文章编号:1004-0609(2013)07-1931-06
超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面的生物相容性
许晓静,张体峰,凌智勇,盛新兰,刘 敏,牛小丫,朱利华
(江苏大学 先进制造与现代装备技术工程研究院,镇江 212013)
摘 要:采用电化学抛光工艺对常规TiNi合金和超细晶TiNi合金的表面进行改性,分析经电化学抛光后其表面形貌、耐腐蚀性能、微动摩擦磨损性能和生物活性。结果表明:与常规TiNi合金电化学抛光表面相比,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面具有更多的小尺寸(纳米尺度)蚀坑、更优的抗模拟体液电化学腐蚀性能(后者的腐蚀速率是前者的1/5)、更小的摩擦因数、更好的耐磨性以及更高的生物活性(后者在模拟体液中Ca-P层的生长速率是前者的2.8倍)。分析认为,以上性能变化是TiNi合金组织超细化使其晶体缺陷增多所致。
关键词:超细晶TiNi合金;电化学抛光;表面形貌;耐腐蚀性能;微动摩擦磨损性能;生物活性
中图分类号:TG 174.4 文献标志码:A
Biocompatibility of electrochemical polished ultrafine-grained TiNi alloy
XU Xiao-jing, ZHANG Ti-feng, LING Zhi-yong, SHENG Xin-lan, LIU Min, NIU Xiao-ya, ZHU Li-hua
(Engineering Institute of Advanced Manufacturing and Modern Equipment Technology, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China)
Abstract: The surfaces of conventional and ultrafine-grained TiNi alloys were modified by the electrochemical polishing process. The surface morphology, corrosion resistance, fretting friction and wear properties and bioactivity of electrochemical polished surface on conventional TiNi alloy and ultrafine-grained TiNi alloy were investigated. The results show that, compared with the electrochemical polished surface of conventional TiNi alloy, the electrochemical polished surface of ultrafine-grained TiNi alloy has more nano-scale corrosion pits, better corrosion resistance (the corrosion rate of the latter is 1/5 of that of the former) in the Kokubo simulated body fluid, lower friction coefficient, better wear resistance and higher bioactivity (the growth rate of Ca-P layer immersed in simulated body fluid is 2.8 times of that of the former). It is believed that the improvements mentioned above are caused by the increase of crystal defects due to the microstructure ultrafinement.
