Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 1537-1542
Effects of cold deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O alloy for biomedical applications
Chun-bo LAN, Guo LI, Yu WU, Li-li GUO, Feng CHEN
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China
Received 16 April 2016; accepted 17 August 2016
Abstract: The Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O (mass fraction, %) alloy was melted under a high-purity argon atmosphere in a high vacuum non-consumable arc melting furnace, followed by cold deformation. The effects of cold deformation process on microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated using the OM, XRD, TEM, Vicker hardness tester and universal material testing machine. Results indicated that the alloy showed multiple plastic deformation mechanisms, including stress-induced α" martensite (SIM α") transformation, dislocation slipping and deformation twins. With the increase of cold deformation reduction, the tensile strength and hardness increased owing to the increase of dislocation density and grain refinement, and the elastic modulus slightly increased owing to the increase of SIM α" phase. The 90% cold deformed alloy exhibited a great potential to become a new candidate for biomedical applications since it possessed low elastic modulus (56.2 GPa), high tensile strength (1260 MPa) and high strength-to-modulus ratio (22.4×10-3), which are superior than those of Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
Key words: Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O alloy; cold deformation; microstructure; mechanical properties; biomedical material
1 Introduction
Titanium and its alloys are widely used as biomaterials due to their low density, interesting mechanical properties and biocompatibility [1]. Pure titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloys are now the most widely used surgical implant materials, but their elastic modulus (103-110 GPa) is much higher than that of human bone (3-35 GPa), which may cause “stress shielding effect” and lead to failure of the implant [2]. Moreover, Al and V elements in Ti-6Al-4V alloy are cytotoxic and harmful to human body [3]. To overcome the above drawbacks, some titanium alloys containing non-toxic elements and having low elastic modulus, such as Ti-35Nb-4Sn-6Mo-9Zr and Ti-35Nb-2Ta-3Zr alloys, were developed [4,5]. However, their tensile strength needs to be enhanced further as compared with Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
In 2003, SAITO et al [6] reported a class of β-type titanium alloys termed “gum metal” (the typical composition is Ti-23Nb-0.7Ta-2Zr-1.2O, mole fraction, %), which possesses high tensile strength, low elastic modulus and high ductility, etc. These superior properties are achieved only when the following conditions are simultaneously satisfied: 1) a composition satisfying three characteristic electronic “magic” numbers (e. g, a compositional average valence electron number (e/a) of ~4.24, a bond order (Bo) of ~2.87 and a d-electron orbital energy (Md) of ~2.45 eV); 2) containing high quantity of oxygen (>0.7%, mole fraction); 3) substantial cold working on the alloy. The gum metal shows good prospect for biomedical applications, such as the materials of bone plate, artificial femoral and dental implant. In addition, the reported dislocation-free plastic deformation mechanism of the gum metal has attracted considerable attention. However, there is much controversy over this deformation mechanism [7].
In the present work, a new β-type Ti-Nb-based alloy Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O (TNZO, mass fraction, %) is developed whose three electronic numbers are different from those of the above mentioned gum metal. The purpose of this study is to investigate the plastic deformation mechanism and reveal the effect of cold deformation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloy, with the hope of finding suitable processing parameters for the alloy used as biomedical materials.
2 Experimental
An alloy with the composition of Ti-35Nb- 2Zr-0.3O was designed, three electronic numbers of which were as follows: e/a ~4.22, Bo ~2.86, Md ~2.45 eV. The added elements are pure solid metals, except oxygen that was introduced through titanium oxide (TiO2) powder. The alloy ingots with the nominal composition were prepared by melting high pure metals in an electric arc furnace using water-cooled copper crucible under argon atmosphere. The ingots were re-melted eight times for ensuring chemical homogeneity. Then, they were hot-forged to the rods and solution treated (ST) at 1273 K for 3.6 ks, followed by water quenching. Finally, the rods with a diameter of 12 mm were obtained by turning and then cold swaging (CS) with reductions of 22%, 55% and 90%, respectively. When the reduction is up to 90%, the rod with a diameter of 3.8 mm was obtained.
