Effect of aging on mechanical properties and localized corrosion behaviors of Al-Cu-Li alloy
JIANG Na(蒋 呐)1, 2, LI Jin-feng(李劲风)1, ZHENG Zi-qiao(郑子樵)1,
WEI Xiu-yu(魏修宇)1, LI Yan-fen(李艳芬)1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University,
Changsha 410083, China;
2. Technology Center, Southwest Aluminum (Group) Co Ltd, Chongqing 401326, China)
Abstract: The effects of aging on mechanical properties, intergranular corrosion and exfoliation corrosion behaviors of a 2197 type Al-Li alloy were investigated, and the mechanisms were studied through microstructure observation and electrochemical measurement of simulated bulk phase. The main strengthening precipitates of the alloy aged at 175℃ and 160℃ are δ′ and T1. T1 precipitation in the alloy aged at 160℃ is delayed, which results in its slower age strengthening and over-aging behavior than the alloy aged at 175℃. Meanwhile, aging temperature of 160℃ causes more uniform distribution and finer size of T1, resulting in its better strengthening effect. As aging time and aging temperature are increased, the size of T1 at grain boundaries and the width of PFZ along grain boundaries are increased, leading to an increase in the susceptibility to intergranular corrosion and exfoliation corrosion. It is suggested that better comprehensive properties can be obtained when the alloy is aged at 160℃.
Key words: 2197 Al-Li alloy; aging; mechanical property; intergranular corrosion; exfoliation corrosion CLC number: TG146.2
Document code: A
1 INTRODUCTION
The addition of 1% Li to Al alloy can lower its density by 3% and increase its elastic modulus by 6%. Compared with traditional Al alloys, Al-Li alloys also possess higher specific strength[1]. In developed countries, Al-Li alloys have been widely used in space shuttles and airplanes[2, 3] and their application would be extended in the near future.
2197 Al-Li alloy was developed by USA in 1990s, which possesses moderate strength with good damage tolerance, and is very applicable for airplane structure. To accommodate aviation development, research on 2197 Al-Li alloy is being carried out in China. Meanwhile, intergranular corrosion and exfoliation corrosion, two main kinds of localized corrosion in 2××× and 7××× series Al alloys, can lower Al alloy strength, plasticity and fatigue properties, and also decrease its service life[4, 5]. So investigating the intergranular corrosion and exfoliation corrosion behaviors of Al-Li alloy is very important to its application, and a substantial amount of research work has been done[6, 7].
This research is to investigate the mechanical properties of a 2197 Al-Li alloy with different aging treatments and to study the effect of aging on its intergranular corrosion and exfoliation corrosion behaviors, trying to find a heat treatment schedule for obtaining good comprehensive properties.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
The alloy was prepared by melting Al of 99.95% purity, Li of high purity, pure Mg and Zn, master alloys of Al-49.35%Cu and Al-4.46%Zr. The ingot underwent homogenization treatment, hot rolling and annealing treatment, and was cold rolled to a plate with a thickness of 2mm. Then the alloy plate was solution treated at 504℃ for 1h, and aged at 175℃ and 160℃ for various times respectively. The tensile properties of the alloys with different aging treatments were measured at a speed of 2mm/min. The TEM samples with different aging treatments were prepared by conventional electrolytic etching method using an electrolyte of 25%HNO3 and 75%CH3OH, and the TEM observation was carried out with a H-800 Transmission Electron Microscope.
Specimens for corrosion study were cut from the alloy plate with various aging treatments. The exposed surface was ground using abrasive papers through 500-grade to 1200-grade, polished with diamond paste, rinsed using acetone, degreased with de-ionized water and then dried in air. The accelerated intergranular corrosion test was performed according to GB 7998—87[8]. The solution of 3.0% NaCl +10mL/L HCl was used, and the ratio of corrosion medium volume to corrosion surface was about 10mL/cm2. The polished alloy plate was continuously immersed in the solution for 24h. Then the corroded specimen was dried and mounted with epoxy. Its section was ground and polished, and the intergranular corrosion depth was measured using metalloscopy.
The accelerated exfoliation test was performed according to EXCO test of ASTM G34—79[9]. The EXCO solution of 4.0mol/L NaCl +0.5mol/L KNO3+0.1mol/L HNO3(pH=0.4) was used and solution temperature was maintained at 25℃ in a thermostat water bath. The ratio of EXCO solution volume to corrosion surface was about 25mL/cm2. The alloy was continuously immersed in the EXCO solution for 96h. During the immersion process, the corrosion morphology was recorded and the corrosion rate was judged.
