文章编号:1004-0609(2008)S1-0143-05
过饱和铝酸钠溶液的分解机制
曾纪术,尹周澜,陈启元
(中南大学 化学化工学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:将高过饱和度的铝酸钠溶液进行水解,并将水解产物快速干燥后进行红外(IR)、X射线衍射、27Al魔角旋转-核磁共振(27Al MAS-NMR)研究。实验发现,高过饱和度的铝酸钠溶液在一定条件下迅速水解得到白色固体。IR及XRD谱显示,水解产物的主要成分为α-Al(OH)3,并有少量杂相存在。27Al MAS-NMR分析结果表明,固体中的Al全部为六配位体,杂相中不包含未转化的四面体或其它过渡态中间体。实验结果表明,氢氧化铝结晶过程中,铝酸根离子的分解所伴随的构型转化可能是在溶液中而不是在固相中完成的。
关键词:铝酸根离子;分解机理;构型转化
中图分类号:TF 111.3 文献标识码:A
Decomposition mechanism of supersaturated sodium aluminate solution
ZENG Ji-shu, YIN Zhou-lan, CHEN Qi-yuan
(School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: High supersaturated sodium aluminate solution was hydrolyzed, and the product of hydrolysis was characterized with IR, XRD and 27Al MAS-NMR, respectively. The results show that high supersaturated sodium aluminate solution is rapidly hydrolyzed into a white sedimentation under certain condition. The spectra of IR and XRD indicate that the main component of sedimentation is α-Al(OH)3, accompanied with minor impurity phase. Further investigation of the sedimentation with 27Al MAS-NMR suggests that all Al atoms are hexacoordinated, and no tetracoordinate Al or intermediate is detected. It is proposed that the inversion of aluminate ion is completed in solution instead of solid phase.
Key words: aluminate ion; decomposition mechanism; configuration inversion
中等浓度以上的铝酸钠溶液中铝酸根阴离子存在的主要形态为 ,经过结晶过程以后,得到Al(OH)3晶体。对于氢氧化铝的析出机制,也已经有许多研究结果。无论其转化机制有多复杂,这个过程都可以用一个化学方程式来表示:
,经过结晶过程以后,得到Al(OH)3晶体。对于氢氧化铝的析出机制,也已经有许多研究结果。无论其转化机制有多复杂,这个过程都可以用一个化学方程式来表示:
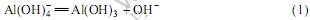
但到目前为止还没有充分的证据表明氢氧化铝的结晶机制是按照上述方程式来进行。相反,ZAMBO[1]的研究表明,反应(1)是一个二级反应,说明了溶液中有其他物种参与这个过程或者离子本身发生了某种变化后生成中间体,再进一步转化为氢氧化铝晶体。陈念贻等[2]提出高浓度铝酸钠溶液中四面体铝酸根离子发生脱水、聚合生成氢氧化铝,但是对于四面体如何转化为八面体却没有解释清楚。也有观点[3]认为四面体铝酸根离子先脱羟基,然后聚合生成氢氧化铝。同样,对于四面体的 如何最终转变为八面体的氢氧化铝晶体也未能清楚阐述。GERSON 等[4]用半经验的量子化学分子模型计算了一系列在铝酸钠溶液 中可能存在的铝酸根形态的生成热后认为,
