文章编号:1004-0609(2013)05-1463-08
W-Mo-H2O体系钨钼分离的热力学分析
张家靓1,赵中伟1, 2,陈星宇1,刘旭恒1
(1. 中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 稀有金属冶金与材料制备湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:绘制25 ℃时W-H2O系、Mo-H2O系以及W-Mo-H 2O系中存在的物种随pH值、钨、钼浓度变化的热力学平衡图,并总结其变化规律。热力学分析表明:W-Mo-H2O系中的钨、钼在酸化过程中一般经历从单体离子到杂多酸根离子再到同多酸根离子的转变过程。在pH值为6.5~7.5的范围内,钨转变成聚合离子的程度均高于钼,表明单钨酸根离子的聚合能力强于单钼酸根离子的;而在pH值为3.0~6.5的弱酸性区间内,溶液中形成浓度较高的钨钼杂多酸根离子,这对于钨钼分离极其不利。
关键词:W-Mo-H 2O系;钨钼分离;热力学分析;钨钼杂多酸;聚合离子
中图分类号:TF801 文献标志码:A
Thermodynamic analysis for separation of tungsten and molybdenum in W-Mo-H2O system
ZHANG Jia-liang1, ZHAO Zhong-wei1, 2, CHEN Xin-yu1, LIU Xu-heng1
(1. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Hunan Key Laboratory for Metallurgy and Material Processing of Rare Metals, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The thermodynamic equilibrium diagrams for the distribution of species at different pH values, tungsten and molybdenum concentrations in W-H2O, Mo-H2O and W-Mo-H2O systems at 25 ℃ were drawn, and the variational regularities of species were also analyzed. The thermodynamic analysis shows that the tungsten and molybdenum are transformed from monomeric anions to heteropolyanions, then to isopolyanions during the acidification process in W-Mo-H2O system. The polymeric degree of tungsten is significantly higher than that of molybdenum in the pH range from 6.5 to 7.5, which indicates that the polymeric ability of monotunstates is stronger. At pH values of 3.0-6.5, the heteropolymolybdotungstate ions with higher concentration are formed, which is extremely unfavorable to the separation of tungsten and molybdenum.