The samples for microstructural observation were mechanically polished and etched in a solution composed of 10% HF, 20% HNO3 and 70% H2O (volume fraction). Microstructural characterization was carried out by optical microscopy (OM, Olympus) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, FEI Tecnai G2 T20). Then, the phase structures of the samples were analyzed by an X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Bruker D8 Discover) with Cu Kα radiation and a graphite monochromator operated at 40 kV and 40 mA, and the microstrains and average grain sizes of all samples were calculated according to the XRD pattern using Jade 5.0 software. The mechanical properties of the alloys such as tensile strength and elastic modulus were obtained by an electronic universal test machine (CMT 5105). The elastic modulus was calculated according to the slope of the linear portion in the stress-strain curves. Microhardness measurement was performed on the polished samples using a Vicker hardness tester (Future-Tech, FM-700) with a load of 3.0 N applied for 10 s.
3 Results
3.1 Microstructure
Figure 1 exhibits the microstructures of the TNZO alloys after different treatments. It is found that the microstructure of the ST alloy is composed of equiaxed grains with sizes of 50 to 80 μm (see Fig. 1(a)). Lenticular deformation bands are observed (i.e., in the view from transverse direction) to appear in the coarse grains after 22% CS (see Fig. 1(b)). Subsequently, as the reduction increases, the deformation bands are gradually distorted as seen in Fig. 1(c). After 90% CS, the microstructure finally changes into a characteristic “marble-like’’ structure (see Fig. 1(d)). The “marble- like’’ (fine filamentary) microstructure is thought to be developed by aggregation of localized elastic strain, which is highlighted by chemical etching that reveals the strain field near the distorted region [8].
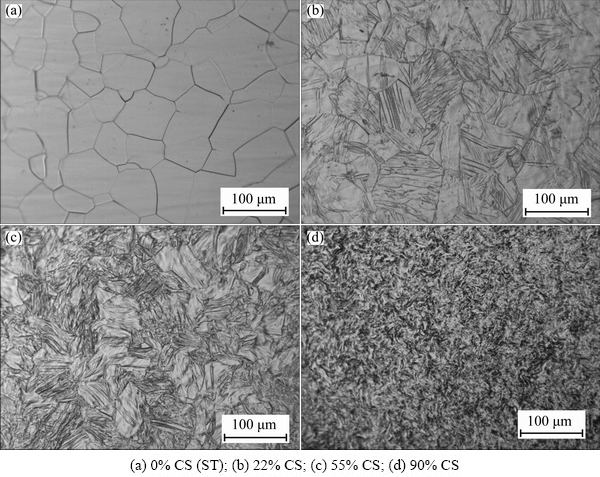
Fig. 1 Microstructures of TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions
Figure 2 shows the XRD profiles of the TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions. In the case of initial state (ST), one can observe the presence of both β and α" phases. The β phase shows the presence of (110), (200) and (211) diffraction peaks, while α" phase shows the presence of (130) and (221) diffraction peaks, which indicates that the temperature-induced martensitic transformation from β to α" occurs during water quenching. Orthorhombic peaks of α" (200) and α" (220) are clearly seen in all the samples after CS, indicating that stress-induced martensitic transformation from β to α" occurs during cold swaging. On the other hand, it is seen that the width of β (110) becomes broadened with the increase of deformation reductions owing to the combination effects of increasing residual stress, texture evolution and grain refinement [9].
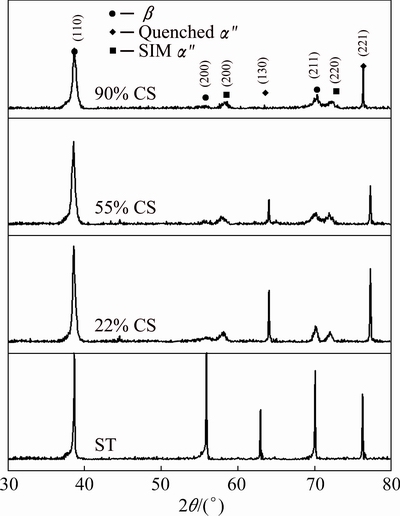
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions
The microstrain of the TNZO alloys can be calculated according to the XRD pattern using the MDI Jade 5.0 software. It is found that the microstrain has been strengthened with increasing deformation reductions, which means the increase of the lattice distortion, as shown in Fig. 3. Meanwhile, the average subgrain sizes (l) of the TNZO alloys can be obtained by Scherrer formula as follows [10]:
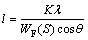 (1)
(1)
where l means the subgrain size (nm); K means constant, usually K=1; λ means X-ray wavelength (nm); WF(S) means full width at half maximum of the diffraction peak (rad); θ means the diffraction angle (rad). The average subgrain sizes of the ST and CS TNZO alloys are also shown in Fig. 3 and it can be seen that the average subgrain size of the alloy decreases gradually with the increase of deformation reductions. It should be noted that the average subgrain size, which is calculated according to the XRD curve, is defined by the size of mosaic block within the crystal, not the size of the large angle grain [11].