如何最终转变为八面体的氢氧化铝晶体也未能清楚阐述。GERSON 等[4]用半经验的量子化学分子模型计算了一系列在铝酸钠溶液 中可能存在的铝酸根形态的生成热后认为, 是最稳定的形态,Al(OH)3(H2O)2、Al(OH)3(H2O)、
是最稳定的形态,Al(OH)3(H2O)2、Al(OH)3(H2O)、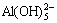 等离子的生成热比较接近,也比较稳定,在溶液中应该少量存在,至于那些带很高负电荷或者空间位阻很大的离子则是很难生成。根据计算结果,提出了如下可能的结晶机制:Al(OH)3(H2O)聚合成[(OH)3Al-(OH)2-Al(OH)3]2-,然后Al(OH)3(H2O)继续与[(OH)3Al-(OH)2-Al(OH)3]2-聚合,内层的Al由四配位变成六配位,而外层的Al继续为四配位。Al(OH)3(H2O)每次叠合都会释放一个水分子,为继续反应提供动力。所有参与这个反应的聚合体都为电中性。在所提出的反应机理中,水起到了催化剂的作用。这似乎和所观察到的实验现象一致。但是对于溶液中的主体离子
等离子的生成热比较接近,也比较稳定,在溶液中应该少量存在,至于那些带很高负电荷或者空间位阻很大的离子则是很难生成。根据计算结果,提出了如下可能的结晶机制:Al(OH)3(H2O)聚合成[(OH)3Al-(OH)2-Al(OH)3]2-,然后Al(OH)3(H2O)继续与[(OH)3Al-(OH)2-Al(OH)3]2-聚合,内层的Al由四配位变成六配位,而外层的Al继续为四配位。Al(OH)3(H2O)每次叠合都会释放一个水分子,为继续反应提供动力。所有参与这个反应的聚合体都为电中性。在所提出的反应机理中,水起到了催化剂的作用。这似乎和所观察到的实验现象一致。但是对于溶液中的主体离子 是如何转化成为Al(OH)3(H2O)却没有说明,且对于Al(OH)3(H2O)又为什么能转化为六配位的构型没有给出依据。也有许多学者[5-8]试图用红外、核磁共振、拉曼、电位滴定等手段在中等浓度以上的铝酸钠溶液中找到氢氧化铝的生长基元。李洁[9]采用拉曼光谱等测试手段,原位跟踪了过饱和铝酸钠溶液结构以及氢氧化铝生长过程中固/液界面溶液结构,认为铝酸钠溶液分解时,固/液界面具有六配位八面体铝酸根离子的结构特征,通过量子化学计算与晶体平衡形貌的计算机模拟,提出了铝酸钠溶液中氢氧化铝生长基元的基本结构和有利生长基元的结构。
是如何转化成为Al(OH)3(H2O)却没有说明,且对于Al(OH)3(H2O)又为什么能转化为六配位的构型没有给出依据。也有许多学者[5-8]试图用红外、核磁共振、拉曼、电位滴定等手段在中等浓度以上的铝酸钠溶液中找到氢氧化铝的生长基元。李洁[9]采用拉曼光谱等测试手段,原位跟踪了过饱和铝酸钠溶液结构以及氢氧化铝生长过程中固/液界面溶液结构,认为铝酸钠溶液分解时,固/液界面具有六配位八面体铝酸根离子的结构特征,通过量子化学计算与晶体平衡形貌的计算机模拟,提出了铝酸钠溶液中氢氧化铝生长基元的基本结构和有利生长基元的结构。
观察四面体结构的 如何向八面体结构的Al(OH)3构型转化是揭示铝酸钠溶液分解机制的关键,而构型转化既可能在溶液中进行,也可能在固/液界面、甚至固体中完成。直接原位观察铝酸钠溶液的结构,往往会因为铝酸钠溶液苛性碱浓度太高、溶液粘度太大而难以得到精确结果,实验事实难于重复甚至容易得出相反的结论。27Al MAS-NMR则可以用来观察固体中Al的微观结构[10]。本文中作者将高过饱和的铝酸钠溶液水解,立刻得到白色沉淀,然后将沉淀物迅速干燥后进行IR、XRD、27Al MAS-NMR等检测,分析白色沉淀的组成并观察其构型,研究铝酸根离子分解过程中可能经历的途径以及判断构型转化发生的场所,为最终完全揭示铝酸钠溶液结晶机制奠定基础。
