Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 3103-3107
Purification of metallurgical grade silicon by electrorefining in molten salts
CAI Jing1, LUO Xue-tao1, LU Cheng-hao1, Geir Martin HAARBERG2, Annabelle LAURENT2, Ole Edvard KONGSTEIN3, WANG Shu-lan4
1. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China;
2. Department of Materials Technology, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim NO-7491, Norway;
3. SINTEF, Trondheim NO-7465, Norway;
4. Department of Chemistry, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China
Received 8 October 2011; accepted 29 March 2012
Abstract: Electrochemical studies on silicon deposition were performed in molten salt electrolytes. Purification of metallurgical grade silicon by electrorefining was carried out in molten Si-chloride salts at temperatures from 973 K to 1223 K. It was found that the use of a liquid alloy anode of silicon and copper was beneficial in molten CaCl2 with NaCl, CaO and dissolved Si. ICP-AES analysis results showed efficient removal of metal impurities, such as titanium, aluminum and iron, which are present in significant quantities in the feedstock. The contents of boron and phosphorus in the silicon after electrorefining were reduced from 36×10-6 and 25×10-6 to 4.6×10-6 and 2.8 ×10-6, respectively. The energy consumption of electrorefining was estimated to be about 9.3 kW·h/kg.
Key words: electrorefining; molten salt; Si-Cu alloy; silicon; purification; energy consumption
1 Introduction
As the second most abundant element in the earth’s crust, silicon has been considered to be one of the most important and attractive materials due to the fact that it is widely used in the manufacture of solar cells and electronic circuits. High purity silicon is quite essential to both these applications.
The production of high purity silicon, so-called solar grade silicon (SOG-Si), has seen a steady increase for more than 10 years. The main reason for the increased demand for SOG-Si is the increased production of solar cells. However, the solar energy contributes to much less than 1% of the total energy generation [1,2]. A further implementation of the solar energy based on silicon is possible only if the price of feedstocks (SOG-Si) might be considerably reduced. New and less costly methods for the production of SOG-Si have been studied for several years. One of the candidate methods is based on molten salt electrolysis, which can in principle be used to purify silicon in a simpler and more energy efficient way compared with the present pyrometallurgical process.
Many studies on molten salt electrolysis of silicon have been published. Most of the literature is connected to possibilities for developing processes for producing high purity silicon. Two excellent review articles were published in 1980's [3,4], at a time when many research groups were active in studies on electrodeposition of silicon in molten salts in the temperature range from 973 K to 1373 K. Silicon is a good electronic conductor at these temperatures. The electrolytes were mainly based on molten fluorides with K2SiF6 as the raw material [5,6], or cryolite (Na3AlF6) containing dissolved SiO2 as the source of silicon [7]. Some studies revealed that high purity silicon could be produced by electrorefining in molten salts using metallurgical grade silicon (MG-Si) as the raw material [8]. It was found that an alloy anode consisting of silicon and copper could improve the effectiveness of the silicon electrorefining process [9-12]. In order to avoid problems with solid deposits and low current density, MATTEI et al [13] electro- deposited liquid silicon in a BaO-SiO2-BaF2 system at 1723 K.
Earlier work has often been carried out in fluoride based melts, and these melts are very corrosive. On this basis it is interesting to explore the possibility of using a chloride based melt. A new method to produce silicon was proposed a few years ago [14-17], which was based on electrochemical deoxygenation of metals (FFC Cambridge process) [18]. In this case, solid SiO2 is used as the cathode, and silicon is directly reduced on the cathode from Si(IV) to Si(0) during electrolysis in molten chlorides.
In spite of many efforts carried out, no industrialization has been achieved for molten salt electrolysis of silicon. The main challenge is to reduce the impurity content, especially the contents of boron and phosphorus, to obtain the desired purity of SOG-Si.
Herein, we report an electrorefining process to purify MG-Si in molten CaCl2 based electrolyte. A mixed Si-chloride electrolyte was selected due to the fact that it is good for the electrorefining of silicon at relatively low temperatures.
