网络首发时间: 2019-04-02 13:16
电子束熔炼法制备高纯金属钒的实验研究
王焱辉 刘奇 李方 薄新维 王小宇 何浩然
重庆材料研究院有限公司
重庆市稀贵金属高效利用工程技术研究中心
国家仪表功能材料工程技术研究中心
摘 要:
金属钒粉通过冷等静压成型和真空烧结成钒坯条后,采用电子束熔炼对钒坯条进行提纯研究。利用EPMA-1720电子探针(EPMA),Olympus-PMG3型光学显微镜(OM)、电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-AES)和氧氮氢分析仪分别对钒坯条和熔炼后钒锭的微观形貌、金相组织以及纯度进行观察和检测。实验研究结果表明:钒坯条存在孔隙,显微组织不致密,而电子束熔炼使得钒晶间孔隙得以消除,钒基体晶界结合紧密,组织变得致密均匀。经电子束熔炼,钒金属间隙杂质元素C,O,N的含量显著降低,去除率分别达到56. 41%,79. 17%和52. 38%。而元素H由于本身含量较少,从熔炼前80×10-6降低到50×10-6,去除率为37. 50%。钒金属非间隙杂质元素Si,Al,Mg,P,Cd的蒸气压与V的蒸气压压差较大,去除效果较明显。元素Mo,B属于高熔点难熔杂质,蒸气压比V的蒸气压小去除率偏低,钒金属经电子束熔炼后纯度达到99. 932%。
关键词:
金属钒 ;电子束熔炼 ;冷等静压 ;真空烧结 ;杂质元素 ;
中图分类号: TG146.413
作者简介: 王焱辉(1986-),男,重庆北碚人,硕士,工程师,研究方向:难熔金属、稀贵金属材料研发及相关技术,E-mail:wangyan-hui@cmri.cc;; *刘奇,教授级高级工程师,电话:023-60315485,E-mail:liuqi@cmri.cc;
收稿日期: 2019-01-02
基金: 国家科技重大专项项目(2017ZX06004004)资助;
Preparation of High Purity Metallic Vanadium by Electron Beam Melting
Wang Yanhui Liu Qi Li Fang Bo Xinwei Wang Xiaoyu He Haoran
Chongqing Materials Research Institute Co.,Ltd
Chongqing Rare Precious Metals High Efficiency Utilization Engineering Technology Research Center
National Instrument Function Material Engineering Technology Research Center
Abstract:
After cold isostatic pressing and vacuum sintering of vanadium powder into vanadium billet,the purification of vanadium billet was studied by electron beam smelting. EPMA-1720 electron microprobe(EPMA),Olympus-PMG3 optical microscope(OM),inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry(ICP-AES)and oxygen-nitrogen-hydrogen analyzer were used to investigate the micro-morphology,metallographic structure and purity of vanadium billet and melted vanadium ingot,respectively. The experimental results showed that voids existed in the vanadium billet and the microstructure was not compact. The electron beam melting could eliminate the intergranular pore,and the grain boundary of vanadium matrix was tightly bonded and the structure became compact and uniform. The contents of interstitial impurities C,O and N in vanadium metal decreased significantly after electron beam melting. The removal rates were 56.41%,79.17% and 52.38%,respectively. The removal rate of element H was only 37.50% because of its low content,which decreased from 80×10-6 to 50×10-6. As the vapor pressure differences between Si,Al,Mg,P,Cd and V were large,so the removal effect was obvious. Mo and B were refractory impurities with high melting point,and the vapor pressures were lower than that of V,so the removal rates were lower. The purity of vanadium metal was 99.932% after electron beam melting.