如何向八面体结构的Al(OH)3构型转化是揭示铝酸钠溶液分解机制的关键,而构型转化既可能在溶液中进行,也可能在固/液界面、甚至固体中完成。直接原位观察铝酸钠溶液的结构,往往会因为铝酸钠溶液苛性碱浓度太高、溶液粘度太大而难以得到精确结果,实验事实难于重复甚至容易得出相反的结论。27Al MAS-NMR则可以用来观察固体中Al的微观结构[10]。本文中作者将高过饱和的铝酸钠溶液水解,立刻得到白色沉淀,然后将沉淀物迅速干燥后进行IR、XRD、27Al MAS-NMR等检测,分析白色沉淀的组成并观察其构型,研究铝酸根离子分解过程中可能经历的途径以及判断构型转化发生的场所,为最终完全揭示铝酸钠溶液结晶机制奠定基础。
1 实验方法
1.1 过饱和铝酸钠溶液的配制
称取40 g分析纯氢氧化钠加入到不锈钢杯中,然后加入200 mL的蒸馏水,加热至氢氧化钠完全溶解。分批将25 g高纯铝片(99.9%,河南鑫威实业发展有限公司)溶解在热的氢氧化钠溶液中。由于反应是一个剧烈的放热过程,溶解过程不需要加热。溶解过程适量补充水,抵消由于反应和蒸发造成的水分损失。反应过程如下:
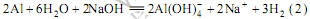
反应约需要1 h才能完全,趁热过滤2次,得到澄清的铝酸钠溶液。用这种方法制备的溶液非常稳 定[11],使用前适当加热浓缩。
1.2 过饱和铝酸钠溶液的水解
将浓缩后的过饱和铝酸钠溶液倾入500 mL蒸馏水中,保持温度恒定,搅拌后静置。当溶液中有少量白色沉淀生成后,立即抽滤,并用无水乙醇将白色固体洗涤几次,然后用电吹风迅速将固体吹干,密封保存。对白色固体分别进行IR、XRD、27Al MAS-NMR等检测。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 水解条件的确定
高纯铝片溶解在氢氧化钠溶液中得到的过饱和铝酸钠溶液非常稳定,故水解条件对固体的析出速率有重要影响。若铝酸根离子或者其缔合离子在析出的固体表面完成构型转化,那么在迅速水解析出并被马上干燥的固体中应该有未发生构型转化的四面体或其它中间态(如五配位体)组分存在,且固体析出速度越快,未发生构型转化的组分含量也越高。实验中,对水解条件进行了优化,尽量加快固体的析出速度。实验中制备的过饱和铝酸钠溶液浓缩后的体积若大于200 mL,则水解后1 h内无固体析出;浓缩后体积小于100 mL,则溶液的粘度过大,流动困难。故将溶液浓缩到150 mL左右,在不同温度下进行水解,水解固体析出速度如表1所示。
表1 水解温度对固体析出速度的影响
Table 1 Effect of temperature on precipitation rate of solid
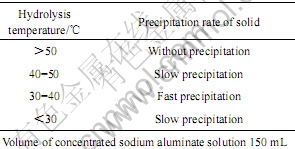
由表1可知,水解的温度过高或过低,都对固体的快速析出不利。本文中作者选择了35 ℃下水解 2 min左右得到的白色固体进行检测。
2.2 IR以及XRD分析
用IR辨别铝的氢氧化物时,一般通过指认羟基的伸缩和弯曲振动产生的谱带,有时也将Al─O振动产生的特征谱带作为辨别的依据之一。但是到目前为止,对α-Al(OH)3,γ-Al(OH)3以及诺三水铝石中Al─O键振动谱带的归属问题还没有一致的结论。这些氢氧化物中羟基伸缩振动和弯曲振动所产生的峰却可以作为识别它们的晶相的依据,谱带的范围分别在 3 700~ 3 000 cm-1和1 200~800 cm-1之间。水解得到的固体样品立即检测及陈化2 d后的IR光谱如图1所示。由图1可知,将水解后得到的白色固体立即检测和陈化2 d后检测得到的红外光谱图基本一致。所得光谱与文献[12]中α-Al(OH)3(拜耳体)的谱基本相同。980 cm-1和1 010 cm-1是α-Al(OH)3羟基伸缩振动产生的峰,3 420 cm-1、3470 cm-1和3 660 cm-1则是羟基弯曲振动所产生的峰。
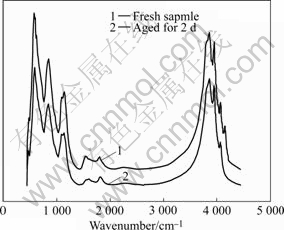
图1 水解产物的IR谱
Fig.1 IR spectra of hydrolysis product