2 Experimental
Commercial MG-Si was used as the main source of silicon. It was mixed with copper and prepared in separate experiments to produce the alloy for the anode (31% Si and 69% Cu in mole fraction). Tungsten was used as the working electrode and quasi-reference electrode during electrorefining. The electrolyte was composed of 85%CaCl2, 5%NaCl, 5%CaO and 5%Si in mole fraction. A previous study showed that the dissolution of silicon in the CaCl2 based melt was quite fast and the dissolved silicon contained complex ions [19]. The experimental setup for electrorefining experiments is shown in Fig. 1.
The Si-Cu alloy was placed in the bottom of the crucible, connected via a tungsten wire to the power supply. A Metrohm Autolab potentiostat (PGSTAT 30) was used to serve as the power supply and perform electrochemical studies.
All experiments were carried out under dry argon atmosphere at temperatures from 973 K to 1223 K. A small and constant potential was applied between the anode and cathode during the electrorefining, which normally were run for a few hours to deposit thin layer of silicon. The electrolysis products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Panalytical X’pert PRO) and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES, PerkinElmer, Optima 7300DV) after ultrasonic cleaning and acid washing.
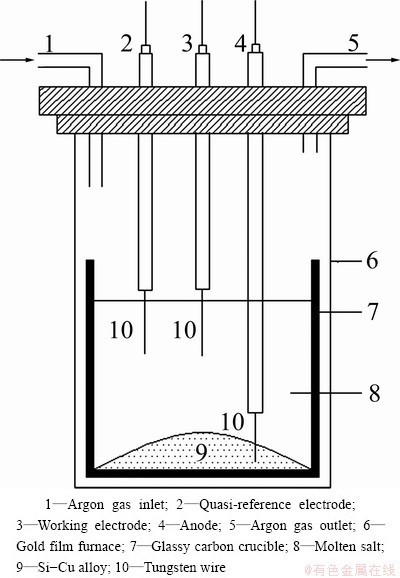
Fig. 1 Schematic drawing of experimental setup for electro-refining
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Cyclic voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry was performed to study the behaviour of silicon during electrorefining in molten CaCl2 based salt. Figure 2 shows a cyclic voltammogram obtained in the molten CaCl2 based salt with dissolved silicon.
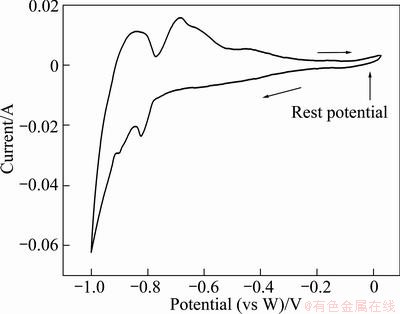
Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammogram in molten 85%CaCl2-5%NaCl- 5%CaO-5%Si in mole fraction at 1123 K (Tungsten electrodes, sweep rate of 0.5 V/s)
The formation of dissolved calcium takes place at potential less than the reversible potential for calcium deposition, and it is observed as steady increasing cathodic current in the potential range from -0.2 V. Dissolved calcium is known to exist as a divalent species, Ca22+. The cathode reaction is likely to be:
2Ca2++2e-→Ca22+ (1)
The cathodic and anodic peak currents at approximately -0.8 V and -0.7 V are due to the deposition and dissolution of silicon respectively. Deposition of silicon is followed by an increased cathodic current due to the deposition of calcium, which is oxidized in the return scan and shown as a current peak at around -0.85 V.
To verify the oxidation-reduction reaction of silicon, the scanning potential range was changed to 0 V to -0.85 V. As shown in Fig. 3, typical cyclic voltammograms were obtained in the same CaCl2 based electrolyte as Fig. 2 with varying potential sweep rates. The cathodic current waves and peaks from -0.7 V to -0.8 V and the corresponding anodic current peaks are due to the formation of solid silicon and the subsequent anodic dissolution. The cathodic current at more positive potentials than silicon deposition is again due to the cathodic formation of dissolved calcium, i.e. reaction (1). The anodic oxidation of dissolved calcium takes place on the return scan, giving rise to an anodic current wave.
