J. Cent. South Univ. (2017) 24: 2215-2221
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3630-6
Effect of Ti on microstructure and strengthening behavior in press hardening steels
WEN Yu-hui(闻玉辉)1, ZHU Guo-ming(朱国明)1, DAI Si-yu(戴思雨)1, KANG Yong-lin(康永林)1, 2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083, China;
2. State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials (University of Science and Technology Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany 2017
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany 2017
Abstract: Effect of Ti addition on the microstructure and strengthening behavior in press hardening steels (PHS) was analyzed by optical metallography (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results show that the microstructure of PHS is martensite, and two sizes of particles disperse in the martensite matrix during the forming and quenching process. The size of the bigger particles is between 100 and 200 nm, and the small particles are nanometer-sized. The quantity of the particles has a positive relation with the Ti content. More importantly, the microstructure and strengthening mechanism are affected by the precipitating behavior of the particles. Besides the prior austenite grain, martensite packet, block and lath are refined by Ti addition. The steels are strengthened by the fine grains, martensite substructure and precipitates. The uniformly distributed dislocation in the martensite lath, the density of which is between 3.0×1014 cm–2 and 5.0×1014 cm–2, strengthens the steels through associating with fine carbide particles.
Key words: martensite; particles; prior austenite grain; martensite lath; press hardening steel
1 Introduction
Due to the demand for reducing vehicle weight and improving crashworthiness qualities, more and more advanced high strength and ultra-high strength steels have been used in the vehicles, such as dual phase (DP) steel, quenching and partitioning (Q&P) steel, transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) steels and press hardening steel (PHS). The vehicle weight has connection with the strength of body parts, it is extremely significant to improve the strength of body parts with the thinner sheet thickness [1]. PHSs, which combine the advantages of high strength, well forming property and excellent geometrical accuracy, have attracted more and more attention since the Saab Automobile AB used the hardened boron steel as the structure component for the Saab 9000, the fraction of PHS in the white body of VOLVO XC90-2015 has achieved 40%. The blank with the microstructure of lath martensite causes an increase of the tensile strength up to 1500 MPa with fine elongation of 6%–8%, which tremendously improves the performance of safety and crashworthiness [2].
Hot stamping has received much attention in recent years [3, 4], it is an effective method for producing automotive parts and a non-isothermal sheet metal forming technique, where the blank is austenitized and then formed in a single process that combines forming and quenching in the dies. The microstructure, property and process parameters of press hardening steels have been discussed through experiments and simulations by many researchers. ZHOU et al [5] carried out thermomechanical experiments to reproduce the hot stamping process and investigated the effects of process parameters, such as the austenitizing temperature, soaking time, initial deformation temperature and cooling rates, on the microstructure and mechanical properties of cold-rolled 22MnB5 steel strips. NAMKLANG and UTHAISANGSUK [6] studied the evolutions of microstructure, temperature of blank and die by experiment and FE simulation, and predicated that local emerged microstructure constituents and corresponding distributed hardness values of the stamped parts were based on time–temperature–transformation (TTT) diagram. CHO et al [7] found that the effect of Ti addition can effectively refine the prior austenite grain and change the precipitation behavior of secondary carbides for the 5%Cr–Mo–V tool steel. The microstructure and mechanical properties of steels after hot stamping were investigated to study the influence of the boron segregation [8–10]. However, the effect of Ti on microstructure, precipitated behaviors and strengthening mechanism in PHS has been rarely reported.
In the present work, PHSs with martensite microstructure were obtained through forming and quenching in the die with cooling paths. The microstructure and precipitated particles were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), the strengthening mechanism and precipitated behaviors were analyzed.
2 Experimental procedure
The materials investigated were boron alloyed steels with 0.025%, 0.039% and 0.048%Ti, respectively. The chemical compositions of the investigated steels are given in Table 1. Steels A, B and C show an increasing trend in the Ti content. All the alloys were prepared as 30 kg ingots using vacuum induction melting (VIM) and then rolled into 1.8 mm in thickness by 7 passes after 2 h austenitized at 1200 °C. Finally the steel sheets were cut into 240 mm×60 mm with the length direction parallel to the rolling direction after cooling to room temperature in the air. All of the steel sheets were austenitized at 950 °C for 300 s to obtain uniform austenite and then transferred to the die (Fig. 1(a)), formed and quenched rapidly at a cooling rate more than 20 °C/s. The U-beams with high-strength and geometrical accuracy were obtained after holding 30 s in the closed die, as shown in Fig. 1(b).
