剪切变形对厚壁圆形贮液池的影响
夏桂云1,李传习1,曾庆元2
(1. 长沙理工大学 土木与建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410076;
2. 中南大学 土木建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410075)
摘 要:
摘 要:将池壁厚度较大的圆形贮液池当作中厚壳圆筒,考虑剪切变形的影响,建立贮液池结构分析的中厚壳理论,其微分方程与Winkler地基上Timoshenko梁的微分方程一致,当贮液池池壁剪切刚度取无穷大时,其可退化成相应薄壳理论,是一个通用模型。利用初参数法,推导微分方程的解和有限元列式,分析底部固结、顶部自由圆形贮液池在三角形分布荷载和池顶弯矩作用下,其环向力系数、弯矩系数随池壁厚度、高度的变化,并与不考虑剪切变形影响的计算结果进行比较。数值计算结果表明:在圆形贮液池中考虑剪切变形影响的挠度等计算结果偏小;壁厚越大,计算结果越小;剪切变形对环向力和径向位移的影响比对弯矩和剪力的影响大,其影响程度与贮液池结构、边界条件及作用荷载形式有关。
关键词:
中图分类号:TU991 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)05-1430-07
Shear deformation influence on cylindrical liquid-storage tank with thick wall
XIA Gui-yun1, LI Chuan-xi1, ZENG Qing-yuan2
(1.School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha 410076, China;
2. School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: Treating cylindrical liquid-storage tank with relatively thick wall as thick shell cylinder, and considering the shear deformation effect, analysis theory of thick shell was established, whose differential equation was the same as the interactive equation of Timoshenko beam on Winkler foundation. When the shear stiffness of tank wall tended to infinite, thick shell theory was degenerated into thin shell theory. So the thick shell theory was a general model. Using initial parameter method, solutions to differential equation were derived and finite element formulation was established. The solutions to the cylindrical liquid-storage tank under triangular distributing load and top moment were analyzed. To demonstrate the shear deflection effect, loop force and moment coefficients were presented to describe the change with the tank height and thickness. Results of thin shell and thick shell theories were compared. The results show that shear deformation leads to small results of deflection and so on. The thicker the tank walls, the less the computing results. Shear deformation affects loop force and radial displacement more than the moment and shear force, which depends on the structures, boundary conditions and loads.
