模内键合聚合物微流控芯片微通道变形研究
楚纯朋,蒋炳炎,廖竞,王璋,黄磊
(中南大学 高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:基于广义Maxwell材料模型,仿真研究聚合物微流控芯片模内键合过程中微通道变形规律。利用单轴压缩实验,得到PMMA材料应变/时间关系,采用有限元软件Marc仿真研究键合温度、键合压力和键合时间对芯片微通道高度和顶部宽度变形的影响规律。研究结果表明:随着键合温度、键合压力和键合时间的增加,芯片微通道的变形增大。键合温度对微通道变形影响最大,其次是键合压力,键合时间对微通道变形影响相对较小。利用微流控芯片注射成型模内键合实验进行验证,仿真结果与实验结果基本吻合,表明采用广义Maxwell模型能准确的预测聚合物微流控芯片模内键合过程中微通道的变形。
关键词:广义Maxwell模型;PMMA;微流控芯片;模内键合
中图分类号:TQ320.63 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)12-4833-07
Study of microchannel deformation of polymer microfluidic chip by in-mold bonding
CHU Chunpeng, JIANG Bingyan, LIAO Jing, WANG Zhang, HUANG Lei
(State Key Laboratory of High-Performance Complex Manufacturing,Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Based on the Maxwell model, the deformation law of micro-channels during the in-mold bonding process was studied. The strain/time behaviour of PMMA was obtained through uniaxial compression experiments, and the finite element software Marc was used to study the influence law of height and top width deformation in micro-channels caused by the bonding temperature, bonding press and bonding time. The results show that the deformation of micro-channels increases with the increase of the bonding temperature, bonding press and bonding time in which the bonding temperature is the most influential factor, following by the bonding pressure, and the bonding time has a relatively small influence. The results of the simulation basically tally with the in-mold bonding experiments of microfluidic chip injection molding, which shows Generalized Maxwell model could precisely predict the deformation of micro-channels during the in-mold bonding process of polymer microfluidic chip.