To clarify the intergranular corrosion mechanism of 2197 Al-Li alloy, the simulated bulk precipitate of T1 was fabricated through melting and casting, and its electrochemical behavior in NaCl solution was measured. Meanwhile, α(Al) was used to substitute for the precipitate-free zone(PFZ) to undergo electrochemical measurement, due to extremely little Cu and Li in the PFZ.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Aging behaviors
Fig.1 shows the tensile strength, yield strength and elongation as a function of aging time for the alloy aged at 175℃ and 160℃. It can be seen that the alloy aged at 175℃ shows more rapid age strengthening and over-aging than the alloy aged at 160℃. However, the peak values of tensile strength(418MPa) and yield strength(358MPa) of the alloy aged at 160℃ are higher than those of the alloy aged at 175℃. As aging time is increased from 10 h to 80 h, the elongation is decreased from 20.2% to 9.3% for the alloy aged at 160℃. While it scatters for the alloy aged at 175℃, ranging from about 12%-13% under the under-aging condition to about 10%-11% under the over-aging condition.
3.2 Intergranular corrosion and exfoliation corrosion
Table 1 lists the intergranular corrosion depth of the alloy aged at 175℃ and 160℃ for various times. It is clearly seen that the average and the maximum intergranular corrosion depth are in-creased with aging time. The alloy aged at 160℃
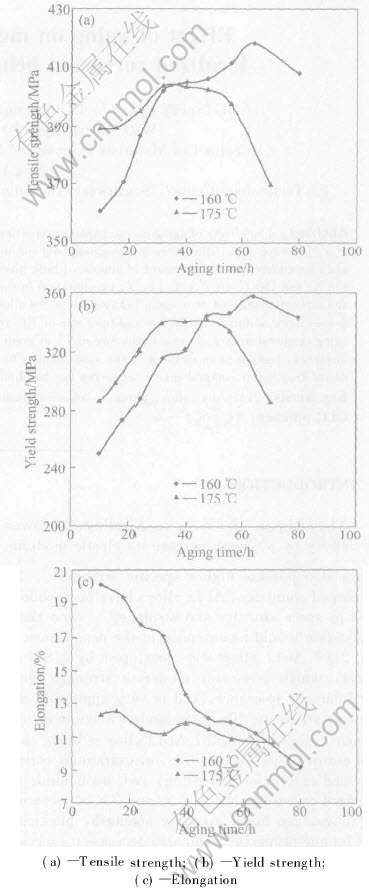
Fig.1 Effect of aging time on mechanical properties of 2197 Al-Li alloy
shows much more shallow intergranular corrosion than that aged at 175℃.
Table 2 lists the corrosion development of the alloy with various aging treatments in the EXCO solution. After 15h of immersion, only pitting corrosion occurs on the alloy aged at 175℃ for 18h, while superficial exfoliation occurs on the alloy aged at 175℃ for 40h and 56h respectively, as shown in Figs.2(a), (b) and (c). As immersion
Table 1 Average depth and Maximum depth of intergranular corrosion
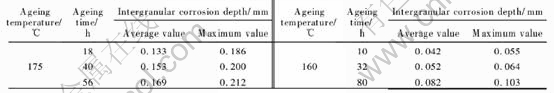
Table 2 Corrosion development of alloy with various aging treatments in EXCO solution
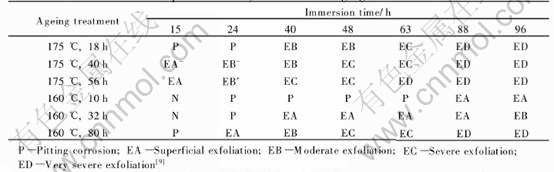

Fig.2 Corrosion morphologies of alloy aged at 175℃
Fig.3 time is increased up to 96h, the corrosion of the three alloys aged at 175℃ are developed to very severe exfoliation, as shown in Figs.2(d), (e) and (f).
Fig.3 shows representative corrosion morphologies of the alloy aged at 160℃ for various time. After 48h of immersion, pitting corrosion occurs on the alloy aged for 10h, and superficial and severe exfoliation is produced on the alloy aged for 32h and 80h respectively, as shown in Figs.3(a), (b) and (c). As immersion time is increased up to 96h, the corrosion on the alloys aged for 10h, 32h and 80h is developed to superficial, moderate and very severe exfoliation, respectively, as shown in Figs.3(d), (e) and (f).