Key words: W-Mo-H2O system; separation of tungsten and molybdenum; thermodynamic analysis; heteropolymolybdotungstate; polymeric ions
钨、钼是化工、冶金、材料等领域的重要元素,但是由于镧系收缩效应的影响,钨、钼的原子半径、化学价态以及在水溶液中的化学性质都极其相近,使得二者的分离成为世界性的难题[1]。近年来,随着优质黑钨资源的日益枯竭,人们不得不转而处理高钙黑钨精矿、白钨矿乃至低品位复杂钨矿物原料。而由于地球化学的原因,在这些矿物原料中,钨、钼往往共生。甚至在一些钨的矿物、原料中,钼的含量与主金属钨的差异并不大[2],这无疑进一步加大了二者分离的难度。
长期以来,国内外学者围绕钨钼分离进行了大量研究,采用的方法主要包括萃取法、沉淀法以及离子交换法[3]。这些方法均在水溶液中进行,并且大多通过大量的试验探索得到了最佳的分离路径与条件。因此,若能从理论上对钨钼混合溶液进行研究,对深入了解该溶液体系的热力学性质,进而指导钨钼分离工艺大有裨益。但是由于钨、钼在水溶液中的存在形态十分复杂,除了存在单体形式的单钨酸根离子、单钼酸根离子以外,在溶液逐渐酸化的过程中,上述离子还会聚合成各种同多酸根离子,甚至还会转变成多种形式更为复杂的钨钼杂多酸根离子[4]。也正因为该体系的复杂性,迄今为止,鲜有文献对其热力学性质进行过报道。有研究者考察了单一钨、钼水溶液体系的热力学行为,并绘制了体系中各物种随pH值变化的热力学平衡图[5-8]。但是上述研究均只是针对钨、钼单一体系进行研究,而忽略了二者之间的相互作用,即没有考虑生成钨钼杂多酸所带来的影响。而在真实的钨钼混合溶液中,杂多酸的形成是不可避免的,并且杂多酸的存在对于钨钼分离有着极其不利的影响,因而不容忽视。
本文作者利用前人所测定的热力学数据,全面考虑钨钼混合体系中存在的各种单体离子、同多酸根离子以及杂多酸根离子,通过热力学计算绘制25 ℃时W-H2O系、Mo-H2O系以及W-Mo-H 2O系中存在物种随pH值、钨、钼浓度变化的热力学平衡图,并总结其变化规律,在热力学计算的基础上,结合现有工艺研究,对该体系进行了初步分析。
1 热力学数据及计算
1.1 热力学数据
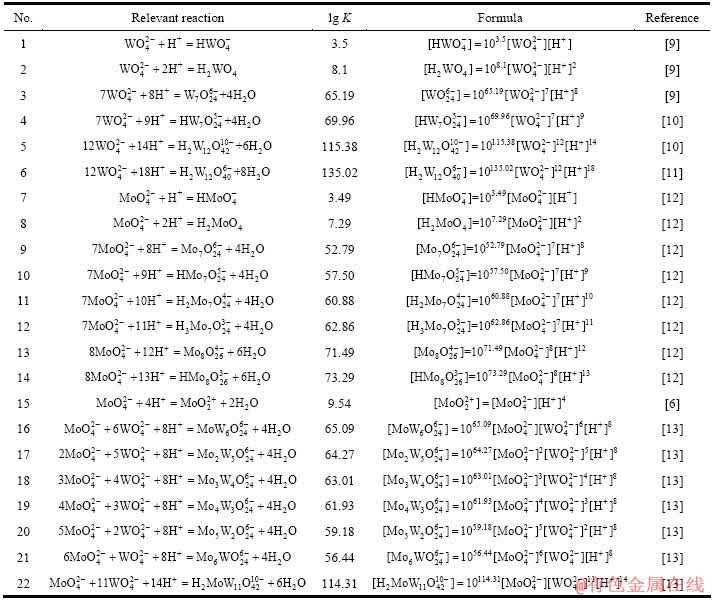
W-H2O系、Mo-H2O系以及W-Mo-H 2O系所涉及各反应的平衡常数及计算式及如表1所列。由于上述体系溶液在pH=1附近易生成钨酸、钼酸沉淀,而在pH>9时,钨、钼又均以性质极为接近的单体盐溶液形式存在,因此,本研究只考虑各体系在pH值为2~9之间的热力学行为。此外,由于缺乏相关物质的活度系数,在本研究计算过程中均以离子的浓度代替活度。
1.2 计算过程
设[W]T、[Mo]T分别为溶液中游离钨、游离钼的总浓度,“[ ]”为溶液中各游离组分的浓度,根据同时平衡和物质守恒原理,可以得到如下方程。
1) 在W-H2O体系中

 (1)
(1)
2) 在Mo-H2O体系中

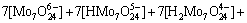
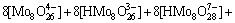
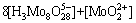 (2)
(2)
3) 在W-Mo-H2O体系中
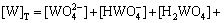

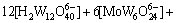
