文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-08-1817-06
降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2分解性能和晶体结构的影响
王 波1, 2,刘佳佳1,孙会兰1,马东东1
(1. 河北科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,石家庄 050018;
2. 河北科技大学 河北省材料近净成形重点实验室,石家庄 050018)
摘 要:
采用分析纯试剂在1500 ℃下保温2 h合成γ-2CaO·SiO2熟料,并通过溶出实验和XRD等手段研究降温速度对其分解性能和晶体结构的影响。结果表明:随着降温速度的加快,制得的γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解性能升高;随着分解时间的延长,降温速度对分解性能的影响更加明显;晶胞体积随降温速度的加快而增大,不同降温速度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2均具有(130)晶面的择优取向;随着降温速度的加快,(130)晶面的择优取向没有变化;晶胞体积的增大促进γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解。
关键词:
中图分类号:TF111.31 文献标志码:A
随着我国铝工业的飞速发展,氧化铝的需求量不断增加[1-4],然而,我国铝资源日益短缺、矿石品位不断下降使得拜耳法生产工艺中有效氧化铝溶出率也在不断下降。针对此类低品位铝矿石,碱石灰烧结法[5]相比拜耳法工艺具有一定的优势,然而能耗高、二次反应严重等特点也制约了碱石灰烧结法的进一步发展。
石灰烧结法[6-7]是提取氧化铝的另一种重要方法,在处理低品位铝土矿、粉煤灰、铁铝共生矿等含铝矿物中有其特定的优势。它的烧结产物主要由12CaO·7Al2O3与γ-2CaO·SiO2组成,可实现干法烧结,能耗较低,并且溶出率较高。硅酸二钙晶体在冷却过程中会发生由介稳的β型向稳定的γ型的转变,体积膨胀12%,引起熟料的粉化;碱石灰烧结法中因Na2O的大量配入,抑制了该晶型的转变,而石灰烧结法配料中无需添加Na2O,节约了成本,也保证了硅酸二钙由β型向γ型的转变[8],促进了熟料的自粉。由于γ-2CaO·SiO2的活性较差,偏惰性,一般认为在溶液中稳定存在,因此,二次反应对其影响较小。然而一些研究结果表明[9-11],当调整液中碳碱、苛碱浓度较高时,γ-2CaO·SiO2依然会被分解为硅酸钠进入溶液,当铝酸钠溶液中硅的含量超出其平衡溶解度时,便会与铝酸钠化合形成不溶性的钠硅渣和水化石榴石进入赤泥,造成氧化铝的损失。因此,研究γ-2CaO·SiO2在碳酸钠溶液中的分解性能具有重要意义。
目前,国内外对于2CaO·SiO2的研究多集中于β型[12-14],结果显示当氧化铝浓度和反应温度较高时,β-2CaO·SiO2的分解率可达47%以上;生产中二次反应造成氧化铝的损失约为4.5%[15]。而对于γ-2CaO·SiO2分解的相关研究依然较少。孙会兰等[16]已通过工艺试验确定γ-2CaO·SiO2的最佳合成条件:钙硅比为2,合成温度为1500 ℃,保温时间为60 min。本文作者拟在此基础上,在不同降温速度下合成相应熟料,利用高碳碱浓度调整液在高液固比(L/S=20)下对其进行分解性能研究,并计算其晶体结构相关参数,为进一步探究γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解机理奠定基础。
1 实验
1.1 实验仪器
试验过程所用设备:电子天平、SFM-Ⅱ行星式混料机、SFM-Ⅰ行星式球磨机、KSL-1700X箱式高温烧结炉、恒温水浴箱、磨口锥形瓶及配套装置。
分析仪器:日本Rigaku公司生产的D/MAX-2500型X射线衍射仪、Bruker公司生产的TESCAN Vega-3SBH扫描电子显微镜、丹东百特仪器有限公司生产的BT-9300S激光粒度分析仪、上海精密科学仪器有限公司生产的722S可见分光光度计。
1.2 实验原料
本试验过程所用氢氧化钙、碳酸钠、石英砂均为分析纯化学试剂。γ-2CaO·SiO2的合成原料为氧化钙和石英砂,氧化钙是由分析纯氢氧化钙在1000 ℃下煅烧150 min制得。
1.3 实验过程
1.3.1 烧结过程
按摩尔比n(CaO)/n(SiO2)=2称取所需量的氧化钙与石英砂,混合均匀后放入石墨坩埚置于高温烧结炉中进行合成,合成温度为1500 ℃,保温60 min,升温速度为10 ℃/min。控制不同的降温速度从而得到相应熟料。
1.3.2 溶出过程
