),产物仍由大量细长凸起组成(见图3(e))。当横切截面抛光平整,细长的针状物更加清晰可见(见图3(f)),厚度可达纳米级别,长度可达20 μm,并且均匀分布在视图界面。粉末形貌图显示细长针状物呈现典型的纳米片状结构(见图4(a)),且大部分层次分明、边缘光滑、梯度明显。XRD衍射结果(见图4(b))表明这些纳米片状三氧化钼纯度较高,所有衍射峰都对应正交三氧化钼(PDF卡片:5-508;a=3.962 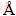 ,b=13.858
,b=13.858 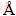 ,c=3.697
,c=3.697 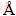 ),并且在晶面指数为(020)、(040)、(060)和(0100)的衍射峰特别强烈,说明此时获得的纳米片状三氧化钼拥有一定的各向异性,具有择优长大特性。
),并且在晶面指数为(020)、(040)、(060)和(0100)的衍射峰特别强烈,说明此时获得的纳米片状三氧化钼拥有一定的各向异性,具有择优长大特性。
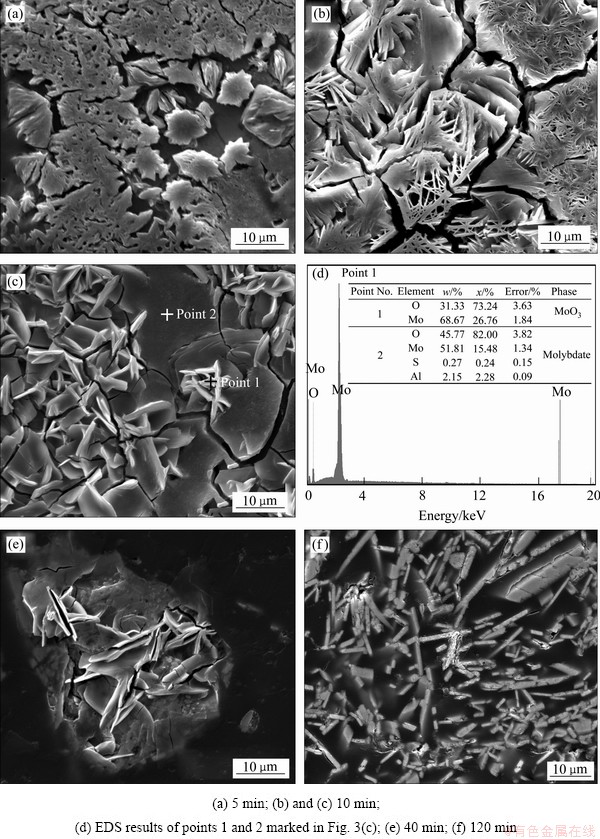
图3 辉钼精矿在873 K氧气气氛中焙烧不同反应时间后产物的横切截面结构图
Fig. 3 Images of cross-section structure of samples obtained by roasting molybdenite concentrate roasted at 873 K for different time
图5所示为Mo-S-O三元体系在873 K下采用FactSage 7.3[12]绘制的优势区图(其他温度,如773 K和723 K,结果与之类似,本文不再提供)。可以看出,MoS2在氧化成MoO3的过程中,需要经历中间产物MoO2这一环节,该发现与图1(b)中的热重曲线结果相符。综合以上结果,辉钼精矿氧化焙烧成片状三氧化钼的反应历程可描述如下:在高温环境的氧气气氛中,精矿在反应的初始阶段会优先氧化生成二氧化钼,如图1(b)和图5所示;由于极高的氧分压和反应温度,新生成的二氧化钼随即快速氧化生成三氧化钼,两者几乎同时发生,同时进行。根据已有研究[10]推知,此时二氧化钼的生成速率应小于其继续氧化的速率,使其几乎不能得到积累,整个反应过程中其积累量始终很低,采用XRD衍射技术甚至不能将其测出,以致造成反应过程二氧化钼不能生成的假象。与此同时,由于三氧化钼较高的挥发特性及精矿氧化焙烧本身的放热属性,在原料表面形成的三氧化钼极易挥发至稍远处(远离反应界面),而后又在较低温度区域重新冷凝回到固体状态。