Key words: ultrafine-grained TiNi alloy; electrochemical polishing; surface morphology; corrosion resistance; fretting friction and wear properties; bioactivity
TiNi合金以其形状记忆效应、超弹性、良好的生物相容性、耐磨性及耐腐蚀性而在临床和医疗器械等方面得到了广泛关注,已被广泛用于牙科和骨科矫形等领域[1]。与现有TiNi合金相比,采用大塑性变形法制备的超细晶TiNi合金具有更高的超弹性、更低的弹性模量等性能,是一种很有应用前景的生物医用金属材料[2]。
近年来,纳米尺度形貌备受关注,大量的研究证明,纳米尺度形貌能有效地提高生物医用材料的生物活性[3-6]。电化学抛光是生物医用金属材料常用的表面处理方法[7-9]。生物医用TiNi合金组织超细化,由于晶界等晶体缺陷显著增多,导致易被腐蚀点增多,因此可以通过电化学抛光获得更高密度纳米尺度形貌。
本文作者研究TiNi合金组织超细化对其电化学抛光表面的形貌、耐腐蚀性能、摩擦磨损性能和生物活性的影响,以期为生物医用金属材料的发展提供科学依据。
1 实验
所用TiNi合金为市购常规TiNi合金和经过大塑性变形制取的超细晶TiNi合金。超细晶TiNi合金的TEM像如图1所示。合金经砂纸打磨、抛光后用丙酮进行超声波清洗。抛光前,采用17%(质量分数)稀硫酸溶液对合金进行活化处理3~5 min。电化学抛光电解液由浓磷酸(ρ=1.68 g/mL)、浓硫酸(ρ=1.84 g/mL)和纯化水按照一定的比例混合制得,电解溶液温度为80~90 ℃,直流电压为10~12 V,频率为800 Hz,处理时间为60 s。
图1 超细晶TiNi合金的TEM像
Fig. 1 TEM image of ultrafine-grained TiNi alloy
采用带有X射线能谱仪(EDS)的JEOL JSM-7001F型场发射扫描电子显微镜 (SEM)观察经电化学抛光表面及在模拟体液中浸泡21 d后合金表面的形貌和成分。采用WYKO-NT1100表面形貌三维测量仪测量经电化学抛光后合金表面的粗糙度,测量速度为100 μm/s,视场范围为0.8~4.8 mm,垂直分辨率为10 nm(Ra)。采用D/max-2500PC型X射线衍射仪 (日本理学公司生产)进行物相分析,扫描速度为7 (°)/min,步宽为0.01°,Cu靶,管电流为200 mA,扫描范围为10°~90°。采用电化学动态极化测试分析合金在室温Kokubo人体模拟体液中的电化学腐蚀特性。采用MGW-01型高频往复微动摩擦磨损试验机测试经电化学抛光后合金表面的摩擦磨损性能,摩擦对偶件采用直径为4 mm的Si3N4球,载荷为1 N,时间为10 min,频率为20 Hz,位移幅值为0.4~0.5 mm,室温Kokubo模拟体液。生物活性采用体外模拟体液(Simulated body fluid,SBF)诱导Ca-P涂层生长(单位面积质量增加量)来表征。按照Kokubo提出的SBF方案配制模拟体液。Kokubo人体模拟体液(1 L)的成分为7.996 g NaCl、0.35 g NaHCO3、0.224 g KCl、0.278 g K2HPO4·3H2O、0.228 g MgCl2·6H2O、0.278 g CaCl2、0.071 g Na2SO4和6.057 g (CH2OH)3CNH2,其余为 H2O(用HCl调节 pH至 7.4 (36.5 °C))[10]。
2 实验结果
2.1 表面形貌与化学成分
图2所示为经电化学抛光后TiNi合金表面的SEM像及其EDS能谱。从SEM像可以看出,与常规TiNi合金电化学抛光表面相比,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面具有更多纳米尺度的蚀坑。从EDS能谱可以看出,电化学抛光都未引入其他元素至合金表面。表1所列为电化学抛光合金表面的粗糙度。由表1可以看出,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面的表面粗糙度相对较小。
2.2 耐腐蚀性能
