J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2009) 16: 0297-0302
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-009-0051-1

Influences of rainfall infiltration on stability of accumulation slope by in-situ monitoring test
ZHOU Zhong(周 中), WANG Hong-gui(王宏贵), FU He-lin(傅鹤林), LIU Bao-chen(刘宝琛)
(School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: In order to improve the understanding of the fundamental mechanism of rainfall infiltration induced landslides in accumulation slope and to clarify some important characteristics of slope performance, artificial rainfall simulation tests and field synthetic monitoring were carried out on a typical accumulation slope of Shangrui Freeway in Guizhou Province, China. The monitoring results show that the most accumulation landslides caused by rainfall infiltration are shallow relaxation failure, whose deformation zone lies within the top 0-4 m soil layer. The deformation of slope gradually reduces from the surface, where the greatest deformation lies in, to the deep part of slope. The average percentage of infiltration during the first 2 h is 86%, and then it reduces gradually with time because of the increase of the surface runoff. The average percentage of infiltration drop to a relatively stable value (50%) after 6 h. Rainfall infiltration causes obvious increase of pore-water pressure, which may result in a reduction of shear strength due to a decrease in effective stress and wetting-induced softening. The double-effect of rainfall infiltration is the main reason of rainfall infiltration induced landslides in accumulation slope.
Key words: accumulation slope; stability; rainfall infiltration; in-situ monitoring
1 Introduction
Accumulation landslide refers to the landslides that take place in the Quaternary System and modern loose accumulation layers [1]. This kind of landslide has such features as a broad range and a large amount of slide mass. Consequently, it is more dangerous. The substance composition of the overburden layer of accumulation landslide is mainly pebbly clay, broken stone, debris soil or other kinds of earth-rock mixture. As a result, it is obviously with the following features: disorder physical structure, poor separation, weak cohesive force between particles and strong permeability [2]. Because of the special substance composition, remarkable deference in physical characteristics and the complexity of the rainfall infiltration, there is much deference between accumulation landslide, with special formation conditions, deformation characteristics and damage slip laws, and other types of landslide.
Due to human engineering activities of growing scale and scope, a large number of accumulation landslides have taken place in water conservancy and hydropower construction, railway road traffic construction, and mineral exploitation [3-5]. Rainfall and its infiltration into an accumulation slope is one of the most important factors affecting slope stability [6-9]. The problem of accumulation slope instability caused by rainfall has been paid close attention by people all the time [10-15], but the study on this problem has not been done systemically and thoroughly. In order to reveal the formation and evolution law of rain-induced accumulation landslide, this paper made a thorough research on the rainfall infiltration law in the accumulation slope, the soil-water interaction mechanism in this type of slope based on the artificial rainfall simulation experiments and field synthetic monitoring result of the typical accumulation slope (K85+650-690) located at the exit of Qinglong Tunnel of Shangrui Freeway in Guizhou Province, China.
2 Experimental
On the basis of comprehensive inspection of Zhenning-Shengjingguan Road of Shangrui Freeway, Guizhou Province, China, according to the geological bored data, external slope morphology and the surrounding environment, Qinglong tunnel K85+650-690 accumulation layer was selected as the artificial rainfall experiment site. The vegetation and other debris within the region were removed at first and then the slope was brushed on the gradient of 1?2.5. In order to prevent atmospheric precipitation and the surrounding soil water infiltration in the region to affect the accuracy of impact tests, the experimental areas should be covered with color cloth in the case of rain.
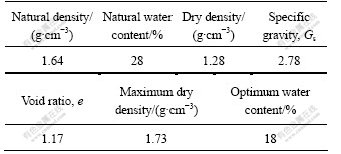
To ascertain the basic physical properties of the soil in the experiment area and the engineering geological characteristics of the slope soil, a series of basic physical and mechanical tests and specialized drilling investigation were carried out. The results are listed in Table 1. 15 groups of particle analysis experiment were carried out in total. The average grading curve shows that: clay (<0.005 mm) content is 0.95%, silt (0.05 to 0.005 mm) content is 8.88%, gravel (>5 mm) is 47.49%. The uneven coefficient Cu is 12.31 and the curvature coefficient Cc is 1.59, which means that many size series have been included in the soil sample. Therefore, there is a great difference in particle size, accordingly the gradation is excellent.
