DOI:10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.202x-hhhhh
晶粒取向对铜镍合金腐蚀形貌的影响
史冰绡1,2,3,谭振江4,曹东东1,2,3,贾荣光1,2,3,马通达1,2,3**
(1 有研科技集团有限公司 国家有色金属及电子材料分析测试中心,北京 100088;
2 国标(北京)检验认证有限公司,北京 100088;
3 北京有色金属研究总院,北京 100088;
4 中国船舶重工集团有限公司第七二五研究所,山东 青岛,266237)
摘 要:铜镍合金管材腐蚀失效分析多集中于表面电化学腐蚀行为及钝化膜结构与耐腐蚀性能的关系。然而,铜镍合金管材表面微观组织结构对其耐腐蚀性能的影响尚未澄清。本文采用扫描电镜背散射电子衍射(SEM-EBSD)和原子力显微镜(AFM)对铜镍合金管材表面晶粒取向和腐蚀形貌演化进行了定位跟踪观察,以揭示不同取向晶粒的腐蚀行为和腐蚀形貌演化规律。研究表明,随着铜镍合金管材表面晶粒取向与<1 1 1>方向之间夹角的减小,晶粒表面腐蚀深度增加,形貌由扇贝状转变为阶梯状或四面体凸起状。这与晶粒表面能直接相关,符合台阶生长模型(TLK)。
关键词:铜镍合金;定位跟踪表征;晶粒取向;腐蚀形貌
文章编号: 中图分类号:TG172.5 文献标志码:A
铜镍合金管材在服役过程中时常发生腐蚀失效,导致重要海洋工程和高技术船舶关键部件发生严重泄漏[1,2]。为了彻底解决上述问题,亟需深入研究铜镍合金管材腐蚀行为的内在机理,优化铜镍合金管材的耐蚀性能。目前,铜镍合金管材的腐蚀研究主要集中于腐蚀产物膜结构与耐腐蚀性能之间的关系[3-7],而关于铜镍合金管材微观组织结构与耐蚀性能关系的研究鲜有报道。初步研究表明,优化晶界特征分布(Grain Boundary Character Distribution,GBCD)[8]和晶粒尺寸[9]可有效提升铜镍合金耐蚀性能。然而,关于铜镍合金晶粒取向对耐蚀性能的影响仍未澄清。
对合金表面腐蚀形貌的观察可用于分析腐蚀过程及耐蚀性机理。Lapeire等[10,11]通过对纯铜表面腐蚀形貌的表征,发现腐蚀后相邻近<1 1 1>和<0 0 1>取向晶粒存在明显高度差。Koroleva[12]采用原子力显微镜(AFM)和扫描电镜(SEM)对纯铝的腐蚀形貌进行表征,发现晶粒取向与腐蚀后晶粒的高度密切相关。Wang等[13]在对镍基合金690的腐蚀试验中,发现了不同取向的晶粒有不同的腐蚀速率和腐蚀形貌,并分析取向接近于较低表面自由能的晶面即<1 1 1>方向的晶粒,更容易腐蚀。综上,可通过将扫描电镜与原子力显微镜相结合的方式对铜镍合金腐蚀形貌进行表征,以探究铜镍合金晶粒取向对耐蚀性能的影响。
为了观察铜镍合金管材表面腐蚀形貌的演化过程,探究微观组织结构对铜镍合金管材耐腐蚀性能的影响,所在课题组开发了基于扫描电镜的定位跟踪表征技术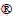 [14]。相关研究进展表明,定位跟踪技术可用于揭示铜镍合金管材表面腐蚀形貌演化与晶粒取向的相关性[14]。为了进一步澄清铜镍合金管材的表面腐蚀机理,还须阐明铜镍合金管材腐蚀形貌与腐蚀速率之间的联系。
[14]。相关研究进展表明,定位跟踪技术可用于揭示铜镍合金管材表面腐蚀形貌演化与晶粒取向的相关性[14]。为了进一步澄清铜镍合金管材的表面腐蚀机理,还须阐明铜镍合金管材腐蚀形貌与腐蚀速率之间的联系。
本文采用人工海水浸泡腐蚀试验,结合基于扫描电镜背散射电子衍射(SEM-EBSD)和原子力显微镜(AFM)的定位跟踪表征技术,对铜镍合金管材晶粒取向及腐蚀形貌进行观察,以揭示铜镍合金管材微观组织与微区腐蚀速率之间的关系,阐释微观组织结构对腐蚀性能影响的内在机理。
1 实验
1.1 化学成分分析
本文以某船舶冷凝器用铜镍合金换热管为实验材料展开研究工作,其合金牌号为CuNi10Fe1.6Mn(B10),管外径89 mm,管壁厚度2.5 mm。采用电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-AES)、光度法、高频燃烧红外吸收法、电解法等对样品进行化学成分检验,检验结果如表1所示。
表1 B10换热管化学成分分析结果
Table 1 The chemical composition of the 90Cu-10Ni alloy used (mass %).