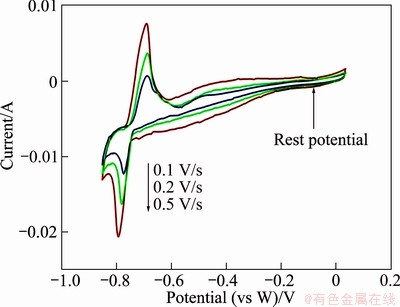
Fig. 3 Cyclic voltammograms with varying sweep rates at 1123 K in molten 85%CaCl2-5%NaCl-5%CaO-5%Si in mole fraction (Tungsten electrodes)
The cathode process was supposed to be diffusion controlled, i.e. diffusion of dissolved Si(IV) complexes. However, the shape of the voltammograms in Fig. 3 did not resemble an ideal diffusion controlled reaction, and the value of the diffusion coefficient could not be calculated accurately at present. This is due to the fact that a chemical reaction involving silicon complexes might take place near the electrode.
3.2 Potentiostatic electrolysis
Preliminary electrorefining experiments using a MG-Si anode were unsuccessful due to the passivation of the anode. The passivation is believed to be caused by the oxidation on the anode surface.
The use of a liquid Si-Cu alloy anode was introduced to avoid the anode passivation problems. Also, the Si-Cu alloy is supposed to have a good segregation effect for some impurity elements by diffusional trapping [9].
When the Si-Cu alloy is used as a liquid anode, elements more noble than silicon, such as boron and phosphorus, will remain at the anode and then the alloy phase can be used as a filter for purifying silicon [9]. Those elements less noble than silicon, such as calcium and aluminum, can be dissolved anodically along with silicon but will not be electrodeposited, and remain in the molten salt as ions. The whole electrorefining process can be expressed as follows:
Si (with impurities)→Si(IV)+4e- (anode reaction) (2)
Si(IV)+4e-→Si (without impurities) (3)
To verify the feasibility of this new concept, potentiostatic electrolysis was carried out in the molten CaCl2 based salt. According to the voltammetric results, the applied potential was kept low in order to prevent the deposition of Ca and other unwanted impurities. The average current density was in the range of 10-80 mA/cm2. As shown in Fig. 4, the current was fairly stable, no passivation of the anode occurred. The slight increase in current was thought to correspond to an enlargement of the reaction area due to the silicon deposition.
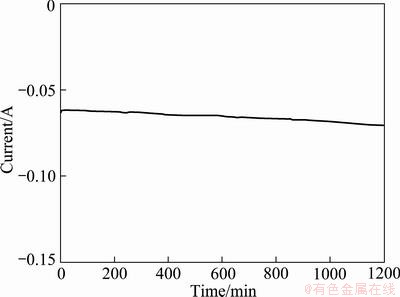
Fig. 4 Current—time during potentiostatic electrolysis at -0.75 V and 1223 K in molten 85% CaCl2-5%NaCl-5%CaO-5%Si in mole fraction
After the potentiostatic electrolysis, a powdery product adhering to the cathode was produced as shown in Fig. 5. And the mixed Si-chloride electrolyte was found to be good for the separation of deposited product from the electrolyte. The white attachment on the product was believed to be the melt residue, which can be efficiently removed by ultrasonic cleaning.