Table 1 Physics parameters of original soil
Survey data show that overlying strata of test area, mainly Quaternary residual hillside waste (Qdl +el), whose thickness is from 10 to 30 m, with an average 20 m deep layer of gravel and some local area clayey soil, is loose and slightly wet. The bedrock is Longtan coal series of Permian System (P2L), which is composed of muddy siltstone, carbon mudstone and silty mudstone. The test area is located in the central area of the mountains with simply hydrological and geological conditions. As a result, the groundwater depends mainly on the meteoric water supplies and varies greatly with the season. The groundwater in test area is mainly bedrock fissure water buried considerably deeply, which has not been found during the survey period. The excavation depth of test is 6 m and the sliding surface is within 5 m. Therefore, the test soil is the earth-rock mixture above the water table. The geological profile of test area is shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Engineering geological section plane: ①—Existing ground line; ②—Ground line of brushed slope (test area); ③—Strong decomposed zone limit; Qdl+el—Quaternary residual hillside waste; P2L—Longtan coal series of Permian System
3 Instrument arrangement and embedment
The test area is 10 m×10 m and the slope gradient is 1?2.5. In the test area, there are totally 12 pore-water pressure gauges, 3 inclinometer tubes and 9 drillings, of which, 3 drillings were used to install inclinometer tubes and the other 6 drillings were used to install the pore-water pressure gauge. The soil on both sides of the test area dug was moved away to form an isolation belt of 0.3 m wide by 0.5 m deep, and white sheet iron of 1 m in height was planted on both sides of the test area to revent rainwater infiltration into the surrounding soil. On the under border of test area, a drainage of 0.5 m in width and 1 m in depth was constructed, which extends across the possible sliding region and connects with the catchment water channel. All the surfaces apart from the one near the slope were protected by cement wall so as to avoid the wastage of water. In order to prevent water leakage, the catchment water channel, a square groove whose length, width and depth are all 2 m, was also been protected by cement. A reservoir of 5 m×4 m×2 m (cement wall protected) was excavated near the upper-right corner of test area. The layout of monitoring points is shown in Fig.2.
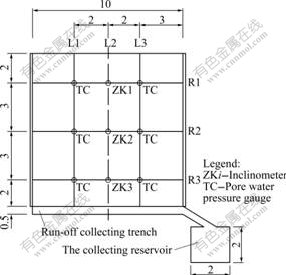
Fig.2 Layout of monitoring points (Unit: m)
4 Monitoring method
4.1 Slope cracks monitoring
To measure the width of the main crack with a steel tape, a simple measurement method was applied in slope cracks measuring. Such job can be done during the slope surface inspection.
4.2 Inclinometer monitoring
The inclinometer measuring device consists of inclinometer tube buried in the landslide body, inclinometer inserted into the inclinometer tube to measure the instantaneous slip of landslide, and digital measuring-reading instrument. The US-made Sinco portable digital drilling inclinometer, whose total accuracy and measure range were from -0.25 mm/m to 0.25 mm/m and from -15? to 15? respectively, was applied in the test.
The planting depth of the 3 inclinometer tubes buried in different locations of the artificial slope is 11 m (see Fig.2).
4.3 Pore-water pressure monitoring
The pore-water pressure was measured by Geokon-made 4500 vibrating string pore-water pressure measurement, whose specification is 133.35 mm in length and 25.40 mm in diameter, which can be buried in the soil or placed in the water pipes.
A total of 12 pore-water pressure measurements were buried in different locations of the slope. Two pore-water pressure measurements were buried in each drilling of L1 and L3 sections (see Fig.2). The pore-water pressure measuring hole depth of L1 section is 4 m and the probe embedded-depth is respectively 1 and 3 m; the pore-water pressure measuring hole depth of L3 section is 5 m and the probe embedded-depth is respectively 2 and 4 m.
