


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 47-52
Effect of quenching rate on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of 7085 aluminum alloy
CHEN Song-yi, CHEN Kang-hua, PENG Guo-sheng, LIANG Xin, CHEN Xue-hai
State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 4 January 2011; accepted 6 April 2011
Abstract: The influence of quenching rate on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of 7085 aluminum alloy was investigated by tensile test, slow strain rate test (SSRT), combined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and electrochemical test. The results show that with decreasing the quenching rate, the size and inter-particle distance of the grain boundary precipitates as well as precipitation free zone width increase, but the copper content of grain boundary precipitates decreases. The SCC resistance of the samples increases first and then decreases, which is attributed to the copper content, size and distribution of grain boundary precipitates.
Key words: 7085 aluminum alloy; quenching rate; microstructure; stress corrosion cracking
1 Introduction
High strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys are extensively used as aircraft structure materials due to their good strength and toughness, but they are susceptible to stress corrosion cracking(SCC) [1, 2]. From the recent researches [3-5], the main mechanism of SCC was attributed to anodic dissolution and hydrogen embitterment. The development of SCC can be divided into two main stages: crack initiation and crack propagation [6].
Many efforts have been made to improve the SCC resistance through heat treatment. Overaging to T7x temper decreased the susceptibility of SCC but at the expense of 10%-15% strength [7]. Retrogression and reaging (RRA) treatment have been developed to obtain SCC resistance equivalent to that of T73 temper together with T6 strength levels [8]. Recently, OU et al [9] and LIN et al [10] proposed that step-quenching aging (SQA) can was improve the SCC resistance without loss of strength. HUANG et al [11] indicated that SCC resistance of alloys improved without decreasing strength and plasticity through a high temperature pre-precipitation (HTPP) process. These previous results showed that the major microstructural features about SCC resistance were associated with grain boundary precipitates (GBPs). The SCC resistance could be improved by increasing both the size and space distance of the GBPs [12].
Quenching rate has great influences on microstructure and properties of super high strength aluminum alloy. It was reported that quenching rate changed the size and distribution of the GBPs, and influenced strength, fracture toughness and aging response [13-18]. Unfortunately, there is no enough information about the correlation between quenching rate and SCC of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, especially for 7085 aluminum alloy, which have been developed by ALCOA since 2003. The purpose of this work is to study the effect of quenching rate on the microstructure and SCC of 7085 aluminum alloy.
2 Experimental
7085 aluminum casting was used as the raw material with the nominal chemical composition (mass fraction, %) of Al-7.5Zn-1.6Mg-1.5Cu-0.13Zr. Cast ingots were homogenized at 450 ℃ for 24 h plus 470 ℃ for 38 h. Three-directional forging was performed at 420 ℃ with a strain of about 0.7 at each step, a total strain of about 3.5, followed by air-cooling. All the specimens for the investigation were sampled at the center of the forging piece in order to ensure a maximum homogeneity of composition and grain structure.
Specimens were solution treated at 470 ℃ for 1 h in a air circulating furnace. In order to acquire different quenching rates, specimens were quenched by three different procedures after solution treatment: cold water quenching (Fast quenching rate 150 ℃/s), oil quenching (Intermediate quenching rate 50 ℃/s), quenching in air (Slow quenching rate 1 ℃/s) [18]. Subsequently, the specimens were immediately subjected to artificial aging at 120 ℃ for 24 h.
Tensile specimens with longitudinal direction for each heat treatment conditions were used to measure mechanical properties on an Instron3369 testing machine at room temperature. The specimens of slow strain rate testing (SSRT) were tested at a strain rate of 6.67×10-6 s-1 in air and in 3% NaCl + 0.5% H2O2 solution. The susceptibility to SCC was evaluated by the elongation loss (LE). The expression is defined as follows [19]:
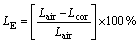
where Lair is the elongation in air; Lcor is the elongation in corrosion solution.
