Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1930-1935
Effects of cooling rate on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of Mg-Zn-Ca alloy
Jing-feng WANG1,2, Song HUANG1,2, Sheng-feng GUO3, Yi-yun WEI1,2, Fu-sheng PAN1
1. National Engineering Research Center for Magnesium Alloys, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China;
2. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
Received 26 March 2012; accepted 30 May 2013
Abstract: Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloys with diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm were fabricated using copper mold injection casting method. Microstructural analysis reveals that the alloy with a diameter of 1.5 mm is almost completely composed of amorphous phase. However, with the cooling rate decline, a little α-Mg and MgZn dendrites can be found in the amorphous matrix. Based on the microstructural and tensile results, the ductile dendrites are conceived to be highly responsible for the enhanced compressive strain from 1.3% to 3.1% by increasing the sample diameter from 1.5 mm to 3 mm. In addition, the Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy with 1.5 mm diameter has the best corrosion properties. The current Mg-based alloys show much better corrosion resistance than the traditionally commercial wrought magnesium alloy ZK60 in simulated sea-water.
Key words: Mg-Zn-Ca alloy; bulk metallic glasses; cooling rate; mechanical properties; microstructure; corrosion resistance
1 Introduction
Compared with the traditional magnesium alloys, Mg-based amorphous alloys are very attractive in many applications due to their ultra-high strength and good corrosion resistance [1]. Recently, various Mg-based bulk metallic glasses (BMGs), such as Mg-(Cu,Ni)-Y and Mg-Cu-Gd, have been discovered with a great deal of efforts [2-4]. Unfortunately, these alloys can not be widely used in engineering applications for their high cost (high pure elements and large amount of rare elements) and brittle failure without noticeable plastic strain at room temperature (less than 1%) [5].
In recent years, great efforts have been devoted to the Mg-Zn-Ca metallic glass due to the relatively low density and good bio-corrosion, which can be served as potential biomaterials in future [6-9]. LI et al [10] found that the best composition range defined both by strength and plastic deformation should be 3%-5% (mole fraction) Ca for Mg72-xZn28Cax (x=0-6). GU et al [9] studied the feasibility as biodegradable metallic materials of Mg66Zn30Ca4 and Mg70Zn25Ca5 and conducted that they had better bio-compatiblity than pure Mg. However, like many other amorphous alloys, these Mg-Zn-Ca alloys possess extremely brittleness at room temperature and need to be prepared by high purity raw materials under strictly environmental conditions. From the viewpoint of applications, it is worthwhile to develop large sized Mg-based alloys with low cost and good corrosion resistances.
In the present work, the influence of cooling conditions on the structure evolution, mechanical properties and corrosion resistances of low-cost Mg-Zn-Ca alloy prepared by industrial raw materials is investigated by controlling the sample size. The underlying mechanism of the improved plasticity achieved in the larger sized Mg-Zn-Ca alloy is discussed in terms of microstructure observation.
2 Experimental
A master alloy with the composition of Mg69Zn27Ca4 (mole fraction, %) was prepared with induction furnace using industrial pure Mg (99.9%, mass fraction), Zn (99.9%) and Mg-30Ca alloy (30% Ca) under the protection of high-purity argon atmosphere. Then it was remelted several times to ensure that the alloy composition was more homogeneous. Sample rods with a length of 50 mm and diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm were produced by copper mold injection casting.
The structure of as-cast alloys was identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku D/MAX-2500PC) using Cu Kα radiation. The thermal stabilities related to crystallization and melting events of the alloys were investigated with a differential scanning calorimeter (PE, DSC-7) at a heating rate of 20 K/min. The compressive specimens with a length-to-diameter ratio of 2:1 were cut using a low speed diamond saw with water cooling, and then compressive tests were performed on a SANS CMT5105 testing machine at a strain rate of 10-4 s-1. Each composition was tested for at least five samples at room-temperature. The morphology of fractured surface was examined with a scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TESCAN VEGA ΙΙ LMU). The corrosion behavior was investigated using an electrochemical workstation (CHI660C, China) in simulated sea water (3.5% NaCl) at room temperature. A three-electrode cell was used for electrochemical measurements. The potentiodynamic polarization tests were carried out at a scanning rate of 5 mV/s and each sample was tested at least three times.