4.4 Rainfall intensity and runoff monitoring
The total rainfall of the test area is recorded by the flow table on the main water supply pipe of the artificial rainfall simulator, and then the unit rainfall intensity, rainfall of per unit of time divided by the test area of 100 m2, can be obtained.
The surface runoff was collected to the header tank through the catchment water channel at the bottom of the test area, and then recycled to the reservoir on the top of the test area by pump. The time per unit surface runoff can be measured by the flow meter connected to the pump.
5 Artificial rainfall simulation test
5.1 Self-made artificial rainfall simulator
By referring to SR-field artificial rainfall simulator [16] developed by the Soil and Water Conservation Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, self-made artificial rainfall simulator was produced (see Fig.3), which consists of pump, flow meter, valve, pressure meter, sprinkler, main pipe, branch pipes, two-way pipes, three-way pipes and four-way pipes.
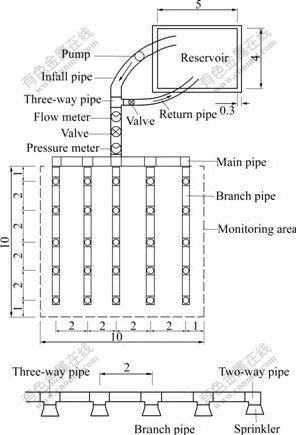
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of artificial rainfall simulator (Unit: m)
The main pipe and branch pipes are assembled by short pipes, whose length is 1 m or 2 m, two-way pipe, three-way pipes and four-way pipes. Multi-level rainfall intensity can be produced by adjusting the control valve.
5.2 Monitoring frequency
When the planted instruments and surrounding soil are harmonic stable, record the initial readings of each instrument, and then the implementation artificial rainfall with an hourly rainfall intensity of 60 mm/h until the slope slump. Stop for 1 h after every 2 h continuous rain and the monitoring data should be recorded during the intervals.
Therefore, the pore-water pressure, slope fissures, deep displacement, actual rainfall intensity and surface runoff should be recorded every three hours. Appropriately increased frequency of observation is needed when the slope may be unstable according to the monitoring data.
5.3 Implementation steps of artificial rainfall simulation on field
The implementation steps of artificial rainfall simulation on field are shown in Fig.4.

Fig.4 Implementation steps of in-situ simulation test
6 Analysis of test results
6.1 Slope fracture
There has not been notable large displacement taken place on the slope surface during the test period. One 3 m-long micro fissure, whose width varies from 1 to 2 mm, caused by tension, has been detected on the slope edge at 4?30 p.m. on April 30, 2005.
6.2 Inclinometer
The accumulative displacement with depth in ZK3 is shown in Fig.5. As can be seen from Fig.5, displacement, which decreases gradually with the increase of depth, occurs basically in the zone of 0-2.5 m below the surface, where the largest displacement (7.67 mm) takes place. The displacement below 2.5 m is close to zero.

Fig.5 Accumulative displacement with depth in ZK3
Fig.6 shows the accumulative displacement and accumulative rainfall intensity curve of feature points in ZK3 (0.5 m, 1.5 m and 4.0 m). As can be seen from Fig.6, the accumulative displacement of feature points increases with rainfall intensity gradually increasing and the deformation gradually decreases with the depth from the slope surface. The displacement in 0.5 m-deep equals two times of the displacement in 1.5 m-deep, while thereis basically no displacement in 4.0 m-deep. The small changes of numerical is caused by measurement error.