The samples were cut from the U-beam to investigate the microstructure, precipitated particles and strengthening mechanism. In this work, the microstructure of the hot-rolled and hot stamping steels were observed by the OM after grinding, polishing, and etching with 4% nital solution, and an quanta FEG 450 SEM was used to observe the detailed microstructure. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was carried out to determine whether retained austenite exists. Samples after replicating and the thin foils after twin-jet electropolishing in 900 mL CH3COOH+100 mL HClO4 solution at –30 °C and 25 V to perforation were observed by an H-8100 TEM to analyze precipitated particles and martensite laths, respectively. The prior austenite grain was observed by OM after mechanical polishing, and 3 min insulation in the saturated picric acid of 70 °C.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
The microstructure of the investigated 22MnB5 hot-rolled sheets contains ferrite and pearlite, as shown in Fig. 2. The tensile strength is 400–500 MPa and the elongation is 20%–30%. Figures 3 (a)–(c) provide the microstructure of U-beam after hot stamping, it can be seen that the main microstructure of the steels is martensite, and is finer with increasing Ti content (0.025%–0.048%). TEM observation was performed to observe the detailed microstructure. As shown in Figs. 3(d)–(f), the martensite lath width decreases obviously with Ti addition increasing from 0.025% to 0.048%. The XRD results in Fig. 4 show that all the steels exhibit a full martensite microstructure without retained austenite [11].
Table 1 Chemical compositions of investigated steels (mass fraction, %)
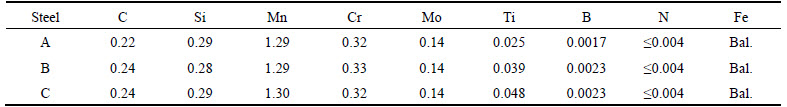
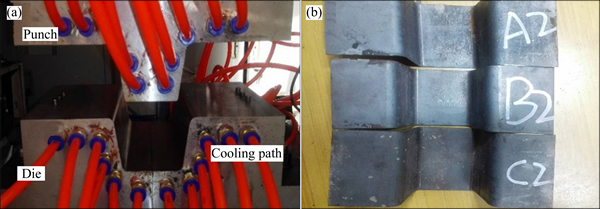
Fig. 1 Photos of die of hot stamping (a) and hot stamping U-beam (b)

Fig. 2 OM images of 22MnB5 hot-rolled steel:
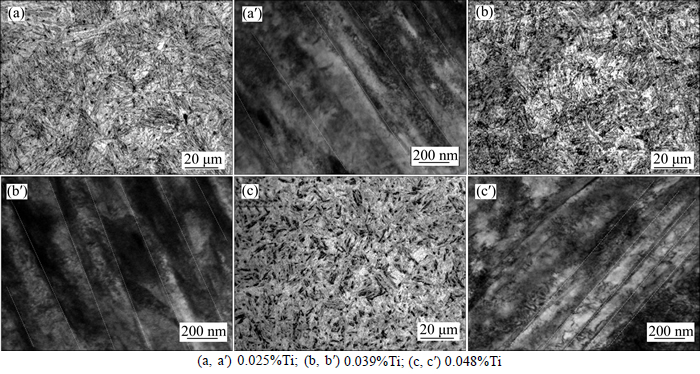
Fig. 3 OM (a, b, c) and TEM (a′, b′, c′) images of martensite lath of 22MnB5 steel after hot stamping:
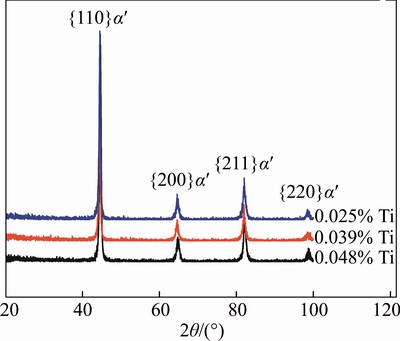
Fig. 4 XRD pattern of U-beam for steels with different Ti addition
3.2 Precipitated particles
The strengthening mechanisms include work hardening, solid-solute strengthening, fine-grain strengthening and second-phase strengthening. The second-phase strengthening and fine-grain strengthening are significant to improve the strength without losing the ductility and formability. The second phase would dissolve in austenite matrix or form particles due to their different solubility when the steels were austenitizing. The solid solubility of second phase in the austenite matrix decreases after quenching, and the particles precipitate as carbide or nitride. According to the solubility formula of TiN and TiC, the temperature of solubility [12] is calculated by
 (1)
(1)
where TAS is the temperature of solubility, A and B are the constants for each precipitation, M and X are the mass fractions of precipitated elements. A and B are 0.32 and 8000 for TiN, and 2.75 and 7000 for TiC, respectively. The solubility temperatures of TiN in the steel is higher than 1580 °C, but the solubility temperatures of TiC is only 1037 °C, which means that most TiN particles would exist in the austenite matrix. Besides, the existent particles would grow with carbon and precipitated as Ti(C, N) during the quenching process because of the lack of nitrogen.