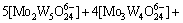

 (3)
(3)
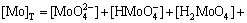
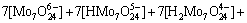
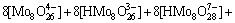
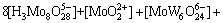
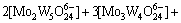

 (4)
(4)
若分别给定各体系中钨、钼的总浓度及溶液的pH值,通过各体系所涉及的与游离态物质相应的计算式及该体系[W]T、[Mo]T的计算式联立求解,即可得到各体系中各游离态物质的浓度。而游离态物质所含钨、钼的摩尔浓度与总钨、总钼摩尔浓度的比值即为该物质的占总钨、总钼的摩尔分数。由此可见,各体系中包含的所有游离态物质含钨与含钼的摩尔分数之和均为1。
表1 涉及反应的平衡常数及计算式(25 ℃)
Table 1 Equilibrium constants and formulas of relevant reactions (25 ℃)
2 结果与讨论
2.1 W-H2O系及Mo-H2O系热力学分析
在单一体系的W-H2O系及Mo-H2O系中,以pH=0.5为间隔,计算出各个pH值下体系中各游离态物质的摩尔分数。图1和2所示分别为不同总浓度下W-H2O系及Mo-H2O系中钨、钼各种存在物种的摩尔分数与pH值的关系图。
从图1可以看到,当W-H2O系中总钨浓度[W]T=0.05 mol/L时,WO42-在pH值约为7.5时开始聚合,并在pH值为5.5时全部转变成聚合离子;聚合后首先形成W7O246-(仲钨酸根A)和H2W12O4210-(仲钨酸根B),之后随着pH值的逐渐降低,二者均转变成H2W12O406- (偏钨酸根)。当溶液pH=4左右时,体系中钨的存在形式已基本为H2W12O406-。 而当总钨浓度升高至0.5 mol/L时,WO42-开始聚合和聚合完成的pH值也随之上升,分别约为8.5和6.5。聚合后首先形成的物种仍以W7O246-和H2W12O4210-为主,但相对于低钨浓度的情况,溶液中含钨原子更多的H2W12O4210-的比例明显上升。可见,溶液中钨浓度越高,越容易发生钨的聚合反应,并且越易形成钨原子数高的含钨物质。而在Mo-H2O系中,也同样存在着单钼酸根离子的各种聚合反应,并且其开始聚合到聚合完成的pH值也同样会随着总钼浓度的增大而升高,分别由[Mo]T=0.05 mol/L时的6和4增大至[Mo]T=0.5 mol/L时的7和5。随着pH值的降低,溶液中的聚合物质逐渐从七钼酸根离子转变成八钼酸根离子。
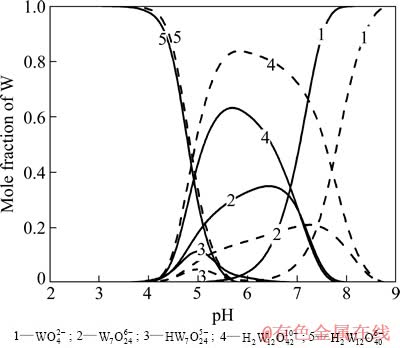
图1 W-H2O系主要存在物种的摩尔分数与pH值的关系
Fig. 1 Mole fraction of W in main species as function of pH value in W-H2O system (Solid line: [W]T=0.05 mol/L, dash line: [W]T=0.5 mol/L, 25 ℃)
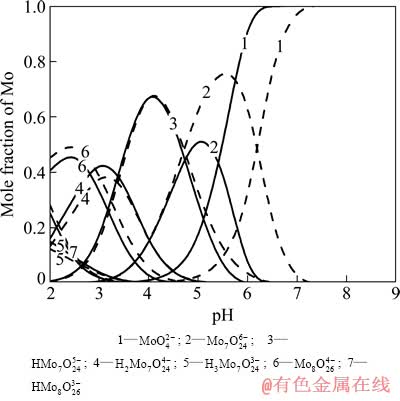
图2 Mo-H2O系主要存在物种的摩尔分数与pH值的关系
Fig. 2 Mole fraction of Mo in main species as function of pH value in Mo-H2O system (Solid line: [Mo]T=0.05 mol/L, dash line: [Mo]T=0.5 mol/L, 25 ℃)