The morphology of the fractured specimens was examined on a scanning electron microscope (JSM-6360LV). Microstructures were studied on a transmission electron microscope (JEOL-2100F) operated at 200 kV. Energy disperse spectroscopy (EDS) attached to TEM was used to determine the composition of grain boundary precipitates. Each datum point was the arithmetic mean of at least 10 measured GBPs obtained at 3 different grain boundaries. Thin foils for TEM were prepared by mechanically polishing to 150 μm and final twin-jet electro polishing in a solution of 25% HNO3+75% CH3OH at -25 ℃.
Open-circuit potential (OCP) measurements were carried out at 25 ℃ in 3.5% NaCl solution (CHI600C). A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) was used as a reference electrode and platinum was used as the counter electrode.
3 Results
The tensile properties of the alloy with different quenching rates are shown in Table 1. It indicates that quenching rate greatly influences the ultimate strength and yield strength. With decreasing the quenching rate, the strength of the samples decreases. Compared with that of the fast quenched (150 ℃/s) specimens, the ultimate and yield strength of intermediate quenched (50 ℃/s) specimens are slightly lower. Whereas the ultimate and yield strength of the slow quenched (1 ℃/s) specimens are obviously decreased. The elongation of the specimens is not significantly changed under three conditions.
Table 1 Tensile properties of AA7085 alloy with different quenching rates

Figure 1 depicts the results of slow strain rate testing in the atmosphere for specimens previously treated at different quenching rates. Tensile strength and elongation are estimated from Fig. 1. It can be seen that when the quenching rate decreases, the tensile strength decreases, which is consistent with the tensile results above. The elongation of the samples decreases in the order of 1 ℃/s>150 ℃/s>50 ℃/s.
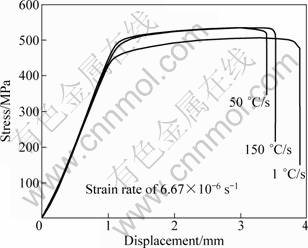
Fig. 1 SSRT results for AA7085 with different quenching rates in air
The slow strain rate testing results for 7085 aluminum alloy at different quenching rates in 3% NaCl + 0.5% H2O2 solution are shown in Fig. 2. The tensile strength decreases in the order: 50 ℃/s>150 ℃/s>1 ℃/s. The elongation decreases in the order: 150 ℃/s>50 ℃/s>1 ℃/s. Comparing the results of Fig. 2 and Fig. 1, it is found that both tensile strength and elongation are lower in the 3 % NaCl + 0.5% H2O2 solution than in the air for the corresponding specimens, indicating that the alloy has SCC susceptibility.
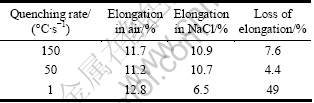
In order to have a better understanding of the relationship between quenching rate and SCC, the loss of elongation (LE) is used to evaluate the SCC resistance of aluminum alloy [13]. The lower the LE, the better the SCC resistance. Table 2 displays that the LE ascends in the order: 50 ℃/s<150 ℃/s<1 ℃/s. In conclusion, the specimens with intermediate quenching rate (50 ℃/s) have a better SCC resistance in a corrosion solution compared with those with slow quenching rate (1 ℃/s) or fast quenching rate (150 ℃/s).
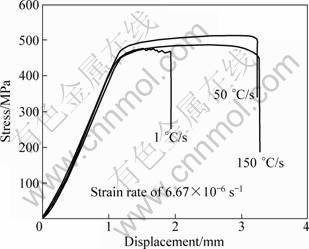
Fig. 2 SSRT results for AA7085 with different quenching rates in 3% NaCl+0.5% H2O2 solution
Table 2 Loss of elongation of samples with different quenching rates
Typical fracture surfaces after SSRT of the specimens in 3% NaCl + 0.5% H2O2 solution are shown in Fig. 3. The fracture surface of fast quenched (150 ℃/s) specimens is dominated by intergranular fracture (Fig. 3(a)). By contrast, the combination of intergranular and trangranular fracture is found in the intermediate quenched (50 ℃/s) specimens (Fig.3 (b)), and some large dimples are also observed on the fracture surface of the specimens. In the slowly quenched (1 ℃/s) specimens, the dimples disappear and the fracture surface is characterized by intergranular fracture (Fig. 3(c)). All fracture surfaces verify the SCC resistance sequence above.