3 Results
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of as-cast Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloys with different diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm, hereafter named Alloy Ι, Alloy ΙΙ and Alloy ΙΙΙ, respectively. It can be observed that Alloy Ι is fully amorphized except for a typical broad halo diffraction peak, confirming the absence of crystalline phase at the sensitivity of XRD. However, with the increased diameter of 2 mm, some crystalline peaks appear on the broad diffraction hump, implying that the Mg-Zn- Ca alloy mainly forms an amorphous phase (d1.5 mm) and turns to be made up by crystalline structure mostly (d3 mm) with the cooling rate reduced. The main Bragg peaks for Alloy ΙΙ are indexed as α-Mg, Ca2Mg6Zn3, Mg7Zn3 and MgZn2 phases, whereas Alloy ΙΙΙ consists of α-Mg, Ca2Mg6Zn3, Mg7Zn3 and MgZn phases.
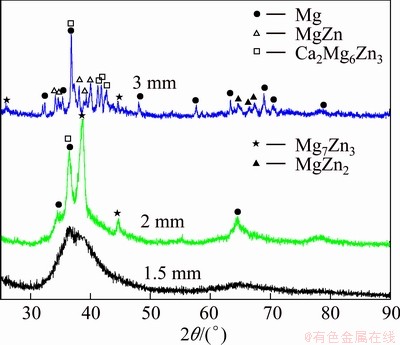
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy with 1.5, 2 and 3 mm diameters
Figure 2 displays the DSC curves of these three alloys revealing the crystallization behaviors (Fig. 2(a)) and melting reaction (Fig. 2(b)) above mentioned. The Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy with a diameter of 1.5 mm shows a clear exothermic crystallization phenomenon similar to Alloy ΙΙ and Alloy ΙΙΙ. However, the onset crystallization temperature Tx rises gradually as well as the heat of crystallization (ΔHx) decreases monotonously as Alloy ΙΙ and Alloy ΙΙΙ. In addition, the high temperature melting of the alloys exhibits two melting peaks as shown in Fig. 2(b). The thermal parameters including Tx, ΔHx, melting temperature Tm and liquid temperature Tl are summarized in Table 1.

Fig. 2 DSC curves of as-cast Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy rods with diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm
Table 1 Key property parameters of as-cast Mg69Zn27Ca4 with diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm
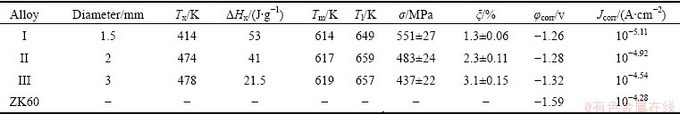
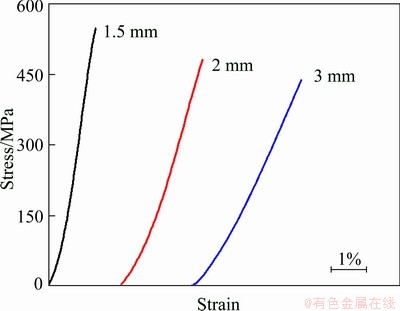
Fig. 3 Engineering stress—strain curves of Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy rods with diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm under room- temperature compression
Figure 3 shows the uniaxial compressive strain—stress curves of as-cast Mg-Zn-Ca alloy with different diameter sizes. The curves have been shifted apart from each other so as to avoid overlapping for a clearer observation. It is clearly seen that all these three alloys exhibit elastic behavior only, failing without any macroscopic yielding and plastic strain. The compressive fracture strength of this novel Mg69Zn27Ca4 BMG is considerable to that of most Mg-Zn-Ca BMGs reported [10]. More interestingly, with increasing the sample diameter from 1.5 mm to 3 mm, the compressive strain increases obviously from 1.3% to 3.1%. The possible reason of such unusual phenomenon will be discussed in details in the discussion section.