Key words: liquid-storage tank; shear deformation; thick shell; initial parameter
贮液池由于具有造价低、结构简单、成型方便、防渗、防腐、耐久等优点,在石油、化工、冶金、给排水等工业和民用建筑中得到广泛应用。当池壁厚度远小于池半径时,可采用薄壳理论进行静力分析[1]。对于贮液池其他力学问题,刘声远等[2]应用理论分析与试验测试的方法分析了温度对圆形贮液池开裂的影响,并提出池壁裂缝补修和设计处理方法;何德湛[3]分析了无粘结预应力技术的特点和优势,指出了其在圆形水池中具有广阔的应用前景;Moncarz等[4]研究了废水处理厂的消化池开裂原因,并对1座消化池倒塌的原因进行了论证和调查;薛明德等[5]对圆柱壳大开孔应力集中问题进行了分析,宋天舒等[6]对圆柱壳小开孔应力集中问题进行了分析,解决了圆形贮液池开孔接管的难题;Malhotra等[7]对圆形贮液池在水平地震作用下的底部掀起问题进行了研究,建立了地震作用下圆形贮液池的动力分析方法;陆铁坚等[8]针对圆筒形结构提出了改进的柱壳曲条元法,对圆形贮液池结构分析有很好的借鉴作用。一般认为,薄壳理论只适用于壁厚与曲面最小半径之比h/R≤1/20的情 况[9],实践中,有些中小型贮液池由于半径较小,池壁较厚,不在薄壳理论研究的范围内,此时,应采用考虑剪切变形影响的中厚壳理论[9-10]。Reissner[10]提出了Reissner扁壳理论,并对受扭球形浅壳的应力集中现象进行了分析。胡超等[11]应用Reissner扁壳理论对厚壁容器圆柱壳任意开孔应力集中问题进行了研究。由于Reissner扁壳理论用法向位移函数w0、应力函数Φ0及广义位移函数f0表示厚圆柱壳在外载作用下的应力状态,微分方程复杂,阶次较高,求解困难,在此,本文作者根据圆形贮液池轴对称特点,建立考虑剪切变形影响的中厚圆柱壳理论,对底部固结、顶部自由圆形贮液池在三角形分布荷载和顶端集中弯矩作用下的受力进行分析,探讨剪切变形的影响。
1 计算理论
将池壁较厚的圆形贮液池简化为中厚圆柱壳,其荷载主要有池内液体侧压力、两端弯矩荷载和边界的约束。由于结构和荷载具有轴对称性(如图1所示),中厚贮液池的中面环向应变(![]() )、竖向应变(
)、竖向应变(![]() )、环向线段主曲率(χθ=-w/R2)仍与薄壳理论[1]的一致。
)、环向线段主曲率(χθ=-w/R2)仍与薄壳理论[1]的一致。
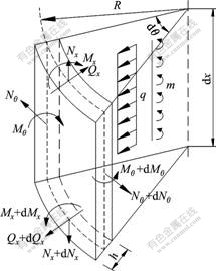
图1 圆形贮液池微元体受力分析
Fig.1 Force analysis of free body for cylindrical liquid-storage tank
考虑剪切变形的影响,中厚贮液池的竖向主曲率取转角对坐标的导数,得[12]:
![]()
贮液池中,距中面为z的任意点应变和中面应变的关系为:
![]()
根据中厚壳小挠度的弹性理论,不考虑垂直于中面方向的正应力σZ,将其作为平面应力问题,壳体中应力—应变关系为:

由小挠度理论可知,式(4)中w/R2较小,可忽略不计[1],则由式(4)的第3式和第4式,可知竖向弯矩和环向弯矩分别为:
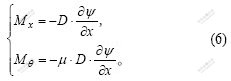
不计自重,在轴对称静水压力作用下,壳体顶端边界轴力为0,由式(4)第1式可知:
![]()
将式(7)代入式(4)的第2式,有:
![]()
考虑剪切变形影响后,中厚圆柱壳结构微段的平衡方程为:

一般地,壳体中较少有分布弯矩作用,令m=0,将式(4),(6)和(8)代入式(9),将挠度w、转角ψ解耦后,可建立圆形中厚壳在分布荷载q作用下的微分方程:
![]()
从式(10)可以看出,考虑剪切变形影响的圆形贮液池微分方程与Winkler地基上Timoshenko深梁的微分方程[13]一致。当剪切刚度C→∞时,式(10)退化成不考虑剪切变形的贮液池微分方程[1],其与Winkler地基上Euler梁的微分方程一致。因此,式(10)是1个从薄壳到中厚壳都适应的通用计算模型。
2 初参数解