从反应界面至新形核处形成一条近似连接桥的三氧化钼区域带,这条连接桥可为后续三氧化钼的挥发-冷凝提供捷径,为后续三氧化钼气相分子的物理沉积提供附着位点。反应过程中精矿和二氧化钼均不断被氧化其含量也逐渐减少,放出的热量也随之不断发生变化,以致后续三氧化钼的挥发-冷凝路程不完全相同,因此,在后续三氧化钼的沉积方面会形成一个近似阶梯状的表面结构。反应放热越多,温度越高,三氧化钼挥发-冷凝路程越长;反应放热越少,温度越低,挥发-冷凝路程则越短。辉钼精矿氧化焙烧的反应历程可简要表述为挥发-冷凝机理,如图6所示,该结果与文献[13]的研究结果基本相符。
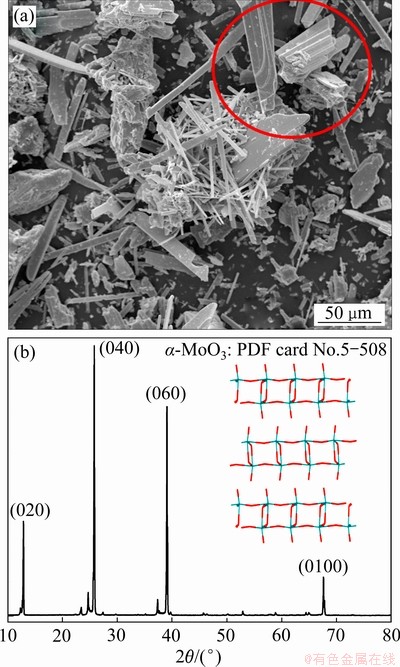
图4 辉钼精矿在873 K氧气气氛中焙烧20 min后获得的针状产物的形貌和XRD谱
Fig. 4 Powder micrograph(a) and XRD pattern(b) of needle-like product obtained by roasting molybdenite concentrate at 873 K for 20 min
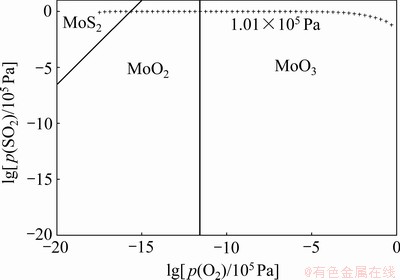
图5 Mo-S-O三元体系在873 K下的优势区图
Fig. 5 Predominance phase diagram of Mo-S-O ternary systems at 873 K
2.3 烧结行为分析
辉钼精矿在纯氧环境中焙烧至接近完全时,烧结现象也会随之发生,即部分产物会牢牢紧密地与坩埚底部结合在一起。温度越高,烧结现象越为严重[14-15]。在实际工业多膛炉焙烧过程中,烧结现象也会时常发生,以致多膛炉耙臂磨损严重,大大降低设备使用寿命[16]。因此,研究焙烧过程中产物的烧结行为对避免烧结现象的发生,减少不必要的设备损耗,降低经济损失尤为重要。为此,论文作者在前期工作[10]基础上,结合能谱结果和热力学数据继续对其烧结行为进行深入分析。
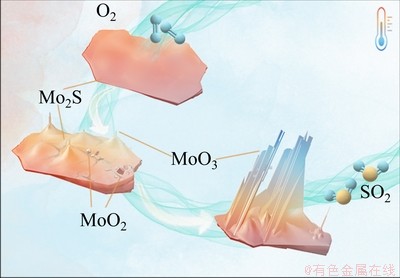
图6 提出的辉钼精矿氧化焙烧反应机理示意图
Fig. 6 Schematic diagram of proposed possible oxidation roasting mechanism
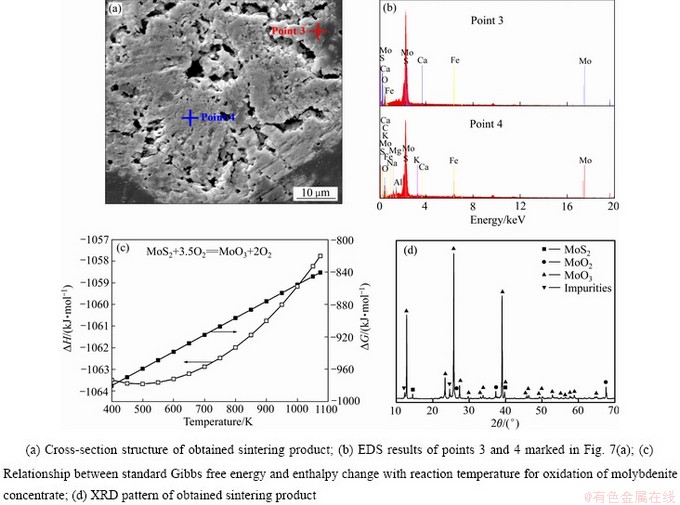
图7 辉钼精矿在873 K氧气气氛中焙烧40 min后的底部烧结产物分析结果
Fig. 7 Analysis results of sintering product obtained by roasting molybdenite concentrate in oxygen atmosphere at 873 K for 40 min