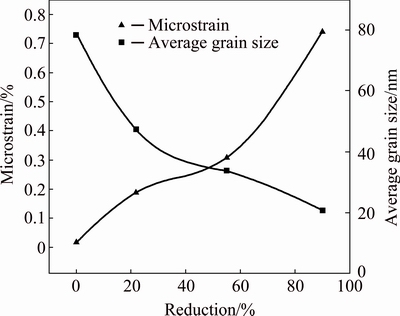
Fig. 3 Microstrains and average grain sizes of TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions
Additional microstructural information is provided by TEM investigation. Figure 4 shows the TEM images of the TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions. The strip deformation twins ({112}<111> type) appear when the reductions are 22% CS and 55% CS, as shown in Figs. 4(a) and (c), respectively, which were also observed in the Ti-36Nb-2Ta-3Zr-0.3O alloy deformed by 90% [12]. Such deformation twins are believed to accommodate the increasing strain during deformation. The twins would often change the hard orientation, which is difficult to continue to deform, into soft orientation, so that the subsequent sliding deformation occurs more easily. The twinning morphology is not observed by TEM when the reduction is relatively high (in the specimens deformed by 90%). Figure 4(b) shows the bright field image of strip-shaped SIM α" phase in the sample deformed by 22%. Generally, the occurrence of SIM α" phase depends on the β stability of the alloy and the extent of deformation on the metastable β titanium alloy. On the other hand, HWANG et al [13] concluded that SIM α″ transformation is easy to occur for the titanium alloys whose d-electron parameters are in the range of e/a < 4.24 and Bo < 2.87. The TNZO alloy has the d-electron parameters of e/a ~4.22 and Bo ~2.86 and follows the above predictions. Figure 4(d) shows the dislocation structure of the sample deformed by 90%. Accompanying with dislocation tangles, much more dislocation cells (dislocation networks) appear due to larger deformation reductions.
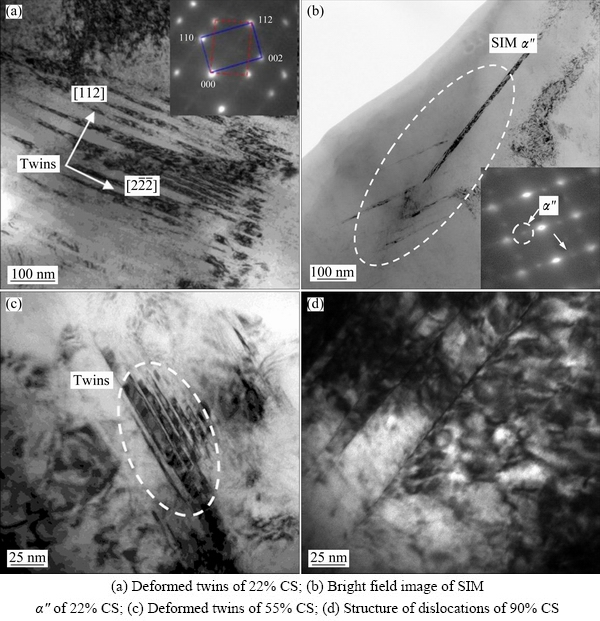

Fig. 4 TEM images of TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions
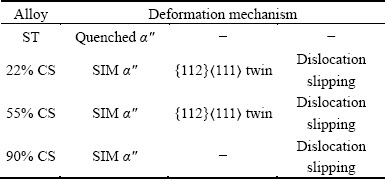
Moreover, dislocation slipping and SIM α" take place in the TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions. The deformation mechanisms of the TNZO alloys are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Deformation mechanisms of TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions
3.2 Mechanical properties
Figure 5 exhibits the mechanical properties of the TNZO alloys at various deformation reductions. As seen in Fig. 5, with the increase of deformation reductions, the tensile strength, elastic modulus and hardness increase gradually. The increase in tensile strength and hardness with increasing cold reduction can be attributed to three primary factors. Firstly, the grain refinement caused by cold deformation contributes to the strengthening. With the increase of deformation reductions, the average subgrain sizes decrease and the grains of the alloy are refined remarkably (see Figs. 1 and 3). Secondly, the increased microstrain caused by cold deformation enhances the lattice distortion, which contributes to the strengthening (see Fig. 3). Thirdly, the increased density of dislocation networks also plays an important role in the strengthening. However, the increase of the dislocation density leads to the decrease of elongation at the same time during the deformation [11], as shown in Fig. 5(b). The increase in elastic modulus after cold swaging is related to the formation of SIM α" phase. As for Ti-23Nb-0.7Ta-2Zr-1.2O gum metal (there is no formation of SIM α"), the elastic modulus was found to decrease with increasing cold working ratio [14]. Generally, the elastic modulus of multiphase materials is mainly determined by phase constitution and the elastic modulus of individual phases. SUN et al [15] and BOENISCH et al [16] reported that SIM α" phase exhibits higher elastic modulus than β phase. In this work, the volume fraction of SIM α" phase continuously increases with the increase of deformation reduction (see Fig. 2), thus leading to the increase in elastic modulus.