Key words: generalized maxwell model; PMMA; microfluidic chip; in-mold bonding
聚合物材料具有加工方便,原料价格低,光学性能好等特点,在微流控芯片制造领域得到了广泛的应用[1]。目前,聚合物微流控芯片一般采用热压法成型芯片微通道,再利用热键合方法封合微通道[2-3],芯片制作过程中存在反复的升降温,造成生产周期长,效率不高。为提高芯片的生产效率,蒋炳炎等[4-5]采用注射成型加工芯片微通道,将热键合工艺集成于注射成型之中,利用模具滑移或转动实现基片和盖片的对准,在抽芯力和模温的作用下实现芯片键合。此工艺避免了芯片的反复升降温,将芯片的制作周期缩短至5 min,为批量制作微流控芯片提供了新思路。微流控芯片微通道的变形是决定微流控芯片键合质量的重要指标[6]。目前对微流控芯片键合过程中微通道变形研究大部分采用实验方式,而理论和仿真研究相对较少,阻碍了从根本上理解和掌握微通道的变形机理。对于芯片模外键合的研究,Roy等[7]采用线弹性材料模型,利用ANSYS分析了芯片键合过程的应力/应变场,结果表明聚合物键合界面的应力非常均匀,应力奇点很少。李经民[8]采用弹性理论建立了微通道变形模型,研究了键合温度、键合压力和微通道尺寸对微通道变形的影响,结果表明微通道的变形主要来源于3个方面:(1) 微通道顶边和底部由于受到挤压作用形成的凸起;(2) 微通道在深度方向被压缩;(3) 微通道在宽度方向发生收缩现象。文伟力[9]采用有限元方法对热键合过程中的温度场分布和非等温键合进行了研究,结果表明,在键合过程中盖片和基片微通道区域产生的微凸起是引起微通道变形的主要因素。对于芯片模内键合的研究,蓝才红等[10-11]采用弹性模型,仿真研究了模内键合过程中PMMA微流控芯片微通道变形规律,但是采用弹性模型不能获得微通道变形随时间变化情况。Hung等[12]对PMMA材料在高温下的力学性能进行了研究,指出PMMA材料在高温下表现出了与时间相关的非线性黏弹性性能,作用时间对聚合物材料变形非常明显。广义Maxwell模型[9]是由一系列理想弹簧和理想黏壶串并联而成,能较好的模拟聚合物材料黏弹性能,并在热压成型工艺中得到广泛应用。本文作者采用广义Maxwell模型分析PMMA微流控芯片模内键合过程中微通道变形随时间变化的情况,得到不同键合工艺参数对微通道变形的影响规律,并采用注射成型与模内键合实验进行验证,为掌握聚合物模内键合过程中芯片微通道变形机理,提高芯片键合质量奠定基础。
1 材料性能测试和微通道变形仿真
1.1 PMMA材料应变与时间关系
微流控芯片材料为台湾奇美公司的CM-205 型PMMA,其力学性能与温度、压力和时间有关。为获得仿真所需的材料力学性能参数,采用Instron 8032试验机进行单轴压缩实验,材料实验样品和实验条件,如表1所示。利用一阶指数衰减函数拟合实验数据,获得的PMMA材料应变与时间关系模拟材料的黏弹性能,结果如图1所示。
表1 单轴压缩实验条件
Table 1 Condition of uniaxial compression test
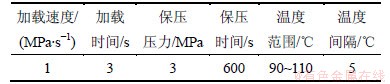
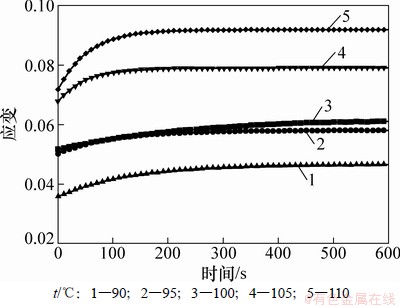
图1 PMMA材料应变与时间关系
Fig. 1 Relationship between material strain and time