图7(a)所示为精矿在纯氧气氛中焙烧40 min后烧结产物的横切截面图。可以发现产物呈现熔融状态,表明部分液相已经生成。液相的生成可能是由强烈的放热反应所致(见图7(c))[12]。虽然升高温度辉钼精矿总的氧化反应(见式(4))的焓变值呈现上升趋势,但总体较小,873 K时焓变能为-1061 kJ/mol,表明放热极多,该部分热量能够使得界面温度大大提升,甚至超出三氧化钼的熔点温度致使其融化。XRD衍射分析结果表明烧结产物中除了含三氧化钼以外,还包含部分未完全氧化的MoS2和MoO2(见图7(d))。此时MoO2可能由辉钼精矿的部分氧化而来(见式(1)),也可能由MoS2和MoO3的固相反应而得(见式(7))。此外,部分杂质的衍射峰也被检测出来,表明此时烧结产物成分复杂多样且杂质得到了富集。XRD检测物质状态具有一定的局限性,当产物浓度低于某一范围时XRD则不能将其测出。为了更好地探究产物的元素组成,本文还采用了能谱分析技术对其进行了检测,结果如图7(b)所示。结果表明,烧结产物不同位置的成分组成均较为复杂,不仅包含XRD结果显示的Mo、O和S,还包括Mg、Ca、Si、Al、Fe和Na等元素,即辉钼精矿的大部分杂质组元均在烧结产物当中得到了富集。
MoS2+6MoO3=7MoO2+2SO2 (7)
对于杂质组元在焙烧过程中的演变规律,本文借助商用热力学软件FactSage 7.3[12]对其进行分析。由于辉钼精矿的主要组分为MoS2,主要杂质组元为Mg、Ca、Si、Al和Fe等,因此本文主要针对这几种杂质组元的热力学相图进行理论分析。
对于杂质元素Mg(以873 K为例),在MoS2存在情况下,主要以MgS形式存在,随后逐渐氧化生成MgO和钼酸镁[(MgO)(MoO3)或MgMoO4];继续升高氧分压,MoS2开始氧化相继生成MoO2和MoO3,此时Mg仍然以(MgO)(MoO3)的形式存在(见图8(c));在氧分压接近1时,Mg的主要存在形式转为硫酸镁(MgSO4)。当温度发生改变时,对比723、773、873、973和1073 K获取的热力学数据可知,Mo-Mg-S-O四元体系物相的稳定存在区间整体右移,即向着氧分压升高的方向移动。温度为723 K、773 K、873 K和973 K时,Mg的最终存在形式主要为MgSO4;然而当温度升至1073 K及以上时,则主要以(MgO)(MoO3)的形式存在(见图8)。这说明高温条件下钼酸镁相比硫酸镁更为稳定,硫酸镁在高温条件下有逐渐转变成钼酸镁的趋势,即钼酸盐相比硫酸盐而言更易在高温区稳定存在。