溶出试验在恒温水浴箱中进行,本试验溶出用调整液为120 g/L碳酸钠溶液,溶出温度85 ℃,液固比20。试验时先将水浴箱预热至指定温度,然后在磨口三口瓶内加入预热好的100 mL调整液及5 g熟料,开动搅拌器并计时,到指定时间后快速取出三口瓶,对瓶内浆液固液分离后,取一定量溶液利用硅钼蓝比色法测定其中二氧化硅的浓度,进而求得熟料的分解率。计算公式如下:
 (1)
(1)
式中: 表示γ-2CaO·SiO2分解后进入溶液中的SiO2浓度,g/L;Vt为调整液的体积,L;ms为熟料的质量,g;w(SiO2)表示熟料中SiO2的质量分数。
表示γ-2CaO·SiO2分解后进入溶液中的SiO2浓度,g/L;Vt为调整液的体积,L;ms为熟料的质量,g;w(SiO2)表示熟料中SiO2的质量分数。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2物相的影响
为确定熟料中的物相组成,对不同降温速度下合成的熟料进行了XRD分析,其结果如图1所示。
由图1可知,在不同降温速度下制得的熟料均为单一的γ-2CaO·SiO2,降温速度的变化并未改变熟料的物相组成,即降温速度对烧得熟料的物相组成无影响。

图1 不同降温速度下烧得熟料的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of clinkers under different cooling rates
2.2 降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2分解性能的影响
选择10 ℃/min的升温速度,分别以5、8、10 ℃/min随炉冷却降温合成相应熟料,研究降温速度对其分解性能的影响,其结果如图2所示。图中左侧纵轴为γ-2CaO·SiO2分解后进入溶液中的SiO2浓度(ρ(SiO2)),右侧纵轴是由ρ(SiO2)在式(1)的基础上求得相应γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解率。
由图2可以看出,在高碳碱浓度、高液固比的溶出条件下,不同降温速度下制得的γ-2CaO·SiO2分解率随溶出时间的延长呈上升趋势;1 h之前,由于溶出时间较短,各曲线间分解率差异很小,最高不超过3%,ρ(SiO2)小于4.7 g/L;而当溶出时间延长至6 h时,各曲线间分解率差异明显,最高可达12%,ρ(SiO2) 可达8.6 g/L。因此,降温速度的变化对烧得γ-2CaO·SiO2分解具有一定影响,随着降温速度的增加,γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解性能上升。

图2 降温速度对制得γ-2CaO·SiO2分解性能的影响
Fig. 2 Influence of cooling rate on decomposition property of γ-2CaO·SiO2
2.3 降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2粒度大小的影响
对不同降温速度下烧得熟料进行粒度分析后,其结果如表1所列。
表1 不同降温速度下烧得熟料粒度分布
Table 1 Granularity distribution of clinker under different cooling rates

从表1可以看出,不同降温速度下烧得熟料粒度十分接近,自粉性较好;而由XRD谱可知,合成物相均为单一的γ-2CaO·SiO2,因此,各个样品间分解性能的差异有必要从晶体结构等微观角度加以分析。
2.4 降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2微观结构的影响
2.4.1 降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2微观形貌的影响
实验考察了不同降温速度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2颗粒的微观形貌,图3所示为各降温速度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2的SEM像。
由图3可知,不同降温速度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2颗粒大小不一,除部分较大颗粒外,大多数颗粒粒径在30 μm之内。颗粒外形呈现出不规则的长条状或块状,说明硅酸二钙的自粉是无规律的自我分裂过程;表层断裂面上为明显的板条状结构,即γ-2CaO·SiO2晶粒在纵向上有明显的生长趋势。
2.4.2 降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2点阵常数的影响
