东营凹陷北带古冲沟古近系多物源沉积模式
张立强1,杨晚2
(1. 中国石油大学 地球科学学院,北京,102249;
2. Department of Geological Sciences & Engineering,Missouri University of Science and Technology, Rolla, Missouri 65409, USA)
摘 要:
构、碎屑组分以及聚类分析等方法,提出东营凹陷北部陡坡带东部Y920古冲沟沙河街组沙四上亚段多物源叠加模式。研究结果表明:沙四上亚段沉积时期,Y920冲沟呈西陡东缓的不对称箕状构造形态。地震相呈东西分带的特点,冲沟西部发育楔形反射、东部发育前积反射、中部发育透镜状反射。冲沟内砂岩充填物的碎屑矿物组成在平面上具有明显的差异性,冲沟西部砂岩的石英含量低、岩屑含量高,岩屑以火成岩岩屑为主;冲沟东部,砂岩的长石和岩屑含量均较高,岩屑以变质岩岩屑为主;中部长石和石英含量较高,岩屑含量较低,含有较多的灰岩岩屑。Y920古冲沟存在3个方向的物源,分别为自北向南、沿冲沟长轴方向的北部物源以及来自冲沟西部和东部的短轴、侧向物源。冲沟西部发育近岸水下扇沉积,东部扇体以扇三角洲为主。
关键词:
中图分类号:TE122.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)08-3159-07
Multi-provenance depositional model of paleo gully in north steep slope of Dongying depression of upper Es4 in Paleogene
ZHANG li-qiang1, YANG Wan2
(1. College of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China;
2. Department of Geological Sciences & Engineering,Missouri University of Science and Technology, Rolla, Missouri 65409, USA)
Abstract: Based on seismic reflections, detrital composition analysis and cluster analysis, a multi-provenance depositional model of the Upper Fourth Member of the Shahejie Formation was proposed about the paleo-valley sedimentation controlled by well Y920 in the east of the northern abrupt slope belt in Dongying depression. The result shows that the paleogeomorphology of the Y920 gully develops asymmetrically as being abrupt in the west yet gentle in the east during this period. The seismic facies can be divided into two types: the west of the gully is dominated by the wedge-shape reflections, while the east is dominated by progradational reflections. And these two types are separated by the lens-shape reflections in the middle. The detrital composition planar distribution of the sand filling of the gully varies greatly: the west has a low content of quartz and a high content of rock fragment mainly in the type of volcanic; while the east has a relatively high abundance in