Figure 4 shows TEM bright-field micrographs of the microstructure of alloy quenched at different rates. Compared with the fast quenched sample, the matrix precipitates of the intermediately quenched sample slightly coarsen, and the size and interval of the GBPs are larger (Figs. 4(a)-(b)). For the slowly quenched specimens, the matrix precipitates and GBPs are coarser, and the precipitate free zones (PFZ) become wide (Fig. 4(c)).
The composition of GBPs at different quenching rate is shown in Table 3. It is found that the contents of Mg and Zn are similar for GBPs at different quenching rate. The content of copper for the specimens increases with increasing the quenching rate.
Open-circuit potential (OCP) is another measure to evaluate the electrochemical reactivity of GBPs on a macroscopic scale [20]. It is also indicated that there is a correlation between OCP and the copper content of GBPs. The OCP measurements for the alloys with different quenching rates carried out at 25 ℃ in 3.5% NaCl solution are shown in Fig. 5. The fast quenched specimen shows a slightly more positive potential (-0.764 V, vs SCE) than the intermediately quenched specimens (-0.775 V, vs SCE), whereas the alloy with slow quenching rate has the most negative average OCP (-0.811 V, vs SCE). The results further confirm that the copper content decreases with decreasing the quenching rate. They are also consistent with the results of EDS.
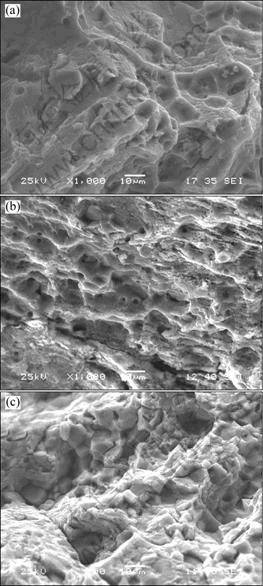
Fig. 3 SEM fractographs of SSRT samples failed in 3% NaCl + 0.5% H2O2 solution: (a) Fast quenching (150 ℃/s); (b) Intermediate quenching (50 ℃/s); (c) Slow quenching (1 ℃/s)
Table 3 EDS results of GBPs composition at different quenching rates
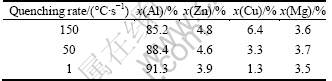

Fig. 4 TEM microstructures of alloys with different quenching conditions: (a) Fast quenching (150 ℃/s); (b) Intermediate quenching (50 ℃/s); (c) Slow quenching (1 ℃/s)
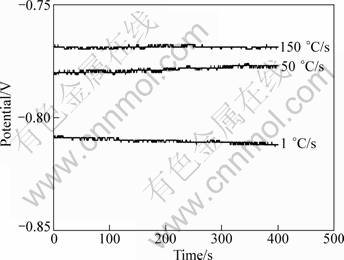
Fig. 5 Open-circuit potential measurements for alloys with different quenching rates
4 Discussion
The AA7085 alloys with three quenching rates investigated in this study have show different microstructures. The size and interspaces of the GBPs by the fast quenching are larger than those of intermediate quenching; the slowly quenched specimens exhibit coarser precipitates and wider PFZ (Fig. 4). These effects can be mainly attributed to heterogeneous precipitation occurring on the grain boundaries and the loss of solute from solid solution. With decreasing the quenching rate, the copper content of grain boundary precipitates decreases. According to the results of STARKE [21], Cr- and Mn-rich dispersoids can eliminate most of copper at a slow quenching rate. Thus, it may be inferred that Al3Zr dispersoids may act as nucleating agent to deplete most of copper from solid solution, allowing little copper to participate in the precipitate process. This explanation needs to be further researched.