It can be found from Tables 1 and 2 and Figs.2, 3 that the susceptibility to intergranular corrosion and exfoliation is increased with aging time. Higher aging temperature(175℃) accelerates the exfoliation development and also increases the susceptibility to exfoliation corrosion.
3.3 Discussion
Fig.4 shows the TEM images of the alloys aged at 175℃ and 160℃. For the alloy aged at 175℃ for 6h, δ′(Al3Li) precipitates in the alloy. As aged for 24h, the main precipitate is T1, as shown in Fig.4(b).
As the aging temperature is decreased, secondary phase precipitates and grows slowly, due to lower atomic diffusion. The TEM images of the alloy aged at 160℃ for 24h are shown in Figs.4(c) and (d). It is seen that main precipitate is fine and dispersed δ′ and only a small quantity of T1 precipitates. It can be deduced from the TEM observa-tion that the main precipitates of this Al-Li alloy
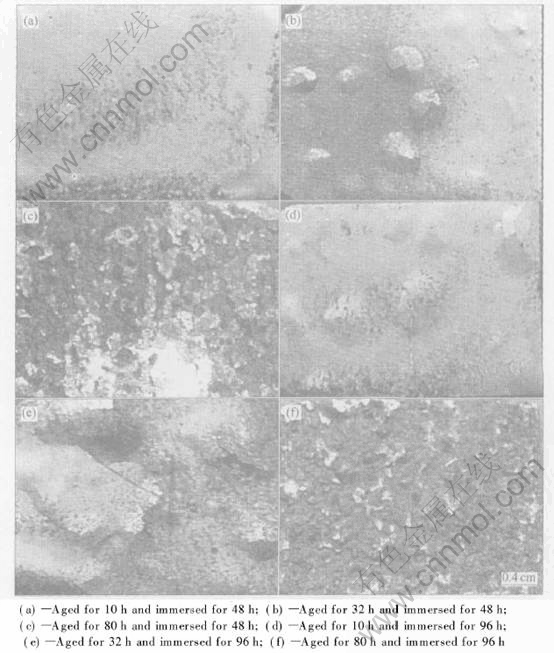
Fig.3 Corrosion morphologies of alloy aged at 160℃

Fig.4 TEM images of alloys aged at 175℃ and 160℃ for various times
are δ′ and T1. δ′ is coherent with the Al-Li alloy matrix and precipitates earlier than T1. Compared with the alloy aged at 175℃, T1 precipitation in the alloy aged at 160℃ is delayed. More rapid precipitation and growth of T1 in the alloy aged at 175℃ result in more rapid age strengthening and over-aging.
It is well known that T1 is apt to nucleate at defects. When the alloy is aged at a higher temperature(175℃), supersaturated vacancies are easy to diffuse to the alloy surface, grain boundaries and subgrain boundaries to annihilate due to rapid diffusion speed, and not many dislocation loops are formed through vacancy cluster collapse. As a result, T1 nucleates preferentially at grain boundaries, subgrain boundaries and some dislocation lines preexisted in the alloy. As aging temperature is decreased(160℃), vacancy diffusion is lowered and dislocation loop is easier to form through vacancy cluster collapse, resulting in the increase of dislocation density within grains. Meanwhile, driving force for T1 nucleation is increased due to higher solute super-saturation. Denser dislocation and higher driving force for nucleation will result in more uniform distribution and finer size of T1. As a result, the alloy aged at 160℃ possesses higher peak strength than that aged at 175℃.
It is generally known that intergranular corrosion is caused by the anodic dissolution of precipitates at grain boundary or precipitate-free zone (PFZ). In 2197 Al-Li alloy, it is found that the main precipitates are δ′ and T1. δ′ is coherent with the alloy matrix, precipitates homogeneously in the alloy matrix, and has no effect on intergranular corrosion of Al-Li alloy[10]. T1 precipitates preferentially at grain boundaries, subgrain boundaries and dislocations. During its precipitation and growth, a T1 precipitate-free zone (PFZ) is formed along grain boundary and subgrain boundary[11], due to the absorption of Cu and Li atoms to T1. The intergranualr corrosion susceptibility difference of the alloy with various aging treatments should be related to T1 distribution or the PFZ.