从红外光谱基本可以初步认为,快速水解析出的氢氧化铝的晶相与铝酸钠溶液在较低温度下缓慢分解得到的产物一样,都是α-Al(OH)3。只是由于Al─O键振动谱带无法精确指认,所以要确定Al的配位数还需要其它分析手段。
水解得到的固体样品以及α-Al(OH)3的标准XRD谱如图2所示。由图2可知,白色固体基本上是由α-Al(OH)3(拜耳体)组成的,这与红外光谱得到的结果相吻合。结合样品的IR和XRD谱基本可以断定:高过饱和的铝酸钠溶液迅速水解得到的产物主要成分为α-Al(OH)3,而不是无定形体、假勃姆石[13]或其它过渡态中间体;只要溶液的过饱和度足够高,晶相的转变非常快[14]。
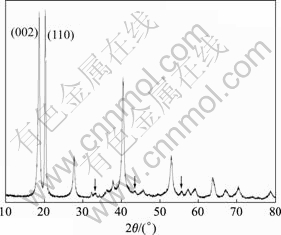
图2 水解产物的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD spectra of hydrolysis product
此外,由图2还可以看出,晶体中仍然有少量杂相存在(如图中箭头标记),通过与标准XRD谱比较,发现不是γ-Al(OH)3,是否为未完全转变的中间态还需要其他手段表征。
2.3 27Al MAS-NMR分析
水解快速沉淀所得固体27Al MAS-NMR如图3所示。位移约为9.3 δ左右有一主峰,另在80 δ附近、-70 δ附近有两个对称的侧峰。
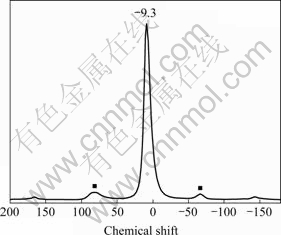
图3 水解产物的27Al MAS-NMR谱
Fig.3 27Al MAS-NMR spectrum of hydrolysis product
由文献[15]可知,以0.1 mol/L的Al(NO3)3溶液作为参比,六配位Al的固体27Al MAS-NMR的理论化学位移为0,四配位体的位移约为80 δ,五配位体的化学位移则在(20-30) δ之间。因此,可以推测位移约为9.3 δ的是八面体α-Al(OH)3所产生的峰,XRD检测到的杂质中并不存在五配位体的过渡态物质,因为(20-30) δ之间没有峰出现。化学位移为80 δ以及-70 δ峰的归属问题需要进一步讨论。
非整数四极核27Al(I=5/2)完整的哈密尔顿函数可表示为
H=HZ+HQ+HD+HCS (3)
式中 HZ、HQ、HD、HCS分别为塞曼、四极、偶极、化学位移的相互作用。快速魔角旋转技术测试时旋转频率足够快,使得HD和HCS相互抵消为零,而观察到的共振频率仍然受到HQ的干扰。在高场下,如果系统只受到一阶四极的干扰,则主峰位移未受影响,但魔角旋转会在主峰两边产生侧峰;但若四极干扰扩展至二阶,则峰会进一步变宽,且主峰和侧峰会发生等方向平移[16]。故对称的80 δ以及-70 δ左右出现的峰可能为受到HQ干扰产生的侧峰。固体中并无四面体的Al存在。
综合以上实验结果可知,高过饱和度的铝酸钠溶液快速水解析出固体的主要成分是α-Al(OH)3,其中少量的杂相中不包含未转化的四面体或其它过渡态中间体。因而可以认为,在本研究的实验条件下,氢氧化铝结晶过程中,铝酸根离子的分解伴随的构型转化是在溶液中完成的,与李洁[9]在固/液界面观察到了六配位的铝酸根离子存在的结果一致。且溶液的过饱和度越高,构型转化越快,结晶速度也越快。下一步的研究目标是借助于快速冷冻、干燥以及魔角旋转-核磁共振技术,直接观察溶液中铝酸根离子是否发生构型转化,相关的深入研究正在进行中。
3 结论
1) 将高过饱和度的铝酸钠溶液在适当条件下水解,迅速析出白色固体。
2) IR和XRD检测结果显示,固体的主要成分是α-Al(OH)3,但其中仍然有少量杂相存在。
3) 27Al MAS-NMR检测的结果显示,固体中的Al全部为六配位体,杂相中不包含未转化的四面体或其它过渡态中间体。
4) 氢氧化铝结晶过程中,铝酸根离子分解伴随的构型转化是在溶液中完成的,溶液的过饱和度越高,构型转化越快,结晶速度也越快。
REFERENCES
[1] ZAMBO J. Structure of sodium aluminate liquors; Molecular model of the mechanism of their decomposition[J]. Light Metals, 1986, 2: 199-215.