Keyword:
vanadium metal; electron beam melting; cold isostatic pressing; vacuum sintering; purity elements;
Received: 2019-01-02
近年随核电工业、航空航天等领域的快速发展,金属钒获得了较好的市场需求,钒产品发展前景良好,进行高纯金属钒制备工艺技术的研发与优化,对促进我国难熔金属材料领域的发展具有重要的意义
[1 ,2 ,3 ]
。高纯金属钒具有中子辐照活性低、传热率高、抗腐蚀性以及优良的高温强度、可加工性能等优点,故成为核电领域候选材料之一
[4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ]
。目前国内外开展了高纯金属钒制备技术及高温下金属钒的力学性能和组织特征的研究
[10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14 ,15 ,16 ,17 ,18 ]
,尤其是探测中子的钒丝作为自给能探测器的关键材料,在国产研发的过程中其纯度、力学性能、使用寿命与国外产品相比还存在差距
[19 ,20 ,21 ,22 ,23 ,24 ]
。
为得到高纯金属钒以便后续加工成钒丝,对钒的纯度和可加工性能提出了更高的要求,而电子束熔炼是一种有效提高金属纯度的方法,工业上广泛用于提纯含有高饱和蒸汽杂质的难熔金属。利用高能量密度的电子束轰击金属,产生高温使难熔金属熔化,由于是在真空条件中进行,利于杂质的蒸发可获得较好的提纯效果。目前关于高纯金属钒的提纯的研究鲜有报道,本文作者拟采用电子束熔炼法制备高纯金属钒,并对其杂质的变化和组织特征进行研究。
1 实验
1.1 钒坯条烧结
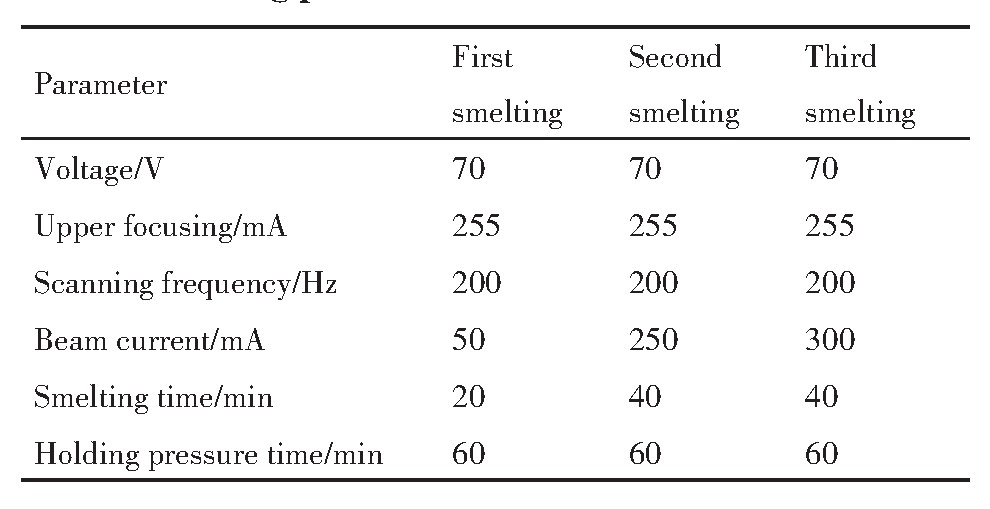
实验原料为市购纯度大于99%的金属钒粉,费氏粒度在10~30μm之间如图1所示(金属钒粉购于南宫盈泰金属材料有限公司)。实验首先将金属钒粉冷等静压成型后再放入真空烧结炉中烧结成坯条,实验设备采用冷等静压机和真空烧结炉。将200 g钒粉装入橡胶模套内,模套内径15 mm、外径20 mm、高度200 mm,两端用橡胶头密封,橡胶头直径15 mm、高度25mm。将装入钒粉的橡胶模套密封好后放入冷等静压机中,压制压力280 MPa,保压时间90 s。冷等静压后将钒坯条脱模,总共压制2 kg钒坯条,然后放入真空烧结炉进行烧结,真空度为1×10-3 Pa,烧结温度制度为500℃保温0.5 h,1100℃保温2 h,1600℃保温1 h,升温速度10℃·min-1 ,随炉冷却。