The particles were precipitated in two forms, the bigger particles and nanometer-sized particles.Figures 5(a)–(c) show that the bigger particles dispersed in the grain are square with the size between 100 and 200 nm. The particles distributed in the three steels with different Ti content are similar. Figures 5(e) and (f) are EDS and SAED results of the particles, it can be obtained that the crystal lattice size is respectively 0.38 nm, 0.38 nm and 0.68 nm, which is the distorted lattice of NaCl structure. Considering the EDS result of the particles (Fig. 5(e)), it can be concluded that the composition of particle is Ti(C, N). Figures 6(a)–(c) are the TEM images of nanometer-sized particles. Many particles, smaller than 20 nm, were observed in the three steels. The particles disperse in the interior and boundary of grains, and more particles would precipitate in the steels with the increasing Ti content. Figure 6(d) shows the TEM image of nanometer-sized particles. The particles are globular with a size of 5–20 nm, because the globular particles have the lowest interfacial energy at the beginning of precipitation and could be existent steadily. It can be concluded that the composition of nanometer-sized particles may be Ti(C, N) from EDS (Figs. 6(e)–(g)) and Refs. [13, 14].
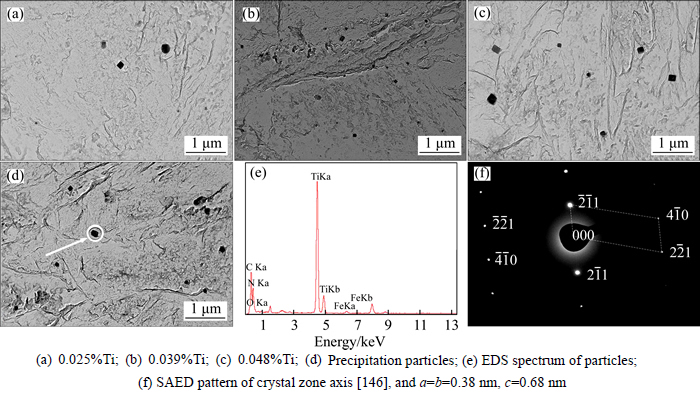
Fig. 5 TEM images of precipitation for steels with different titanium contents:
3.3 Fine-grain strengthening
Figure 7 shows the optical micrographs of the prior austenite grain and SEM micrographs of martensite microstructure for the steels with different Ti contents. In order to analyze quantitatively the relationship between prior austenitic grain size and Ti content, the average size of prior austenite grain was obtained by the intercept method through the measurement of a large amount of grains, which is respectively 22 μm, 17 μm and 10 μm. Figure 8(a) shows the relationship between the size of prior austenite grain and Ti content, it is obvious that the size of prior austenite grain has a negative liner relation with Ti content in the steels. The reason is that the existent particles hinder the growth of austenite grain during the austenitizing and refine the primary grains.
The increase of the strength of the titanium micro-alloyed steels mainly depends on the fine grain strengthening. The direct determinant of strength is the size of three substructure in the prior austenite grain for the martensite steels [15–17], which is the packet, block and martensite lath, as shown in Fig. 9 [18]. The prior austenite grain can be divided into some packets which consist of a group of laths with the same habit plane, and each packet is further subdivided into several blocks containing laths with the same orientation. Owing to the microstructure of hot-pressing being affected by the prior austenite grain, the martensite packets and blocks inherit from the prior austenite grain. As can be seen in Figs. 3 and 7, the packets and blocks of the steels with 0.048% Ti are narrower than those of steels with 0.039%Ti and 0.025%Ti, and conform to the relation between the size of prior austenitic grain and Ti content. Over 50 laths in the TEM images are measured to obtain the average width of martensite lath by the line-intercept method, which are respectively 318 nm, 194 nm and 94 nm (Fig. 8(b)). Since yield strength has the Hall–Petch relationship with packet and block [15], block width (effective grain sizes in lath martensite structure) can be regarded as a microstructural factor controlling the strength of the steels [18–20]. Packet and block are affected by prior austenite grain and have a negative relation with Ti content. What is more, the martensite lath is only relevant to the compositions and decreases with increasing Ti content, as reported by ROBERTS [21].