式(10)可采用多种方法进行求解,如解析法、差分法、级数法、初参数解法等,其中,初参数解法是一种较优方法。
当不考虑作用荷载时,经推导,式(10)的解用初参数表示为:
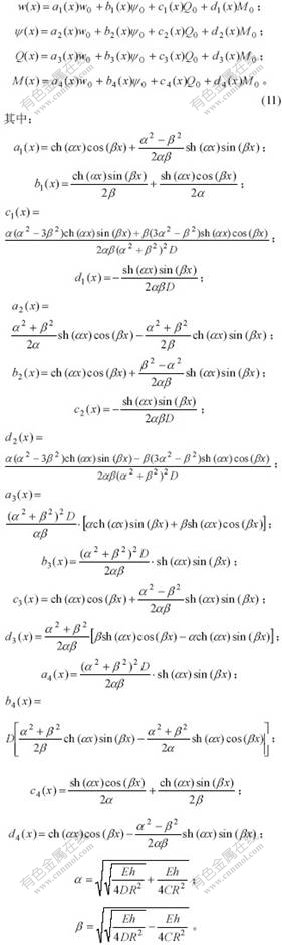
3 底部固结和顶部自由的圆形贮液池受三角形分布荷载作用的参数解
如图2所示,底部固结和顶部自由的圆形贮液池受三角形分布荷载作用,其初参数可由边界条件确定。由底部固结和顶部自由边界条件知:
当x=0时,M(0)=M0=0,Q(0)=Q0=0;
当x=H时,w(H)=0,ψ(H)=0。
结合三角形分布荷载,解得挠度、转角的初参数值如下:
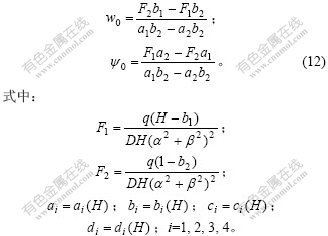
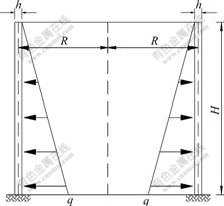
图2 底部固结和顶部自由贮液池受三角形荷载作用
Fig.2 Cylindrical liquid-storage tank under triangular distributing load with fixed-free end
解出初参数值后,圆形贮液池沿池高不同位置的变形、内力可根据式(11)和(12)进行推导,相应的环向内力、剪力、弯矩系数[1]分别为:
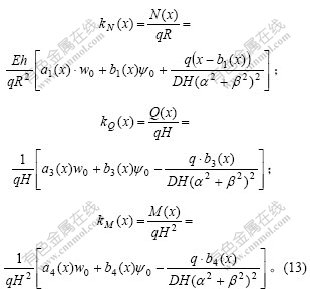
4 底部固结和顶部自由圆形贮液池受顶部集中弯矩M0作用的参数解
底部固结和顶部自由的圆形贮液池如图3所示。在顶部受集中弯矩M0作用,其初参数可由边界条件确定。由底部固结、顶部自由边界条件知:
当x=0时,M(0)=M0,Q(0)=Q0=0;
当x=H时,w(H)=0,ψ(H)=0。
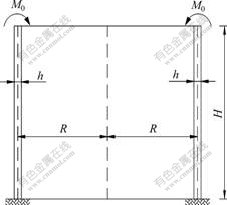
图3 顶端弯矩作用的贮液池
Fig.3 Cylindrical liquid-storage tank under top moment with fixed-free end
由边界条件确定的顶部位移和转角的初参数值为:
![]()
相应的轴力、剪力、弯矩系数[1]为:
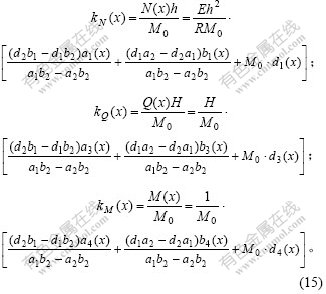
对于其他形式的作用荷载和边界条件,文献[1]运用薄壳理论对16种情况进行了分析,并给出了计算结果。采用本文的中厚壳理论和初参数法同样可以进行推导。
5 有限元列式
初参数解法一般只便于计算贮液池壁厚相同的情况,对于变厚度情况则非常复杂,可采用有限元方法求解。定义单元的结点位移、结点力方向如图4所示,根据初参数解法,将其内力与位移关系改成矩阵形式,则有限元平衡方程为:
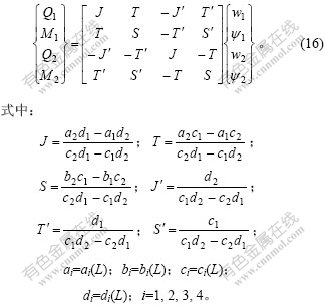
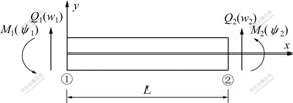
图4 有限元模型
Fig.4 Finite element model
6 算 例
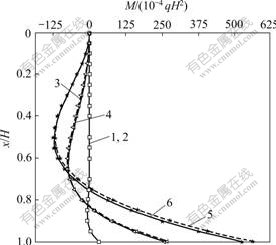
算例1 如图2所示的圆形贮液池底端固结,顶端自由,高H=4.0 m,半径R=5.0 m,池壁材料为C50混凝土,弹性模量E=3.45×104 MPa,剪切模量G=1.38×104 MPa,改变壁厚h(计算中取h/H分别为0.001,0.1和0.3共3种情况),在三角形分布荷载作用下,分别采用薄壳理论[1]和本文中厚壳理论,用初参数法和有限元法计算环向力系数、竖向弯矩系数随池高、壁厚的变化结果如图5~6所示。由于采用有限元法所得结果与采用初参数法所得结果完全一致,故在图5和图6中只列出薄壳理论结果与中厚壳理论的初参数法结果。
从图5和图6可以看出,当贮液池池壁厚度较薄(h/H为0.001和0.1)时,考虑剪切变形与不考虑剪切变形的影响,其环向力系数、弯矩系数几乎相同。当贮液池池壁厚度较大(h/H为0.3)时,考虑剪切变形影响,其环向力系数、弯矩系数比不考虑剪切变形影响的相应计算结果偏小。本算例中环向力系数最大时,其偏差为20.38%(当x/H=0时),弯矩系数最大时,其偏差为6.13%(当x/H=1.0时)。由此可见,剪切变形对厚壁圆形贮液池的受力有一定影响。

1—h/H=0.001,薄壳理论;2—h/H=0.001,中厚壳理论;
3—h/H=0.1,薄壳理论;4—h/H=0.1,中厚壳理论;
5—h/H=0.3,薄壳理论;6—h/H=0.3,中厚壳理论
图5 三角形荷载作用环向力系数与池高的变化关系