1.2 钒电子束熔炼
实验所用的电子束熔炼炉如图2所示,其原理是由电子枪发射出的电子束在加速电压作用下,轰击在钒坯条上,使钒坯条熔化滴落到坩埚内形成钒金属液熔池,一些气体杂质和高蒸汽压杂质随之挥发逸出,从而实现钒金属的提纯净化
[16 ]
。实验时将钒坯条装入水冷铜坩埚中,用机械泵、罗兹泵和扩散泵分别抽炉体和电子枪真空,熔炼真空度可达1×10-5 Pa。接通电子枪的电源,电子束光斑形态为圆形,以便使电子束熔炼过程中始终以圆形光斑状态轰击钒坯条,钒坯条熔化后滴入水冷铜坩埚,通过观察窗观察熔炼过程中钒坯条熔化状态,共进行3次熔炼,待完全熔化结束后关闭电源,4 h后打开炉体,取出钒锭。电子束熔炼过程中的实验参数如表1所示。
图1 高纯金属钒粉形貌
Fig.1 EPMA image of high purity vanadium powder
图2 电子束熔炼炉
Fig.2 Electron beam melting furnace
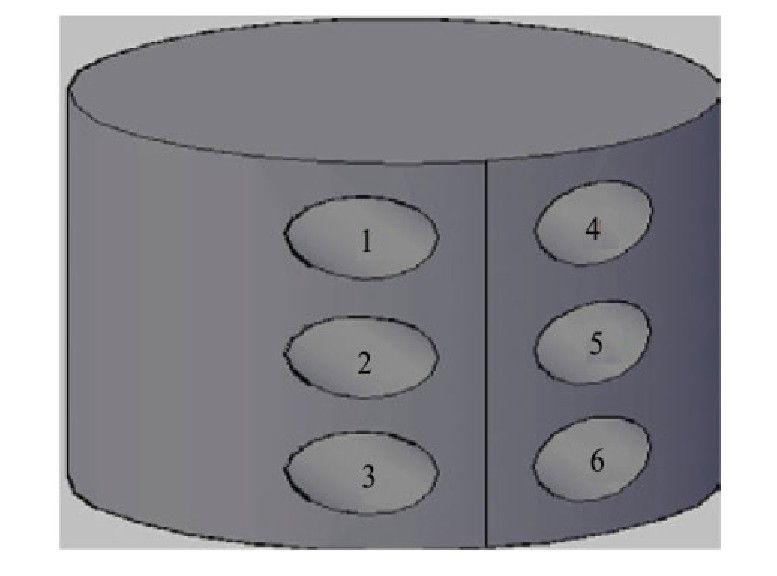
在钒锭的轴向从上向下依次取两组试样,每组3个,如图3所示。其中第一组3个样用碳硫分析仪和氧氮氢分析仪测定样品中的间隙杂质C,H,O,N的含量。第二组3个样,采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱(ICP-AES)检测非间隙杂质元素含量,如B,Cd,Cr,Si,Al,Mg,Mo,P,Fe,取平均值为杂质的含量。采用15%HNO3 ,40%HF和H2 O按体积比1∶1∶2配制腐蚀液,对钒坯条和钒锭抛光后的试样表面进行腐蚀,在Olympus-PMG3型光学显微镜(OM)观察显微金相组织。采用EPMA-1720电子探针(EPMA)观察钒锭底部粗糙表面微观形貌,并用波长分散谱仪(WDS)分析测定杂质元素。
表1 电子束熔炼过程主要实验参数 下载原图
Table1 Main experimental parameters of electron beam melting process
图3 钒锭取样部位示意图
Fig.3 Sampling site sketch map of vanadium ingot
2 结果与讨论
2.1 钒锭形貌
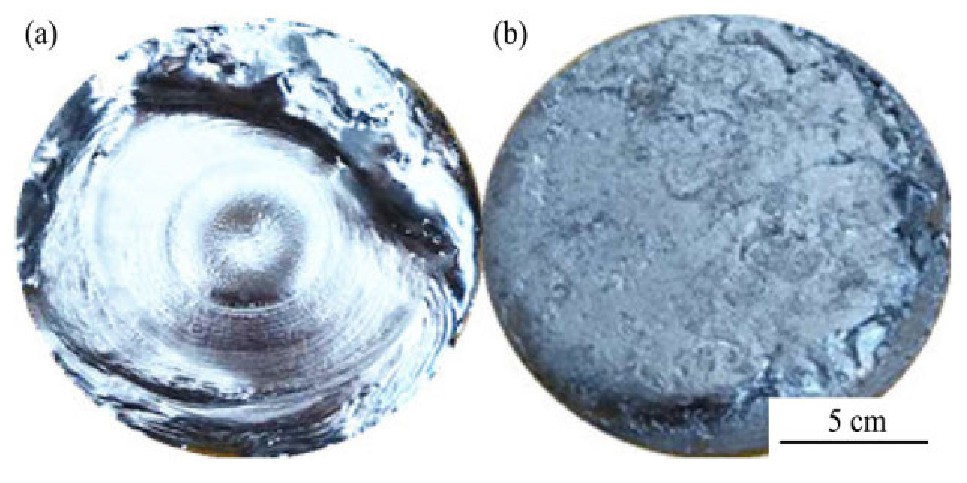