both the feldspar and the rock fragment mainly in the type of metamorphic detritus; and in the central part the proportions of feldspar and quartz are overwhelming yet the content of detritus mainly in the type of limestone is low. There are three provenances for the Y920 gully including the northern one which provides sediments southward along the long axis and the western and the eastern ones on either side of the gully along the short axis. Thus, the nearshore subaqueous fan and fan delta mainly develop on the west and the east sides respectively.
Key words: paleo-valley; provenance analysis; Shahejie formation; Dongying depression
在陆相湖盆的边缘,特别是陆相断陷湖盆的陡坡带发育有规模不等的古冲沟,是沉积物进入湖泊的主要通道[1],也是湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩体的主要沉积充填区。虽然古冲沟在湖盆中仅占很小的一部分,但他们是非常重要的石油勘探目标[2-12]。姜在兴等[2]认为湖缘峡谷的沉积特征与下切谷[13-15]有些类似。目前,国内外关于古冲沟的研究成果较少[1],前人对半地堑湖盆古冲沟的研究主要是利用地震和测井数据研究古冲沟的分布[3]、大尺度地层的结构[1]、沉积相类型[4-6],或在某些层序地层模型[9]中提到。这些研究仅仅提供了关于古冲沟及其充填的粗略的信息,对古冲沟充填层序及其结构的认识不够深入,前人提出的古冲沟仅为单物源充填[7-13],没有涉及到古冲沟内充填叠加结构及其油气勘探方面的应用,这种单物源充填模式与现今裂谷充填特征有较大差异。本文作者以东营凹陷北部陡坡带发育的古冲沟为例,利用地震反射结构、碎屑组分以及聚类分析等方法,重点探讨了古冲沟的物源体系,提出了古冲沟多物源叠加模式,为不同成因类型砂体的分布及利用结构模式预测盆地边缘古冲沟发育区的勘探目标提供了基础。
1 研究区概况
东营凹陷是渤海湾盆地东南部的一个北断南超的“箕状”裂陷盆地,北部为陈家庄凸起,东临青坨子凸起,由利津、博兴、牛庄、民丰4个生油洼陷及北部陡坡带、南部斜坡带等构造单元组成。东营凹陷北部陡坡带具有沟梁相间的古地貌特征,发育有10条规模较大的古冲沟。古冲沟内发育大量的砂砾岩体沉积,前人称之为“沟扇对应”[10],古冲沟内的砂砾岩体是东营凹陷陡坡带重要的油气储集体[7]。
前人通过对陈家庄凸起两侧凹陷内钻遇前第三纪基底的井分析,认为陈家庄凸起为古生界的海相、海陆交互相和中生代火山岩及陆相火山岩碎屑沉积。陈家庄凸起上普遍缺失古近系和中生界,在高部位甚至连古生界也全部被剥蚀,馆陶组与太古代片麻岩呈角度不整合直接接触[1]。
研究区(永安镇地区)位于东营凹陷的北部陡坡带东段(图1),关于工区砂砾岩体的沉积相类型及石油地质条件,许多学者已进行了探讨[3-12]。但前人对古冲沟沉积物源的分析较少,针对深层沙四上亚段,前人提出的沉积模式均为沿古冲沟长轴方向单一物源的扇三角洲[4-6,12]或近岸水下扇沉积[11],古冲沟中的砂砾岩体与民丰洼陷主要生油岩临近,成为油气聚集的重要场所。随着深层油藏勘探的进一步发展,发现单一物源的沉积模式与勘探成果有一定的差异,深层砂砾岩体相互叠加,砂砾体的期次划分与对比、空间分布及其成因等难题制约了砂砾岩油气藏的进一步勘探。
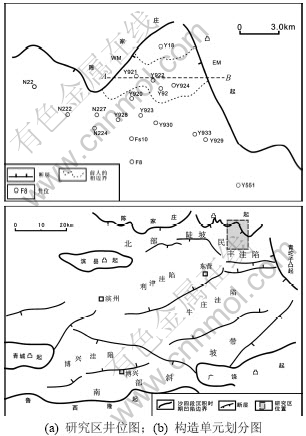
图1 研究区位置图
Fig.1 Maps showing location of study area
2 古冲沟的地震反射结构特征
根据地震剖面分析,古冲沟的基底为断超面[1],剖面形态表现为西陡东缓,呈明显不对称的箕状构造样式。根据古冲沟的基底坡度、断层产状,可将陡坡带Y920冲沟分为3部分,即长轴、西坡和东坡(图2)。