由于实验中最高温度为873 K,因此本文主要以873 K为例进行其他杂质元素组元存在形式演变规律的探讨。对于杂质元素Ca,其演变规律与Mg基本相似,在MoS2存在情况下杂质元素Ca主要以CaS的形式存在;随着氧分压的升高,CaS逐渐氧化成硫酸钙(CaSO4)和钼酸钙[(CaO)(MoO3)或CaMoO4];继续升高氧分压,MoO2和MoO3与(CaO)(MoO3)的混合物也将相继生成;氧分压接近1时,Ca主要以CaSO4形式存在,如图9(a)所示。继续升高反应温度,从杂质元素Mg的演变规律可推知,CaSO4最终会被(CaO)(MoO3)所取代,产物最终会转变为(CaO)(MoO3)(热力学相图未给出)。对于杂质元素Si,由于其含氧化物为酸性氧化物,在873 K下不与同样为酸性氧化物的三氧化钼发生反应,因此其在反应过程中始终以SiO2的形式存在,如图9(b)所示。此时即使继续升高温度,Si的存在形式仍然为SiO2(热力学相图未给出)。对于杂质元素Al,在MoS2存在的情况下,Al主要由Al2O3的形式存在;随着氧分压的逐渐升高,MoS2先氧化成MoO2,然后生成MoO3,如图9(c)所示,当氧分压接近1时,最终产物为MoO3和硫酸铝(Al2(SO4)3)。虽然873 K的热力学相图未能发现钼酸铝(Al2(MoO4)3)的形成,但事实上高温条件下MoO3和Al2O3会发生化学反应生成钼酸铝。论文作者在前期工作[17]中曾对含Ca、Al和Si等杂质组元组成的工业氧化钼进行高温挥发实验,温度为1273 K,结果表明当三氧化钼完全挥发时,杂质元素Ca、Al和Si分别以CaMoO4、Al2(MoO4)3和SiO2的形式存在,与本文热力学分析结果相符。文献[17]同样对摩尔比为3:1的 MoO3和Al2O3的混合物1273 K下进行了高温焙烧实验,发现当反应时间仅为10 min时Al2(MoO4)3就会生成,更加说明高温条件下Al2(MoO4)3能够稳定存在。对于杂质元素Fe,由Mo-Fe-S-O四元体系相图可知在氧分压极低时其主要物相组成为MoS2和FeS2;随着氧分压的升高,FeS2优先氧化生成Fe3O4,随后MoS2氧化生成MoO2;继续升高氧分压,Fe3O4将氧化生成Fe2O3,随后MoO2和MoO3与钼酸亚铁(FeO)(MoO3)的混合物也相继生成;进一步升高氧分压,产物为MoO3和Fe2O3。理论计算结果表明在反应后期相应的硫酸铁盐也会生成,如图9(d)所示。结合杂质元素Mg随温度变化的演变规律可推知,随着反应温度的继续升高,图9(d)所得物相存在的稳定区域相应也会右移,并最终形成相应的含铁钼酸盐。
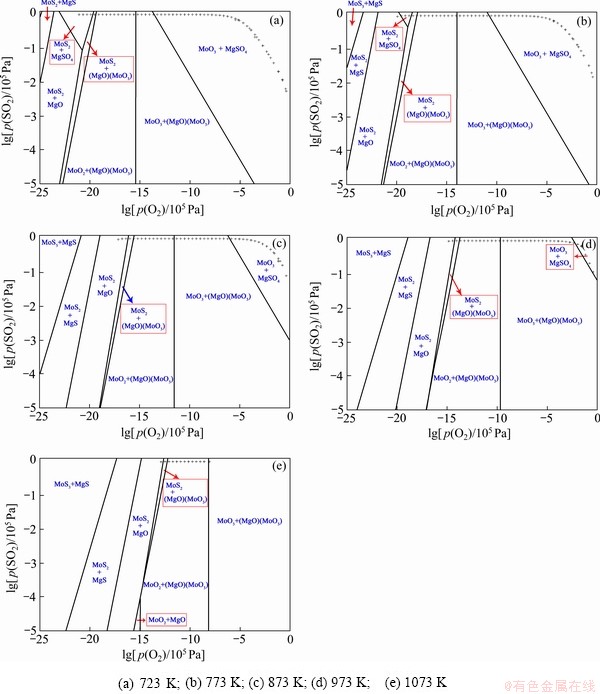
图8 不同温度下Mo-Mg-S-O四元体系的优势区图
Fig. 8 Predominance phase diagrams of Mo-Mg-S-O quaternary systems at different temperatures (“+”=1.01×105 Pa)