1.2 模内键合微通道变形仿真
1.2.1 微通道变形仿真模型建立
单通道十字型微流控芯片的整体尺寸(长×宽×高)为50 mm×28 mm×1.4 mm, 微通道截面形状为等腰梯形,开口宽度为0.1 mm,高为0.04 mm,腰与高的夹角为37°,基片厚度为0.8 mm,盖片厚度为0.6 mm,如图2所示。
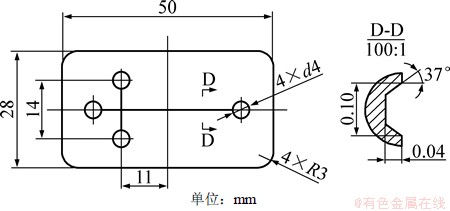
图2 微流控芯片基片几何形状
Fig. 2 Substrate geometry of microfluidic chip
采用Marc有限元软件对PMMA微流控芯片模内键合进行仿真,为简化模型做如下假设:(1) 芯片微通道在长度方向的截面形状相同,微通道截面变形问题简化为平面应变问题处理,取微通道附近进行建模;(2) 键合时基片和盖片接触面粗糙, 盖片和基片在接触面无滑移;(3) 坐标原点取基片底部中点,沿厚度方向为y,位移为uy,宽度方向为x,位移为ux;(4) 芯片的宽度大于厚度,忽略重力效果。仿真的几何模型如图3所示。
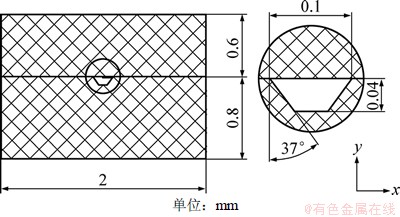
图3 仿真的几何模型
Fig. 3 Geometric model for simulation
1.2.2 载荷工况与边界条件
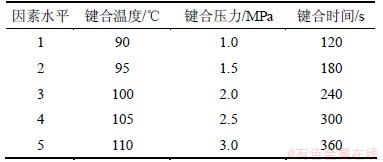
注射成型时模温初始温度为80 ℃,芯片在模具内升温过程中四周位移为0,在ux=±1和uy=0,1.4处施加位移边界条件为0;设定键合温度和键合时间,在uy=1.4处施加向下的键合压力,模具周围环境温度设定为20 ℃。具体载荷工况如表2所示。仿真研究所参考工艺参数组合如表3所示,逐一改变单个工艺参数,研究各工艺参数对微通道变形的影响。各因素的水平取值[6, 13-14]见表4。
表2 载荷工况
Table 2 Load conditions

表3 参考工艺参数
Table 3 Reference parameters
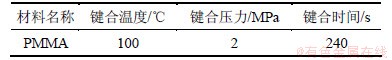
表4 因素水平
Table 4 Levels of factors
2 芯片微通道变形实验验证
2.1 实验设备与模具
微流控芯片的微通道尺寸达到微米级,属于薄壁零件微注塑成型。采用德国Arburg 370S精密注塑机,最大锁模力为500 kN,最大注塑压力为250 MPa,螺杆直径为20 mm,配备三组液压抽芯,能够满足芯片的成型与键合的动作需求。
微流控芯片模具设计采用“1+1”式型腔设计方案,基片和盖片在一套模具中成型,利用湿法刻蚀和精密电铸技术制作微流控芯片基片模芯,成型模具和模芯如图4所示。
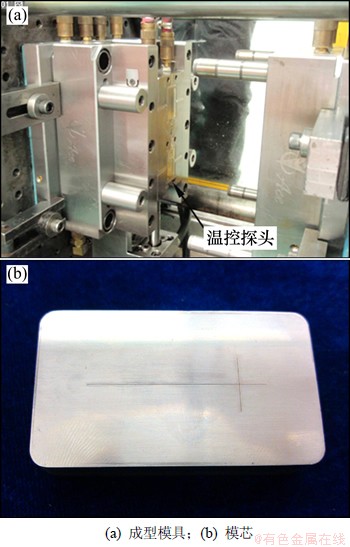
图4 模芯镶块及成型模具
Fig. 4 Insert with microstructure and mold
2.2 微流控芯片模内键合实验
按照仿真研究方案进行微流控芯片模内键合实验,验证采用广义Maxwell模型分析PMMA微流控芯片模内键合过程中微通道变形的合理性,聚合物微流控芯片模内键合实验的基本流程如图5所示。本实验采用模具温度90 ℃、注射速率35 cm2/s、熔体温度245 ℃、保压时间3 s、保压压力140 MPa、冷却时间20 s完成芯片基片和盖片的注射成型[15]。模内键合实验考察键合温度、键合压力和键合时间3个工艺参数对微通道变形的影响,键合参考工艺参数如表3所示,按照表4的参数组合进行实验。实验指标为芯片微通道高度和顶宽变形量,采用VMS-1500影像测量仪测量芯片微通道形貌尺寸。
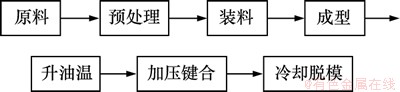