Fig.5 Relationship between loop axial parameter and height for cylindrical liquid-storage tank under triangular distributing load
1—h/H=0.001,薄壳理论;2—h/H=0.001,中厚壳理论;
3—h/H=0.1,薄壳理论;4—h/H=0.1,中厚壳理论;
5—h/H=0.3,薄壳理论;6—h/H=0.3,中厚壳理论
图6 三角形荷载作用弯矩系数与池高的变化关系
Fig.6 Relationship between moment parameter and the height for cylindrical liquid-storage tank under triangular distributing load
算例2 如图3所示的顶部自由、底部固结的圆形贮液池,其材料、结构尺寸与算例1的相同,改变壁厚h(计算中取h/H分别为0.001,0.1和0.3这3种情况),在顶端集中弯矩M0作用下,分别采用薄壳理论[1]和中厚壳理论计算的环向力系数、竖向弯矩系数随池高、壁厚变化如图7~8所示。
从图7和图8可以看出,当贮液池壁厚较小(h/H为0.001和0.1)时,考虑剪切变形与不考虑剪切变形的影响,所得环向力系数、弯矩系数几乎相同。当贮液池池壁厚度较大(如h/H为0.3)时,考虑剪切变形影响,环向力系数、弯矩系数比不考虑剪切变形影响的相应计算结果偏小,本算例中,当环向力系数最大时,其偏差为9.82%(当x/H=0时);当竖向弯矩系数最大时(x/H=1.0)虽无偏差,都为1.0,但竖向弯矩系数的最大偏差为2.8%(x/H=0.360 2)。该算例再次证明了剪切变形的影响。
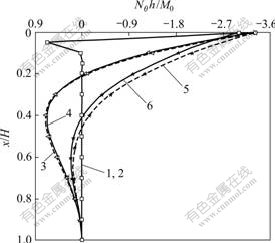
1—h/H=0.001,薄壳理论;2—h/H=0.001,中厚壳理论;
3—h/H=0.1,薄壳理论;4—h/H=0.1,中厚壳理论;
5—h/H=0.3,薄壳理论;6—h/H=0.3,中厚壳理论
图7 顶端弯矩作用下环向力系数与池高的变化关系
Fig.7 Relationship between loop axial load parameter and the height for cylindrical liquid-storage tank under concentrated moment at top
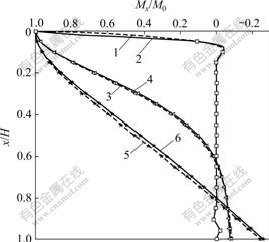
1—h/H=0.001,薄壳理论;2—h/H=0.001,中厚壳理论;
3—h/H=0.1,薄壳理论;4—h/H=0.1,中厚壳理论;
5—h/H=0.3,薄壳理论;6—h/H=0.3,中厚壳理论
图8 顶端弯矩作用竖向弯矩系数与池高的变化关系
Fig.8 Relationship between moment parameter and the height for cylindrical liquid-storage tank under concentrating moment at top
7 结 论
a. 将圆形贮液池作为中厚壳结构,建立了考虑剪切变形影响的圆形贮液池微分方程。这是一种中厚壳理论,也是传统薄壳理论的推广和发展。当不考虑剪切变形影响时,该方程可退化为贮液池薄壳理论,因此,本文提出的中厚壳理论是圆形贮液池从薄壳到中厚壳都适应的通用模型。
b. 考虑剪切变形影响的中厚圆形贮液池微分方程与Winkler地基上Timoshenko梁微分方程一致,当不考虑剪切变形影响时,与Winkler地基上Euler梁的微分方程一致。导出的初参数解、有限元可作为Winkler地基上Timoshenko梁的求解方法。
c. 当贮液池池壁厚度较小时,考虑剪切变形影响与不考虑剪切变形影响所计算的环向力系数和竖向弯矩系数几乎一致,证明本文所建立的圆形贮液池中厚壳理论的正确性;当贮液池壁厚度较大时,考虑剪切变形影响的中厚壳理论与不考虑剪切变形影响的薄壳理论计算结果有一定偏差,说明剪切变形在池壁厚度较大时有一定影响;池壁厚度越大,其偏离程度越大,影响程度与圆形贮液池结构、边界条件和作用荷载形式有关。
d. 考虑剪切变形影响计算的环向力系数、弯矩系数都比不考虑剪切变形影响的计算结果偏小。
参考文献:
[1] 湖北给水排水设计院. 钢筋混凝土圆形水池设计[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1977: 12-74.