一方面,杂质组元在氧化焙烧过程中其存在形式随着氧分压和温度的变化在不断发生变化;另一方面,结构发生变化的杂质组元具有与三氧化钼发生反应生成相应钼酸盐的趋势[18],从而对焙烧行为产生影响,且不同的杂质组元其影响程度不同。Al在873 K下的主要存在形式为Al2(SO4)3,几乎不会生成相应的钼酸铝,表明Al在氧化焙烧过程中几乎不会生成相应的低熔点共晶体(本文所述低熔点共晶体为金属氧化物与相应钼酸盐发生反应而形成的一类化合物),对烧结现象无明显影响,文献[19]也证实了这一点。Fe在反应过程中会形成部分中间产物钼酸盐,并且随着温度的升高,钼酸盐存在的稳定区域也会增加,这与Ca和Mg的结果类似。因此,温度越高,杂质Fe和MoO3会形成部分低熔点共晶体,对烧结现象具有一定影响。杂质Ca和Mg具有相似的热力学相图,在氧化焙烧过程中均会生成相应的钼酸盐,温度越高,钼酸盐生成越稳定,低熔点共晶体也更易形成。如MoO3和CaMoO4在999 K左右即会生成低熔点共晶体,相应的热力学相图参见文献[20]。MoO3和MgMoO4之间的热力学相图如图10所示[21]。由图10可以发现,MoO3和MgMoO4极易形成低熔点共晶体,如在MgMoO4含量为19.5%时,形成的共晶体熔点温度约为1018 K。虽然该温度大于本文的研究温度(873 K),但在强烈放热的焙烧反应条件下,反应过程中反应位点的局部区域温度极有可能过度升高,甚至高于该熔点温度及MoO3的熔点值。局部反应温度的升高能够促使产物(钼酸盐或三氧化钼)熔化,形成的液体具有吸附周边固体小颗粒的能力,将周边未完全氧化的MoS2吸附其中,致使部分MoS2不能进一步氧化。与此同时,未完全氧化的MoS2能够与MoO3发生反应生成MoO2。杂质K和Na均具有极高的反应活性,焙烧反应过程中,它们形成的钼酸盐均极易与MoO3发生反应形成相应的低熔点共晶体,其中MoO3与K2MoO4形成低熔点共晶体的温度约为753 K(MoO3与K2MoO4的热力学相图参见文献[14])。MoO3与Na2MoO4形成的二元相图如图11所示[22]。由图11可知,在MoO3含量约为78%的条件下,Na2MoO4和MoO3形成的共晶体熔点温度为813 K。在此条件下,即使焙烧过程放热效应不明显,反应后期烧结现象也极易发生。可以预测,形成低熔点共晶体的温度越低,烧结现象越易发生。结合本文结果和参考文献[14, 19]可知,杂质K和Na对焙烧过程中烧结现象的影响最为严重,Ca、Fe和Mg次之,Al对烧结现象影响不大,杂质含量最多的Si对烧结现象几乎没有影响。烧结现象发生的原因在于各种杂质元素与MoO3之间形成的低熔点共晶体在焙烧过程中不断熔化成液体;同时,由于辉钼精矿氧化焙烧强烈的放热效应,反应过程中很容易导致反应局部区域温度升高,致使杂质元素钼酸盐和MoO3形成的低熔点共晶体熔化,最终导致烧结现象发生。