1.2 微观组织观察
为了易于微观组织观察,将样品在1000℃加热保温5 min,而后空冷。将热处理后的样品镶嵌起来,依次用120#、220#、500#、1000#、2400#砂纸进行研磨后,再经2.5 μm和1.0 μm的金刚石抛光膏抛光,去除划痕直至获得光亮表面。利用显微维氏硬度仪在样品表面打1~3个硬度压痕作为定位标记。为了消除样品表面的残余应力,使用70wt.%H3PO4+30wt.%CH3CH2OH溶液进行电解抛光,用酒精作为介质超声清洗抛光后的样品,去除残留的电解液。
微观组织表征采用JSM-7900F热场发射扫描电子显微镜(FE-SEM),配EDAX Pagaus XM2及OIM-Analysis 8软件,获取晶粒取向、晶界类型、晶粒尺寸分布、残余应力等晶体学信息。进行扫描电镜观察时,加速电压为15 kV,电流10 mA;EBSD测试加速电压为20 kV,电流为15 mA,扫描步长为1 μm。
1.3 表面轮廓特征
将样品静置于3.5wt.%NaCl溶液浸泡2小时,取出后采用电解抛光去除表面腐蚀产物,观察定位点附近去除腐蚀产物后的样品表面形貌。
利用原子力显微镜(型号为Bruker Multimode 8)对去除腐蚀产物后的样品进行表面轮廓表征,采用Gwyddion软件实验数据分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 扫描电子显微镜分析
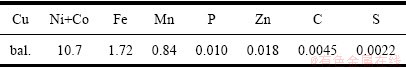
图1为人工海水浸泡腐蚀试验前铜镍合金样品扫描电镜形貌及EBSD的定位表征结果。选取区域A和区域B,如图中黑色方框所示。区域A和区域B内均存在取向接近于<1 1 1>、<0 0 1>或<1 0 1>方向的晶粒及少量孪晶。
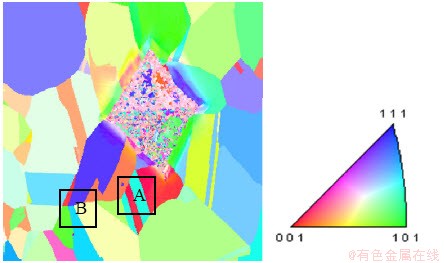
图1 铜镍合金样品的EBSD测试结果及其相应的反极图
Fig. 1 EBSD results of the electropolished 90Cu-10Ni sample with the corresponding inverse pole figure