由以上对W-H2O系、Mo-H2O系的热力学分析可知,纯钨、纯钼溶液在酸化的过程中均会发生聚合反应,并形成各种聚合离子,聚合离子的存在形态与溶液pH值、离子浓度密切相关。聚合过程中,pH值越低、离子浓度越高,溶液中就越易形成聚合离子。另外,通过对比上述两种体系可以看到,在离子浓度相同的条件下,单钨酸根离子开始聚合与聚合完成的pH值均比单钼酸根离子高1.5左右。由此可见,单钨酸盐的聚合能力要强于单钼酸盐。
2.2 W-Mo-H2O系热力学分析
在钨钼混合溶液中,由于形成了各种钨钼杂多酸,因此体系中各物种的存在形态更趋复杂。不同钨钼浓度下W-Mo-H2O系各主要游离态物种含钨、钼的摩尔分数与溶液pH值的关系如图3所示。当溶液中 [W]T=[Mo]T=0.05 mol/L时(见图3(a)),单钨酸盐、单钼酸盐在pH值约为7.5时开始聚合。但是随着pH值的逐渐降低,钨聚合的程度明显高于钼,钨酸盐聚合后首先形成W7O246-和钨钼原子比较大的杂多酸MoW6O246-,之后随着钼酸盐的大量聚合,体系中的游离态物质逐渐转化为各种钨钼杂多酸离子,并且生成杂多酸的钨钼摩尔比随着pH值的降低不断变小。当pH值继续降低,体系中存在的物种逐渐转化为各种钨、钼的同多酸根离子。而当溶液中总钨与总钼浓度均升高至0.5 mol/L时(见图3(b)),单钨酸盐、单钼酸盐开始聚合的pH值也相应升高至8.5左右。钨酸盐刚开始聚合时除了生成W7O246-和MoW6O246-以外,还生成了少量H2W12O4210-。之后,随着pH值的降低,体系中游离态物质的转变历程与低钨钼时几乎相同。
当体系中总钨浓度高于总钼浓度时(见图3(c)),聚合过程中,单体钨酸盐与钼酸盐聚合程度的差异更为明显。当溶液中[W]T=0.5 mol/L、[Mo]T=0.05 mol/L、pH=7.5时,体系中钨的聚合离子的摩尔分数达到80%,而聚合钼离子的摩尔分数还不到15%。钨酸盐聚合后的离子以仲钨酸根离子W7O246-和H2W12O4210-为主,同时包括少量钨钼摩尔比大的H2 MoW11O4210- 。而钼酸盐聚合后的形态主要以各种钨钼摩尔比较大的杂多酸根离子H2 MoW11O4210-、 MoW6O246- 和Mo2W5O246-为主。之后,随着pH值的降低,溶液中的钨开始转变成偏钨酸根离子,形成杂多酸的钨减少,钼以Mo3W4O246- 、Mo4W3O246-和 Mo5W2O246-存在。当pH<2.5时,溶液中的钨、钼均以各自的同多酸根离子形式存在。
而当体系中总钨浓度低于总钼浓度时(见图3(d)),在pH值降低过程中,开始钨的聚合程度高于钼,体系中形成Mo3W4O246-和Mo4W3O246-杂多酸根离子,而后随着钼的大量聚合,溶液中的钨逐渐转化为钨钼原子比较小的Mo5W2O246-和Mo6WO246-杂多酸根离子,而此时钼存在的形态除了杂多酸以外,还形成了部分七钼聚合离子。之后随着pH值的降低,与其他钨钼比的情况相同,钨、钼逐步形成各自的同多酸根离子。
为了更直观地分析不同类型的游离态物质在酸化过程中的变化情况,将W-Mo-H2O体系中各种单体离子、同多酸根离子、杂多酸根离子分别求和,得到不同钨钼浓度下3种类型离子含钨、钼的摩尔分数随pH值变化的曲线图,如图4所示。从图4可以看到,在酸化过程中,首先发生单体离子的聚合反应,但钨酸根离子的聚合程度的增加明显高于钼酸根离子。在pH值为6.5~7.5的范围内,体系中钨的聚合程度均高于钼。
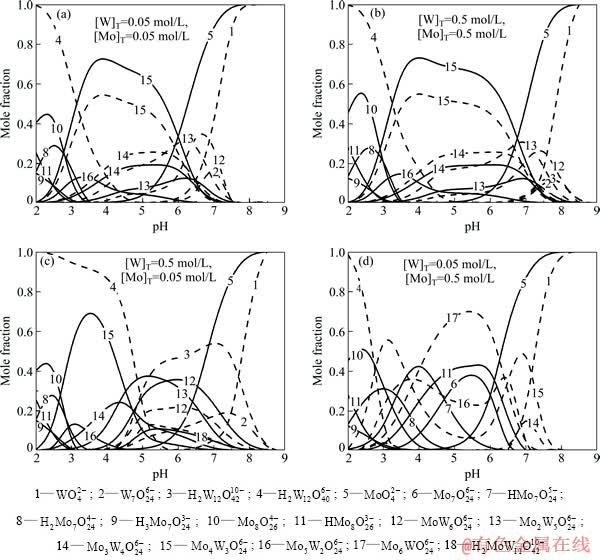
图3 不同钨钼浓度下W-Mo-H2O系主要存在物种含钨、钼的摩尔分数与pH值的关系