Figure 4 displays the fractographs of the failed compressive specimens, which are examined with SEM to clarify the fracture mechanism. The monolithic glass sample, akin to other brittle BMGs, exhibits a lot of fragments after failure as shown in Fig. 4(a), which is called “fragmentation mode” [11]. By careful observation of these fragments, numerous vein-like patterns are formed to arrange in long narrow ridges (Fig. 4(b)) due to local adiabatic heating caused by the rapid propagation of shear bands [12-14]. As the cooling rate decreases, Alloy ΙΙ possesses a visible shear banding deformation fashion as shown in Fig. 4(c), indicating that the deformation is localized into shear bands. With a higher magnification of the sample (Fig. 4(d)), the fracture surface reveals robust plastic flow patterns, which is usually observed in some other ductile BMGs [14]. Furthermore, some cracks on the fracture surface of Alloy ΙΙ (by the arrow) do not shatter the specimen, which means this alloy is relatively tough [7]. Alloy ΙΙΙ also exhibits the large-fragments after failure with two kinds of fracture morphologies. One is formed by dendrites splitting into several parts as shown in Fig. 4(e) and another is the rough vein-like patterns as shown in Fig. 4(f), which are probably caused by the amorphous phase softening due to the adiabatic heating [15].
Figure 5 shows the polarization curves of the Mg-Zn-Ca alloy with different diameters in simulated sea water along with traditional commercial wrought magnesium alloy ZK60 for comparison. It can be observed that these three Mg-Zn-Ca alloys exhibit a higher polarization potential (φcorr) and lower polarization current density (Jcorr) than traditional ZK60 alloy. After polarization, both Alloys I and II have the plateau, which is limited by the breakdown potential, corresponding to the rupture of the protective film on the sample surface [16]. However, the ZK60 alloy shows no noticeable passive region, implying a rapid pitting corrosion action [17]. The main parameters of the corrosion resistance about these alloys are also summarized in Table 1.
4 Discussion
In this work, the microstructure of as-cast Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy is obviously changed by controlling the cooling rate via increasing the sample size during solidification. Faster cooling rate leads to a fully amorphous structure at 1.5 mm scale. A slow cooling rate is able to alter the as-cast alloy from amorphous phase into an in-situ composite structure. In order to illustrate the effect of cooling rate on the structure evolution, these three alloys are further examined by SEM/EDS. From the SEM backscattered electron images shown in Fig. 6, the differences between Alloys Ι, ΙΙ and ΙΙΙ can be obviously observed. No distinct crystalline contrast is seen over the entire cross-section of Alloy Ι in the SEM image (Fig. 6(a)). While for Alloy ΙΙ, a spot of white dendritic phases is labeled on the gray amorphous matrix (Fig. 6(b)). For Alloy ΙΙΙ, the volume fraction of the dendritic phase increases in a large extent (Fig. 6(c)).
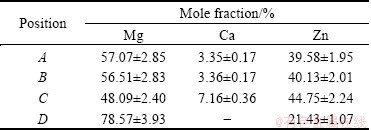
It has been well known that in-situ formed ductile phase reinforced BMGs usually have higher compressive plasticity than the monolithic BMGs [5,12,18]. While under compressive load, the slip systems existing in the dendrites or the ductile phase are activated and readily accommodate the strain and consequently lead to the enhancement of compressive plasticity [19,20]. Table 2 summarizes the EDS results of the dendritic phases as shown in Fig. 7, which indicates that the main phases of Alloys ΙΙ (Fig. 7(a)) and ΙΙΙ (Fig. 7(b)) are Mg7Zn3 and α-Mg respectively (consist well with the XRD results). Unfortunately, the Mg7Zn3 is a kind of brittleness phase which will predominantly pose a threat to the mechanical properties of the amorphous/ crystalline phase interface. Alloy ΙΙΙ exhibits much better compressive strain than Alloy ΙΙ because the main phases are ductile α-Mg dendrites. The Mg-Zn-Ca alloy (3 mm in diameter) with good mechanical properties (compressive strength of 440 MPa, fracture strain of 3.1%) has been achieved by controlling the microstructure evolution. These findings will pave the way for the further mechanical improvement of the Mg-Zn-Ca BMG at large size and their feasibility for the applications.