在东西向地震剖面中,地震相呈东西分带的特点。沿古冲沟西部边界断层发育楔形反射,古冲沟东部发育前积反射,冲沟中部发育透镜状反射。南北向剖面上,沿边界断层向湖盆中心方向,依次发育楔形、透镜状、平行席状等反射结构。
平面上,沙四上亚段地震相主要有楔形反射、前积反射、透镜状反射和平行-亚平行反射等类型。其中,楔形或楔形杂乱反射主要集中在北部及西部断层边界,振幅多变、连续性差;前积反射主要分布在冲沟东部,前积方向自东向西。楔形及前积反射结构与物源方向一致,透镜状反射往往垂直物源方向,这些反射结构代表了工区受到了多个方向物源的影响(图2),分别来自Y920冲沟西部、冲沟东部及冲沟的长轴方向。西部坡陡,发育冲积扇、近岸水下扇等相类型;东部坡度较缓,发育扇三角洲相,扇体规模相对较大。平面上,扇体横向连片,沿边界断裂裙带状分布。
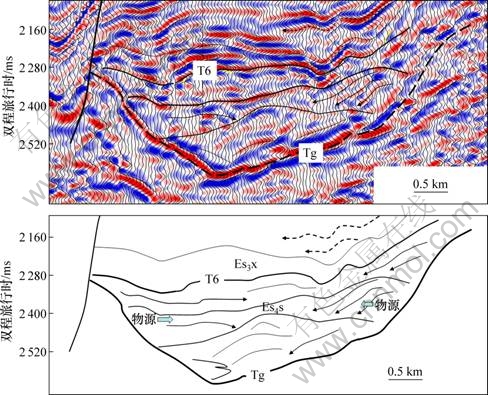
图2 东营凹陷北带东部过Y920古冲沟东西向典型剖面(测线位置见图1中AB)
Fig.2 Typical seismic profile of Y920 paleo-valley in north steep slope of Dongying depression
3 多物源沉积作用的岩石学证据
3.1 碎屑矿物组成及平面差异性
由于砂岩的骨架矿物成分对物源区的性质和构造环境有着敏感的反应,可以根据砂岩的成分判断物源区。研究区砂岩的碎屑组分主要是石英、长石和岩屑,颗粒含量为75%~95%,砂岩的类型在平面上具有明显的差异性。根据相似程度,将其分为沿冲沟长轴方向和冲沟东、西两侧3个区块。
西部的N224和N227等井的石英含量低(平均含量为15%~16.7%)、岩屑含量高(平均含量为40%~48%),岩屑类型以火成岩岩屑为主;如N224和N227等井,火成岩岩屑的含量(35%~36%)明显高于变质岩岩屑,x3=0.8~0.9(表1)。
东部的Y933等井的长石和岩屑含量均较高(石英平均含量为30%~45%、长石含量为35%~45%、岩屑平均含量为15%~35%)。岩屑类型以变质岩岩屑为主,变质岩岩屑含量(25%~35%)明显多于火成岩和沉积岩岩屑,x4=0.8~0.9;长石中的斜长石含量相对较高。
中部Y922,Y923和Y930等井的长石和石英含量较高(石英平均含量为32.9%~45%,长石含量为35%~65%),岩屑含量较低(岩屑平均含量为15%~32%)。岩屑类型以变质岩岩屑为主,并含有较多的鲕粒灰岩等灰岩岩屑,沉积岩岩屑的平均含量5%~10%。
洼陷中部的F8和FS10等井石英、长石含量高,石英平均含量为39.5%,长石含量为53.83%,岩屑的平均含量为5.66%。由统计数据可知:从古冲沟的西、东及北等3个方向向洼陷中心,石英、长石含量增加,石英平均含量由26.46%左右增至39.5%;岩屑含量由26.18%~31.13%减少至5.66%。
图3所示为沙四上亚段岩屑类型及含量平面展布图,岩屑类型的差异性反映了不同的物源方向,分别为西、东短轴方向及北部长轴方向的物源。
此外,还选用了Q型相关系数进行砂岩成分的聚类分析,以8个碎屑组分含量为变量,对砂岩样品之间的相似性进行了对比,编制了谱系图(图4)。结果表明,在相关系数为0.7的时候,研究区的砂岩可被明显地分为西部、中部、东部和洼陷等4个区块,N222井属于工区西侧盐家冲沟的充填沉积,与研究区的砂岩成分有差异。
表1 Y920古冲沟沙四上亚段砂岩碎屑矿物成分含量统计表
Table 1 Content of detrital minerals of sandstone of upper Es4 in Y920 paleo-valley
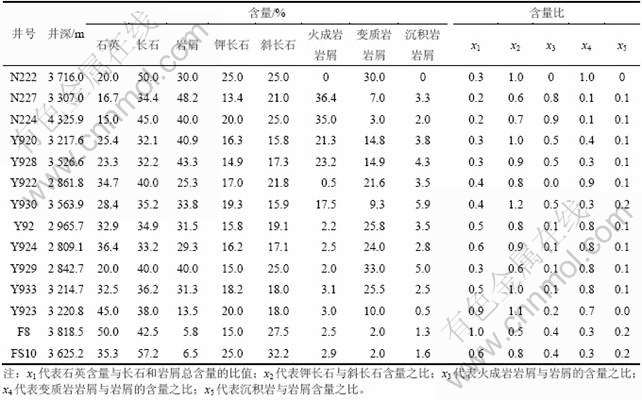
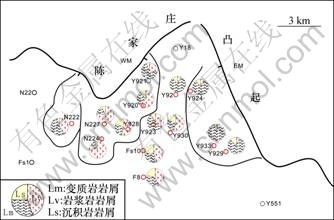
图3 Y920古冲沟沙四上亚段砂岩岩屑类型分布图
Fig.3 Distribution of types of rock fragments in sandstone of upper Es4 in Y920 paleo-valley
3.2 砂岩成分成熟度特征
砂岩中石英代表碎屑中的稳定组分,长石、岩屑为不稳定组分,稳定与不稳定组分的含量比(x1)代表矿物成熟度,反映物源方向的变化。