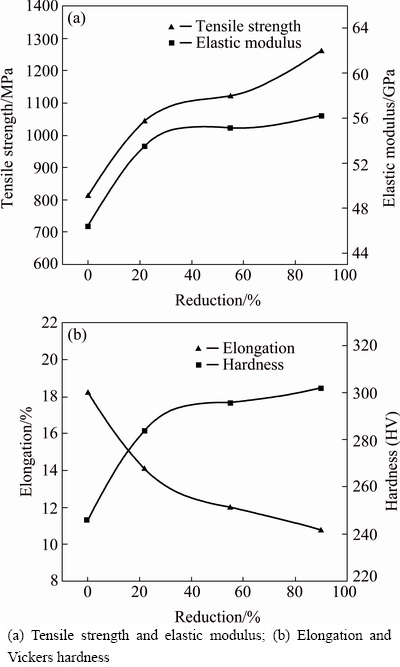
Fig. 5 Relationship between swaging reduction and mechanical properties of ST and CS samples along swaging direction
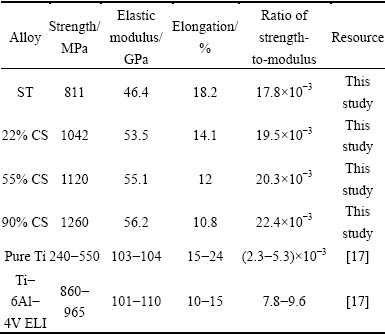
In addition, a useful parameter in orthopedic applications is the elastic admissible strain, defined as the strength-to-modulus ratio. Generally, the higher the elastic admissible strain is, the more desirable the material for such applications is. A brief summary of the mechanical properties of the TNZO alloys and some typical metallic biomaterials (pure Ti and Ti-6Al-4V ELI) is listed in Table 2. It is seen that the strength-to-modulus ratio of TNZO alloy increases markedly with increasing deformation reduction, and the ratios of the TNZO alloys before and after deformation are much higher than those of pure Ti and Ti-6Al-4V ELI. The TNZO alloy cold deformed by 90% reduction exhibits low elastic modulus (56.2 GPa), high tensile strength (1260 MPa), high strength-to-modulus ratio (22.4×10-3) and moderate elongation (10.8%), showing great potential as biomedical materials.
Table 2 Mechanical properties of TNZO alloys and some typical metallic biomaterials
4 Conclusions
1) Multiple plastic deformation mechanisms of TNZO alloys during cold deformation include stress-induced α" martensitic transformation, dislocation slipping and twinning.
2) With increasing cold deformation reduction, the tensile strength and hardness increase owing to the increase of dislocation density and grain refinement, and the elastic modulus slightly increases owing to the increase in the volume fraction of SIM α" phase.
3) The 90% cold deformed alloy possesses low elastic modulus (56.2 GPa), high tensile strength (1260 MPa) and high strength-to-modulus ratio (22.4×10-3), showing great potential as biomedical materials.
References
[1] WANG Xiao-hua, LI Jin-shan, HU Rui, KOU Hong-chao. Mechanical properties and pore structure deformation behaviour of biomedical porous titanium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(5): 1543-1550.
[2] GEETHA M, SINGH A K, ASOKAMANI R, GOGIA A K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopedic implants—A review [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2009, 54(3): 397-425.
[3] OKAZAKI Y, ITO Y, KYO K, TATEISHI T. Corrosion resistance and corrosion fatigue strength of new titanium alloys for medical implants without V and Al [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 213: 138-147.
[4] DAI Shi-juan, WANG Yu, CHEN Feng, YU Xin-quan, ZHANG You-fa. Design of new biomedical titanium alloy based on d-electron alloy design theory and JMatPro software [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(10): 3027-3032.