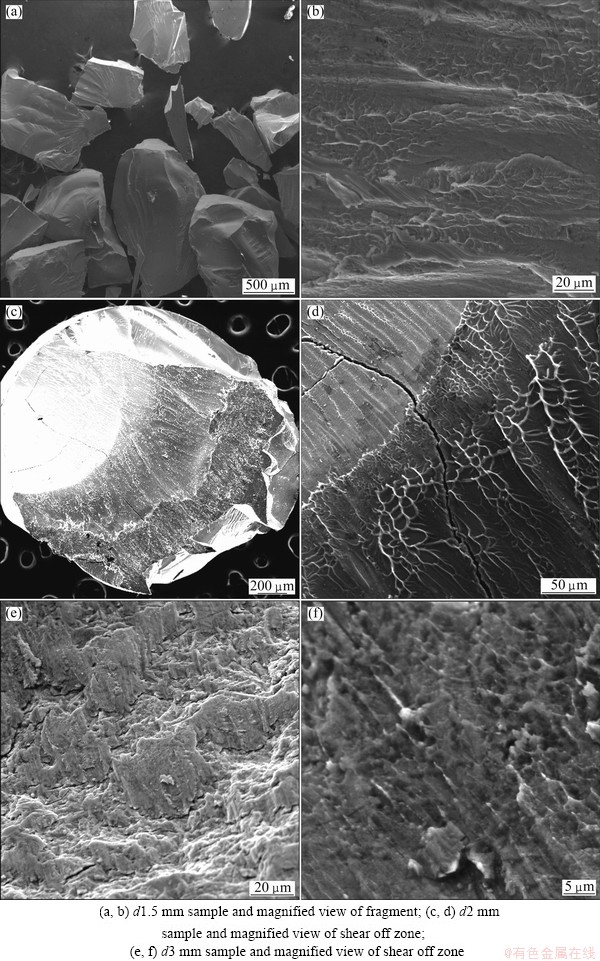
Fig. 4 Morphologies of fractured surface of Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy
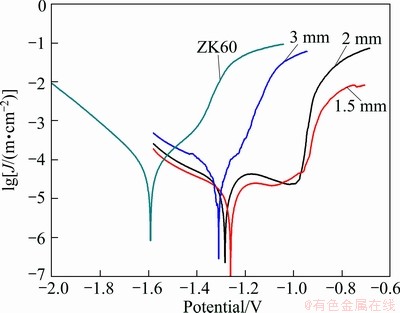
Fig. 5 Potentiodynamic polarization curves of ZK60 and Mg69Zn27Ca4 samples with different diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm in 3.5% NaCl solution
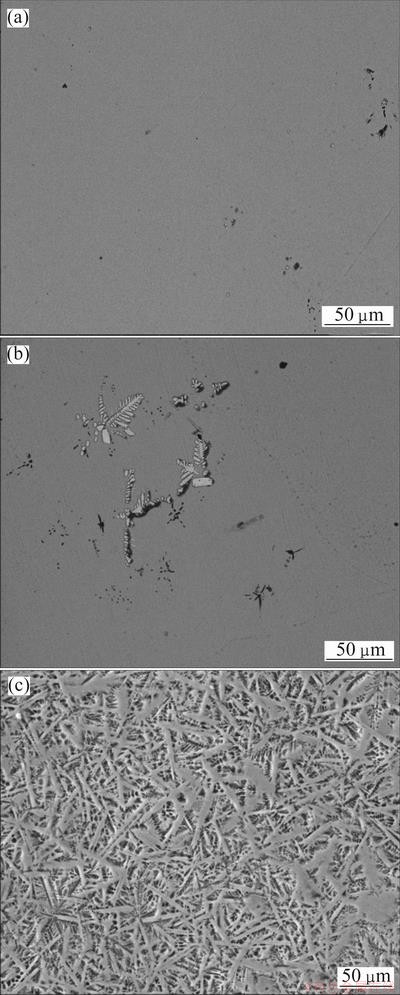

Fig. 6 SEM backscattered electron images of Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy with 1.5 mm (a), 2 mm (b) and 3 mm(c) diameters
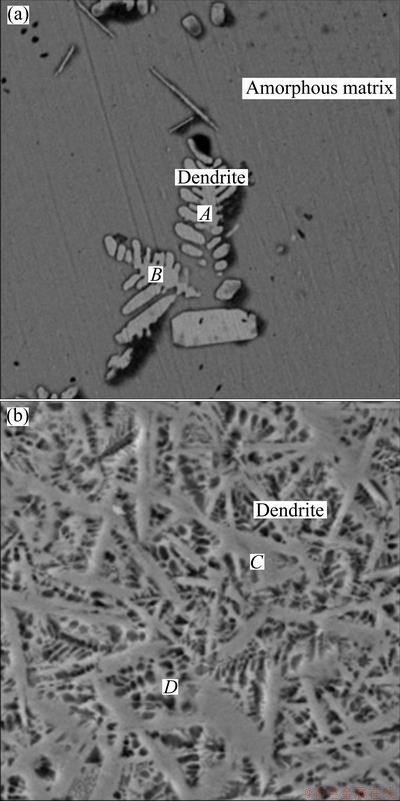
Fig. 7 SEM/EDS images of Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy rod with 2 mm (a) and 3 mm (b) in diameter
Table 2 EDS results of as-cast Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy with 2 and 3 mm in diameter
For corrosion behavior, it can be seen that Alloy Ι shows clearly the best properties. It can be attributed to the chemical homogeneity, or the homogeneous structure, which has no galvanic corrosion in the amorphous matrix [9]. In addition, Alloys ΙΙ and ΙΙΙ show the similar φcorr and Jcorr with Alloy Ι, implying the formation of the dendrites does not have much effect on the corrosion properties.
5 Conclusions
1) Low-cost Mg69Zn27Ca4 alloy with diameters of 1.5, 2 and 3 mm were synthesized by copper mold injection casting method using industrial raw materials. The single glassy phase was obtained in the alloy rod with 1.5 mm diameter.
2) As the cooling rate decreases, the glass forming ability decreases dramatically as the brittle MgZn and ductile α-Mg dendrite phases precipitate. Furthermore, these Mg-Zn-Ca have good mechanical properties.