As can be seen from Table 1, with decreasing the quenching rate, the strength of the specimens decreases. This can be explained as the formation of incoherent-type precipitates and loss of vacancies, leading to less efficient age-hardening [22]. As can be seen from Table 2, intermediately quenched (50 ℃/s) specimens show the best SCC resistance, attributing to relative high content of copper on the GBPs and large GBPs size (about 50 nm) as well as wide GBPs spacing, which decreases the anodic dissolution rate and reduces the concentration of hydrogen at the crack tip. Moreover, the coalescence of cracks is retarded due to larger individual segment of crack. Therefore, the initiation and propagation rate of crack can be effectively decreased. The fast quenched (150 ℃/s) specimens show relatively worse SCC resistance compared with the intermediately quenched specimens. The higher content of copper on the GBPs may decrease the electrochemical activity and increase the crack initiation resistance [23]. The smaller size and continuous distribution of GBPs have an adverse effect on the SCC resistance. The GBP with size of about 20 nm (see Fig. 5(a)) can take no advantage to act as trapping sites of atomic hydrogen to nucleate hydrogen bubbles, leading to hydrogen embitterment occurs according to the results by CHRISTODOULOU and FLOWER [24]. On the other hand, the continuous GBPs accelerate the rate of crack propagation. By the combination of two aspects, fast quenched specimens exhibit relatively bad SCC resistance. The slowly quenched (1 ℃/s) specimens have the worst SCC resistance. The reason is attributed to the low content of copper on the GBPs, resulting in higher anodic dissolution reaction and cathode reaction generation of hydrogen at crack-tips, promoting the corrosion crack initiation and propagation.
5 Conclusions
1) With decreasing the quenching rate, the strength of 7085 alloy samples decreased because of the formation of incoherent-type precipitates and loss of vacancies, leading to less efficient age-hardening. With decreasing the quenching rate, the size and inter-particle distance of grain boundary precipitates increase, and the copper content of GPBs decreases. Thus, the SCC resistance of the samples increases first and then decreases.
2) The intermediate quenching rate (50 ℃/s) improves the SCC resistance with the retention of strength, which is attributed to the relative high copper content and large interspace of grain boundary precipitation.
References
[1] HEINZ A, HASZLERA, KEIDEL C. Recent development in aluminum alloys for aerospace applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 280(3): 102-107.
[2] POULOSE P K,MOREAL J E, MCEVILY A J. Stress corrosion crack velocity and grain boundary precipitates in an Al-Zn-Mg alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1974, 5(6): 1393-1400.
[3] VISWANADHAM R K, SUN T S, GREEN J A S. Grain boundary segregation in Al-Zn-Mg alloys—Implications to stress corrosion cracking [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1980, 11(1): 85-89.
[4] PICHENS J R, LANGAN T J. The effect of solution heat-treatment on grain boundary segregation and stress-corrosion cracking of Al-Zn-Mg alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1987, 18(10): 1735-1744.
[5] SONG R G, DIETZEL W, ZHANG B J. Stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(16): 4727-4743.
[6] NAJJAR D, MAGNIN T, WARNER T J. Influence of critical surface defects and localized competition between anodic dissolution and hydrogen effects during stress corrosion cracking of a 7050 aluminum alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 238(2): 293-302.
[7] OLIVEIRA A F Jr, De BARROS M C, CARDOSO K R, TRAVESSA D N. The effect of RRA on the strength and SCC resistance on AA7050 and AA7150 aluminum alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 379(1-2): 321-326.
[8] TALIANKER M, CINA B. Retrogression and reaging and the role of dislocations in the stress corrosion of 7000-type aluminum alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions Transactions A, 1989, 20(10): 2087-2093.
[9] OU B L, YANG J G, WEI M Y. Effect of homogenization and aging treatment on mechanical properties and stress-corrosion cracking of 7050 alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38(10): 1760-1773.