通过计算研究区不同井的矿物成熟度,绘制了平面矿物成熟度等值线图(图5)。沿北西-南东方向,由N224,N227井至Y928地区,矿物成熟度由0.3增大至0.5~0.6;冲沟东部,自西向东矿物成熟度增大,Y929,Y933等井矿物成熟度为0.3~0.5,洼陷中部的F8,FS10等地区成熟度可以达到0.6~1.0,矿物成熟度增大的方向代表不同的物源方向。
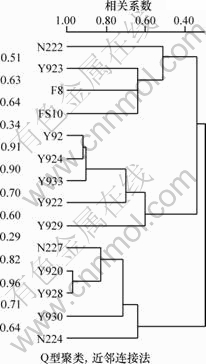
图4 Y920古冲沟沙四上亚段砂岩成分聚类图
Fig.4 Cluster analysis of sandstone components of upper Es4 in Y920 paleo-valley
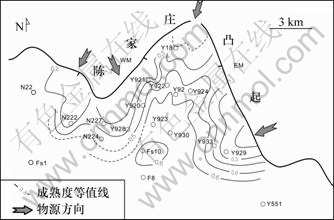
图5 Y920古冲沟沙四上亚段成分成熟度分布图
Fig.5 Distribution of sandstone maturity of upper Es4 in Y920 paleo-valley
3.3 砾岩分布及其砾石类型
砾岩常分布在盆地的边缘近物源区,其成分可直接反映物源区母岩成分。砾岩中砾石的成分、砾径等是确定物源的直接证据。对区内砾岩中砾石成分进行统计,结果表明,研究区沙四上亚段砾岩的主要砾石成分有片麻岩、中酸性岩浆岩,少量灰岩和泥岩砾等。平面上,砾石的成分有较大差异,西部的N227和N224等井花岗岩等中酸性侵入岩砾石含量高、砾径大,砾石的砾径一般为30~50 mm,有的可达100 mm以上,分选极差,具有近岸水下扇的沉积特点[11];东部的Y929,Y933等井以花岗片麻岩、中酸性侵入岩为主,砾径稍小,一般为20~35 mm。中部Y922,Y930井等含有较多的灰岩砾石,如Y922井沙四上亚段砂砾岩中,砾石占15%~70%左右,砾石成分主要为石英、结晶岩、长石和鲕粒灰岩等,砾径较小,一般为10~15 mm,磨圆度相对较好,砾石有定向性,具有扇三角洲的沉积特点[5-7]。上述砾石成分的差异性反映了西部物源含有较多的中酸性火成岩等侵入岩体,东部物源区以花岗片麻岩为主;长轴方向的物源含有一定的灰岩地层。
4 古冲沟多物源叠加沉积模式
图6所示为沙四上亚段4砂岩组砂砾岩厚度含量平面等值线图,按砂砾岩含量大于60%的条带作为划分古水系分布范围的标准,将研究区划分为东部、中部和西部3条砂体条带,作为该冲沟区古水系注入湖泊的3条主要通道。其中东部地区的砂体条带呈NE-SW向延伸,砂体条带的宽度由向北南逐渐增加;中部地区的砂体条带沿SN向延伸;西部地区的砂体条带呈NW-SE向延伸。
Y920古冲沟多物源叠加充填模式见图7。古冲沟发育早期,冲沟形态不对称,冲沟两侧及长轴方向凸起地形高差、剥蚀程度不同。沙四段沉积时期,冲沟西部断层活动性较强、地形高差大,容易产生机械破碎的大块碎屑,被剥蚀的凸起中含有大量的火成岩体或岩脉;冲沟东部,断层活动性相对较弱、地形高差较小,物源以花岗片麻岩为主;长轴方向,冲沟的延伸范围较远,被剥蚀的物源区层位相对较为复杂,包含部分古生界地层,母岩碎屑物质中碳酸盐岩含量相对较高。
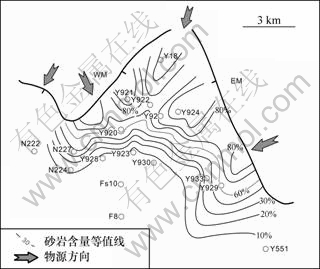
图6 Y920古冲沟沙四上亚段4砂岩组砂岩含量
Fig.6 Isopach of sandstone ratio of upper Es4 in Y920 paleo-valley
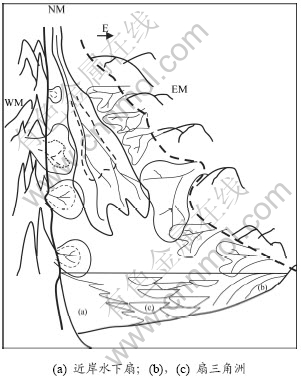
图7 Y920古冲沟沙四上亚段多物源沉积模式
Fig.7 Diagrams illustrating Multi-Provenance depositional model in Y920 paleo-valley of upper Es4
受短轴及长轴等3个不同方向物源的影响,冲沟内的扇体为不同方向扇体的叠加。在古冲沟两侧,粗粒砂砾岩扇体分布范围较小,冲沟西部受高角度断层边界的影响,冲沟边缘坡度陡,发育近岸水下扇沉积体系;东部为断超接触,坡度较缓,扇体规模稍大,以湖泊和扇三角洲沉积体系为主。冲沟中间及向盆地方向,不同物源的砂体相互叠合。在古冲沟前端喇叭状沟口,砂体叠加、呈凹形展布,与前人提出的冲沟单一物源形成的砂体外凸形态[6-12]明显不同。
5 结论
(1) 在古近系沙河街组沙四上亚段沉积时期,东营凹陷北部陡坡带Y920古冲沟呈明显不对称的箕状构造样式,剖面形态表现为西陡东缓。古冲沟的地震相呈东西分带的特点,古冲沟西部发育楔形反射、东部发育前积反射、中部发育透镜状反射,具有多物源叠加的沉积充填结构特点。
(2) Y920古冲沟砂岩的碎屑矿物组成在平面上具有明显的差异性。冲沟西部石英含量低、岩屑含量高,岩屑类型以火成岩岩屑为主;东部长石和岩屑含量均较高,岩屑类型以变质岩岩屑为主;中部长石和石英含量较高,岩屑含量较低,并含有较多的鲕粒灰岩等灰岩岩屑。