3) The Mg-Zn-Ca alloy studied in this work exhibits much higher corrosion potential and lower corrosion current density than the traditional wrought magnesium alloy ZK60 in simulated sea water, which can open up an innovative opportunity for the development of Mg-based alloy with potential applications.
References
[1] HUANG J C, CHU J P, JANG J S C. Recent progress in metallic glasses in Taiwan [J]. Intermetallics, 2009, 17(12): 973-987.
[2] INOUE A, KATO A, ZHANG T. Mg-Cu-Y amorphous alloys with high mechanical strengths produced by a metallic mold casting method [J]. Mater Trans JIM, 1991, 32: 609-616.
[3] CHEN H M, ZHONG H M, XIA P, OU Y, Y I F. Composition range of amorphous Mg-Ni-Y alloys [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2003; 21(5): 567-570.
[4] WANG Y C, WANG Y R, WEI B C. Kinetics of glass transition and crystallization in carbon nanotube reinforced Mg-Cu-Gd bulk metallic glass [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2006, 24: 327-331.
[5] HUI X, DONG W, CHEN G L, YAO K F. Formation, microstructure and properties of long-period order structure reinforced Mg-based bulk metallic glass composites [J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55: 907-920.
[6] ZHAO Y Y, MA E, XU J. Reliability of compressive fracture strength of Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glasses: Flaw sensitivity and Weibull statistics [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 58: 496-499.