图4为电子束熔炼后钒锭的上部和底部的形貌。图4(a)钒锭上端表面有不规则的圆形熔池,当电子束轰击钒坯条时,钒金属液不断滴入水冷铜坩埚,并逐渐形成金属液熔池。由于顶部熔池的存在,维持液态的时间较长,促进了钒金属液中非金属夹杂物浮起,使钒金属内部组织变得致密均匀。在冷却过程中,熔池中间温度最高,钒锭从水冷铜壁逐渐向内凝固。图4(b)钒锭底部较粗糙且有孔隙,可以明显观测到块状的熔滴形状布满钒锭底部外围一圈。这说明相较于钒锭底部,上端中间的钒锭保持液态的时间更长。其原因一方面是钒液在外圈的熔滴最先与水冷铜坩埚接触,由于铜坩埚有良好的传热效果,导致熔池底部大量的热量被冷却水带走,导致熔炼不充分;另一方面由于电子束轰击产生的热量使中间区域熔池维持较长的液态时间,有利于杂质的挥发和气体排出,而外圈的熔滴由于较早的凝固,气体和杂质来不及排出,导致钒锭底部较粗糙和孔隙的产生。
图4 钒锭上部和底部表面形貌
Fig.4 Top(a)and bottom(b)surface topography of vanadi-um ingot
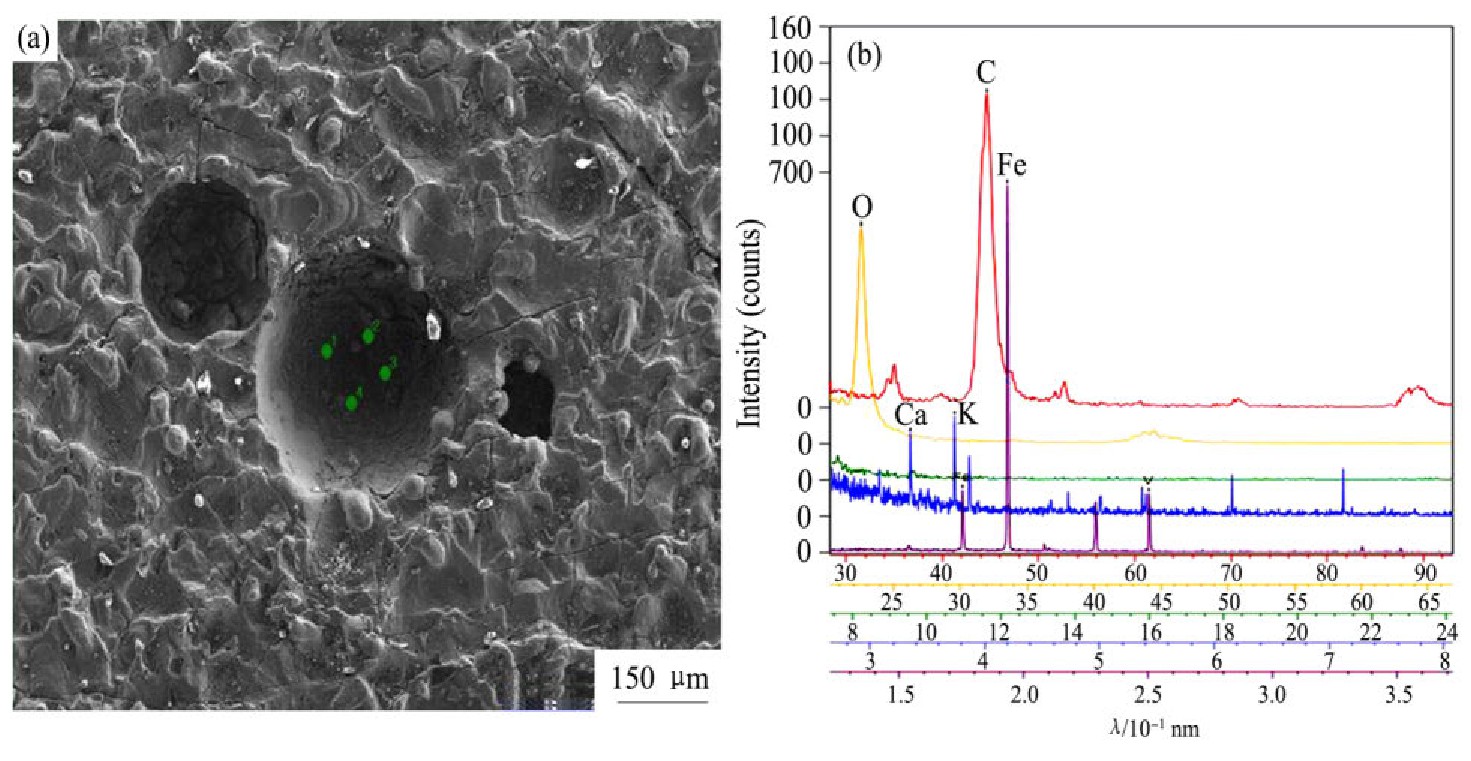
图5(a)为钒锭底部试样微观形貌,可以观察到底部粗糙的表面和明显的气孔、凹坑,尺寸从几十微米至三百微米不等。图5(b)为气孔中WDS波谱分析,分析表明有C,O,Fe,V,K,Ca元素,其中主要含有Fe,C,V,O,而K,Ca元素产生X射线强度较低,含量分别为0.14%和0.08%。
2.2 钒金属组织结构特征
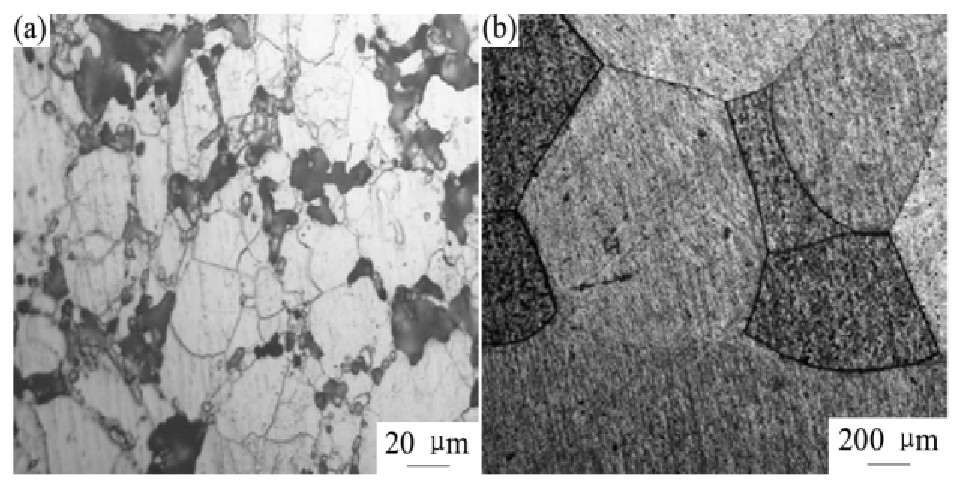
图6(a)为钒烧结坯条金相组织,从图中观察到钒粉经冷等静压和真空烧结后,颗粒依然存在,白色颗粒周围布满烧结空隙。根据Hirschhorn提出的球形颗粒烧结模型,用来分析粉末烧结的致密化过程
[21 ,22 ]
。烧结的早期阶段,粉末接触部分首先产生烧结颈并长大,在此阶段位错等缺陷向孔隙运动引起物质的迁移是材料致密化的主要动力。烧结中期阶段,早期形成的孔隙逐渐发展为连通的圆柱状孔,随致密化进行孔隙收缩,部分孔隙开始封闭,此阶段晶界扩散导致的物质迁移是致密化的主要机制。后期晶粒进一步长大,孔隙聚集形成相互独立的闭孔,因此烧结的致密化达不到理论金属密度。图6(b)为电子束熔炼后钒锭金相组织,钒坯条经电子束熔炼后,钒金属液随温度降低而逐渐凝固,钒晶粒形核并长大转变为晶界面,晶间孔隙得以消除,组织变得较均匀,钒基体晶界结合紧密,金属致密度得到大幅提高
[23 ]
。