低温条件下辉钼精矿不能完全氧化,且Na2MoO4与MoO3能够形成813 K的极低熔点共晶体,因此,降低反应温度对抑制烧结现象的发生似乎不太理想。一个较为可行的方法是尽可能减少精矿中的杂质组分含量[23],尤其是对易与三氧化钼形成低熔点共晶体的元素,如K、Na、Ca、Fe和Mg等。该研究可为工业辉钼精矿焙烧过程中避免烧结现象的发生,提高产物质量以及延长多膛炉或回转窑炉使用寿命具有重要指导意义。
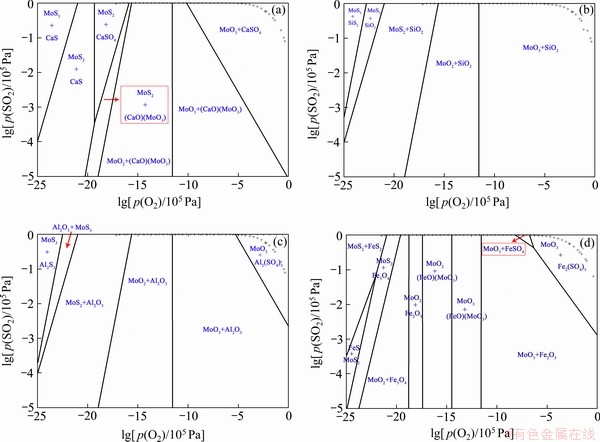
图9 不同组元873 K下Mo-Me-S-O四元体系的优势区图(Me代表Ca,Si,Al和Fe)
Fig. 9 Predominance phase diagram of Mo-Me-S-O quaternary systems at 873 K (Me represents Ca, Si, Al, and Fe) (“+”=1.01×105 Pa)
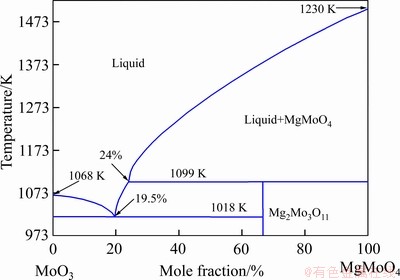
图10 MoO3和MgO(MgMoO4)之间的二元相图[21]
Fig. 10 Binary phase diagram of MoO3-MgO (MgMoO4) systems[21]
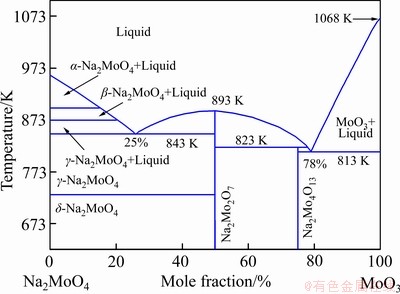
图11 MoO3和Na2O(Na2MoO4)之间的二元相图[22]
Fig. 11 Binary phase diagram of MoO3-Na2O (Na2MoO4) systems[22]
3 结论
1) 873 K下辉钼精矿能够完全氧化生成片状MoO3,氧化过程符合化学反应模型;773 K和723 K条件下,产物由MoO3和部分未完全氧化的MoS2组成,反应速率分别由化学反应和混合模型控制。
2) 辉钼精矿焙烧成三氧化钼的过程中伴随着少量中间产物二氧化钼的生成,产物形态由颗粒形状逐渐转变成片状结构,生成的最终产物具有一定的各向异性;并且发现辉钼精矿焙烧成片状三氧化钼的过程符合挥发-冷凝机理。
3) 理论计算结果表明杂质组元在焙烧过程中其存在形式会随着氧分压和温度的变化不断发生变化;并且认为烧结现象的发生是局部温度的升高和低熔点共晶体的形成共同作用所致;降低杂质元素含量,尤其是K、Na、Ca、Fe和Mg等,比降低反应温度在避免烧结现象的发生方面更加切实可行。
REFERENCES
[1] 姚 远, 罗东卫, 符新科. 辉钼精矿焙烧工艺评述[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2008, 37(2): 24-26.