图5 微流控芯片模内键合实验基本流程图
Fig. 5 Basic flowchart of in-mold bonding microfluidic chip
3 结果与分析
3.1 芯片微通道变形过程分析
聚合物材料的在玻璃态转化温度附近具有复杂的黏弹性能,研究芯片模内键合过程中微通道的变形能较好的预测芯片微通道的变形机理。在键合温度为100 ℃、键合压力为3 MPa和键合时间为300 s作用下,芯片微通道高度变形量、顶部宽度变形量在键合过程中的变化情况如图6和图7所示。
微流控芯片注射成型后直接在模具内升温至键合温度,不考虑温升对微通道变形的影响。施加键合压力后,芯片发生瞬间弹性变形,微通道顶部向下凸起,微通道底部向上凸起。由于PMMA材料具有黏弹性能,芯片微通道会持续发生变形,当键合时间达到300 s时,芯片微通道高度最大变形量达到14.5 μm。图8所示为芯片微通道变形云图。键合过程中微通道顶部与两侧黏合,芯片微通道顶部宽度变形较大,如图8
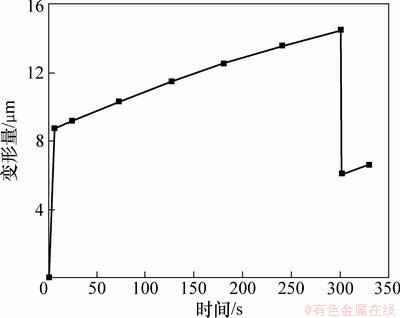
图6 高度变形量与时间的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between deformation of high degree and time
所示。卸去压力后,芯片的弹性形变发生恢复,微通道高度变形减小至6.1 μm。由于微通道顶部与两侧的黏合,顶部宽度变形恢复较小,黏合处始端主要为压应力,表明此处具有较好的黏合强度,不容易分开。图9所示为微通道在顶部与两侧黏合处的应力云图。随着黏合区域的增加,压应力逐渐减小,黏合区域末端主要为拉应力,应力集中非常明显,此处容易产生撕裂,如图9所示。
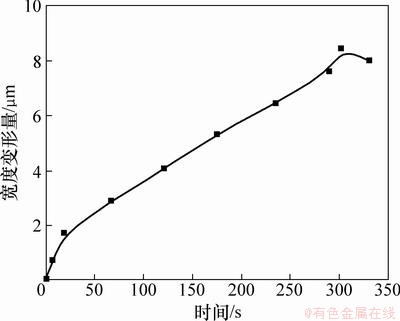
图7 顶部宽度变形量与时间的关系
Fig. 7 Relationship between deformation of top width and time
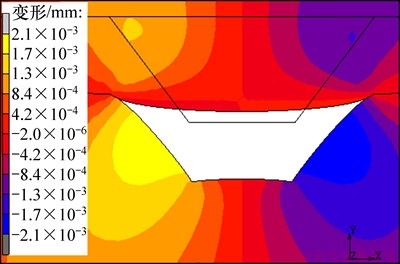
图8 芯片微通道变形云图
Fig. 8 Deformation image of micro-channel
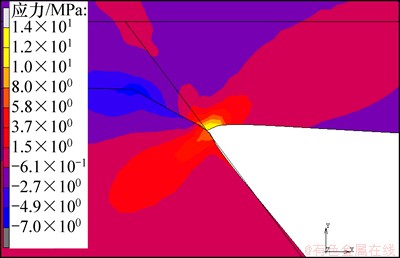
图9 微通道顶部与侧壁黏合处的应力云图
Fig. 9 Bonding stress contour of micro-channel
3.2 键合工艺参数对微通道变形的影响
键合温度对芯片微通道变形的影响如图10和图11所示。由图10和图11可见:键合温度低于100 ℃时,微通道变形很小,主要表现在高度方向,变形量达到了7.5%,而在宽度方向变形很小,不到2%。键合温度超过100 ℃后,微通道高度、顶部宽度会产生较大变形。当键合温度接近105 ℃时,由于PMMA材料的玻璃态转化温度约为105 ℃,材料的弹性模量发生剧降,黏弹性能增加。在键合压力的作用下,芯片微通道会发生较大变形,变形量达到22%。在键合过程中芯片微通道的顶部与侧壁会发生黏合现象,温度越高,黏合区域也越大,微通道变形也相应的增大。键合温度对芯片微通道变形程度影响的仿真结果与实验结果吻合较好,采用黏弹性模型可以较好的模拟芯片微通道变形随键合温度变化的规律。但键合温度达到110 ℃时,实验数值和仿真数值相差较大,这是因为在黏合的区域末端主要为拉应力,存在应力集中现象,撤除键合压力后,微通道黏合区域减小,使微通道的变形减小。
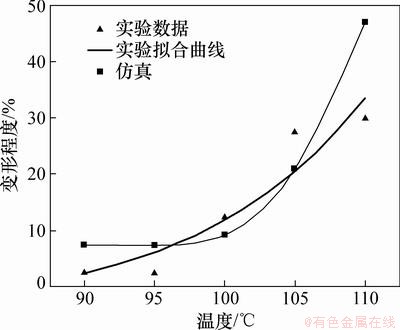
图10 键合温度对高度变形的影响