Hubei Design Institute of Water Supply and Drainage. Design of reinforced concrete circular water tank[M]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 1977: 12-74.
[2] 刘声远, 孙 颖, 齐向阳. 钢筋混凝土水池裂缝的分析与处理[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报, 2007, 26(2): 228-231.
LIU Sheng-yuan, SUN Ying, QI Xiang-yang. Analysis and treatment of reinforced concrete pool crevice[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University, 2007, 26(2): 228-231.
[3] 何德湛. 无粘结预应力技术在圆形水池中的推广和应用[J]. 土木工程学报, 2002, 35(4): 109-110.
HE De-zhan. Application of unbonded prestress technique to circular water tank[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(4): 109-110.
[4] Moncarz P D, Griffith M, Noakowski P. Collapse of a reinforced concrete dome in a wastewater treatment plant digester tank[J]. ASCE: Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2007, 21(1): 4-12.
[5] 薛明德, 陈 伟, 邓 勇. 圆柱壳大开孔的薄壳理论解[J]. 力学学报, 1995, 27(4): 482-488.
XUE Min-de, CHEN Wei, DENG Yong. The thin shell theoretical solution for cylindrical shells with large openings[J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 1995, 27(4): 482-488.
[6] 宋天舒, 刘殿魁. 圆柱壳小开孔理论解在工程实践中的应用[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2000, 21(9): 961-965.
SONG Tian-shu, LIU Dian-kui. An Application of theoretical solutions about cylindrical shells with small openings[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2000, 21(9): 961-965.
[7] Malhotra P K, Veletsos A S. Uplifting analysis of base plates in cylindrical tanks[J]. ASCE: Journal of Structural Engineering, 1994, 120(12): 3489-3505.
[8] 陆铁坚, 余志武, 蒋有良. 高层建筑筒体结构三维静力分析的改进条元法[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 35(1): 133-137.
LU Tie-jian, YU Zhi-wu, JIANG You-liang. Improved finite strip method of three dimensional static analysis of tall building framed tube and tube-in-tube structure[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2004, 35(1): 133-137.
[9] Reissner E. On the effect of transverse shear deformability on stress concentration factors for twist and sheared shallow spherical shells[J]. ASME: Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1986(53): 597-601.
[10] Reissner E. A note on the linear theory of shallow shear deformable shell[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 1982, 33: 425-427.
[11] 胡 超, 刘殿魁, 马兴瑞, 等. 厚壁圆柱壳开孔应力集中问题的复变函数解法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 1998, 19(5): 376-384.
HU Chao, LIU Dian-kui, MA Xing-rui, et al. On the stress concentration in thick cylindrical shells with an arbitrary cut out[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1998, 19(5): 376-384.
[12] 胡海昌. 弹性力学的变分原理及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981: 512-564.
HU Hai-chang. Variational principal of elasticity and its applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1981: 512-564.
[13] Metin A. Stiffness-matrix formulation of beams with shear effect on elastic foundation[J]. ASCE: Journal of Structural Engineering, 1995, 121(9): 1265-1270.
收稿日期:2008-09-08;修回日期:2008-11-25
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50778024);中国博士后基金资助项目(20080441177)
通信作者:夏桂云(1972-),男,湖南湘阴人,博士,副教授,从事桥梁与结构工程的教学和科研工作;电话:13974885367;E-mail: xiagy72@163.com