Fig. 5 Photograph of product on tungsten cathode after potentiostatic electrolysis at -0.75 V and 1223 K for 20 h in molten 85%CaCl2-5%NaCl-5%CaO-5%Si in mole fraction with liquid Si-Cu alloy as anode
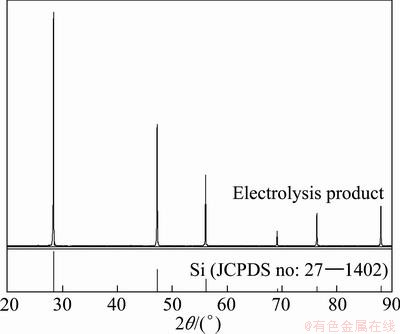
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of product after potentiostatic electrolysis at -0.75 V and 1223 K for 20 h in molten 85%CaCl2- 5%NaCl-5%CaO-5%Si in mole fraction
XRD analysis (Fig. 6) of the product after ultrasonic cleaning showed only the presence of silicon with no other impurity detected. However, the XRD method cannot be used for a real quantitative analysis of the produced silicon.
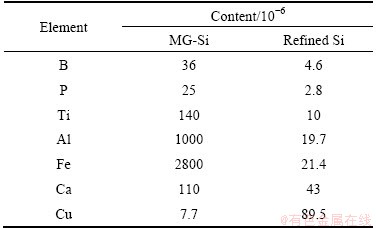
For more reliable quantitative analysis, the produced silicon was washed in HF and analyzed by ICP-AES. Table 1 shows the impurity content in the produced silicon. It could be observed that the purifying effects of electrorefining were good for some of the key elements, and the contents of boron and phosphorus were found to be reduced by 87.2% and 88.8%, respectively. The level of copper was found to increase slightly during the electrorefining due to the co-deposition of such impurity brought by the electrolyte. But it is believed that these elements may be efficiently removed by improving the cell design. Nevertheless, these results are very promising for the prospects of developing an electrorefining process of MG-Si to produce SOG-Si in molten Si-chloride salts.
The current efficiency with respect to the silicon effectively deposited was estimated to be 31%, where the relatively low yield was presumably due to the poor quality and brittleness of the silicon deposits, which might fall off into the electrolyte. The energy consumption (electrolysis only) can be estimated according to the following equation:
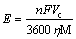 (4)
(4)
where n is the electron transfer number in the electrorefining process; F is the Faraday constant; Vc is the cell voltage; η is the current efficiency; M is the molar mass of silicon. As calculated by Eq. 4, the energy consumption E is estimated to be about 9.3 kW·h/kg.
Table 1 ICP-AES analysis results of MG-Si and refined silicon after electrorefining in molten 85%CaCl2-5%NaCl-5%CaO- 5%Si in mole fraction at -0.75 V and 1223 K for 20 h
4 Conclusions
Electrorefining of MG-Si was studied in molten 85%CaCl2-5%NaCl-5%CaO-5%Si in mole fraction at relatively low temperatures. The results of cyclic voltammetry showed the feasibility of this new process. And it was found that the anode passivation problems can be effectively avoided by using an alloy anode of MG-Si and copper. The purified silicon can be deposited in such molten Si-chloride electrolyte, which was found to be a promising solution for the continuous operation during the electrolytic process. The contents of boron and phosphorous were reduced by 87.2% and 88.8%, and the low estimated energy requirement (~9.3 kW·h/kg) may allow for applying several electrorefining steps in series to obtain the required solar grade purity.
References
[1] STEVENS C. Annual world solar photovoltaic industry report [R]. San Francisco: Solarbuzz LLC, 2009.
[2] DESPOTOU E, GAMMAL A E. Global market outlook for photovoltaics until 2014 [R]. Brussels: The European Photovoltaics Industry Association (EPIA), 2010.
[3] ELWELL D, FEIGELSON R S. Electrodeposition of solar silicon [J]. Solar Energy Materials, 1982, 6: 123-145.
[4] ELWELL D, RAO G M. Electrolytic production of silicon [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1988, 18: 15-22.
[5] RAO G M, ELWELL D, FEIGELSON R S. Electrowinning of silicon from K2SiF6-molten fluoride systems [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1980, 127: 1940-1944.