图2 铜镍合金样品的定位跟踪观察结果
Fig. 2 Results of indentation-tracking characterization of copper-nickel alloy sample
图3、图4分别为图1中区域A、区域B及对应区域内晶粒及少量孪晶的腐蚀形貌扫描电镜定位跟踪表征结果,可见,经3.5wt.%NaCl溶液浸泡腐蚀后,区域A和区域B内晶粒的腐蚀形貌主要呈现为四面体凸起状、台阶状及扇贝状。
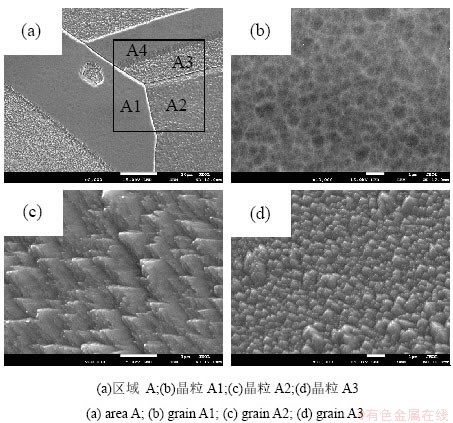
图3 区域A及其内晶粒的腐蚀形貌图
Fig. 3 Corrosion morphology of area A and its grains

图4 区域B及其内晶粒的腐蚀形貌图
Fig. 4 Corrosion morphology of area B and its grains
表2 区域A、B的晶粒取向及腐蚀形貌观察结果
Table 2 Grain orientation and surface morphology observation results of Regions A and B
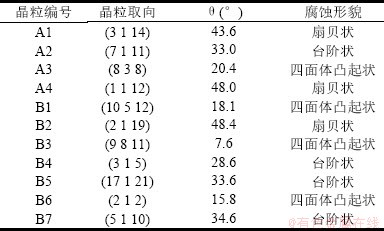
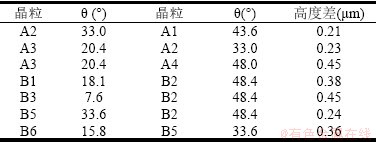
为了揭示铜镍合金管材表面不同取向晶粒的腐蚀速率及腐蚀机理,本文将晶粒表面的法向量即晶粒取向与<1 1 1>取向之间的夹角记为θ。表2为区域A、区域B内部晶粒取向、扫描电镜形貌统计及计算结果。样品经3.5wt.%NaCl溶液浸泡腐蚀后出现了腐蚀各向异性,并且其腐蚀形貌随角度θ的增加而发生变化。当角度θ为7.6°~20.4°时,如A3,B1,B3和B6晶粒,晶粒在腐蚀后出现四面体凸起状;当角度θ为28.6°~34.6°时,如A2,B4,B5和B7晶粒,晶粒表面呈现出台阶状特征;当角度θ为34.6°~48.4°时,如A1,A4,B2晶粒,晶粒表面上没有生成凸起状,而是出现了许多倒矩形锥体孔并形成了扇贝状表面。图5为铜镍合金晶粒的表面法向向量的反极图(IPF)图,不同颜色代表的不同的晶粒表面形貌,证实了晶粒表面的取向会严重影响其腐蚀行为。经人工静态海水浸泡腐蚀试验后,铜镍合金在同一个晶粒内沿不同暴露表面的法线方向发生的腐蚀会有所差异,这与对面心立方晶格(FCC)合金的许多研究结果相一致[15-18]。