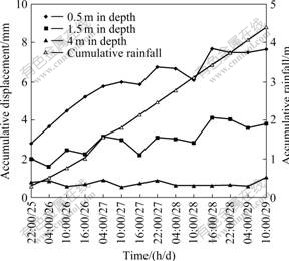
Fig.6 Accumulative displacement and accumulative rainfall intensity of feature points in ZK3
6.3 pore-water pressure
Fig.7 shows the pore-water pressure changes with time in R2 section. As can be seen from Fig.7, in the early rainfall infiltration, soil permeability is very strong. Therefore, the pore-water pressure is at a relatively low level. The pore-water pressure increases rapidly and achieves stable value with rainfall. The pore-water pressures in 1 m and 2 m are close to 0, while the average value in 3 m and 4 m is respectively 16.2 and 19.2 kPa, which is equivalent to 1.65 m and 1.96 m water column pressure respectively. The reason for this phenomenon is that the rainfall intensity in this field test is rather great. Therefore, the soil permeability will decrease after saturation, and transient stagnation water will come into being because of poor drainage. The transient stagnation water is about 4 m from the surface, which is also the outcome of the inclinometer test, in which the sliding surface is 3.5 m from the ground. The existence of transient stagnation water is extremely negative to the stability of accumulation slope. Firstly, the formation of stagnant water results in the increase of pore-water pressure but the decrease of effective stress, which will cause a decease in the shear strength of soil decreased. Secondly, the formation of stagnant water provides favorable conditions for the original non-saturated soil to absorb enough water and soften, which will also lead to the decrease in shear strength of soil. The dual effect of infiltration may be one of the main reasons of accumulation slope instability induced by rainfall.

Fig.7 Pore-water pressure versus time on R2 section
6.4 Rainfall intensity and runoff
Fig.8 shows the average percentage of infiltration during the rainfall time, which is calculated based on the measure results of rainfall intensity and runoff quantity. As can be seen from Fig.8, the average percentage of infiltration is 86% in the first two hours of rainfall implementation. Then the percentage of infiltration gradually reduces with time due to the increase in surface runoff. After 6 h the percentage of infiltration drops to a relatively stable value (50%), which means half of the rainfall turns into runoff after 6 h implementation of artificial rain. The drop of percentage of infiltration may be the result of the close of original open fractures due to water saturation of slope soil.

Fig.8 Average hourly rainfall (infiltration) and percentage of infiltration
6.5 Sliding surface formation
The monitoring depth of inclinometer is 11 m from the mouth of test tube. The monitored sliding surface depth means the distance from the mouth of the test tube to the sliding surface, while there is still certain distance from the mouth of the test tube to the slope surface. Therefore, the length of the exposure part of the test tube should be subtracted to get the actual sliding surface depth. Based on the monitoring results, the sliding surface depth of ZK1-ZK3 is respectively 4.2, 3.2 and 2.2 m from the surface after being revised. Combining the sliding surface depth with tension fracture position, the location and formation of L2 cross-section can be plotted, as shown in Fig.9. As can be seen from Fig.9, the sliding surface depth of accumulation landslide is quite shallow, all within 3-4 m below the surface, which belongs to shallow landslide.
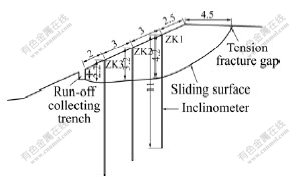
Fig.9 Sliding surface formation of L2 cross-section (Unit: m)
6.6 Mechanical analysis of accumulation landslides
The accumulation slope has its unique engineering geology character, deformation and destroying characteristics, rainfall infiltration law as well as evolution and failure mechanisms. Under strong rainfall, the slope soil will become water saturation and some pores in soil will close, which will result in permeability decrease. Therefore, transient stagnation water will come into being because of poor drainage. The existence of stagnant water is extremely negative to the stability of accumulation slope. Firstly, the formation of stagnant water results in the increase of pore-water pressure but the decrease of effective stress, which will cause the decease in the shear strength of soil decreased. Secondly, the formation of stagnant water provides favorable conditions for the original non-saturated soil to absorb enough water and soften, which will also lead to the decrease in shear strength of soil. The dual effect of infiltration may be one of the main reasons of accumulation slope instability induced by rainfall.
7 Conclusions
(1) The accumulation landslide caused by rainfall infiltration is mostly shallow loose damage, whose sliding deformation zone is 0-4 m from the slope surface. The deformation gradually decreases from the slope surface, where the largest deformation occurs, to inside of the slope.