3.4 Precipitated-phase strengthening
The particles in the austenite matrix would pin the grain boundary migration to retard the growth of prior austenite grain in the process of austenitizing. The quantity of particles of steel with 0.048% Ti is more than those of the steels with 0.039% Ti and 0.025% Ti, so the size of the grain is smaller than others, as shown in Figs. 7(a)–(c). Many nanometer-sized particles precipitate during the fast cooling process, but some existent particles in the austenite matrix would grow up through the combination with carbon and form bigger particles (100–200 nm), which loses the ability to strengthen steels and deteriorate the toughness or ductility. When the micro-crack comes across the big particles, it would propagate along the boundary of the bigger particles and martensite. The nanometer-particles improve the strength through the interaction between the particles and dislocation, and the dislocation movement would be hindered and bended by the particles, which is conformed to the Orowan mechanism [22–24]. A series of dislocation loops were left after by passing the particles when the stress suffered by the dislocation exceeds the critical stress of dislocation slipping. The left dislocation loops will prevent the dislocation moving to enhance the strength. The contributed yield strength due to the Orowan mechanism [25] is given by
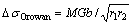 (2)
(2)
where M is the Taylor factor, G is the shear modulus and b is the magnitude of burgers vector, r1 and r2 are the linear intercarbide spacing and projected value of the perpendicular sheet spacing. DsOrowanhas negative relation with r1r2 due to M, G and b are constants. For the limited fraction of particles in the steels, the smaller the particle size is, the larger its amount is and the smaller the average spacing is, so the strengthening effect is more significant [25]. More dislocation loops around the particles will be formed to hinder the movement of dislocation under the condition of more precipitating particles. The martensite phase can be strengthened by most nanometer-sized particles. But owing to the limitation of the replica method to observe the particles, a few nanometer-sized particles are not separated from the martensite matrix.
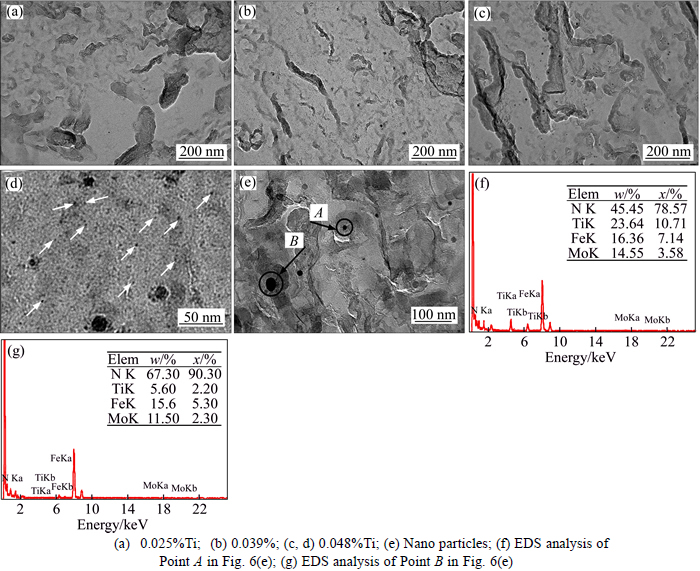
Fig. 6 TEM images of different Ti contents:(White arrows show nanometer sized particles and black arrows show particles of EDS)
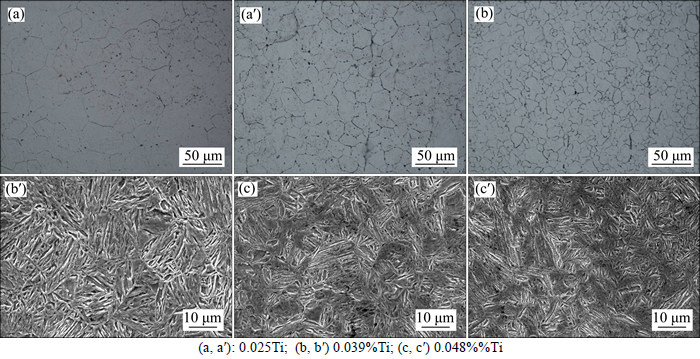
Fig. 7 OM images of prior austenite microstructure (a, b, c) and SEM images (a′, b′, c′) of martensite microstructure:
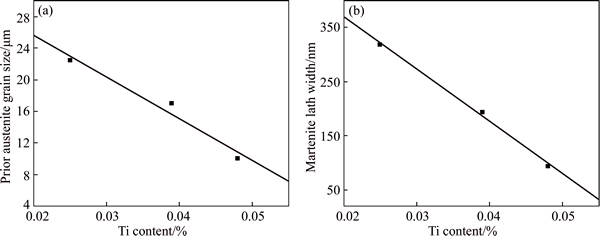
Fig. 8 Relationship between Ti content and prior austenite grain size (a) and martensite lath width (b)
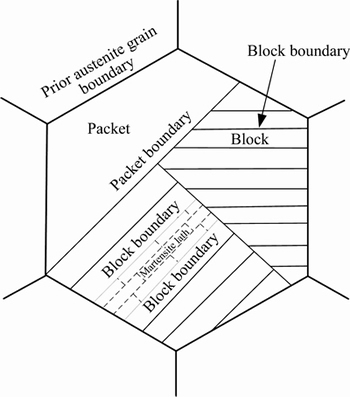
Fig. 9 Microstructural hierarchy of lath martensite structure