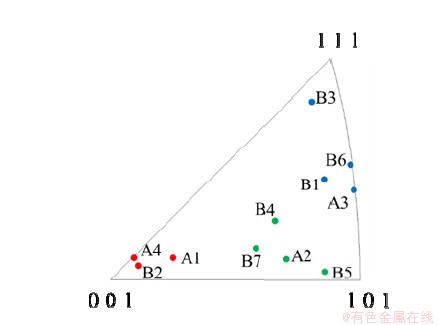
图5 铜镍合金晶粒的表面法向向量的IPF图
Fig. 5 IPF diagram of the surface normal vector of copper-nickel alloy grains
2.2 原子力显微镜分析
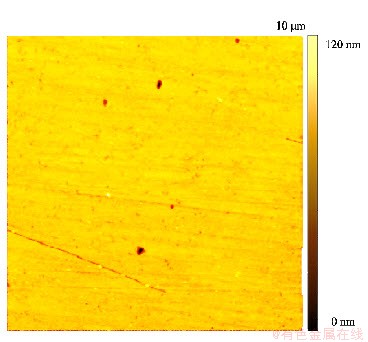
图6 人工海水浸泡腐蚀前AFM测试结果
Fig. 6 2-D AFM image before artificial seawater immersion corrosion
在人工海水腐蚀试验前,样品经AFM测试,只存在少量的划痕及表面污染物,并未出现明显高度差异,如图6所示。人工海水浸泡腐蚀试验后,对区域A、区域B及对应内域内部晶粒进行AFM表征,结果显示样品表面可见明显表面高度差异,如图7和图8所示。
图7为区域A及其内部晶粒的AFM测试结果。其中,图7(a)为区域A的AFM测试2-D图,图7(b)、图7(c)和图7(d)分别为沿图7(a)中箭头1、2和3方向分别绘制的相邻晶粒表面轮廓图。图8为区域B及其内部晶粒的AFM测试结果,同样沿图8(a)中箭头方向绘制相邻晶粒的表面轮廓。
在同一观察区域内,取向相对远离<1 1 1>的晶粒与取向相对靠近<1 1 1>的相邻晶粒的高度差为正,计算得到相邻晶粒的θ角及高度差结果,如表3所示。晶粒的θ角越大,腐蚀后该晶粒的相对高度越高,说明经过相同的腐蚀时间后,该晶粒较相邻较小θ角晶粒溶解更少。有研究[12,18-20]认为,对于晶体结构为面心立方的金属,<0 0 1>取向的晶粒更容易吸附氧。正因为如此,面心立方的铜镍合金<0 0 1>取向晶粒表面较比其<1 1 1>和<1 0 1>取向晶粒表面更易吸附外来原子包括导致腐蚀失重的氧原子[21]。正是这种吸附外来原子能力的差异,作为重要因素之一,直接导致了不同取向铜镍合金晶粒在相同作用时间内发生的腐蚀失重不同,即腐蚀速率的不同。
