文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0633-06
功率对电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸高铌钛铝合金温度场的影响
陈瑞润1,杜志强1,2,董书琳1,丁宏升1,苏彦庆1,郭景杰1,傅恒志1
(1. 哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 天津航天长征火箭制造有限公司,天津 410083)
摘 要:利用实验测量和数值模拟方法研究电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸高铌钛铝合金的温度场,利用Ansys软件建立温度场的计算模型。结果表明:冷坩埚内的感应加热由集肤层开始,向炉料内部和底部传热,经过一段时间后达到热传递平衡,温度不再升高;随着加热功率的增加,高铌钛铝熔体稳态温度和最高温度都升高,50 kW时,具有一定的过热度,在0.7 mm/min抽拉速度和50 kW条件下可成功实现冷坩埚连续熔铸高铌钛铝合金锭。
关键词:高铌钛铝合金;电磁冷坩埚;温度场;连续熔铸;数值模拟
中图分类号:TF 804.3 文献标志码:A
Effect of power on temperature field in electromagnetic cold crucible continuous melting and solidifying of high Nb containing TiAl alloys
CHEN Rui-run1, DU Zhi-qiang1,2, DONG Shu-lin1, DING Hong-sheng1, SU Yan-qing1, GUO Jing-jie1, FU Heng-zhi1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
2. Tianjin Spaceflight Changzheng Missile Manufacture Limited Company, Tianjin 410083, China)
Abstract: The temperature field in electromagnetic cold crucible continuous melting and solidifying of high Nb containing TiAl alloys was researched by experimental and numerical simulation methods, the calculation model was established with Ansys software. The results show that, the induction heating originates from the skin layer of the ingot in the cold crucible, and then transfers to the inner and lower parts, thermal equilibrium will be reached after some time, and the temperature will not increase further. Both the steady temperature and highest temperature of the melt increase with the power increasing, the melt is overheated when the power is 50 kW. The electromagnetic cold crucible continuous melting and solidifying high Nb containing TiAl alloy is achieved successfully under the condition of 50 kW and 0.7 mm/min.
Key words: high Nb containing TiAl alloy; electromagnetic cold crucible; temperature field; continuous casting; numerical simulation
TiAl合金的低塑性缺点至今尚未改善,国内以北京科技大学陈国良院士为首的研究组提出了高铌合金,并对高铌钛铝合金的性能和组织进行了研究,对中国高铌高温合金发展做出了重要贡献[1-3]。高铌钛铝合金有着比普通钛铝合金更高的高温强度、抗氧化性能和抗蠕变性能,高熔点Nb的加入使其熔点比普通钛铝合金的高60~100 ℃,也导致其更难熔炼,目前的熔炼方法包括感应熔炼、真空自耗重熔、等离子熔炼等。针对高铌钛铝合金的高熔点、高活性特点,本课题组提出冷坩埚连续熔铸高铌钛铝合金,即用具有自主知识产权的电磁冷坩埚设备,对高铌钛铝合金进行熔化和组织控制,本技术是将电磁冷坩埚的优点与连续铸造和定向凝固相结合,期待制备出具有良好组织和性能的高铌钛铝合金锭。