[10] LIN J C, LIAO H L, JEHNG W D, CHANG C H, LEE S L. Effect of heat treatment on the tensile strength and SCC-resistance of AA7050 in an alkaline saline solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(10): 3139-3156.
[11] HUANG L P, CHEN K H, LI S, SONG M. Influence of high-temperature pre-precipitation on local corrosion behaviors of Al-Zn-Mg alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56(4): 305-308.
[12] WANG D, NI D R, MA Z Y. Effect of pre-strain and two-step aging on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of 7050 alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 494(1-2): 360-366.
[13] LIU Sheng-dan, ZHANG Yong, LIU Wen-jun, DENG Yun-lai, ZHANG Xin-ming. Effect of step-quenching on microstructure of aluminum alloy 7055 [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(1): 1-6.
[14] HE Yong-dong, ZHANG Xin-ming, YOU Jiang-hai, YE Ling-ying, LIU Wen-hui. Effect of precipitate free zone quench-induced on fracture behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(3): 392-399. (in Chinese)
[15] DESCHAMPS A, TEXIER G, RINGECAL S, DELFAUT-DURUT L. Influence of cooling rate on the precipitation microstructure in a medium strength Al-Zn-Mg alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 501(1): 133-139.
[16] ROBINSON J S, TANNER D A. Residual stress development and relief in high strength aluminum alloys using standard and retrogression thermal treatments [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2003, 19(4): 512-518.
[17] XIAO Dai-hong, CHEN Song-yi, CHEN Kang-hua. Effect of quenching technique on properties of forged aluminum alloy AA7150 with minor Sc [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(2): 226-232. (in Chinese)
[18] DORWARD R C, BEERNTSEN J. Grain structure and quench-rate effect on strength and toughness of AA7050 AI-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy plate [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1995, 26(1): 2481-2484.
[19] LIAO H L, LIN J C, LEE S L. Effect of pre-immersion on the SCC of heat-treated AA7050 in an alkaline 3.5%NaCl [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(2): 209-216.
[20] KNIGHT S P, BIRBILIS N, MUDDLE B C, TRUEMAN A R, LYNCH S P. Correlations between intergranular stress corrosion cracking, grain-boundary microchemistry, and grain-boundary electrochemistry for Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(12): 4073-4080.
[21] STARKE E A Jr. Aluminium alloys of the 70’s: Scientific solutions to engineering problems. An invited review [J].Materials Science and Engineering, 1977, 29(2): 99-115.
[22] DUMONT D, DESCHAMPS A, BRECHET Y. On the relationship between microstructure, strength and toughness in AA7050 aluminum alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 356(1-2): 326-336.
[23] RAMGOPAL T, GOUMAP I, FRANKEL G S. Role of grain-boundary precipitates and solute-depleted zone on the intergranular corrosion of aluminum alloy 7150 [J]. Corrosion, 2002, 58(8): 687-697.
[24] CHRISTODOULOU L, FLOWER H M. Hydrogen embrittlement and Trapping in Al-
6%Zn-3%Mg [J]. Acta Materialia, 1980, 28(4): 481-487.
淬火速度对7085铝合金显微组织和应力腐蚀的影响
陈送义,陈康华,彭国胜,梁 信,陈学海
中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:采用力学性能测试、慢应变速率拉伸实验,结合扫描电镜和透射电镜及电化学测试等方法,研究淬火速度对7085铝合金组织和应力腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明,随着淬火速度的降低,合金晶界析出相的尺寸和间距增大,晶界析出相的Cu含量降低;合金的抗应力腐蚀性能随着淬火速度的减少先增强后减弱。晶界析出相的尺寸和分布以及Cu含量是影响合金抗应力腐蚀性能的主要因素。
关键词:7085铝合金;淬火速度;显微组织;应力腐蚀开裂
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Projects (2010CB731701, 2012CB619502) supported by National Basic Research Program of China; Project (51021063) supported by the Creative Research Group of National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: CHEN Kang-hua; Tel: +86-731-88830714; Fax: +86-731-88710855; E-mail: khchen@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61138-2