2.3 钒金属杂质元素分析
间隙杂质元素分析:C,O,N,H是钒金属中非常有害的间隙杂质元素,在高温下与V易生成VN,VH,VC以及V2 O3 ,V2 O5 等化合物,显著降低钒的塑性和强度,严重影响钒金属的纯度和可加工性能
[23 ]
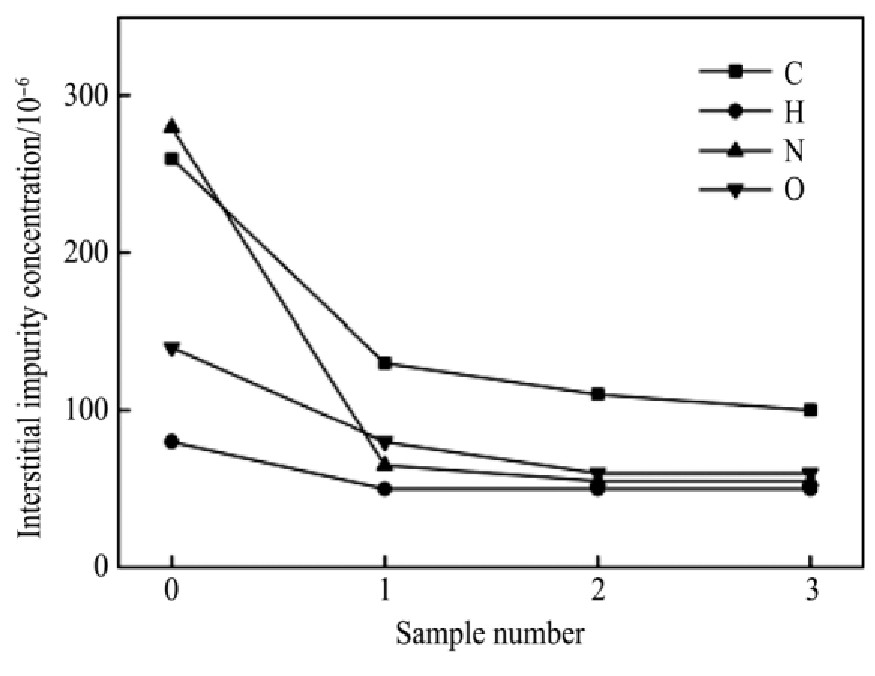
。钒坯条经真空电子束熔炼后,其间隙杂质元素可能在钒锭中分布不均匀,为研究间隙杂质元素在熔炼前后的变化情况,分别取钒坯条初样(图7样品0)和钒锭轴向样品1,2,3,分析间隙杂质元素熔炼前后变化,如图7所示。从图7看出,经过电子束熔炼后,钒金属间隙杂质元素C,O,N的含量显著降低,其去除率分别达到56.41%,79.17%,52.38%(以熔炼后样品1,2,3平均值计算),而H含量本身较少,从熔炼前80×10-6 降低到50×10-6 ,去除率为37.5%。在电子束熔炼过程中,大部分间隙杂质元素向熔体表面扩散,并以气体的形式蒸发,C元素可与O,H反应生成CO,CH气态挥发产物而去除。
图5 钒锭底部试样微观形貌和WDS
Fig.5 Micromorphology of vanadium ingot bottom sample(a)and WDS(b)
图6 钒金相组织
Fig.6 OM images of vanadium
(a)Vanadium sintered billet;(b)Vanadium ingot
非间隙杂质元素分析:根据真空电子束熔炼提纯的原理,在高真空度、高温条件下,饱和蒸气压大的元素挥发性大于饱和蒸气压小的元素。利用不同杂质元素与钒的蒸气压的差异,来达到去除杂质元素的目的。经过电子束熔炼处理后的钒锭取第二组样品4,5和6分析非间隙杂质元素的含量,取其平均值如表2所示。从表2可以看出,非间隙杂质元素Si,Al,Mg,P,Cd含量明显降低,其去除率大于50%,而Mo,B,Cr,Fe含量有所降低但不明显,去除率小于30%。各元素蒸气压(P)随温度(T)高低而异,其关系可用克劳修斯-克莱普朗方程表示为
[25 ]
:
图7 间隙杂质含量变化
Fig.7 Interstitial impurity content change
式中,Vl 为1 mol液体体积;Vg 为蒸发后得体积;L为吸收蒸发潜热。变形后得:
式中,A,B,C和D均为常数,可根据热力学数据手册查询
[26 ]