在电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸过程中,温度场决定温度梯度的大小以及固液界面的形状和位置。固液界面前沿的温度梯度大小直接影响了晶体生长的速率和晶体的质量,凝固界面前沿的溶质和热流的传动方向,决定了凝固组织是否由胞状晶向树枝晶转变。电磁连续熔铸过程中许多现象都是温度的函数。因此,电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸过程中温度场对提高工艺可控性、防止铸件缺陷、改善熔体质量、提高材料性能等方面有着十分重要的意义[4-8]。本文作者利用实验和数值模拟的方法研究功率对电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸高铌钛铝合金温度场的影响,从而为电磁冷坩埚技术和感应熔炼提供帮助和指导。
1 实验方法与计算模型
1.1 连续熔铸用电磁冷坩埚
电磁冷坩埚用方形铜块机械铣削,后用线切割开缝,最后是将通水孔焊接连通,电磁冷坩埚如图1所示。冷坩埚必须考虑拔模斜度,内部尺寸为27 mm×27 mm,底部为30 mm×30 mm,高度为110 mm。坩埚外绕以感应线圈,感应线圈与高频交变电源相连,在坩埚内产生高频磁场,可以熔化坩埚内高铌钛铝合金并对其产生电磁压力,从而可以进行熔铸。
1.2 温度场的测量方法与测量位置
采用K型热电偶和XJY-16通路巡检仪进行测温,测温系统示意图如图2所示。由于测温系统在真空密闭的环境下进行,炉体内外部通过炉壁上的铜接线柱连接,外部由补偿导线连接,巡检仪的数据通过数据线传输到PC,内部由5根热电偶直接插入试样内部的测量,在某功率下,温度不再升高,达到稳态,然后卸载掉功率,巡检仪停止记录数据。
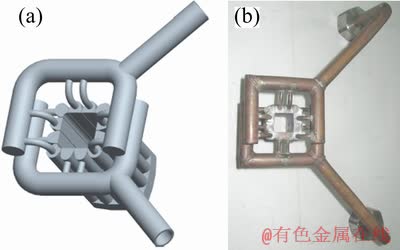
图1 电磁冷坩埚模拟图及实物照片
Fig.1 3D drawing (a) and photo (b) of electromagnetic cold crucible
1.3 温度场数学模型
在本模拟中,采用ANSYS计算温度场,使用耦合场中的顺序耦合方法,首先计算电磁连续铸造过程中电磁场,然后将电磁场计算完成的热生成率(HGEN)作为载荷加载在温度场模型中进行计算[9]。
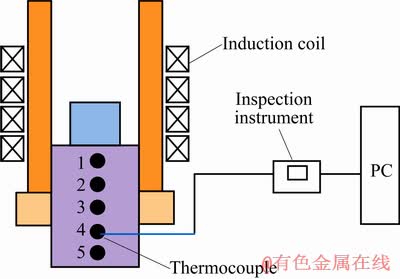
图2 温度测量系统的示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of temperature measuring system
在电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸过程中热量传递方式主要是以热传导和辐射为主并且低功率和高功率下传递对象还有变化。ANSYS中计算温度场正是以这3种导热方式为基础。在电磁连续铸造过程中,坩埚内的温度、热流率、内能以及边界条件都随时间有很大变化,为瞬态热分析,这样,根据能量守恒定律,瞬态热平衡可以表示为
 (1)
(1)
式中:K为传导系数矩阵,包括各种系数如热系数、辐射和形状系数等;C为比热矩阵,为温度对时间的导数;T为节点温度向量;Q包括热生成(HGEN)。为节点热流率向量[10],热生成在电磁连续熔铸过程中即为焦耳热生成率。
1.4 前处理与网格剖分
由于在实验过程中,低功率时,高铌钛铝不能熔化,而高功率时,高铌钛铝可以熔化,因此,在模拟时也分为低功率和高功率两部分,低功率下数值模拟所加载功率与测温的功率相同,因此,温度场需要建造两种不同的模型,对应两种不同的功率条件,一种为有上料棒,同时加载功率为高功率,另一种为无上料棒,加载功率为低功率,所用模型及其网格划分如图3所示。
温度场模拟中所用材料物性参数如下:经测定Ti44Al6Nb0.5B合金的密度为ρ=4 148 kg/m3;黑度为0.64;表面传热系数为3600W/(m2·K)[11]。由于高功率下存在液相与坩埚的接触热传导导热,根据文献[9],确定侧向导热系数为λ′=0.14λ。
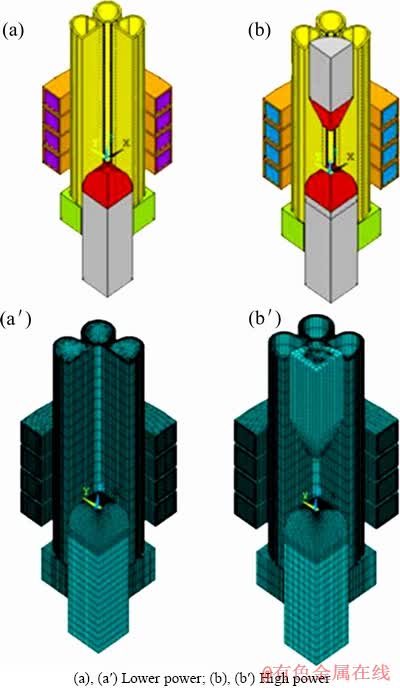
图3 模型及网格剖分
Fig.3 Models (a, b) and grid generation (a′), (b′) of low and high power
2 结果与讨论
2.1 实验测量与数值模拟温度场
当功率为3 kW时,实验测量和数值计算的温度场如图4所示。由图4可以看出,热量由集肤效应引起,热量由外集肤层向内和向下传递,经过一段时间后,系统处于热平衡状态,即感应热与高铌钛铝合金锭的辐射热、传导热和对流热相平衡,此时温度不再上升。因此,欲熔化高铌钛铝合金,必须施加高功率。
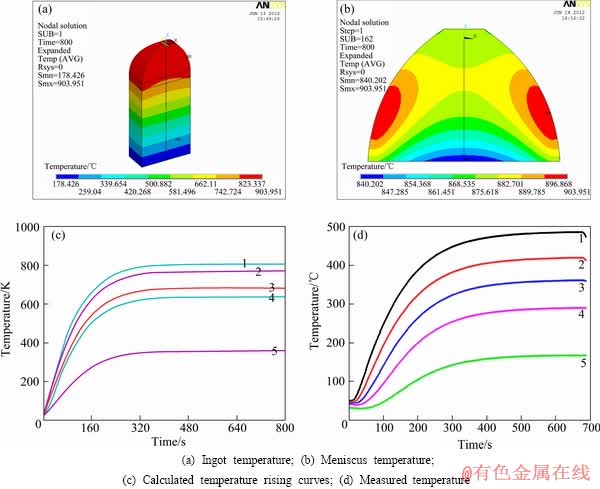
图4 3 kW时温度场和温度升温曲线
Fig.4 Temperature field and temperature rising curves at power of 3 kW (Curves 1-5 correspond to five thermocouple positions shown in Fig. 2)