Fig. 3 Mole fraction of W, Mo in main species as function of pH value at different [W]T and [Mo]T in W-Mo-H2O system (Dash line: W, solid line: Mo, 25 ℃)
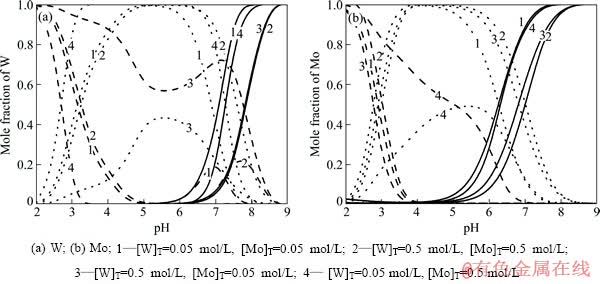
图4 不同钨钼浓度下W-Mo-H2O系中单体离子、同多酸离子、杂多酸离子含钨、钼的摩尔分数随pH值的变化
Fig. 4 Mole fraction of W, Mo in monomeric anions, isopolyanions, heteropolyanions as function of pH at different [W]T, [Mo]T in W-Mo-H2O system (Solid line: monomeric anions; Dash line: isopolyanions;Dot line: heteropolyanions, 25 ℃)
可见在钨钼混合体系中,单钨酸盐依然表现出更强的聚合能力。之后随着单体离子的不断聚合,杂多酸离子浓度逐渐增大并占据主要地位,略有不同的是在钨钼浓度相差较大的体系中,较高浓度的物质除了形成杂多酸离子外,还以同多酸根离子形式存在。继续降低pH值,体系中的杂多酸根离子逐渐转变成同多酸根离子。
总体上来说随着pH值的降低,体系中的钨、钼大致上都经历从单体离子到杂多酸根离子再到同多酸根离子的转变过程。而在pH值为3~6.5的弱酸性区间内,溶液中有浓度较高的钨钼杂多酸根离子形成,这对于钨钼的分离显然是极其不利的。因此在不破坏体系中杂多酸的前提下,该pH值区间内是无法进行钨钼的有效分离的。
2.3 热力学分析在钨钼分离中的应用
通过上述热力学分析,发现在pH=6.5~7.5的范围内,W-Mo-H2O体系中钨的聚合程度均高于钼,并且在任意钨、钼浓度时,均可以通过控制一定的pH值,使溶液中绝大部分的钨转变成聚合离子,而绝大部分的钼仍以单体离子形式存在。相对于单体离子,聚合离子在溶解度和被某些吸附剂所吸附的吸附性能及沉淀结晶性能等方面与单体离子有较大差异,因而利用这些差异,采用结晶、沉淀、萃取、吸附等分离方法可实现钨钼的分离。
(NH4)2WO4溶液蒸发结晶时可与钼进行初步分离的方法已工业化多年,其实加热脱氨的过程相当于溶液的酸化,在pH值降低的过程中,溶液中的钨首先聚合并结晶析出,而钼由于浓度低并且聚合能力弱,绝大部分仍以单体离子形式存在,进而残留在结晶母液中,从而实现钨钼的初步分离。文献[14]给出了APT结晶时钨钼析出率与蒸发程度的关系。当料液含WO3 250~260 g/L,m(Mo)/m(W)=0.14%时,蒸发至钨结晶率为60%,钼结晶率仅为7%,但当钨结晶率为80%时,钼结晶率急剧升高,达到20%。这主要是因为一方面母液体积减少使钼浓度升高,更易发生聚合,另一方面蒸氨使pH值持续下降,使钼开始聚合并与钨以杂多酸的形式一起析出,因而钼结晶率迅速上升。而郭超等[15]则研究了不同钼浓度的钨酸铵溶液在结晶过程中的钨钼分离效果,结果表明,对于钨钼比高的铵盐溶液,其蒸发结晶过程中钨钼的分离效果较好。这与热力学分析是一致的:钨钼比越大,二者聚合能力的差异亦会进一步拉大,分离的效果也会越好。
类似的,蒋安仁等[16-17]同样利用钨、钼聚合能力的差异,将含杂质钼的钨酸钠溶液的pH值控制在7~8的范围内,此时绝大部分的钨形成仲钨酸盐,他们选择硝酸胍作沉淀剂沉淀仲钨酸根离子,而MoO42-不与沉淀剂发生反应,进而达到分离的目的。实际上胍是一种含有氨基的中强碱,仲钨酸胍沉淀与上面提到的的仲钨酸铵沉淀过程十分类似。分离过程中钨的沉淀率达98%以上,除钼率在95%以上。