Figure 10 shows the TEM image of martensite laths, white arrows show particles and blue arrows show dislocations. It can be seen that the dislocations are uniformly distributed. According to the modified Williamson–Hall method [26], the dislocation density is between 3.0×1014 cm–2 and 5.0×1014 cm–2 for PHSs. The dislocation in the martensite lath intertwines with the particles to improve the strength.

Fig. 10 TEM image of martensite lath
4 Conclusions
1) The microstructure and second-phase in the PHSs with different Ti additions are investigated to analyze the precipitating behaviors and strengthening mechanism. The microstructure of PHS is lath martensite without retained austenite after hot stamping.
2) The bigger particles and nanometer-sized particles are precipitated in the martensite lath, both of their compositions are Ti(C, N). The magnitude of the nanometer sized particles increases with Ti content, and the particles interact with the dislocation to strengthen the steels.
3) Due to the pinning effect of the particles and the inheritance of microstructure, the prior austenite grain, martensite packets and blocks become fine, the size of prior austenite grain and the width of martensite lath have a negative relation with the Ti content. What is more, the uniformly distributed dislocation whose density is between 3.0×1014 and 5.0×1014 cm–2 in the martensite lath of PHS steels, strengthens the martensite matrix through intertwining with the precipitated particles.
References
[1] LIU Hong-sheng, XING Zhong-wen, LEI Cheng-xi. Hot formation quality of high strength steel BR1500HS for hot stamping without cooling system [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 542–547.
[2] KARBASIAN H, TEKKAYA A E. A review on hot stamping [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2010, 210: 2103–2118.
[3] NIKRAVESH M, NADERI M, AKBARI G H. Influence of hot plastic deformation and cooling rate on martensite and bainite start temperatures in 22MnB5 steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 540: 24–29.
[4] LIU He-ping, LU Xian-wen, JIN Xue-jun, DONG Han, JIE Shi. Enhanced mechanical properties of a hot stamped advanced high-strength steel treated by quenching and partitioning process [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 64: 749–752.
[5] ZHOU Jing, WANG Bao-yu, HUANG Ming-dong, CUI Dong. Effect of hot stamping parameters on the mechanical properties and microstructure of cold-rolled 22MnB5 steel strips [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2014, 21: 544–555.
[6] NAMKLANG P, UTHAISANGSUK V. Description of microstructures and mechanical properties of boron alloy steel in hot stamping process [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2016, 21: 87–100.
[7] CHO K S, PARK S S, CHOI D H, KWON H. Influence of Ti addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a 5% Cr–Mo–V steel [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 626: 314–322.