,通过计算所得绘制各非间隙杂质元素蒸气压与温度的关系曲线图,如图8所示。从图8可看出,Cd,P,Mg与V的蒸气压压差较大;其次Si,Al,Cr,Fe与V的蒸气压相近;而Mo,B属于高熔点难熔杂质,蒸气压较低。结合表2数据可以发现,与钒蒸气压差较大的杂质元素,去除率较大,反之则较小,杂质的去除率基本符合各元素与钒蒸气压差的变化规律。经电子束熔炼后钒金属纯度达到99.932%,说明电子束熔炼利用蒸气压差能有效去除钒金属中的杂质。
图8 杂质元素蒸气压与温度的关系图
Fig.8 Relation diagram of vapor pressure and temperature of impurity element
表2 非间隙杂质含量 下载原图
Table 2 Non-interstitial impurity content
3 结论
1.钒粉经过冷等静压和真空烧结,钒坯条金相显微组织存在孔隙不致密。经电子束熔炼后,晶间孔隙得以消除,钒基体晶界结合紧密,组织变得致密较均匀。
2.经过电子束熔炼后,钒金属间隙杂质元素C,O,N的含量显著降低,其去除率分别达到56.41%,79.17%和52.38%,而H含量本身较少,从熔炼前80×10-6 降低到50×10-6 ,去除率为37.50%。
3.非间隙杂质元素Si,Al,Mg,P,Cd的蒸气压与V的蒸气压压差较大,去除效果较明显。而Mo,B属于高熔点难熔杂质,蒸气压差小去除率偏低,钒金属经电子束熔炼后纯度达到99.932%。
参考文献
[1] Yang S L. Vanadium Titanium Material[M]. Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press,2007. 62.(杨绍利.钒钛材料[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,2007. 62.)
[2] Liao S M,Bo T L. Foreign Vanadium Metallurgy[M].Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press,1985. 3.(廖世明,柏谈论.国外钒冶金[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,1985. 3.)