(3) 沙河街组四段上亚段沉积时期, Y920古冲沟存在3个方向的物源,分别为沿冲沟长轴方向的北部物源以及来自冲沟西部和东部的短轴、侧向物源。
(4) 冲沟受短轴及长轴等3个不同方向物源的影响,冲沟内的扇体为不同方向扇体的叠加。Y920古冲沟西部坡度陡,发育近岸水下扇沉积;东部为断超接触、坡度较缓,扇体以扇三角洲为主;冲沟中间及向盆地方向,不同物源的砂体相互叠合。在古冲沟前端喇叭状沟口,砂体叠加、呈凹形展布。
参考文献:
[1] 许淑梅, 张晓东, 刘怀山, 等. 济阳坳陷陈家庄凸起东南坡古冲沟沉积充填特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2005, 35(2): 344-34.
XU Shu-mei, ZHANG Xiao-dong, LIU Huai-shan, et al. Characteristics of ancient gullies in the south slope of Chenjiazhuang structural high in Jiyang depression[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2005, 35(2): 344-34.
[2] 姜在兴, 杨伟利, 于雯泉, 等. 湖缘峡谷及其含油性[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 186-194.
JIANG Zai-xing, YANG Wei-li, YU Wen-quan, et al. The lake-margin canyon and its hydrocarbon potential[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 186-194.
[3] 张维冈, 刘怀山. 东营北部凸起带古冲沟储层分布规律研究[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2002, 32(4): 603-607.
ZHANG Wei-gang, LIU Huai-shan. Studies on reservoir prediction of platfood in the paleogully in the north of dongying[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2002, 32(4): 603-607.
[4] 张春生, 赖志云, 李春光, 等. 永安镇油田沙四段冲积扇扇三角洲沉积[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1995, 20(1): 95-100.
ZHANG Chun-sheng, LAI Zhi-yun, LI Chun-guang, et al. Alluvial fan-fan delte deposits of Sha4 member in Yong’anzhen oil field[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1995, 20(1): 95-100.
[5] 杨剑萍, 石德文. 东营凹陷北部永921地区渐新世沙三段和沙四段扇三角洲沉积[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 24(1): 10-17.
YANG Jian-ping, SHI De-wen. Fan delta deposits of Sha3 and Sha4 members at Oligocene Shahejie Formation at Yong 921 area in the north of Dongying depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2000, 24(1): 10-17.
[6] 王蛟, 姜在兴, 操应长. 山东东营凹陷永921地区沙四上亚段扇三角洲沉积与油气[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2005, 35(6): 725-732.