[2] CHEN N Y, LIU M X. Studies on the anionic species of sodium aluminate solutions[J]. Science in China, Series B, 1993, 36(1): 32-36.
[3] 杨重愚. 氧化铝生产工艺学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1993: 43.
YANG Zhong-yu. Production technology of alumina[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1993: 43.
[4] GERSON A R, RALSTION J, SMART R S C. An investigation of the mechanism of gibbsite nucleation using molecular modelling[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1996, 110: 105-117.
[5] SIPOS P, SCHIBECI M, PEINTLER G, MAYA P M, HEFTERA G. Chemical speciation in concentrated alkaline aluminate solutions in sodium, potassium and caesium media: Interpretation of the unusual variations of the observed hydroxide activity[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2006, 15(6): 1858–1866.
[6] SIPOS P, MAY P M, HEFTERA G. Quantitative determination of an aluminate dimer in concentrated alkaline aluminate solutions by Raman spectroscopy[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2006(2), 368–375.
[7] CHEN Yun, FENG Qi-ming, LIU Kun, CHEN Yuan-dao, ZHAN Guo-fan. Study on the structure of Bayer liquor with spectroscopy and MD simulation[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2006, 422: 406-411.
[8] MA Shu-hua, ZHENG Shi-li, XU Hong-bin, ZHANG Yi. Spectra of sodium aluminate solutions[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2007, 17(4): 853-857.
[9] 李 洁. 过饱和铝酸钠溶液结构及分解机理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2002.
LI Jie. Study on the structural characteristic and decomposition mechanism of supersaturated sodium aluminate solution[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2002.
[10] ALEMANY L B, KIRKER G W. First observation of 5-coordinate aluminum by MAS 27AlNMR in well- characterized solids[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1986, 108(20): 6158-6162.
[11] HARRIS D R, KEIR R I, PRESTIDGE C A, THOMAS J C. A dynamic light scattering investigation of nucleation and growth in supersaturated alkaline sodium aluminate solutions (synthetic Bayer liquors)[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1999, 154: 343-352.
[12] WOLSKA E, SZAJDA W.Use of infrared spectroscopy to identify crystalline aluminum hydroxides of the Al(OH)3- Fe(OH)3 system[J]. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 1983, 38(1): 137-140.
[13] LI Hui-xin, ADDAI-MENSAHA J, THOMAS J C, GERSON A R. The crystallization mechanism of Al(OH)3 from sodium aluminate solutions[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 279: 508-520.
[14] ANTUNES M L P, SANTOS H S, SANTOS P S. Characterization of the aluminum hydroxide microcrystals formed in some alcohol-water solutions[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2002, 76: 243-249.
[15] BRADLEY S M, HANNA J V. 27Al and 23Na MAS NMR and powder X-ray diffraction studies of sodium aluminate speciation and the mechanistics of aluminum hydroxide precipitation upon acid hydrolysis[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1994, 116: 7771-7783
[16] CRUICKSHANK M C, GLASSER L S D, BARRI S A 1, POPLETT I J F. Penta-co-ordinated aluminium: A solid-state 27AI N.M. R. study[J]. J Chem Soc Chem Commun, 1986, 23 23-24.
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2005CB623702)
通讯作者:尹周澜,教授,博士;电话:0731-8877364;E-mail: xhli@mail.csu.edu.cn
(编辑 杨 兵)