[8] JIANG Chao, SHAN Zhong-de, ZHUANG Bai-liang, RONG Wen-juan, ZHANG Mi-lan. Microstructure and properties of hot stamping 22MnB5 steel [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012(33): 78–81. (in Chinese)
[9] CHENG Jun-ye, ZHAO Ai-min, CHEN Yin-li, JIN Hai-liang, LI Zhen, GAO Xu-tao. Effect of Ti addition on martensite transformation in hot stamping steel [C]// 8th CSM Annual Meeting (2011). Beijing, China, 2011: 701–706. (in Chinese)
[10] NADERI M, KETABCHI M, ABBASI M, BLECK W. Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties of different high strength carbon steels after hot stamping [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2011, 211(6): 1117–1125.
[11] NADERI M, DURRENBERGER L, MOLINARI A, BLECK W. Constitutive relationships for 22MnB5 boron steel deformed isothermally at high temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 478(1): 130–139.
[12] YONG Qi-long. Second phase in iron and steel materials [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006.
[13] DUAN Xiu-gang, CAI Qing-wu, WU Hui-bin, TANG Di. Precipitation law of ultra-fine carbides in ferrite matrix Ti-Mo micro-alloy steel [J]. Journal of University Science and Technology of Beijing, 2012, 34(6): 644–650. (in Chinese)
[14] WANG Tzu-pin, KAO Fang-hsin, WANG Shing-hoa, YANG Jer-ren, HUANG Ching-yuan, CHEN Hsueh-ren. Isothermal treatment influence on nanometer-size carbide precipitation of titanium-bearing low carbon steel [J]. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(2): 396–399.
[15] MAKI T, TSUZAKI K, TAMURA I. The morphology of microstructure composed of lath martensites in steels [J]. Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1980, 20(4): 207–214.
[16] KITAHARA H, UEJI R, TSUJI N, MINAMINO Y. Crystallographic features of lath martensite in low-carbon steel [J]. Acta Materials, 2006, 54(5): 1279–1288.
[17] MORITO S, YOSHIDA H, MAKI T, HUANG X. Effect of block size on the strength of lath martensite in low carbon steels [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 438–440: 237–240.
[18] HSU T Y, (XU Zu-yao). Effect of lath martensite morphology on the mechanical properties of steel [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2009, 24 (3): 1–6. (in Chinese)
[19] MORITO S, TANAKA H, KONISHI R, FURUHARA T, MAKI T. The morphology and crystallography of lath martensite in Fe-C alloys [J]. Acta Materials, 2003, 51(6): 1789–1799.
[20] LI Sheng-ci, ZHU Guo-ming, KANG Yong-lin. Effect of substructure on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of lath martensite in 0.1C–1.1Si–1.7Mn steel [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 675: 104–115.
[21] ROBERTS M J. Effect of transformation substructure on the strength and toughness of Fe-Mn alloys [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1970, 1(12): 3287–3294.
[22] FURUHARA T, AARONSON H I. On the mechanisms of interphase boundary carbide precipitation [J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1988, 22(10): 1635–1637.
[23] KOCKS U F. On the spacing of dispersed obstacles [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1966, 14(11): 1629–1631.
[24] LI Xiao-lin, WANG Zhao-dong. Interphase precipitation behaviors of nanometer-sized carbides in a Nb-Ti-bearing low-carbon microalloyed steel [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 4(51): 417–424.
[25] YEN Hung-wei, CHEN Po-yu, HUANG Ching-yuan, YANG Jer-ren. Interphase precipitation of nanometer-sized carbides in a titanium–molybdenum-bearing low-carbon steel [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(16): 6264–6274.
[26]  A, LENDVAI J. Dislocations and grain size in ball-milled iron powder [J]. Nanostructured Materials for Energy Storage and Conversion-Proceedings of the International Symposium, 1996, 7(7): 779–788.
A, LENDVAI J. Dislocations and grain size in ball-milled iron powder [J]. Nanostructured Materials for Energy Storage and Conversion-Proceedings of the International Symposium, 1996, 7(7): 779–788.
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Cite this article as: WEN Yu-hui, ZHU Guo-ming, DAI Si-yu, KANG Yong-lin. Effect of Ti on microstructure and strengthening behavior in press hardening steels [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(10): 2215–2221. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3630-6.
Foundation item: Project(U1460101) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(20120006120002) supported by Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China
Received date: 2016-04-28; Accepted date: 2016-10-06
Corresponding author: ZHU Guo-ming, Associate Professor, PhD; Tel/Fax: +86–10–62332335; E-mail: zhuguoming@ustb.edu.cn