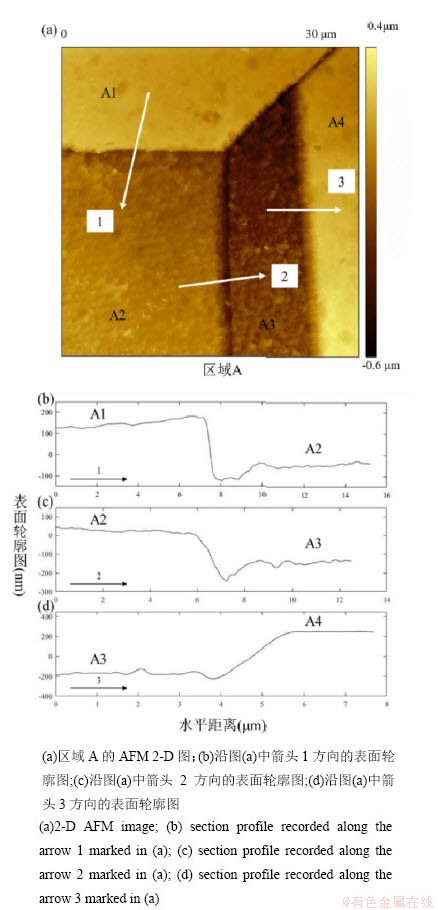
图7 区域A及其内部晶粒的AFM测试结果
Fig. 7 AFM height differences between grains in Region A

图8 区域B及其标记晶粒的AFM测试结果
Fig. 8 AFM height differences between grains in Region B
表3 相邻晶粒的θ角及高度差
Table 3 Angle θ and height difference of adjacent grains
腐蚀后铜镍合金晶粒可新生成较小晶面。利用EBSD和AFM实验结果,可以计算出小晶面的法向量。下面以晶粒A2、B1和B2为例,分别对三种腐蚀形貌的晶粒进行计算分析。
去除腐蚀产物形貌为台阶状A2晶粒的AFM测试结果及分析数据如图9所示。通常每个台阶有两种表面分别为台阶的顶面和侧面。这些台阶的顶面是平的,即图9(b)中的方向“a”为顶面的测试方向,方向“b”和“c”为侧面的测试方向。经计算,小晶面中顶面取向为(26 1 35),所述侧面取向分别为(8 1 13)和(6 1 11)。
去除腐蚀产物表面形貌为四面体凸起状B1晶粒的AFM测试结果及分析数据如图10所示,可以看到晶粒表面有很多四面体状凸起,每个四面体状凸起均由3个小晶面组成。结合EBSD和AFM实验结果,可以计算出各小晶面的晶体学取向。由于这些四面体形凸起在晶粒表面是分散的,所以用于测量表面轮廓的每条线只穿过一个或两个锥体。为了提高测量的准确性,沿着每个方向测量三个面(在字母a,b,c后面用数字1,2,3标记)。图10(c)、(d)、(e)分别为沿图10(b)中标记的三个方向测试的表面轮廓及示意图。通过计算,这些小晶面的取向分别为(9 11 1),(2 15 40),(11  6)。
6)。
样品表面形貌为扇贝状B2晶粒的AFM测试结果及分析数据如图11所示。观察发现,晶粒表面除了扇贝状以外,还存在一些小的倒矩形锥体孔,如图11(a)所示的白色方框所包围的区域,图11(b)为该区域的AFM 2-D图。计算得到这四个小晶面的取向分别为(