图3所示为电化学抛光合金在室温Kokubo模拟体液中的动电位极化曲线。表2所列为其自腐蚀电位(φo)、腐蚀电流密度(Jo)、腐蚀速率(R)。由表2可以看出,相比之下,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面的腐蚀电流密度和腐蚀速率大幅降低(后者是前者的1/5),说明超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面的抗腐蚀性能大幅提高。
以上实验结果说明,大变形材料组织超细化后其抗腐蚀性能提高,这一结论已被证实[11],本实验中超细晶TiNi合金的抗腐蚀性提高,这一方面是因为材料活性增加,促进抗腐蚀被动膜的形成,增加腐蚀阻力;另一方面是因为材料晶界面积增加,晶界上的杂质偏聚程度减轻,晶界与晶内的电位差减小。
2.3 摩擦磨损性能
图4所示为电化学抛光试样表面摩擦因数随磨损时间变化。由图4可以看出,与常规TiNi合金电化学抛光表面相比,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面具有较小的摩擦因数,其平均值分别约为0.113 9和0.098 2。
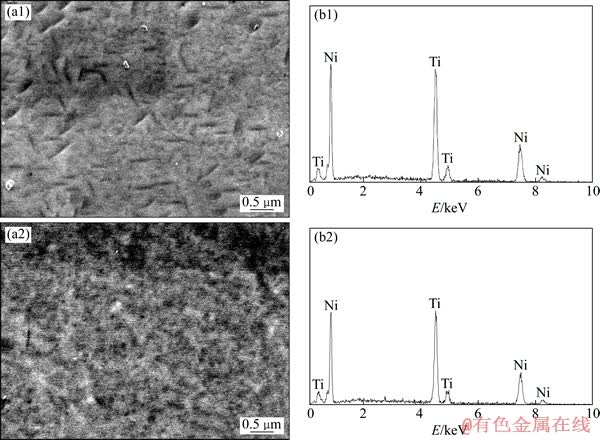
图2 电化学抛光合金表面的SEM像和EDS能谱
Fig. 2 SEM images ((a1), (a2)) and EDS spectra ((b1), (b2)) of electrochemical polished surfaces on conventional TiNi alloy ((a1), (b1)) and ultrafine-grained TiNi alloy ((a2), (b2))
表1 电化学抛光合金表面的粗糙度
Table 1 Surface roughness of alloys after electrochemical polishing
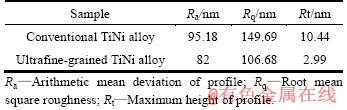
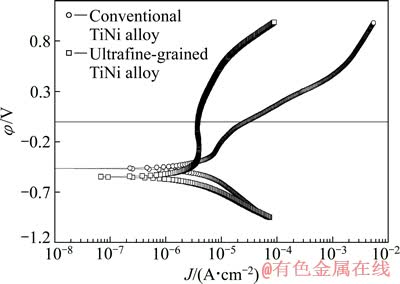
图3 电化学抛光试样在室温Kokubo模拟体液中的动电位极化曲线
Fig. 3 Potentiodynamic polarization curves of electro- chemical polished samples in Kokubo simulated body fluid at room temperature
表2 电化学抛光试样在室温Kokubo模拟体液中的动电位参数
Table 2 Potentiodynamic parameters of electrochemical polished samples in simulated body fluid at room temperature
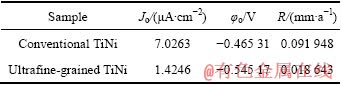
图5所示为电化学抛光试样表面磨痕的SEM像及其EDS能谱。从低倍形貌可以看出,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面的磨损宽度明显较窄,说明其耐磨性能较优。从EDS能谱可以看出,超细晶TiNi合金磨损表面含有模拟体液的元素(Si、P)亦较少。从高倍形貌可以看出,超细晶TiNi合金磨损表面较为平坦,腐蚀坑较少,这与前述电化学腐蚀性能测试结果是一致的。
以上实验结果说明,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面具有较小的摩擦因数和较优的耐磨性能,一方面是因为材料组织超细化后其硬度提高;另一方面是因为电化学抛光表面具有更多纳米尺度蚀坑,有助于驻存模拟体液,起到润滑作用,降低粘着磨损倾向。此外,耐磨性能的提高还可能与材料的抗腐蚀性能提高有关。
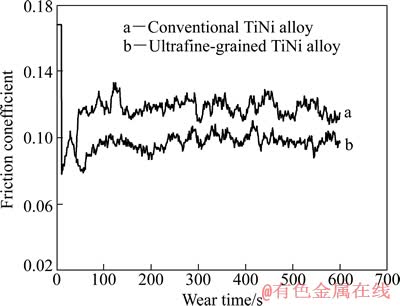
图4 电化学抛光试样表面摩擦因数随磨损时间的变化
Fig. 4 Variation of friction coefficient on surface of electrochemical polished samples with wear time
2.4 体外生物活性