YAO Yuan, LUO Dong-wei, FU Xin-ke. Comments on molybdenite concentrate roasting process[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2008, 37(2): 24-26.
[2] WANG L, SUN W,ZHANG J, et al. A novel self-heated roasting technology for molybdenum concentrate[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44(11): 2618-2622.
[3] 卜春阳, 曹维成, 王 璐, 等. 辉钼矿冶炼工艺综述及展望[J]. 中国钼业, 2017, 41(6): 5-11.
BU Chun-yang, CAO Wei-cheng, WANG Lu, et al. Overview and prospect for the smelting process of molybdenite [J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 2017, 41(6): 5-11.
[4] 王连勇, 张井凡, 蔡九菊, 等. 钼精矿氧化焙烧机理研究[J]. 中国钼业, 2011, 35(2): 17-19.
WANG Lian-yong, ZHANG Jing-fan, CAI Jiu-ju, et al. Study on mechanism of molybdenum concentrate roasting[J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 2011, 35(2): 17-19.
[5] 张 建, 王 凯, 王 喆, 等. 首钢京唐1号高炉富氧率与炉况的匹配分析[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2020, 32(8): 720-726.
ZHANG Jian, WANG Kai, WANG Zhe, et al. Matching analysis of oxygen enrichment rate with furnace condition of No.1 blast furnace in ShougangJingtang[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2020, 32(8): 720-726.
[6] 郭晓鹏. 浅析富氧对高炉炼铁的影响[J]. 天津冶金, 2019(1): 18-20.
GUO Xiao-peng. Brief analysis on the effect of oxygen enrichment on ironmaking[J]. Tianjing Metallurgy, 2019(1): 18-20
[7] UTIGARD T. Oxidation mechanism of molybdenite concentrate[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2009, 40(4): 490-496.
[8] PAUL R, THOMAS A. The oxidation kinetics of molybdenite at 525 ℃ to 635 ℃[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1971, 2(3): 889-893.
[9] FU Y, XIAO Q, GAO Y. Pressure aqueous oxidation of molybdenite concentrate with oxygen[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 174: 131-139.
[10] WANG L, ZHANG G H, DANG J, et al. Oxidation roasting of molybdenite concentrate[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(12): 4167-4174.
[11] SHIGEGAKI Y, BASU S, WAKIHARA M. Thermal analysis and kinetics of oxidation of molybdenum sulfides[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 1988, 34(5): 1427-1440.
[12] BALE C, CHARTRAND P, DEGTEROV S. FactSage thermochemical software and databases[J]. Calphad- computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 2002, 33(2): 295-311.
[13] WILKOMIRSKY I, WATKINSON A, BRIMACOMBE J. Kinetics of oxidation of molybdenite[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy Section C, 1997, 87: C16-C22.
[14] 卜春阳, 曹维成, 王 璐, 等. 辉钼矿烧结现象研究[J]. 中国钼业, 2018, 42(1): 8-11.
BU Chun-yang, CAO Wei-cheng, WANG Lu, et al. Study on the sintering phenomenon during the roasting processes of molybdenite by air[J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 2018, 42(1): 8-11.
[15] MARIN T, UTIGARD T, HERNANDEZ C. Roasting kinetics of molybdenite concentrates[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2009, 48(1): 73-80.
[16] 琚成新, 宫玉川. 多膛炉焙烧钼精矿的温度调节与控制[J]. 中国钼业, 2010, 34(5): 28-31.
JU Cheng-xin, GONG Yu-chuan. Temperature adjustment and control of roasting molybdenite in multi-hearth roaster[J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 2010, 34(5): 28-31.
[17] WANG L, ZHANG G H, SUN Y J, et al. Preparation of ultrafine β-MoO3 from industrial grade MoO3 powder by the method of sublimation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(35): 19821-19829.
[18] 甘 敏, 范晓慧, 张 麟, 等. 低品位钼精矿氧化焙烧过程的反应行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(12): 3115-3122.
GAN Min, FAN Xiao-hui, ZHANG Lin, et al. Reaction behavior of low grade molybdenum concentrates in oxidation roasting process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(12): 3115-3122.