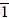
 )、(2
)、(2 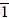 20)、(23 20 14)和(18
20)、(23 20 14)和(18 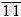 19),其表面轮廓及示意图如图11(c)和图11(d)所示。
19),其表面轮廓及示意图如图11(c)和图11(d)所示。
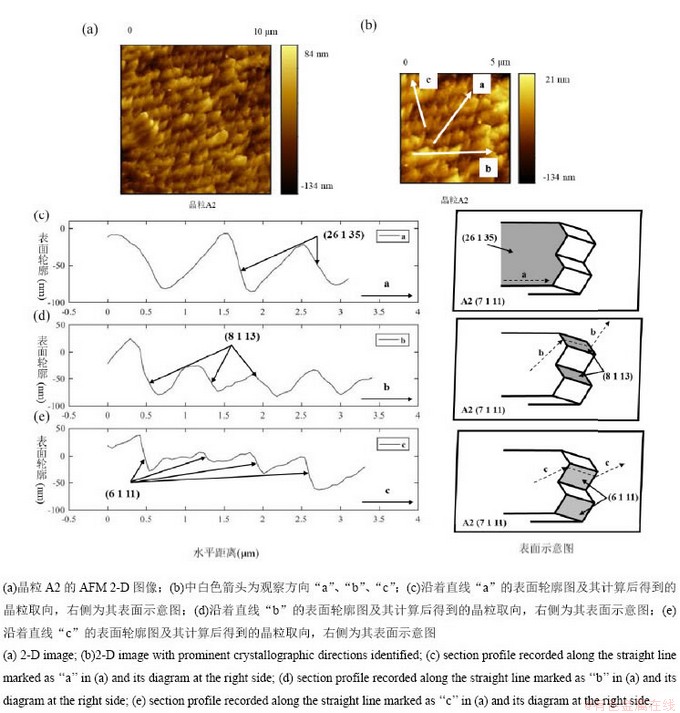
图9 晶粒A2的AFM测试及分析计算结果
Fig. 9 AFM images of A2
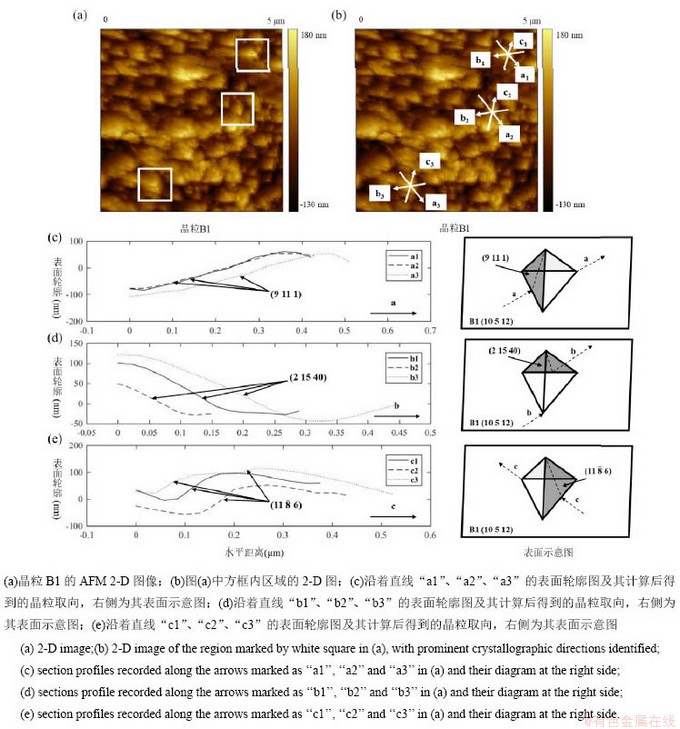
图10 晶粒B1的AFM测试及分析计算结果
Fig. 10 AFM images of B1
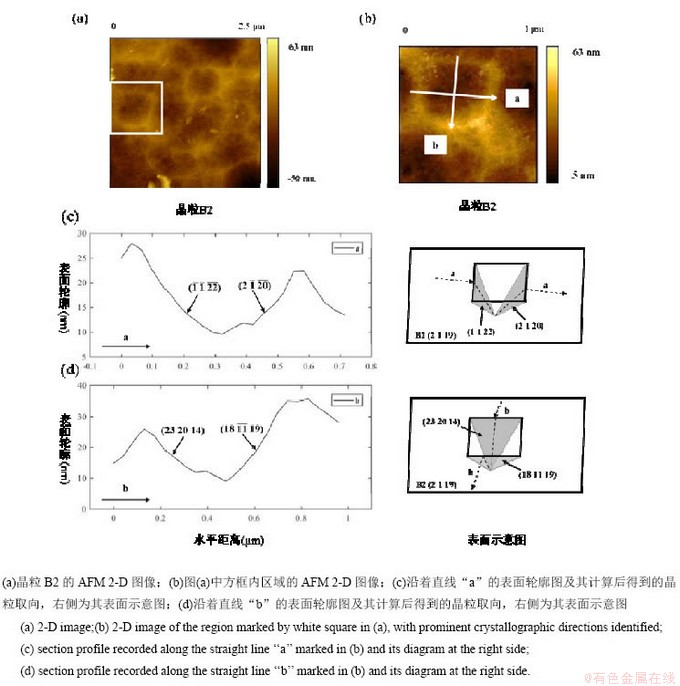
图11 晶粒B2的AFM测试及分析计算结果
Fig. 11 AFM images of B2
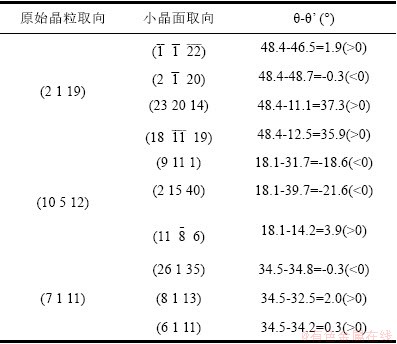
腐蚀后晶粒表面小晶面的法向量与<1 1 1>取向之间的夹角记为θ’。表4为A2、B1、B2及小晶面θ’角的计算结果,可见每个晶粒均有θ’角大于和小于原始晶粒θ角的小晶面。台阶生长(TLK)模型[19]描述了晶粒表面通过重构以降低表面能的过程。腐蚀后小晶面为原始晶粒表面为了降低表面能而形成的台阶平面。当小晶面的θ’角小于原始晶粒的θ角时,该方向小晶面的表面能更高,更易与外来原子吸附,以降低表面能,进而优先发生腐蚀。结合表2和表3可知,因铜镍合金原始晶粒θ角不同,导致不同取向晶粒腐蚀行为不同,最终呈现出差异化的腐蚀形貌。
表4 原始晶粒θ角与小晶面θ’角之间的关系
Table 4 Relationship between angle θ of the base grain and angle θ’ of the newly exposed facet.