[3] Xie D H,Ye L S,Len B Y,Zeng J Q,Li Y Q. Study of microstructure and properties of vanadium manufactured by hot isostatic pressing[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology,2007,25(5):360.(谢东华,叶林森,冷邦义,曾家权,李耀强.热等静压钒的组织和性能研究[J].粉末冶金技术,2007,25(5):360.)
[4] Len B Y,Xian X B,Pang X X,Ye L S,Liu T T. High temperature mechanical properties and characteristics of pure vanadium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2011,40(8):1470(冷邦义,鲜晓斌,庞晓轩,叶林森,刘婷婷.纯钒的高温力学性能及断口特征[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2011,40(8):1470.)
[5] Xian X B,Ye L S,Len B Y,Xie D H,Xie M L,Chi Y G. Study of hot isostatic pressing preparation and properties of pure vanadium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2010,39(5):928.(鲜晓斌,叶林森,冷邦义,谢东华,谢茂林,迟永刚.纯钒制备及其性能[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2010,39(8):928.)
[6] Lei K P V,Campbell R E,Sullivan T A. Electrolytic preparation of vanadium from vanadium carbide[J].Journal of Electrochemical Society,1973,120(2):211.
[7] Lei K P V,Sullivan T A. Electrorefining of vanadium prepared by carbothermic reduction of V2 O5 [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B,1971,2(8):2312.