同样利用钨、钼聚合能力的差异,李绍秀等[18]进行了以N263为载体的乳状液膜法分离钨钼的研究。控制pH值使溶液中的钨聚合成更易被载体迁移的聚合离子,从而实现钨钼的分离。研究结果表明,溶液pH值对钨、钼的迁移影响很大,当处理含WO3(0.2156 mol/L)和Mo(0.0026 mol/L)的料液时,pH值从8.0降至6.3时,传质5 min,钨的迁移率从63%升高到98.26%。这一现象可根据图4进行分析,当溶液酸度在此区间内变化时,钨的聚合程度一直是增大的,故迁移率持续上升。而对于钼,当pH值从8.0下降到7.5,传质5 min,钼的迁移率从28.22%下降到14.04%,这是因为此时钨开始聚合,其竞争作用导致钼的迁移率下降;而当pH值从7.5下降到6.3时,钼与钨形成杂多酸的量增多,钼的迁移率上升。这些现象均与热力学分析的结果是一致的。
在溶剂萃取方面,由于单体离子聚合后其电荷密度(比电荷)变小,水化程度更低[19],因而预计相比于单体离子,其更有利于被萃取。NING等[20]采用弱碱性的伯胺萃取剂N1923对c(Mo)=53.4 g/L、c(WO3)=0.93 g/L的钼酸钠溶液进行了萃取分离,平衡pH值控制在7.07,此时过程中88.22%的钨被萃取,而钼的萃取率仅为1.389%。顾珩及其合作者[21]采用强碱性季铵盐萃取剂N263萃取分离高钼的钨酸钠溶液。当控制溶液pH=7.0时分离效果较好,钨对钼的分离系数达到18。经过6级串级萃取后,料液中钨的萃取率达到99%,反萃液钼钨比仅为0.005 8%。
钨和钼还可以用Fe(OH)3吸附法分离,也需要调节pH=7.0使溶液中的钨转变成更易被Fe(OH)3吸附的聚合离子,而使绝大部分的钼则保留在溶液中。对于m(WO3)/m(Mo)=0.446的料液,一次吸附后可使m(WO3)/m(Mo)降为0.17~0.19,经二次吸附后可降为0.108左右。最终产出的钼酸钠产品中含钨量可降至2.7%[22]。
上述工艺均利用了钨、钼在酸化过程中生成聚合离子能力的差异,实现了钨、钼的有效分离,也进一步证明了该分离路线的可行性。而通过热力学分析均可从理论上对工艺中的现象进行较为合理的解释。同时也可以看到,钨、钼的聚合程度对pH值的变化十分敏感,因而适宜进行分离的pH值范围也较为狭窄,并且该pH值范围还会随着钨、钼浓度的不同而发生改变。这就需要在处理不同的料液时,应结合具体的原料与生产工艺,对溶液pH值进行相应的调整,以获得最优的钨钼分离效果。传统上只能在处理料液前通过试验得到适宜的分离条件,这在实际生产中显然是无法实现的。此时我们针对该体系的热力学分析可以全部或部分的代替试验探索,来对分离条件进行优化,从而为钨钼分离的实现提供理论指导。
3 结论
1) 全面考虑了钨钼混合体系中存在的各种离子,通过热力学计算,绘制了25℃时W-H2O系、Mo-H2O系以及W-Mo-H 2O系中存在物种随pH值、钨、钼浓度变化的热力学平衡图,并总结了其变化规律。
2) W-Mo-H 2O系中的钨、钼在酸化过程中一般经历从单体离子到杂多酸根离子再到纯聚合离子的转变过程。在pH值为3~6.5的弱酸性区间内,溶液中有浓度较高的钨钼杂多酸根离子形成。在不破坏体系中杂多酸的前提下,该pH值区间内无法进行钨钼的有效分离。
3) 在pH值为6.5~7.5的范围内,钨转变成聚合离子的程度均高于钼,表明单钨酸根离子的聚合能力强于单钼酸根离子。对现有基于该差异实现钨钼分离的研究进行了理论上的解释。通过热力学分析,可对分离条件进行优化,从而为钨钼分离的实现提供理论指导。
REFERENCES