点阵常数是晶体物质的重要参量,它会因物质成分与外界条件的变化而变化,所以可通过其变化揭示晶体的物理本质及变化规律。
由于γ-2CaO·SiO2属于斜方晶系[17],z=4,点阵常数a≠b≠c,α=β=γ=90°,因此,利用XRD数据以及晶面间距公式[18]:
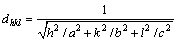 (2)
(2)
即可计算出它的点阵常数,在利用晶胞体积计算公式V=abcsinα·sinβ·sinγ得出其晶胞体积。不同降温速度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2的XRD数据及相关计算结果如表2和3所列。
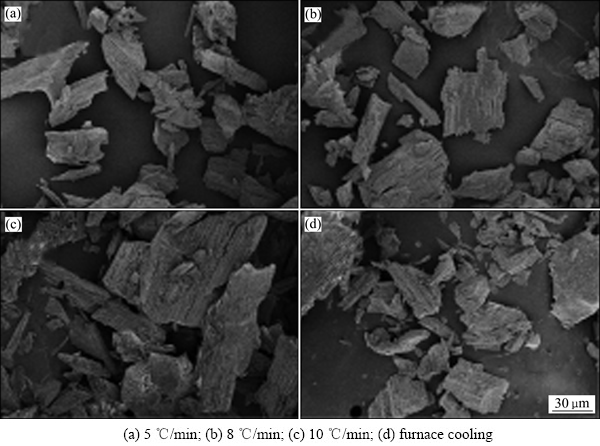
图3 不同降温速度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2的SEM像
Fig. 3 SEM images of γ-2CaO·SiO2 under different cooling rates
表2 不同降温速度下样品的晶面间距
Table 2 Interplanar distance of samples at different cooling rates

表3 不同降温速度下样品的晶胞参数
Table 3 Cell parameters of samples at different cooling rates

从表2和3可以看出,样品的点阵常数伴随着降温速度的变化而变化,当降温速度持续递增时,样品的晶胞体积不断变大。这是由于硅酸二钙在冷却过程中会发生如下晶型转变[19-20]:

 (3)
(3)
随着降温速度的加快,晶型转变速率也随之加快,导致新产生的晶型体系不稳定,晶胞内形成的新键键能较低,键长较长,继而表现为晶胞体积的增大。由于新键键能较低,易断裂,化学反应就容易进行,反应程度加剧,宏观上表现为分解性能的提高,这也解释了图2中合成物相均为γ-2CaO·SiO2的前提下,其分解性能随降温速度加快而上升的原因。
2.4.3 降温制度对γ-2CaO·SiO2晶粒择优取向的变化
晶粒的取向一般是任意分布的,但由于晶粒在形成过程中会受到力、热、磁等外界条件的影响,使得多晶体中的各晶粒会沿着某些方向上呈现出一定的有序性,这种晶粒在某些方向上聚集排列的现象,称之为择优取向。由于硅酸二钙晶体在冷却过程中会发生一系列的晶型转变,因此研究降温制度对γ-2CaO·SiO2晶粒择优取向的变化,也能表征γ-2CaO·SiO2晶粒微观结构的变化。
由XRD谱可知,不同降温制度下合成的γ-2CaO·SiO2最强峰对应晶面(130),故合成产物在该晶面上具有择优取向。择优取向因子(C(hkl))的计算见式(4)[21]:
 (4)
(4)
式中:I(hkl)为衍射面强度的试验值;I0(hkl)为衍射面强度的标准卡片值;n为选取的衍射峰数量。
不同降温制度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2的XRD谱强峰相对强度及标准卡片相对强度见表4,由表4数据计算得出(130)晶面的择优取向因子如图4所示。

图4 降温速度对晶粒择优取向因子的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of cooling rate on preferred oriented factor of crystal grains
表4 不同降温制度下熟料的XRD衍射峰的相对强度和标准卡片的相对强度
Table 4 Relative intensity of XRD diffractions peaks and standard cards of clinkers at different cooling rates

由图4可以看出,随着降温速度的加快,(130)晶面的择优取向因子无明显变化,所以,降温速度的变化对(130)晶面的择优取向无影响。
3 结论
1) 降温速度对γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解性能有一定影响,降温速度加快,制得γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解性能上升。
2) 合成γ-2CaO·SiO2的点阵常数随降温速度改变而改变,降温速度加快,晶胞体积增大,γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解性能相应升高。
3) 制得γ-2CaO·SiO2在(130)晶面上具有择优取向,降温速度变化对(130)晶面的择优取向无影响。