[5] GUO Yong-yuan, CHENG Meng-qi, CHEN De-sheng, XUE Xiao-bing, ZHANG Xian-long. In vitro corrosion resistance and cytotoxicity of novel TiNbTaZr alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 221(S1): s175-s180.
[6] SAITO T, FURUTA T, HWANG J H, KURAMOTO S, NISHINO K, SUZUKI N, CHEN R, YAMADA A, ITO K, SENO Y, NONAKA T, IKEHATA H, NAGASAKO N, IWAMOTO C, IKUHARA Y, SAKUMA T. Multifunctional alloys obtained via a dislocation-free plastic deformation mechanism [J]. Science, 2003, 300(5618): 464-467.
[7] KIM H Y, WEI L, KOBAYASHI S, TAHARA M, MIYAZAKI S. Nanodomain structure and its effect on abnormal thermal expansion behavior of a Ti-23Nb-2Zr-0.7Ta-1.2O alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(13): 4874-4886.
[8] ZHANG Wei-dong, LIU Yong, WU Hong, LIU Bin, CHEN Zi-jin, TANG Hui-ping. Microstructural evolution during hot and cold deformation of Ti-36Nb-2Ta-3Zr-0.35O alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(5): 1310-1316.
[9] XU Y F, YI D Q, LIU H Q, WU X Y, WANG B, YANG F L. Effects of cold deformation on microstructure, texture evolution and mechanical properties of Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-Fe alloy for biomedical applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 547: 64-71.
[10] GONCALVES N S, CARVALHO J A, LIMA Z M, SASAKI J M. Size-strain study of NiO nanoparticles by X-ray powder diffraction line broadening [J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 72: 36-38.
[11] DAI Shi-juan, WANG Yu, CHEN Feng, YU Xin-quan, ZHANG You-fa. Effects of cold deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-35Nb-9Zr-6Mo-4Sn alloy for biomedical applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 575: 35-40.
[12] TALLING R J, DASHWOOD R J, JACKSON M, DYE D. On the mechanism of superelasticity in Gum metal [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(4): 1188-1198.
[13] HWANG J, KURAMOTO S, FURUTA T, NISHINO K, SAITO T. Phase-stability dependence of plastic deformation behavior in Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-O alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005, 14(6): 747-754.
[14] FURUTA T, KURAMOTO S, HWANG J, NISHINO K, SAITO T. Elastic deformation behavior of multi-functional Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-O alloys [J]. Materials Transactions, 2005, 46(12): 3001-3007.
[15] SUN J, YAO Q, XING H, GUO W Y. Elastic properties of beta, alpha" and omega metastable phases in Ti-Nb alloy from first-principles [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2007, 19: 48621548.
[16] BOENISCH M, CALIN M, van HUMBEECK J, SKROTZKI W, ECKERT J. Factors influencing the elastic moduli, reversible strains and hysteresis loops in martensitic Ti-Nb alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2015, 48: 511-520.
[17] NIINOMI M. Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243: 231-236.
冷形变对生物医用Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O合金显微组织和性能的影响
蓝春波,李 果,吴 雨,郭丽丽,陈 锋
东南大学 江苏省先进金属材料重点实验室,南京211189
摘 要:采用高真空非自耗电弧熔炼炉对在高纯氩气气氛中Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O(质量分数,%)合金进行熔炼。运用金相显微镜、X射线衍射仪、透射电子显微镜、维氏硬度计和万能试验机对冷形变前后的合金材料进行显微组织分析和力学性能测试,探讨冷形变对合金组织与性能的影响。结果表明:Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O合金具有多种塑性变形机制,主要包括应力诱发α"马氏体相变、位错滑移和形变孪晶。随着冷形变率的增加,合金的晶粒细化且位错密度增加,导致合金的抗拉强度和硬度增加。形变过程中α″马氏体的增多使合金的弹性模量略有增加。90%冷变形后的Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O合金具有较低的弹性模量(56.2 GPa),较高的抗拉强度(1260 MPa)和强度模量比(22.4×10-3)等优异性能,比Ti-6Al-4V合金更适合作为生物医用材料。
关键词:Ti-35Nb-2Zr-0.3O 合金;冷变形;显微组织;力学性能;生物医用材料
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (20133069014) supported by the National Aerospace Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Feng CHEN; Tel: +86-13813811605; E-mail: fengchen@seu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60174-2