[1] LASSNER E, SCHUBERT W D. Tungsten, properties, chemistry, technology of the element, alloys, and chemical compounds[M]. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 1999: 42-56.
[2] ZHAO Z, CAO C, CHEN X, HUO G. Separation of macro amounts of tungsten and molybdenum by selective precipitation[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108: 229-232.
[3] 李洪桂, 羊建高, 李 昆. 钨冶金学[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2010: 211-228.
LI Hong-gui, YANG Jian-gao, LI Kun. Tungsten metallurgy[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2010: 211-228.
[4] SYKES A G. Advances in inorganic chemistry(Vol. 49)[M]. San Diego: Elsevier, 1999: 127-182.
[5] NEKOVAR P, SCHROTTEROVA D. Extraction of V(Ⅴ), Mo(Ⅵ) and W(Ⅵ) polynuclear species by primene JMT[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2000, 79: 229-233.
[6] SANO M, SHIBATA J, HARADA M. Extraction of molybdenum and tungsten with D2EHPA and LIX63[J]. Journal of the Mining and Metallurgical Institute of Japan, 1988, 104: 475.
[7] 肖 超, 肖连生, 曹佐英. 从钼酸盐溶液中分离微量钨的机理研究[J]. 中国钼业, 2011, 35(2), 29-32.
XIAO Chao, XIAO Lian-sheng, CAO Zuo-ying. Study on mechanism of removing trace tungsten from molybdate solution[J]. The China Molybdenum Industry, 2011, 35(2): 29-32.
[8] 杨幼明, 张小林, 聂华平, 卢 博, 乔 珊. Mo(W)-H2O系溶液化学行为研究[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2011, 2(2): 15-18.
YANG You-ming, ZHANG Xiao-lin, NIE Hua-ping, LU Bo, QIAO Shan. The Chemical behaviors of Mo(W)-H2O system solution[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2011, 2(2): 15-18.
[9] BAES C F, MESMER R E. The hydrolysis of cations[M]. New York: Wiley, 1976: 259.