REFERENCES
[1] 张军伟. 中国铝土矿资源形势及对策[J]. 价值工程, 2012, 31(21): 4-6.
ZHANG Jun-wei. Situation and countermeasures of China’s bauxite resources[J].Value Engineering, 2012, 31(21): 4-6.
[2] 冯 聪, 薛亚洲. 我国铝资源开发利用现状及综合利用对策建议[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2013(3): 55-58.
FENG Cong, XUE Ya-zhou. The status of development and utilization of alumium in China and the countermeasures of comprehensive utilization[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2013(3): 55-58.
[3] 许国栋, 敖 宏, 畲元冠. 可持续发展背景下世界铝工业发展现状、趋势及我国的对策[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 2040-2051.
XU Guo-dong, AO Hong, SHE Yuan-guan. Current status and development trend of aluminum industry in world and strategy suggestions in China under background of sustainable development[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(7): 2040-2051.
[4] 许 斌, 李帅军. 高铁铝土矿铝铁分离研究现状[J]. 矿业工程, 2014(2): 17-20.
XU Bin, LI Shuai-jun. Research status of separation of aluminum and iron from high-ferric bauxite[J]. Mining Engineering, 2014(2): 17-20.
[5] 俞小花, 刘 康, 杨大锦, 谢 刚. 碱石灰烧结法处理霞石的试验研究[J]. 轻金属, 2013(2): 20-23.
YU Xiao-hua, LIU Kang, YANG Da-jin, XIE Gang. The experimental study on soda lime sintering process to treat nepheline[J]. Light Metals, 2013(2): 20-23.
[6] 任根宽, 朱登磊. 石灰烧结法从煤系高岭土提取氧化铝的研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2012, 35(1): 7-9.
REN Gen-kuan, ZHU Deng-lei. Technology process of extraction of alumina from coal-measures kaoline by sintering method of limestone[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2012, 35(1): 7-9.
[7] 袁致涛, 张 松, 李丽匣, 于福家. 我国高铁铝土矿铝铁分离技术现状[J]. 金属矿山, 2013, 42(9): 100-103.
YUAN Zhi-tao, ZHANG Song, LI Li-xia, YU Fu-jia. Research status on ferrous and aluminum separation of high-ferric bauxite in China[J]. Metal Mine, 2013, 42(9): 100-103.
[8] SUN Hui-lan, WANG Bo, YU Hai-yan, BI Shi-wen, TU Gan-feng. Effect of Na2O on alumina leaching and self-disintegrating property of calcium aluminate slag[C]// Light Metals 2010. Seattle: Minerals, Metals&Materials Society, 2010: 29-32.