3 结论
本文基于SEM-EBSD和AFM定位跟踪技术,对铜镍合金基体表面晶粒取向和腐蚀形貌进行表征,发现晶粒取向与腐蚀行为密切相关。随着晶粒取向与<1 1 1>方向之间夹角的减小,晶粒表面腐蚀深度增加,腐蚀形貌由扇贝状转变为阶梯状或四面体凸起状。经台阶生长模型(TLK)分析及计算结果表明,晶粒取向与<1 1 1>方向之间夹角越小,该晶粒表面能量越高,将优先发生腐蚀,且腐蚀速率高于能量较低的晶粒表面,由此晶粒表面呈现出扇贝状、台阶状及四面体凸起状三种腐蚀形貌。
REFERENCES
[1] 张启林. 船用B30铜镍合金管材腐蚀原因分析[J]. 材料开发与应用, 1986, 01: 22-32.
Zhang Q L, Analysis of corrosion causes of B30 copper-nickel alloy pipe for ships[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 1986(01):22-32.
[2] 杨辉, 杨瑞. 某船海水管路泄漏失效原因分析[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2016, 31(3): 28-32.
Yang H, Yang R. Failure Analysis of Leaking of Seawater Tube in a Ship[J]. Devel-opment and Application of Materials, 2016, 31(3): 28-32.
[3] Wallinder I O, Zhang X, Goidanich S, et al. Corrosion and runoff rates of Cu and three Cu-alloys in marine environments with increasing chloride deposition rate[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 472: 681-694.
[4] Yuan S, Pehkonen S. Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of 70/30 Cu–Ni alloy in pristine and sulfide-containing simulated seawater[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(3): 1276-1304.
[5] 马爱利. 海水管路用B10合金腐蚀机制、晶界工程及腐蚀产物膜研究[D]. 中国科学院大学, 2014.
Ma A L, Studies on Corrosion Mechanism, Grain Boundary Engineering and Corrosion Product Film of the Marine 90/10 Cu-Ni Tubes[D]. Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014
[6] North R, Pryor M. The influence of corrosion product structure on the corrosion rate of Cu-Ni alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 1970, 10(5): 297-311.
[7] Burleigh T D, Waldeck D H. Effect of Alloying on the Resistance of Cu-10% Ni Alloys to Seawater Impingement[J]. Corrosion, 1999, 55(8): 800-804.
[8] 冯兴宇. 白铜BFe10-1-1合金晶界特征分布优化及耐蚀性能研究[D]. 江西理工大学, 2018.
Feng X Y, Optimization of Grain Boundary Characteristic Distribution and Corrosion Resistance of White Copper BFe10-1-1 Alloy[D]. Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2018
[9] Tan Z J, Ma T D, Zhang L M, et al. Relationship between Corrosion Resistance and Microstructure of Copper-Nickel Alloy Pipes in Marine Engineering[J]. Materials ence forum, 2019, 944(PT.1): 389-397.
[10] Lapeire L, Lombardia E M, Verbeken K, et al. Effect of neighboring grains on the microscopic corrosion behavior of a grain in polycrystalline copper[J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 67(FEB.): 179-183.
[11] Lapeire L, Lombardia E M, Verbeken K, et al. On the Role of the Crystallographic Grain Characteristics in the Corrosion Behavior of Polycrystalline Copper[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2014, 783-786: 1658-1663.
[12] Koroleva E V, Thompson G E, Skeldon P, et al. Crystallographic Dissolution of High Purity Aluminium[J]. Proceedings: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2007, 463(2083).