[7] WU X F, SI Y, SUO Z Y, KANG Y. Synthesis and mechanical behavior of ternary Mg-Cu-Dy in situ bulk metallic glass matrix composite [J]. J Mater Sci, 2009, 44: 6035-6039.
[8] GAO J H, GUAN S K, REN Z W, SUN Y F, ZHU S J, WANG B. Homogeneous corrosion of high pressure torsion treated Mg-Zn-Ca alloy in simulated body fluid [J]. Materials Letters, 2011, 65: 691-693.
[9] GU X N, ZHENG Y F, ZHONG S P, XI T F, WANG J Q, WANG W H. Corrosion of, and cellular responses to Mg-Zn-Ca bulk metallic glasses [J]. Biomaterials, 2010, 31: 1093-1103.
[10] LI Q F, WENG H R, SUO Z Y, REN Y L, YUAN X G, QIU K Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of bulk Mg-Zn-Ca amorphous alloys and amorphous matrix composites [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 487: 301-308.
[11] ZHAO X J, QU R T, WANG F F, ZHANG Z F, SHEN B L, STOICA M, ECKERT J. Fracture mechanism of some brittle metallic glasses [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 105: 103519.
[12] XU Y K, MA H, XU J, MA E. Mg-based bulk metallic glass composites with plasticity and gigapascal strength [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 1857-1866.
[13] PAN D G, LIU W Y, ZHANG H F, WANG A M, HU Z Q. Mg–Cu–Ag–Gd–Ni bulk metallic glass with high mechanical strength [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 438: 142-144.
[14] LIU C T, HEATHERLY L, EASTON D S. Test environments and mechanical properties of Zr-base bulk amorphous alloys [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 1998, 29(7): 1811-1820.
[15] ARGON A S. Plastic deformation in metallic glasses [J]. Acta Materialia, 1979, 27: 47-58.
[16] LIU N, WANG J L, WANG L D, WU Y M, WANG L M. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of Mg-5Al-0.4Mn-xNd in NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51: 1328-1333.
[17] SONG G L, ATRENS A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 1999, 1: 11-33.
[18] JASON S C J, JIAN S R, LI T H, HUANG J C, LIU C T. Structural and mechanical characterizations of ductile Fe particles-reinforced Mg-based bulk metallic glass composites [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 485: 290-294.
[19] ZHANG Z F, HE G, ECKERT J, SCHULTZ L. Fracture mechanisms in bulk metallic glassy materials [J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 91(4): 045504.
[20] HAYS C C, KIM C P, JOHNSON W L. Microstructure controlled shear band pattern formation and enhanced plasticity of bulk metallic glasses containing in situ formed ductile phase dendrite dispersion [J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 84(14): 2901.
冷却速率对Mg-Zn-Ca合金显微组织、力学性能及腐蚀性能的影响
王敬丰1, 2,黄 崧1,2,郭胜锋3,魏怡芸1,2,潘复生1
1. 重庆大学 国家镁合金工程中心,重庆 400044;2. 重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆 400044;
3. 西南大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆 400715
摘 要:采用铜模喷铸法制备直径为1.5、2和3 mm的Mg69Zn27Ca4合金。采用X射线衍射(XRD)、力学性能实验及电化学实验研究冷却速率对合金的显微组织、力学性能及腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明:当直径为1.5 mm时,合金为完全非晶态;随着冷却速率的下降,合金中出现韧性的α-Mg和Mg-Zn相,使得3 mm直径样品的压缩应变量达到3.1%,优于1.5 mm非晶合金的1.3%。此外,制备的Mg-Zn-Ca合金在模拟海水中的抗腐蚀性能远好于传统的ZK60镁合金。
关键词:Mg-Zn-Ca合金;块体非晶;冷却速率;力学性能;显微组织;腐蚀性能
(Edited by Chao WANG)
Foundation item: Project (NCET-11-0554) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University; Project (2011BAE22B04) supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China; Project (51271206) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Jing-feng WANG; Tel: +86-23-65112153; Fax: +86-23-65112153; E-mail: jfwang@cqu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62679-5