[9] RAYZMAN V L, ATURIN A V, PEVZNER I Z, SIZYAKOV V M, NI L P, FILIPOVICH I K. Extracting silica and alumina from low-grade bauxite[J]. JOM, 2003, 55(8): 47-50.
[10] 毕诗文, 于海燕. 氧化铝生产工艺[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006: 253-254.
BI Shi-wen, YU Hai-yan. Alumina production process[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006: 253-254.
[11] SUN Hui-lan, WANG Bo, ZHANG Jian-xin, ZONG Shu-feng, LIU Jia-jia. Secondary reaction mechanism of leaching process of calcium aluminate slag[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(4): 1334-1340.
[12] 李小斌, 张 建, 刘桂华, 陈 滨, 齐天贵. 原硅酸钙在铝酸钠溶液中的反应行为[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(2): 275-281.
LI Xiao-bin, ZHANG Jian, LIU Gui-hua, CHEN Bin, QI Tian-gui. Reactive behaviors of calcium silicate in aluminate solutions[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2009, 40(2): 275-281.
[13] LIU Gui-hua, LI Xiao-bin, PENG Zhi-hong, ZHOU Qiu-sheng. Stability of calcium silicate in basic solution[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2003, 13(5): 1235-1238.
[14] ZENG Lan-mu, LI Zhi-bao. Solubility of dicalcium silicate in the NaOH-NaAl(OH)4-Na2CO3 solutions: Determination and prediction[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 147/148: 127-133.
[15] 彭志宏, 陈彦虎, 周秋生, 刘桂华, 李小斌, 齐天贵. 流态化分离洗涤对熟料高质量浓度溶出浆液二次反应的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(6): 2036-2042.
PENG Zhi-hong, CHEN Yan-hu, ZHOU Qiu-sheng, LIU Gui-hua, LI Xiao-bin, QI Tian-gui. Effect of fluidized separating-washing of red mud on secondary reactions of leached slurry with high alumina concentration[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2012, 43(6): 2036-2042.
[16] 孙会兰, 于海燕, 王 波, 周怀敏, 涂赣峰, 毕诗文. γ-2CaO·SiO2合成及分解性能研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2008, 28(5): 59-63.
SUN Hui-lan, YU Hai-yan, WANG Bo, ZHOU Huai-min, TU Gan-feng, BI Shi-wen. Study on synthesis and decomposition property of γ-2CaO·SiO2[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2008, 28(5): 59-63.
[17] SAITO T, SAKAI E, MORIOKA M, OTSUKI N. Carbonation of γ-Ca2SiO4 and the mechanism of vaterite formation[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 2010, 8(3): 273-280.
[18] 范建春, 李丽琳, 陈超球. 晶面间距d(hkl)的两种求法[J]. 广西师院学报(自然科学版), 1999, 16(1): 92-97.
FAN Jian-chun, LI Li-lin, CHEN Chao-qiu. Two solution of crystal plane distance[J]. Journal of Guangxi Teachers College (Natural Science Edition), 1999, 16(1): 92-97.
[19] ZHAO Ming. Quantitative control of C2S crystal transformation[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012, 121: 311-315.
[20] MORI K, KIYANAGI R, YONEMURA M, IWASE K, SATO T, ITOH K, SUGIYAMA M, KAMIYAMA T, FUKUNAGA T. Charge states of Ca atoms in β-dicalcium silicate[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2006, 179(11): 3286-3294.
[21] MOUANGA M, RICQ L, DOUGLADE G, DOUGLADE J, BER OT P. Influence of coumarin on zinc electrodeposition[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 201(3/4): 762-767.
OT P. Influence of coumarin on zinc electrodeposition[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 201(3/4): 762-767.