[13] Wang S, Wang J. Effect of grain orientation on the corrosion behavior of polycrystalline Alloy 690[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 85.
[14] 谭振江. 船舶用铜镍合金管材微观组织结构表征与耐腐蚀机理研究[D]. 北京有色金属研究总院, 2019.
Tan Z J, Study on Microstructure Characterization and Corrosion Resistance Mecha-nism of Copper-Nickel Alloy Pipes for Ships[D], General Research Institute for Non-ferrous Metals, 2019.
[15] Dong S, Chen X, Plante E C L, et al. Elucidating the grain-orientation dependent corrosion rates of austenitic stainless steels[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 191.
[16] Verchère L, Aubert I, Devos O. Influence of the crystallographic orientation on the electrochemical reactivity measured by Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy on nickel-based alloy 600[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 313.
[17] Wang W, Alfantazi A. An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and polarization study of the role of crystallographic orientation on electrochemical behavior of niobium[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 131: 79-88.
[18] Liang X, Hai-Wei L, Yuan Y, et al. Stability and Reactivity: Positive and Negative Aspects for Nanoparticle Processing[J]. Chemical reviews, 2018, 118(7).
[19] Martinson C, Flodstrom S. Oxygen adsorption on aluminum single crystal faces studied by AES, XPS and LEED[J]. Surface Science, 1979, 80: 306-316.
[20] Liu H-T, Armitage A F, Woodruff D P. Anisotropy of initial oxidation kinetics of nickel single crystal surfaces[J]. North-Holland, 1982, 114(2-3).
[21] Eiselstein L E, Syrett B C, Wing S S, et al. The accelerated corrosion of CuNi alloys in sulphide-polluted seawater: Mechanism no. 2[J], 1983, 23(3): 223-239.
Effect of Grain Orientation on Corrosion Morphology of Copper-Ni Alloy
Shi Bingxiao1,2,3, Tan Zhenjiang4, Cao Dongdong1,2,3, Jia Rongguang1,2,3, Ma Tongda1,2,3**
(1. GRINM Group Co., Ltd, National Analysis and Testing Center for Nonferrous Metals and Electronic Materials, Beijing 100088, China;
2. Guobiao (Beijing) Testing & Certification Co., Ltd.,Beijing 100088,China;
3. General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals,Beijing 100088, China;
4. Luoyang Ship Material Research Institute, Shandong Qingdao, 266237)
Abstract: The corrosion failure analysis of copper-nickel alloy pipes was mostly focused on the sur-face electrochemical corrosion behavior and the correlation between the structure of the passive film and the corrosion resistance. However, the effect of the surface microstructure of the copper-nickel alloy pipe on the corrosion resistance had not been clarified by now. In this paper, both the scanning electron microscopy with back scattered electron diffraction (SEM-EBSD) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) were utilized to characterize the orien-tation and corrosion morphology of the grains of the copper-nickel alloy pipe by indenta-tion-tracking, so as to reveal the corrosion behavior and corrosion morphology evolution of the differently oriented grains. The results showed that the corrosion depth of the grains increased and the morphology changed from scallop-like to step-like or tetrahedral convex shape as the angle between the grain orientation and the <1 1 1> direction decreased. It was directly related to the surface energy of the grains, which was in line with the Terrace ledge kink (TLK) model.
Key words: Copper-nickel alloy; Indentation-tracking; Grain orientation;Corrosion morphology
Foundation item: Project supported by The National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFB0702100) and New Material Testing and Evaluation Platform-Non-Ferrous Metal Materials Industry Center (TC190H3ZW/2)
Received date: ; Accepted date:
Corresponding author: MA Tong-da; Tel: +86-13651067279; E-mail: matongda@126.com
(编辑 某某某)
基金项目:国家重点研发计划资助项目(2017YFB0702100),国家新材料测试评价平台-有色金属材料行业中心项目(TC190H3ZW/2)
收稿日期: ;修订日期:
通信作者:马通达,教授级高工,博士;电话:13651067279;E-mail:matongda@126.com