图6所示为试样电化学抛光表面在模拟体液中浸泡21 d后表面的SEM像及其EDS能谱。由图6可以看出,Ca-P层都表现为典型的层状结构生长[12-15],完整地覆盖基体,Ca与P的摩尔比分别为1.46和1.53。表3所列为Ca-P层的生长速率。可以看出,超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面Ca-P层的生长速率大幅提高(后者是前者的2.8倍),说明TiNi合金的组织超细化大幅提高了其电化学抛光表面的生物活性。
图7所示为电化学抛光试样表面在模拟体液中浸泡21 d后Ca-P层的XRD谱。由图7可以看出,XRD谱中除了来自基体的TiNi衍射峰外,其余的衍射峰都为磷灰石(Apatite)的衍射峰,说明Ca-P层的相组成主要为磷灰石。
以上实验结果说明,TiNi合金大应变变形组织超细化显著提高了其电化学抛光表面的抗腐蚀性、摩擦磨损性能和生物活性。TiNi合金超细化使其电化学抛光表面的生物活性提高,一方面是因为材料表面纳米尺度蚀坑增多、表面粗糙度增加,有利于磷灰石的成核与生长[16];另一方面,抗腐蚀性能的提高,也有助于已沉积Ca-P层与基材表面的结合,降低Ca-P层的脱落、回溶倾向。
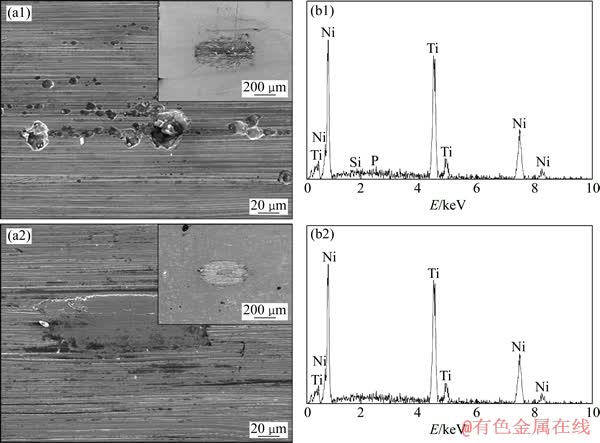
图5 电化学抛光试样摩擦磨损表面磨痕的SEM像和EDS能谱
Fig. 5 SEM images ((a1), (a2)) and EDS spectra ((b1), (b2)) of worn tracks of electrochemical polished surface on conventional TiNi alloy (a1), (b1)) and ultrafine-grained TiNi alloy ((a2), (b2))
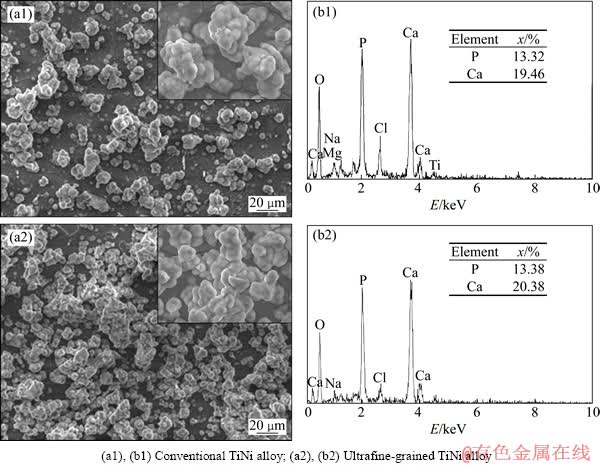
图6 电化学抛光试样在模拟体液中浸泡21 d后表面Ca-P层的SEM像和EDS能谱
Fig. 6 SEM images ((a1), (a2)) and EDS spectra ((b1), (b2)) of Ca-P layer on surface of electrochemical polished samples after immersed in simulated body fluid for 21 d
表3 电化学抛光试样表面Ca-P层的生长速率
Table 3 Growth rate of Ca-P layer on surface of electrochemical polished samples
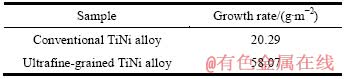
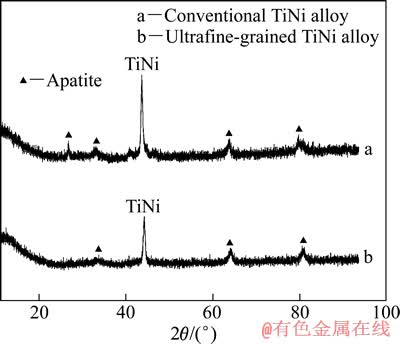
图7 在模拟体液中浸泡21 d后电化学抛光试样表面Ca-P层的XRD谱
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of Ca-P layer on surface of electrochemical polished samples after immersed in simulated body fluid for 21 d
3 结论
1) 超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面比常规TiNi合金电化学抛光表面具有更多纳米尺度的蚀坑、更优的抗模拟体液电化学腐蚀性能(后者的腐蚀速率是前者的1/5)、更小的摩擦因数、更好的耐磨性能(后者的磨痕宽度较前者明显较窄)以及更高的生物活性。
2) 经电化学抛光处理后,常规TiNi合金和超细晶TiNi合金试样在模拟体液中浸泡21 d后,其表面都被Ca-P层完整覆盖,Ca-P层都表现为典型的层状结构生长,其中,Ca与P的摩尔比分别为1.46和1.53,Ca-P层的相组成都主要为磷灰石,表明超细晶TiNi合金电化学抛光表面具有更高的生物活性。
REFERENCES
[1] MACHADO L G, SAVI M A. Medical applications of shape memory alloys[J]. Brazilian Journal of Medical Biological Research, 2003, 36(6): 683-691.