Effect of cooling rate on decomposition property and crystal structure of γ-2CaO·SiO2
WANG Bo1, 2, LIU Jia-jia1, SUN Hui-lan1, MA Dong-dong1
(1. School of Material Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang 050018, China;
2. Hebei Key Laboratory of Material Near-net Forming Technology, Hebei University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang 050018, China)
Abstract: γ-2CaO·SiO2 clinkers were synthesized by analytically pure reactants at 1500 ℃ for 2 h. The effect of cooling rate on decomposition property and crystal structure of γ-2CaO·SiO2 was investigated by leaching experiment and XRD method. The results show that the decomposition property of γ-2CaO·SiO2 increases with the cooling rate speeding up. The influence of cooling rate on decomposition property of γ-2CaO·SiO2 prefers more obviously with the leaching time prolonging. The crystal cell volume increases with the cooling rate speeding up. The clinkers under different cooling rate has preferred orientation on crystal face (130). With the increase of the cooling rate, the preferred orientation on crystal face (130) is constant. The increase of crystal cell volume promotes the decomposition of γ-2CaO·SiO2.
Key words: γ-2CaO·SiO2; cooling rate; decomposition property; crystal structure
Foundation item: Project(51104053) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (QN2015002, BJ2016023) supported by the Science and Technology Foundation of Higher Education Institution of Hebei Province, China
Received date: 2015-07-09; Accepted date: 2016-01-18
Corresponding author: WANG Bo; Tel: +86-311-81668705; E-mail: wangbo1996@gmail.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51104053);河北省高等学校科学技术研究资助项目(QN2015002,BJ2016023)
收稿日期:2015-07-09;修订日期:2016-01-18
通信作者:王 波,副教授,博士;电话:0311-81668705;E mail: wangbo1996@gmail.com
摘 要:采用分析纯试剂在1500 ℃下保温2 h合成γ-2CaO·SiO2熟料,并通过溶出实验和XRD等手段研究降温速度对其分解性能和晶体结构的影响。结果表明:随着降温速度的加快,制得的γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解性能升高;随着分解时间的延长,降温速度对分解性能的影响更加明显;晶胞体积随降温速度的加快而增大,不同降温速度下制得γ-2CaO·SiO2均具有(130)晶面的择优取向;随着降温速度的加快,(130)晶面的择优取向没有变化;晶胞体积的增大促进γ-2CaO·SiO2的分解。
[1] 张军伟. 中国铝土矿资源形势及对策[J]. 价值工程, 2012, 31(21): 4-6.
[2] 冯 聪, 薛亚洲. 我国铝资源开发利用现状及综合利用对策建议[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2013(3): 55-58.
[3] 许国栋, 敖 宏, 畲元冠. 可持续发展背景下世界铝工业发展现状、趋势及我国的对策[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 2040-2051.
[4] 许 斌, 李帅军. 高铁铝土矿铝铁分离研究现状[J]. 矿业工程, 2014(2): 17-20.
[5] 俞小花, 刘 康, 杨大锦, 谢 刚. 碱石灰烧结法处理霞石的试验研究[J]. 轻金属, 2013(2): 20-23.
[6] 任根宽, 朱登磊. 石灰烧结法从煤系高岭土提取氧化铝的研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2012, 35(1): 7-9.
[7] 袁致涛, 张 松, 李丽匣, 于福家. 我国高铁铝土矿铝铁分离技术现状[J]. 金属矿山, 2013, 42(9): 100-103.
[10] 毕诗文, 于海燕. 氧化铝生产工艺[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006: 253-254.
[12] 李小斌, 张 建, 刘桂华, 陈 滨, 齐天贵. 原硅酸钙在铝酸钠溶液中的反应行为[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(2): 275-281.
[16] 孙会兰, 于海燕, 王 波, 周怀敏, 涂赣峰, 毕诗文. γ-2CaO·SiO2合成及分解性能研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2008, 28(5): 59-63.
[18] 范建春, 李丽琳, 陈超球. 晶面间距d(hkl)的两种求法[J]. 广西师院学报(自然科学版), 1999, 16(1): 92-97.