As to the function of T1 and PFZ on the intergranular corrosion of Al-Li alloys, there have been two viewpoints. Buchheit et al[12] suggested that the anodic dissolution of T1 originate the intergranular corrosion. However, Kumai et al[13] thought that it was caused by the anodic dissolution of PFZ.
Fig.5 shows the XRD pattern of the ingot corresponding to chemical composition of T1. It is clearly seen that T1 is the main phase in the ingot, and only a small quantity of θ′ and TB(Al7Cu4Li) exist. The simulated bulk T1 could be substituted for the real aging precipitate T1 to undergo electrochemical measurement.
Fig.6 shows the polarization curves of T1 and α(Al) immersed in 4.0% NaCl solution(pH=6.5) for 30min and 10d respectively. The corresponding free corrosion potentials(φcorr) are shown in Table 3. It can be found that the corrosion po-tential of T1 is negative to that of α(Al) at the ini-

Fig.5 XRD pattern of simulated T1(Al2CuLi)

Fig.6 Polarization curves of individual T1 and α(Al) in 4.0%NaCl solution
Table 3 Free corrosion potential (V vs SCE) of T1 and α(Al) in 4.0% NaCl solution(pH=6.5) for 30min and 10d
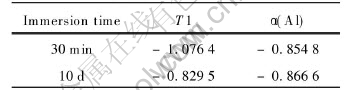
tial stage, while it moves to positive direction after 10d of immersion, so it becomes positive to that of α(Al).
The φcorr of T1 moves to positive direction can be explained by the dealloying of Li from T1. It was reported that as 2024 Al alloy was immersed in NaCl solution, active Mg in S(Al2CuMg) particle was preferentially dissolved, resulting in Cu-rich remnants[14-16]. In this case, due to the high chemical activity of Li in T1, Li will be preferentially dissolved, resulting in the enrichment of Al and noble Cu, especially Cu. As a result, the potential of T1 becomes positive to that of α(Al). Then, if T1 and α(Al) are coupled together, anodic dissolution occurs on α(Al).
In real Al-Li alloy, the size of T1 is very fine, and the de-alloying process of T1 particle is rapid, which will accelerate its potential change. Hence, an intergranular corrosion process of 2197 Al-Li alloy can be advanced. T1 acts as anodic phase and undergoes anodic dissolution at the initial stage, due to its negative potential with respect to the PFZ. During this dissolution process, active Li in T1 is preferentially dissolved, resulting in the enrichment of Al and noble Cu, especially Cu. This de-alloying process will make the potential of T1 move towards positive direction. As the de-alloying process develops to some extent, potential of de-alloyed T1 becomes positive to the PFZ, and an alternative galvanic cell is established. That is to say, T1 is cathodic to PFZ at the later stage, and anodic dissolution of PFZ occurs. During the development of PFZ dissolution, other T1 will be exposed to the corrosion medium, and the above process will be repeated. So the intergranular corrosion of 2197 Al-Li alloy should be caused by the alternate anodic dissolution of T1 and PFZ.
In this case, T1 precipitates preferentially at grain boundaries, subgrain boundaries and dislocations during aging, and T1 at grain boundaries and subgrain boundaries is easier to be coarsened with aging time, due to faster atomic diffusion. During the growth and coarsening of T1, the PFZ width increases. Both the coarsening of T1 at grain boundaries and the broadening of the PFZ can increase the susceptibility of the 2197 Al-Li alloy to intergranular corrosion.
As aging temperature is decreased, it is known from the above analysis that T1 precipitation is delayed, its distribution is more uniform and PFZ width is decreased. As a consequence, electrochemical driving-force for intergranular corrosion is decreased, which causes lower intergranualr corrosion susceptibility of the Al-Li alloy aged at 160℃.
Exfoliation corrosion is developed from intergranular attack[17]. During corrosion process, the corrosion product accumulates on grain boundary, resulting in a wedging force and finally lifting off the alloy surface. The more susceptible to intergranular corrosion the alloy is, the more susceptible to exfoliation corrosion the alloy is. This can explain why longer aging time and higher aging temperature can increase the exfoliation corrosion susceptibility.
4 CONCLUSIONS
1) The main strengthening phases of the 2197 Al-Li alloy aged at 175℃ and 160℃ are δ′ and T1, and δ′ precipitates earlier than T1. T1 precipitation in the alloy aged at 160℃ is delayed, which results in slower age strengthening and over-aging behavior than the alloy aged at 175℃. Meanwhile, aging temperature of 160℃ causes more uniform distribution and finer size of T1, and improves strengthening effect.