[2] VALIEV R, GUNDERO D, PROKOFIEV E, PUSHIN V, ZHU Y T. Nanostructuring of TiNi alloy by SPD processing for advanced properties[J]. Materials Transactions, 2008, 49(1): 97-101.
[3] PARK J W, KIM Y J, PARK C H, LEE D H, KO Y G, JANG J H, LEE C S. Enhanced osteoblast response to an equal channel angular pressing-processed pure titanium substrate with microrough surface topography[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5(8): 3272-3280.
[4] TRUONG V K, LAPOVOK R, RUNDELL S, WANG J Y, FLUKE C J, CREWFORD R J, IVANOVA E P. The influence of nano-scale surface roughness on bacterial adhesion to ultrafine-grained titanium[J]. Biomaterials, 2010, 31(13): 3674-3683.
[5]  F J L, COOPER L F. Advancing dental implant surface technology—From micron- to nano-topography[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(28): 3822-3835.
F J L, COOPER L F. Advancing dental implant surface technology—From micron- to nano-topography[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(28): 3822-3835.
[6] VENKATSURYA P K C, THEIN-HAN W W, MISRA R D K, SOMANI M C, KARJALAINEN L P. Advancing nanograined/ultrafine-grained structures for metal implant technology: Interplay between grooving of nano/ultrafine grains and cellular response[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2010, 30(7): 1050-1059.
[7] TAJIMA K, HIRONAKA M, CHEN K K, NAGAMATSU Y, KAKIGAWA H, KOZONO Y. Electropolishing of CP titanium and its alloys in an alcoholic solution-based electrolyte[J]. Dental Materials Journal, 2008, 27(2): 258-265.
[8] WU W, LIU X J, HAN H M, YANG D Z, LU S D. Electropolishing of NiTi for improving biocompatibility[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2008, 24(6): 926-930.
[9] CHU C L, WANG R M, HU T, YIN L H, PU Y P, LIN P H,WU S L, CHUNG C W, YEUNG K W K, CHU P K. Surface structure and biomedical properties of chemically polished and electropolished NiTi shape memory alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2008, 28(8): 1430-1434.
[10] KOKUBO T, KUSHITANI H, SAKKA S, YAMAMURO T. Solutions able to reproduce in vivo surface-structure changes in bioactive glass-ceramic A-W[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1990, 24(6): 721-734.
[11] LI P J, KANGASNIEMI I, GROOT K, KOKUBO T. Bonelike hydroxyapatite induction by a gel-derived titania on a titanium substrate[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society , 1994, 77(5): 1307-1312.
[12] SONG D, MA A B, JIANG J H, LIN P H, YANG D H. Corrosion behavior of ultra-fine grained industrial pure Al fabricated by ECAP[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(5): 1065-1070.
[13] MIYAMOTO H, HARADA K, MIMAKI T, VINOGRADOV A, HASHIMOTO S. Corrosion of ultra-fine grained copper fabricated by equal-channel angular pressing[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(5): 1215-1220.
[14] BALYANOV A, KUTNYAKOVA J, AMIRKHANOVA N A, STOLYAROV V V, VALIEV R Z, LIAO X Z, ZHAO Y H, JIANG Y B, XU H F, LOWE T C, ZHU Y T. Corrosion resistance of ultra fine-grained Ti[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51(3): 225-229.
[15] VINOGRADOV A, MIYAMOTO H, MIMAKI T, HASHIMOTO S. Corrosion, stress corrosion cracking and fatigue of ultra-fine grain copper fabricated by severe plastic deformation[J]. Annales de Chimie Science des Matériaux, 2002, 27(3): 65-75.
[16] CHEN X B, LI Y C, HODGSON P D, WEN C. The importance of particle size in porous titanium and nonporous counterparts for surface energy and its impact on apatite formation[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5(6): 2290-2302.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:江苏省高校自然科学基金重大项目(11KJA430004);江苏大学优秀学术青年骨干培养对象基金资助项目(1211110001)
收稿日期:2012-04-23;修订日期:2013-03-22
通信作者:许晓静,教授,博士;电话:0511-88792058;传真:0511-88792058;E-mail:xjxu67@ujs.edu.cn