Fig. 10 Effect of temperature on deformation in height
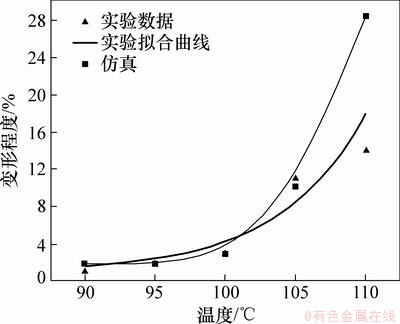
图11 键合温度对顶宽变形的影响
Fig. 11 Effect of temperature on deformation in width
键合压力对微通道变形的影响如图12和图13所示。由图12和图13可见:芯片微通道的高度和顶部宽度的变形量随着键合压力的提高而增加,芯片微通道尺寸的变形与键合压力的关系近似于线性关系,键合压力对芯片微通道高度变形的影响更为明显。微通道高度变最大形量为14%,顶部宽度最大变形量为7%。为保证芯片微通道变形尽可能的小,在键合强度满足要求的情况下尽量选择较小的键合压力。仿真结果与实验结果基本吻合,但在高度方向上相差相对较大。当键合压力逐渐增大时,芯片微通道处产生的残余应力也会相应提高,残余应力释放,会使高度方向变形缩小,所以仿真结果与实验结果在高度方向上的偏差应是键合后制品残余应力释放引起的。
键合时间对微通道变形的影响如图14和图15所示。由图14和图15可见:芯片微通道的高度和顶部宽度的变形量随着键合时间的增加而增加,在120~360 s的键合时间范围内,芯片微通道尺寸的变形与键合时间的关系近似于线性关系,键合压力对对芯片微通道高度变形的影响更为明显,高度最大变形量为12.5%,顶部宽度最大变形量为4.2%。仿真结果与实验结果基本吻合,但在高度方向上相差相对较大,同样是由于键合后制品残余应力释放引起的。
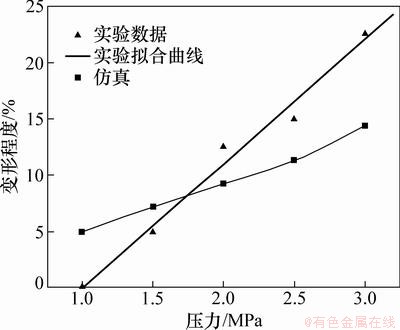
图12 键合压力对高度变形的影响
Fig.12 Effect of pressure on deformation in height
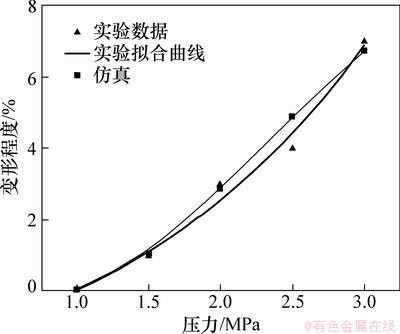
图13 键合压力对顶宽变形的影响
Fig. 13 Effect of pressure on deformation in width
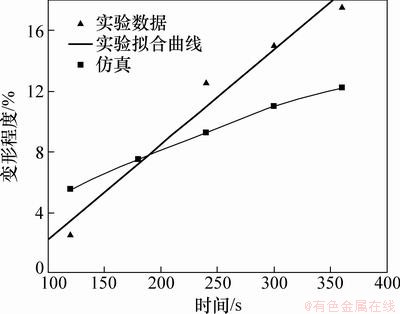
图14 键合时间对高度变形的影响
Fig. 14 Effect of time on deformation in height
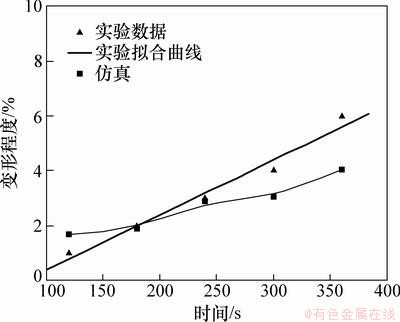
图15 键合时间对顶宽变形的影响
Fig. 15 Effect of time on deformation in width
4 结论
(1) 微流控芯片模内键合过程中,微通道顶部与侧壁会产生粘合现象,黏合处始端主要为压应力,此处具有较好的粘合强度,不容易分开;黏合区域末端主要为拉应力,应力集中非常明显,此处容易产生撕裂。黏合现象对微通道变形具有很大的影响。
(2) 随着键合温度、键合压力和键合时间的增加,芯片微通道的变形增大。键合温度对微通道变形影响最为复杂,键合温度低于100 ℃时,微通道变形很小,主要表现在高度方向;键合温度超过100 ℃后,微通道高度、顶部宽度都会产生较大变形;当键合温度接近105 ℃时,材料的弹性模量发生剧降,黏弹性能增加,在键合压力的作用下,芯片微通道的形貌会急剧变化。键合压力和键合时间对微通道高度变形影响更为显著。
(3) 采用广义Maxwell材料模型能较好的模拟聚合物微流控芯片键合过程中微通道的变形,对聚合物微流控芯片微结构的优化设计以及模内键合工艺参数的优化具有指导作用。
参考文献:
[1] 郑小林, 鄢佳文, 胡宁, 等. 微流控芯片的材料与加工方法研究进展[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2011, 30(6): 1-7.