2) It is suggested that the intergranular corrosion of 2197 Al-Li alloy is caused by the alternate anodic dissolution of T1 and PFZ. As aging time and aging temperature are increased, the size of T1 at grain boundaries and the width of PFZ along grain boundaries are increased, leading to an increase in the susceptibility to intergranular corrosion. Hence, the exfoliation susceptibility is also increased.
3) Better comprehensive properties can be obtained as the alloy is aged at 160℃.
REFERENCES
[1]YIN Deng-feng. History and current status of aluminum-lithium alloys research and development [J]. Materials Review, 2003, 17(2): 18-20.(in Chinese)
[2]XIONG Huan. Cryogenic tank and application of aluminium-lithium alloy [J]. Missile and Space Vehicles, 2001(6): 33-40, 46.(in Chinese)
[3]WEI Jian-feng, HE Ming. Advance on the development of Al-Li alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1994, 23(1): 1-6.(in Chinese)
[4]HE Jian-ping, CHEN Wen-li, XU Wei, et al. Effect of exfoliation on structure and tensile strength of LC4CS aluminium alloy at constant temperature [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1999, 31(5): 575-579.(in Chinese)
[5]HE Bin, SUN You-chao, FAN Wei-xun. Influence of exfoliation corrosion on the fatigue of aluminium alloy [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1998, 30(3): 306-310.(in Chinese)
[6]LI Jin-feng, ZHANG Zhao, CAO Fa-he, et al. Intergranular corrosion and exfoliation corrosion behaviors of AA2090 and AA8090 Al-Li alloys [J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2004, 23(3): 135-138, 142.(in Chinese)
[7]CAI Chao, LI Jin-feng, ZHENG Zi-qiao, et al. Exfoliation corrosion susceptibility of 8090 Al-Li alloy examined by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2004, 14(4): 742-746.
[8]Standard test method for intergranular corrosion susceptibility in Al alloys [S]. GB7998—87. (in Chinese)
[9]Standard Test Method for Exfoliation Corrosion Susceptibility in 2×××and 7××× Series Aluminum Alloys (EXCO test) [S]. ASTM G34—79.
[10]ZHANG Yun, ZHU Zi-yong, WANG Zheng-fu, et al. Intergranular and exfoliation corrosion behavior of Al-Li alloy [J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Corrosion and Protection, 1992, 12(2): 180-184.(in Chinese)
[11]WEI Xiu-yu, TAN Cheng-yu, ZHENG Zi-qiao, et al. Influence of aging on corrosion behavior of 2195 Al-Li alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(7): 1195-1200.(in Chinese)
[12]Buchheit R G, Moran J P, Stoner G E. Electrochemical behavior of T1(Al2CuLi) intermetallic compound and its role in localized corrosion of Al-2%Li-3%Cu alloys [J]. Corrosion, 1994, 50(2): 120-130.
[13]Kumai C, Kusinski J, Thomas G, et al. Influence of aging at 200℃ on the corrosion resistance of Al-Li and Al-Cu-Li alloys [J]. Corrosion, 1989, 45(4): 294-302.
[14]Buchheit R G, Grant R P, Hlava P F, et al. localized dissolution phenomena associated with S phase (Al2CuMg) particles in aluminium alloy 2024-T3 [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1997, 144(8): 2621-2628.
[15]Zhu D Q, van Ooij W J. Corrosion protection of AA 2024 T3 by [bis-[3-triethoxysilyl]propy1]tetrasulfide in neutral sodium chloride solution. Part 1: Corrosion of AA2034-T3 [J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45: 2163-2175
[16]Shao M H, Fu Y, Hu R G, et al. A study on pitting corrosion of aluminium alloy 2024-T3 by scanning micro-reference electrode technique [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2003, A344: 323-327.
[17]Kelly D J, Robinson M J. Influence of heat treatment and grain shape on exfoliation corrosion of Al-Li alloy 8090 [J]. Corrosion, 1993, 49(10): 787-795.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Project(50401012) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project supported by the Key Program of the 10th Five-year Plan of China; Project supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of Central South University
Received date: 2004-08-02; Accepted date: 2004-11-15
Correspondence: LI Jin-feng, Associate Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-731-8830270; E-mail: lijinfeng@mail.csu.edu.cn