[6] RAO G M, ELWELL D, FEIGELSON R S. Electrodeposition of silicon onto graphite [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1981, 128: 1708-1711.
[7] MONNIER R, BARAKAT D, GIACOMETTI J C. Refining of silicon and germanium: US, 3254010 [P]. 1966-05-31.
[8] SHARMA I G, MUKHERJEE T K. A study on purification of metallurgical grade silicon by molten salt electrorefining [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1986, 17: 395-397.
[9] OLSON J M, CARLETON K L. A semipermeable anode for silicon electrorefining [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1981, 128: 2698-2699.
[10] CARLETON K L, OLSON J M, KIBBLER A. Electrochemical nucleation and growth of silicon in molten fluorides [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1983, 130: 782-786.
[11] OLSEN E, ROLSETH S. Three-layer electrorefining of silicon [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010, 41: 295-302.
[12] LAI Yan-qing, JIA Ming, TIAN Zhong-liang, LI Jie, YAN Jian-feng, YI Ji-guang, WANG Zhi-gang, LIU Ye-xiang. Study on the morphology evolution and purification of electrorefined silicon [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2010, 41: 929-935.
[13] de MATTEI R C, ELWELL D, FEIGELSON R S. Electrodeposition of silicon at temperatures above its melting point [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1981, 128: 1712-1714.
[14] NOHIRA T, YASUDA K, ITO Y. Pinpoint and bulk electrochemical reduction of insulating silicon dioxide to silicon [J]. Nature Materials, 2003, 2: 397-401.
[15] JIN Xian-bo, GAO Pei, WANG Di-hua, CHEN G Z. Electrochemical preparation of silicon and its alloys from solid oxides in molten calcium chloride [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2004, 43: 733-736.
[16] PISTORIUS P C, FRAY D J. Formation of silicon by electrodeoxidation, and implications for titanium metal production [J]. Journal of the South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2006, 106: 31-41.
[17] ERGUL E, KARAKAYA I, ERDOGAN M. Electrochemical decomposition of SiO2 pellets to form silicon in molten salts [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: 899-903.
[18] CHEN G Z, FRAY D J, FARTHING T W. Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium dioxide to titanium in molten calcium chloride [J]. Nature, 2000, 407: 361-364.
[19] KONGSTEIN O E, WOLLAN C, SULTANA S, HAARBERG G M. Electrorefining of silicon in molten calcium chloride [J]. ECS Transactions, 2007, 3: 357-361.
熔盐电解精炼提纯金属硅
蔡 靖1,罗学涛1,卢成浩1,Geir Martin HAARBERG2,Annabelle LAURENT2,Ole Edvard KONGSTEIN3,王淑兰4
1. 厦门大学 材料科学与工程系,厦门 361005;
2. Department of Materials Technology, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim NO-7491, Norway;
3. SINTEF, Trondheim NO-7465, Norway;
4. 东北大学 化学系,沈阳 110004
摘 要:对熔盐电解质中硅的沉积过程进行电化学研究。在973~223 K,在硅-氯化物熔盐中采用电解精炼提纯金属硅。结果表明,液态硅铜合金阳极有利于CaCl2-NaCl-CaO-Si熔盐体系的电解精炼。ICP-AES分析结果显示,通过电解精炼可有效去除原料中大量的钛、铝、铁等金属杂质,硅中的硼和磷含量分别由36×10-6和25×10-6降低至4.6×10-6和2.8×10-6,电解能耗约为9.3 kW·h/kg。
关键词:电解精炼;熔盐;硅铜合金;硅;提纯;能耗
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project (2007J0012) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China; Project (019811) supported by Foxy in the 6th Framework Program, European Commission
Corresponding authors: LUO Xue-tao; Tel: +86-592-2184881; E-mail: xuetao@xmu.edu.cn; Geir Martin HAARBERG; Tel: +47-73594036; E-mail: geir.m.haarberg@material.ntnu.no
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61577-X