温度场测量位置是驼峰以下8 mm。从图4可以看出,3 kW时测量点模拟最高温度为800 K,即为523 ℃,与测量值486 ℃相差47 ℃。对达到稳态所用时间比较,模拟所用时间为560 s左右,而测量所用时间为600 s。可以看出,模拟达到稳定状态所用的时间短,并且模拟达到的稳态温度要比测量值要高。这可能是由于测量过程中热电偶并不是与测温试样冶金接触,这样就会造成热电偶与测量试样之间存在热阻,导致测温数值偏低。并且由于数值模拟过程中将钛铝合金的电阻率定为定值,但是实际钛铝合金的电阻率是随温度升高而升高的,在电磁感应加热中,电阻越大,生热率越大,虽然在实际中电阻率的变化幅度不是很大,但是也足以影响结果的精确度,这样在计算过程中数值模拟数值就会与测量值存在偏差,其测量值比数值模拟值要低。整体来看,此模型可以用于预测电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸过程的温度场和规律。
2.2 功率对温度场的影响数值模拟结果
当功率分别为25、40、45和50 kW时,温度场计算结果如图5、6、7和8所示。25kW时,底托引料已经达到熔点,并且出现一定的过热度,但是上料棒并没有达到熔点;而在40 kW时,底托引料和上送料均处于熔化状态;45和50 kW时,底托引料和上送料具有较高的热过度,因此,可以进行不同抽拉速度的连续熔铸。比较不同功率的温度场可看出,随着功率的增加,稳定温度逐步增加,最高温度也逐步增加。
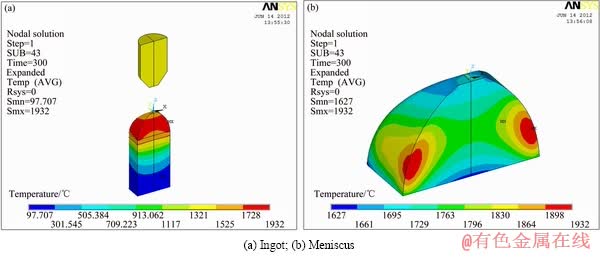
图5 25kW时料棒和熔池温度场
Fig.5 Temperature field at power of 25 kW
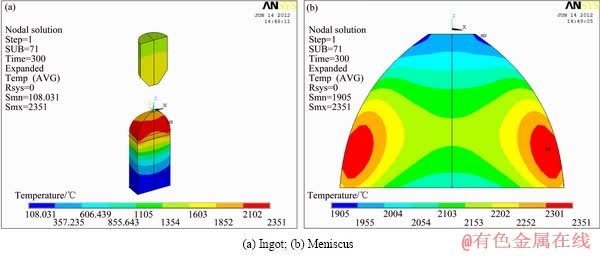
图6 40kW时温度场
Fig.6 Temperature field at power of 40kW
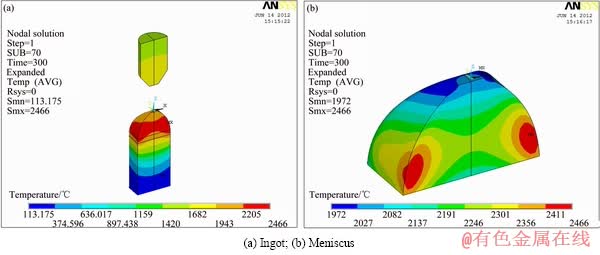
图7 45 kW时温度场
Fig.7 Temperature field at power of 45 kW
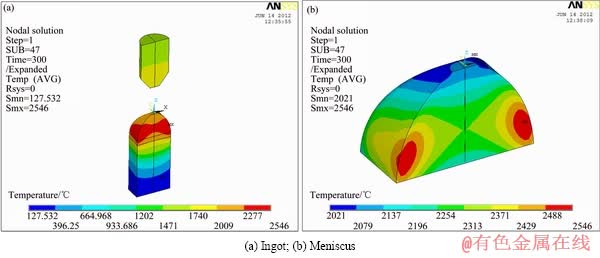
图8 50 kW时温度场
Fig.8 Temperature field at power of 50kW
2.3 电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸实验
根据计算结果,采用50 kW功率和抽拉速度为0.7 mm/min进行连续熔铸实验,实验过程照片和所得高铌钛铝合金锭照片如图9所示,由此可见,采用本工艺可以实现高铌钛铝合金的冷坩埚连续熔铸。
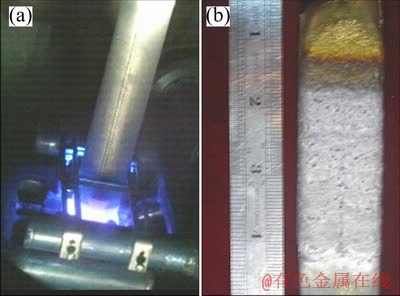
图9 电磁连续熔铸过程和制备的高铌钛铝合金锭照片
Fig.9 Photos showing preparation of ingot by cold crucible continuous casting (a) and experimental ingot (b)
3 结论
1) 电磁冷坩埚连续熔铸时,热量由集肤层产生,并向内和向下传热,经过一段时间后处于热平衡状态,此时温度不再升高;数值计算模型可以用于计算温度场。
2) 数值计算结果表明,25 kW时,坩埚内高铌钛铝合金可以熔化,随功率升高,坩埚内高铌钛铝合金的稳态温度和最高温度都随着上升;50 kW时,熔体具有较高的过热度,可进行连续熔铸。
3) 50 kW和0.7 mm/min时,可成功实现冷坩埚连续熔铸高铌钛铝合金,制出表面质量好的铸锭。
REFERENCES
[1] LIN J P, ZHAO L L, LI G Y, ZHANG L Q, SONG X P, YE F, CHEN G L. Effect of Nb on oxidation behavior of high Nb containing TiAl alloys original research article[J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(2): 131-136.
[2] CHENG Liang, CHANG Hui, TANG Bin, KOU Hong-chao, LI Jin-shan. Deformation and dynamic recrystallization behavior of a high Nb containing TiAl alloy original research article[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2013, 552(5): 363-369.
[3] 孔凡涛, 张树志, 陈玉勇. Ti-46Al-3Cr-4Nb-Y合金的高温变形及加工图[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s233-s236.