ZHENG Xiaolin, YAN Jiawen, HU Ning, et al. Research progress of materials and fabrication methods of microfluidic chip[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2011, 30(6): 1-7.
[2] Becker H, Heim U. Hot embossing as a method for the fabrication of polymer high aspect ratio structures[J]. Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical, 2000, 83(1): 130-135.
[3] Tsao C W, Devoe D L. Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2009, 6(1): 1-16.
[4] 蒋炳炎, 蓝才红, 刘瑶, 等. 一种用于聚合物微流控芯片模内键合的方法: 中国, CN101575084[P]. 2009-11-11.
JIANG Bingyan, LAN Caihong, LIU Yao, et al. A method for in-mold bonding of polymer microfluidic chip. China, CN101575084[P]. 2009-11-11.
[5] 蓝才红. 聚合物微流控芯片模内键合微通道变形研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学机电工程学院, 2009: 19-20.
LAN Caihong. Research of microchannel deformation of polymer microfluidic chip by in-mold bonding[D]. Changsha: Central South University. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, 2009: 19-20.
[6] Zhu X, Liu G, Guo Y, et al. Study of PMMA thermal bonding[J]. Microsystem Technologies, 2007, 13(3): 403-407.
[7] Xu L R, Sengupta S, Kuai H. An experimental and numerical investigation of adhesive bonding strengths of polymer materials[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2004, 24(6): 455-460.
[8] 李经民. 热塑性聚合物立体结构微流控器件制作方法及相关理论研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2010: 81-86.
LI Jingmin. Research on the theory and fabrication of thermoplastic micrfluidic device with three-dimensional microstructures[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2010: 81-86.
[9] 文伟力. 聚合物微流控芯片的制作、检测及仿真研究[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学机械科学与工程学院, 2007: 66-74.
WEN Weili. Study on the manufacture, measurement and simulation of polymer microfluidic chips[D]. Jilin: Jilin University. School of Mechanical Science and Engineering, 2007: 66-74.
[10] 蓝才红, 蒋炳炎, 刘瑶, 等. 聚合物微流控芯片键合微通道变形仿真研究[J]. 塑料工业, 2009, 37(5): 31-34.
LAN Caihong, JIANG Bingyan, LIU Yao, et al. Simulation study of microchannel distortion of polymeric microfluidic chip with bonding technique[J]. China Plastics Industry, 2009, 37(5): 31-34.
[11] 蒋炳炎, 刘瑶, 李代兵, 等. PMMA微流控芯片高效键合工艺研究[J]. 塑料工业, 2010, 38(4): 33-36.
JIANG Bingyan, LIU Yao, LI Daibing, et al. Research on eff icient bonding procedure of PMMAM icrof luidic chip[J]. China Plastics Industry, 2010, 38(4): 33-36.
[12] Hung C, Chen R H, Lin C R. The characterisation and finite-element analysis of a polymer under hot pressing[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2002, 20(3): 230-235.
[13] Martynova L, Locascio L E, Gaitan M, et al. Fabrication of plastic microfluid channels by imprinting methods[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1997, 69(23): 4783-4789.
[14] 姚李英, 张瑜, 陈涛, 等. 激光制备PMMA基PCR微流控芯片的热压键合研究[J]. 激光杂志, 2006, 27(1): 75-77.
YAO Liying, ZHANG Yu, CHEN Tao, et al. Thermal bonding technology for PMMA based micro flow through PCR chip[J]. Laser Journal, 2006, 27(1): 75-77.
[15] 楚纯朋. 微流控芯片注射成型工艺参数优化[D]. 长沙: 中南大学机电工程学院, 2009: 59-60.
CHU Chunpeng. The process parameters optimization of microfluidic chip by injection molding[D]. Changsha: Central South University. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, 2009: 59-60.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2013-03-11;修回日期:2013-05-29
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划(“973”计划)项目(2012CB025905);国家大学生创新训练项目(AL11496)
通信作者:蒋炳炎(1963-),男,浙江浦江人,博士,教授,从事高分子材料精密成型技术研究;电话:0731-88836035;E-mail:jby@csu.edu.cn