WANG Jiao, JIANG Zai-xing, CAO Ying-chang. Fan delta deposits and relation to hydrocarbon of upper Es4 at Yong 921 area in Dongying depression[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2005, 35(6): 725-732.
[7] 孔凡仙. 东营凹陷北带砂砾岩扇体勘探技术与实践[J]. 石油学报, 2000, 21(5): 27-31.
KONG Fan-xian. Exploration technique and practice of sandy-conglomeratic fans in the northern part of Dongying depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2000, 21(5): 27-31.
[8] 高祥成, 钟建华, 雷敏, 等. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带深层砂砾岩体沉积特征及控制因素: 以丰深1地区为例[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2008, 22(1): 5-8.
GAO Xiang-cheng, ZHONG Jian-hua, LEI Min, et al. Sedimentation feature and controlling factors of the deep glutenite fans in the northern steep slope, Dongying sag: Taking Well Fengshen-1 area as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2008, 22(1): 5-8.
[9] 纪友亮, 张世奇. 陆相断陷湖盆层序地层学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1996: 100-121.
JI You-liang, ZHANG Shi-qi. Sequence stratigraphic models of the fault depression lake basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Indystry Press, 1996: 100-121.
[10] 鲜本忠, 王永诗, 周廷全, 等. 断陷湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩体分布规律及控制因素: 以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷车镇凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(4): 50-57.
XIAN Ben-zhong, WANG Yong-shi, ZHOU Ting-quan, et al. Distribution and controlling factors of glutinite bodies in the actic region of a rift basin: An example from Chezhen Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(4): 50-57.
[11] 鄢继华, 陈世悦, 姜在兴. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带近岸水下扇沉积特征[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 29(1): 12-16.
YAN Ji-hua, CHEN Shi-yue, JIANG Zai-xing. Sedimentary characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fans in steep slope of Dongying depression[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 2005, 29(1): 12-16.
[12] 张金亮, 张鑫. 胜坨地区沙河街组沙四上亚段砂砾岩体沉积相与油气分布[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(3): 361-368.
ZHANG Jin-liang, ZHANG Xin. The glutenite sedimentary facies and hydrocarbon distribution in the upper fourth member of Shahejie formation in shengtuo area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(3): 361-368.
[13] Bowen D W, Weimer P. Regional sequence stratigraphic setting and reservoir geology of Morrow incised-valley sandstones (lower Pennsylvanian), eastern Colorado and western Kansas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2003, 87(7): 781- 815.
[14] Bowen D W, Weimer P. Reservoir geology of Nicholas and Liverpool Cemetery fields (lower Pennsylvanian), Stanton County, Kansas, and their significance to the regional interpretation of the Morrow Formation incised-valley-fill systems in eastern Colorado and western Kansas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2004, 88(1): 47-70.
[15] Deibert J E, Phyllis A C. Sedimentologic and tectonic origin of an incised-valley-fill sequence along an extensional marginal-lacustrine system in the Basin and Range province,United States: Implications for predictive models of the location of incised valleys[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(2): 209-235.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2011-09-19;修回日期:2011-12-25
基金项目:国家油气科技重大专项(2008ZX05008-004,2011ZX05008-004)
通信作者:张立强(1970-),男,山东曲阜人,博士,教授,从事油气储层沉积学研究;电话:18678986578;E-mail:liqiangzhangwxm@163.com
摘要:利用地震反射结构、碎屑组分以及聚类分析等方法,提出东营凹陷北部陡坡带东部Y920古冲沟沙河街组沙四上亚段多物源叠加模式。研究结果表明:沙四上亚段沉积时期,Y920冲沟呈西陡东缓的不对称箕状构造形态。地震相呈东西分带的特点,冲沟西部发育楔形反射、东部发育前积反射、中部发育透镜状反射。冲沟内砂岩充填物的碎屑矿物组成在平面上具有明显的差异性,冲沟西部砂岩的石英含量低、岩屑含量高,岩屑以火成岩岩屑为主;冲沟东部,砂岩的长石和岩屑含量均较高,岩屑以变质岩岩屑为主;中部长石和石英含量较高,岩屑含量较低,含有较多的灰岩岩屑。Y920古冲沟存在3个方向的物源,分别为自北向南、沿冲沟长轴方向的北部物源以及来自冲沟西部和东部的短轴、侧向物源。冲沟西部发育近岸水下扇沉积,东部扇体以扇三角洲为主。