(2) The average percentage of infiltration is 86% in the first 2 h of rainfall implementation. Then the percentage of infiltration gradually reduces with time due to the increase in surface runoff. After 6 h the percentage of infiltration drops to a relatively stable value (50%). The drop of percentage of infiltration may be the result of the close of original open fractures due to water saturation of slope soil.
(3) The accumulation slope in test area has encountered 4.5 m of rainfall in nearly four days and nights, which greatly exceeds the actual potential of the rainfall intensity, and the average percentage of infiltration reaches 50%. But there has been only deformation rather than slump damage taken place in the slope, which means the damage condition of accumulation slope is not only just rainfall, but also the slope rate and geological conditions.
References
[1] ZHOU Zhong, FU He-lin, LIU Bao-chen, TAN Han-hua, LUO Qiang, LONG Wan-xue. Scheme design of field simulation test of accumulation landslide [J]. Journal of Highway, 2006(1): 74-79. (in Chinese)
[2] ZHOU Zhong. Study on the fluid-solid coupling characteristic of soil and rock blending landslide and its prediction and forecast [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2006. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHOU Zhong, FU He-lin, LIU Bao-chen, TAN Han-hua, LONG Wan-xue, LUO Qiang. Study on in-situ monitoring of cut tests on a well-instrumented colluvial slope [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(10): 2065-2070. (in Chinese)
[4] LI Ai-guo, YUE Zhong-qi, TAN Guo-huan, LEE Zhuo-fen, LUO Jin-tan. Design and installation of comprehensive instrumentation system for slope in Hong Kong [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(5): 790-796. (in Chinese)
[5] AU S W. Rain-induced slope instability in Hong Kong [J]. Q J Engng Geol, 1998, 51(1): 1-36.
[6] YANG Xiao-li, SUI Zhi-rong. Seismic failure mechanisms for loaded slopes with associated and nonassociated flow rules [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(2): 276-279.
[7] KEEFER D K, WILSON R C, MARK R K, BRABB E E, BROWN III W M, ELLEN S D, HARP E L, WIECZOREK G F, ALGER C S, ZATKIN R S. Real-time landslide warning during heavy rainfall [J]. Science, 1987, 238: 921-925.
[8] FINLAY P J, FELL R, MAGUIRE P K. The relationship between the probability of landslide occurrence and rainfall [J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1997, 34: 811-824.
[9] ZHAN Lang-tong, WU Hong-wei, BAO Cheng-gang, GONG Bi-wei. Artificial rainfall infiltration tests on a well-instrumented unsaturated expansive soil slope [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2003, 24(2): 151-158. (in Chinese)
[10] LAN Heng-xing, WU Fa-quan, ZHOU Cheng-hu, WANG Ling-juan. Spatial hazard analysis and prediction on rainfall-induced landslide using GIS [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(7): 703-708.
[11] DAI F C, LEE C F. Frequency-volume relation and prediction of rainfall-induced landslides [J]. Engineering Geology, 2001, 59(3/4): 253-266.
[12] YANG Xiao-li, YIN Jian-hua. Slope stability analysis with nonlinear failure criterion [J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 130(3): 267-273.
[13] YANG Xiao-li, LI Liang, YIN Jian-hua. Seismic and stability analysis for rock slopes by a kinematical approach [J]. Geotechnique, 2004, 54(8): 543-549.
[14] CROSTA G. Regionalization of rainfall thresholds: An aid to landslide hazard evaluation [J]. Environmental Geology, 1998, 35(2/3): 131-145.
[15] LIN M L, JENG F S. Characteristics of hazards induced by extremely heavy rainfall in central Taiwan-typhoon herb [J]. Engineering Geology, 2000, 58(2): 191-207.
[16] CHEN Wen-liang,TANG Ke-li. A new SR style field artificial rainfall simulator [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2000, 7(4): 106-110. (in Chinese)
Foundation item: Project(50678175) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2008-05-29; Accepted date: 2008-07-23
Corresponding author: ZHOU Zhong, PhD; Tel: +86-731-2239906; E-mail: zzcsu@mail.csu.edu.cn
(Edited by YANG You-ping)