[10] CRUYWAGEN J J, MERWE F J. Tungsten(VI) equilibria: A potentiometric and calorimetric investigation[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions, 1987(7): 1701-1705.
[11] ROZANTSEV G M, SAZONOVA O I. Thermodynamic parameters of interconversions of isopolyanions in solutions of tungsten(Ⅵ)[J]. Russian Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 2005, 31(8): 552-558.
[12] TYTKO K H, BAETHE G, CRUYWAGEN J J. Equilibrium studies of aqueous polymolybdate solutions in 1M NaCl medium at 25 ℃[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1985, 24(2): 3132-3136.
[13] ANDERSSON I, HASTINGS J J, HOWARTH O W, PETTERSSON L. Aqueous molybdotungstates[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions, 1994, 7: 1061-1066.
[14] 张启修, 赵秦生, 赵慕岳, 赵宝华. 钨钼冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2005: 146.
ZHANG Qi-xiu, ZHAO Qin-sheng, ZHAO Mu-yue, ZHAO Bao-hua. Tungsten and molybdenum metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005: 146.
[15] 郭 超, 肖连生. 钼酸铵结晶过程中的钨钼分离研究[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2010, 38(3): 1-4.
GUO Chao, XIAO Lian-sheng. Study on tungsten and molybdenum separation in the ammonium molybdate crystallization process[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2010, 38(3): 1-4.
[16] 蒋安仁, 蒋伟中, 庞 震. 仲钨酸B的形成及其在钨钼分离中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1990, 11(8): 793-796.
JIANG An-ren, JIANG Wei-zhong, PANG Zhen. The formation of paratungstate B and its use in the separation of tungsten and molybdenum[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 1990, 11(8): 793-796.
[17] 蒋安仁, 庞 震, 蒋伟中. 可高效除钼的仲钨酸铵或钨酸钠的生产方法. 中国, CN1033978A[P]. 1989-07-19.
JIANG An-ren, PANG Zhen, JIANG Wei-zhong. Preparation of ammonium paratungstate or sodium tungstate with high molybdenum removal efficiency. CN Patent 1033978A[P]. 1989-07-19.
[18] 李绍秀, 王向德, 张秀娟. 乳状液膜法分离钨钼的研究-弱碱性体系[J]. 膜科学与技术, 1996, 16(2): 8-14.
LI Shao-xiu, WANG Xiang-de, ZHANG Xiu-juan. Separation of tungsten and molybdenum by emulsion liquid membrane-weak basic separation system[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 1996, 16(2): 8-14.
[19] 徐光宪. 萃取化学原理[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1984: 42-56.
XU Guang-xian. Principles of extraction chemistry[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1984: 42-56.
[20] NING P, CAO H, ZHANG Y. Selective extraction and deep removal of tungsten from sodium molybdate solution by primary amine N1923[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2009, 70: 27-33.
[21] 顾 珩, 汪剑岭, 王继民. 高钼钨酸钠溶液萃取分离钨钼的研究[J]. 中国钨业, 1987(7): 12-15.
GU Heng, WANG Jian-ling, WANG Ji-min. Study on the solvent extractive separation of tungsten and molybdanum from sodium tungstate solution containing high molybdanum[J]. China Tungsten Industry, 1987(7): 12-15.
[22] 吕 莹, 孙放. Fe(OH)3吸附法从高钨钼酸钠溶液中分离钨钼的研究[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2005, 33(3): 1-3.
 Ying, SUN Fang. Study of separation of tungsten and molybdenum from high W-containing molybdate acid sodium solution by Fe(OH)3 adsorption[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2005, 33(3): 1-3.
Ying, SUN Fang. Study of separation of tungsten and molybdenum from high W-containing molybdate acid sodium solution by Fe(OH)3 adsorption[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2005, 33(3): 1-3.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50974137)
收稿日期:2012-08-01;修订日期:2012-11-12
通信作者:赵中伟,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830476;E-mail:zhaozw @csu.edu.cn