[8] Lei K P V,Sullivan T A. High purity vanadium[J].Journal of the Less Common Metals,1968,14:145.
[9] Wang C T,Baroch E F,Worcester S A,Shen Y S.Preparation and properties of high-purity vanadium and V-15Cr-5Ti[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B,1970,1(6):1683.
[10] Carlson O N,Owen C V. Preparation of high-purity vanadium metal by the iodide refining process[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Society,1961,108(21):88.
[11] Schmidt F A,Warner J C. Electrotransport of carbon,nitrogen and oxygen in vanadium[J]. Journal of LessCommon Metals,1967,13(5):493.
[12] Carlson O N,Schmidt F A,Alexander D G. Electrotransport purification and some characterization studies of vanadium metal[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B,1972,3(5):1249.
[13] Campbell T T,Schaller J L,Block F E. Preparation of high-purity vanadium by magnesium reduction of vanadium by magnesium reduction of vanadium dichloride[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B,1973,4(1):237.
[14] Chun Y B,Ahn S H,Shin D H,Hwang S K. Combined effects of grain size and recrystallization on the tensile properties of cryorolled pure vanadium[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2009,508(1):253.
[15] Zhang Z Z,Yu S H,Chun Y B,Shin D H,Hwang S K.Grain refinement of pure vanadium by equal channel angular pressing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2008,479(1):285.
[16] Cai Z F,Zhang Z M,Guo Z C,Hui Q T. Direct electrochemical reduction of solid vanadium oxide to metal vanadium at low temperature in molten CaCl2 -NaCl[J].International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials,2012,19(6):499.
[17] Xie D H,Liu K Z,Xian X B,Ye L S,Chen Y P. Effect annealing temperature on the microstructure and properties of pure vanadium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2008,37(9):1566.
[18] Luo L,Wu W Y,Bian X,Qi J B. Research progress of vanadium-based soild solution hydrogen storage alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2017,41(11):1265.(罗龙,吴文远,边雪,齐健博.钒基固溶体贮氢合金的研究进展[J].稀有金属,2017,41(11):1265.)
[19] Xiong W H,Wu J,Zhang Z H,Yu Y J,Zhang Y,Deng P. Domestic development of self-powered vanadium detector for qinshan third nuclear power plant[A].The 5th Nuclear Reactor Instrument Conference. Xining[C]. 2009. 201.(熊伟华,吴军,张振华,俞亦军,张云,邓鹏.秦山第三核电厂堆芯自给能钒探测器国产化研制[A].第五届核反应堆用核仪器学术会议[C].西宁,2009. 201.)
[20] Zhang H L,Sun T,Li J Y. The smelting of electron beam and the smelting equipment[J]. Metallurgical Equipment,2003,(4):32.(张文林,孙涛,李娟莹.电子束熔炼及其设备[J].冶金设备,2003,(4):32.)
[21] Hirschhorn J S. Introduction to Power Metallurgy[M].New York:American Powder Metallurgy Institute,1969. 172.
[22] Huang P Y. Theory of Power Metallurgy.(2nd Ed.)[M]. Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press,2004. 267.(黄培云.粉末冶金原理(第2版)[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,2004. 267.)
[23] Cui Z Q,Tan Y C. Physical Metallurgy and Heat Treatment.(2nd Ed.)[M]. Beijing:Machine Industry Press,2011. 33.(崔忠圻,覃耀春.金属学与热处理(第2版)[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2011. 33.)
[24] Li R H,Zhang P B,Li X Q,Zhang C,Zhao J J. Firstprinciples study of the behavior of O,N and C impurities in vanadium solids[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials,2013,435(3):71.
[25] Dai Y N,Yang B. Vacuum Metallurgy of Nonferrous Metal Materials[M]. Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press,2000. 21.(戴永年,杨斌.有色金属材料的真空冶金[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,2000. 21.)
[26] Liang Y J,Che Y C. Thermodynamic Date Manual of Inorganic Substance[M]. Shenyang:Northeastern University Press,1993. 513.(梁英教,车荫昌.无机物热力学数据手册[M].沈阳:东北大学出版社,1993. 513.)