KONG Fan-tao, ZHANG Shu-zhi, CHEN Yu-yong. Hot deformation and processing map of Ti-46Al-3Cr-4Nb-Y[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s233-s236.
[4] 尹 权, 黄泽文. 热暴露对Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Hf-1B 合金显微结构和力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(12): 3050-3056.
YIN Quan, HUANG Ze-wen. Effect of long-term thermal exposure on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-44Al-4Nb-4Hf-1B alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(12): 3050-3056.
[5] 陈 光, 傅恒志. 非平衡凝固新型金属材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 141.
CHEN Guang, FU Heng-zhi. Non equilibrium solidification of new metallic materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 141.
[6] 傅恒志, 魏炳波, 郭景杰. 凝固科学技术与材料[J]. 中国工程科学, 2003, 5(8): 1-18.
FU Heng-zhi, WEI Bing-bo, GUO Jing-jie. Solidification science and technology and materials[J]. Engineering Science, 2003, 5(8): 1-18.
[7] FLEMINGS M C. Solidification processing[M]. NewYork: McGray-Hill, 1974: 31-92, 154-176.
[8] 胡汉起. 金属凝固原理[M]. 2版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2000: 168-204.
HU Han-qi. Solidification theory of metal[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2000: 168-204.
[9] CHEN Rui-run, YANG Jie-ren, DING Hong-sheng, HUANG Feng, SU Yan-qing, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of configuration on magnetic field in cold crucible using for continuous melting and directional solidification[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(2): 404-410.
[10] 阎照文. ANSYS10.0工程电磁分析技术与实例详解[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2006.
YAN Zhao-wen. ANSYS10.0 engineering electromagnetic analysis technique and detailed examples[M]. Beijing: China Water Power Press, 2006.
[11] 薛冠霞. 感应凝壳熔炼过程温度场及流场耦合数值模拟[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2007.
XUE Guan-xia. Numerical simulation of thermal and flow fields in induction skull melting process[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2007.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51274076),教育部新世纪优秀人才资助项目(NCET-12-0153)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:陈瑞润,教授, 博士; 电话: 0451-86413931; E-mail: ruirunchen@hit.edu.cn