[19] WANG L, ZHANG G H, WANG J S, et al. Influences of different components on agglomeration behavior of MoS2during oxidation roasting process in air[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2016, 47(4): 2421-2432.
[20] CHYCHKO A, TENG L, SEETHARAMAN S. MoO3 evaporation studies from binary systems towards choice of Mo precursors in EAF[J]. Steel Research International, 2010, 81: 784-791.
[21] ZHUKOVSKII V, YANUSHKEVICH T. Phase equilibria in the system MoO3-MgMoO4[J]. Physics of Metals and Metallography, 1968, 26(5): 959-960
[22] PETROSYAN Y, ZHUKOVSKII V, USTINOV O, et al. Phase equilibria in the system Na2MoO4-MoO3-NiO[J]. Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 1977, 22(10): 2841-2844.
[23] 王 磊, 郭培民, 孔令兵, 等. 加碳条件下钼精矿真空冶炼过程中主要杂质元素的行为分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2020, 30(2): 438-446.
WANG Lei, GUO Pei-min, KONG Ling-bing, et al. Behavior analysis of main impurity elements in vacuum smelting of molybdenum concentrate with carbon[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 30(2): 438-446.
Oxidation roasting of molybdenite concentrate
WANG Lu1, 4, LI Meng-chao1, QUE Biao-hua1, XUE Zheng-liang2, ZHANG Guo-hua3, LAN Wen-tao4
(1. Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory for New Processes of Ironmaking and Steelmaking, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
2. The State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
4. Foshan (Southern China) Institute for New Materials, Foshan 528200, China)
Abstract: The current work focus on the oxidation roasting behavior of molybdenite concentrate in high-purity oxygen atmosphere on the basis of the authors’ previous paper. The best modeling fit, TG-DTA, SEM-EDS and thermodynamic calculation method were adopted to analyze the experimental data. The results show that molybdenite concentrate cannot be reacted completely at 773 K and 723 K; when the temperature is increased to 873 K, however, the raw material can be oxidized to molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) completely. Combining the normalization and model fit methods, the work concludes that the rate-controlling step for the oxidization of molybdenite concentrate in the range of 773 K to 873 K is the interfacial chemical reaction. When the temperature is below 773 K, however, interfacial chemical reaction and nucleation and growth models both worked. It is also found that the morphology of obtained product transforms from previous particle shape to the final needle-like structure during the whole reaction process. XRD patterns show that the obtained needle-like product has an intense diffraction peak for the crystal indices of (020), (040), (060), and (0100), indicating its anisotropy and prior growth up tendency. Oxidation roasting processes of molybdenite concentration obey the vaporization- condensation mechanism with the formation of molybdenum dioxide (MoO2) as the intermediate product is also obtained. The study results also conclude that the occurrence of sintering phenomenon are due to the combined actions of the increase of local temperature and the formation of low-melting-point eutectics during the roasting process. With the help of FactSage 7.3 thermodynamic software, the transformation laws of the main impurities components and its effect on the sintering phenomenon during the roasting processes were also theoretically analyzed. The current work may play positive roles on understanding the roasting behavior of molybdenite concentrate and improve the service life of multiple heart furnaces.
Key words: molybdenite concentrate; oxidation roasting; molybdenum trioxide; sintering phenomenon
Foundation item: Project(2020CFB121) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, China; Projects(2019A1515110361P) supported by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, China; Project(2019ZYYD076) supported by the Central Government for Local Science and Technology Development of Hubei Province, China
Received date: 2019-09-28; Accepted date: 2020-12-20
Corresponding author: WANG Lu; Tel: +86-15600563937; E-mail: wanglu@wust.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:湖北省自然科学基金资助项目(2020CFB121);广东省基础与应用基础研究基金项目(2019A1515110361P);中央引导地方科技发展专项(2019ZYYD076)
收稿日期:2019-09-28;修订日期:2020-12-20
通信作者:王 璐,讲师,博士;电话:15600563937;E-mail:wanglu@wust.edu.cn