地基沉降对弹性地基梁的影响
夏桂云1,李传习1,曾庆元2
(1. 长沙理工大学 土木与建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410076;
2. 中南大学 土木建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410075)
摘要:考虑剪切变形的影响,采用Timoshenko梁理论和初参数法分析两端固结、两端简支的弹性地基梁由于地基沉降造成的影响,建立确定悬空长度的超越方程,导出变形和内力的解析解。通过算例分析悬空长度随荷载的变化,比较局部悬空Winkler地基梁在均布荷载作用下挠度、转角、剪力、弯矩的Bernoulli-Euler梁理论结果和Timoshenko梁理论结果,比较地基不同沉降下的变形与内力。研究结果表明:采用Bernoulli-Euler梁理论计算的悬空长度偏大,采用Bernoulli-Euler梁理论计算的局部悬空弹性地基梁的挠度、转角、剪力、弯矩比相应的Timoshenko梁的理论结果大,地基沉降分析中应考虑剪切变形的影响。
关键词:
中图分类号:O342;TB115 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)06-1780-06
Influence of foundation settlement on elastic foundation beam
XIA Gui-yun1, LI Chuan-xi1, ZENG Qing-yuan2
(1. School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha 410076, China;
2. School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: Considering the effect of shear deformation, Timoshenko beam theory and initial parameter method were used to analyze the settlement influences of elastic foundation beam with two fixed-edges and two simply-supported edges. The transcendent equation of hanging length was established. The solutions of deformations and internal forces were presented. The changing relationship between hanging length and load was studied by examples. Deflections, slopes, shear forces and moments of Bernoulli-Euler beam theory and Timoshenko beam theory were compared for locally hanged beams on Winkler foundation under distributing load. Deflections and internal forces of different settlements were compared. The results show that hanged length derived by Bernoulli-Euler beam theory is relatively large. Deflection, slope, shear force and moment calculated by Bernoulli-Euler beam theory are larger than those by Timoshenko beam theory. Shear deformation influence must be considered for the analysis of foundation settlement.
Key words: elastic foundation beam; shear deformation; foundation settlement; initial parameter
弹性地基梁在土木工程中获得了广泛应用,特别是在铁路、公路、船坞、船闸、房屋基础、地下结构等工程设计中以其简单、适用而备受青睐[1-5]。在实践中经常遇到弹性地基梁、板的地基沉降问题,如公路桥梁的桥头搭板由于地基沉降造成内力加大而出现开裂和损毁现象;水泥混凝土路面由于地基沉降而出现唧泥现象;工业与民用建筑的条型基础由于地基沉降而引起房屋开裂现象等。若沉降较小,则地基梁成为一部分为地基梁、另一部分为悬空的普通梁结构;若沉降过大,则地基梁悬空成完全的普通梁。为此,刘人通[6]研究了局部塌陷Winkler地基梁的受力问题,并按概率预测的最危险塌陷中心位置和半径来确定最大内力和位移,以此作为梁的设计和验算依据,其不足是没有考虑梁的剪切变形影响。Selvadurai[2]认为,弹性地基梁的剪切变形影响显著,其影响程度受梁的刚度和地基刚度比值的支配,一般弹性地基短梁、厚梁和局部高度承载的地基梁应考虑剪切变形的影 响[7-12]。胡海昌[13]研究了刚性地基的沉降问题,采用Timoshenko深梁理论,得到地基反力为分布力,在分界点上没有像初等梁理论那样出现反力集中现象。但其不足之处是采用刚性地基,将其作为一接触问题处理。袁聚云等[14]分析了在中心荷载作用下刚性板的地基沉降及地基反力,比较了各物理参数的影响。在此,本文作者采用Timoshenko深梁理论研究Winkler地基沉降的影响,并讨论地基整体沉降情况。
1 两端固结的弹性地基梁
对于两端固结的弹性地基梁,在均布荷载和地基沉降的作用下,其计算模型可简化为如图1所示的结构。由于地基整体沉降Δ,造成端部I段范围内悬空,为普通梁结构;Ⅱ段由于地基的支承反力,为弹性地基梁。对于Ⅰ段,在均布荷载作用下,用考虑剪切变形影响的Timoshenko深梁理论进行分析,其微分方 程[13]如下:
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
式中:D=EI;C=nGA;E为弹性模量;G为剪切模量;I为抗弯惯矩;A为截面面积;n为剪切系数。
取梁与地基接触处的临界点O为坐标原点,以原点的挠度w0、转角ψ0、剪力Q0和弯矩M0为初参数,显然w0=Δ。利用初参数法,可得到I段梁的变形和内力解为:
![]() (3)
(3)
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() (5)
(5)
![]() (6)
(6)
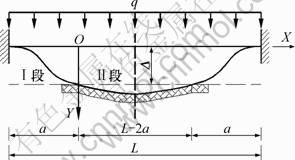
图1 局部悬空的两端固结弹性地基梁
Fig.1 Elastic foundation beam of local hang
对于Ⅱ段,由于地基沉降Δ,采用Winkler地基模型,其地基反力p=K(w-Δ)。采用考虑剪切变形影响的Timoshenko深梁理论,在均布荷载作用下,其微分方程如下:
![]() (7)
(7)
![]() (8)
(8)
上式可简化为w的微分方程[15]:
![]() (9)
(9)
从式(9)可以看出:地基沉降效应在微分方程中相当于KΔ的均布荷载。不考虑q的变化,得式(9)用初参数表示的解为:
![]()
![]() (10)
(10)
![]()
![]() (11)
(11)
![]()
![]() (12)
(12)
![]()
![]() (13)
(13)
式中:
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]()
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]()
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;![]() 。
。
根据结构左端固结的边界条件,由式(3)和(4)可知,当x=-a时,有以下公式成立:
![]() (14)
(14)
![]() (15)
(15)
根据结构的对称性,当x=L/2-a时,ψ=0,Q=0,有:
![]() (16)
(16)
![]() (17)
(17)
式中:Ai,Bi,Ci和Di分别为函数Ai(x),Bi(x),Ci(x)和Di(x)在x=L/2-a时的值;i=1,2,3,4。
结合式(15)~(17),得:
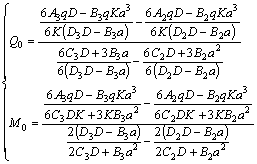 (18)
(18)
将式(18)的Q0和M0解代入式(15),可得ψ0的解:
![]() (19)
(19)
将式(18)和(19)的Q0,M0和ψ0解代入式(14),得到关于a的超越方程:
![]() (20)
(20)
解此超越方程,即可确定悬空长度a。
2 两端简支的弹性地基梁
两端简支的弹性地基梁如图2所示。采用与两端固结的弹性地基梁相同的分析方法,可得相应的Q0,M0和ψ0解,如式(21)~(23)所示,求解悬空长度a的超越方程仍为式(20)。
![]() (21)
(21)
![]() (22)
(22)
![]() (23)
(23)
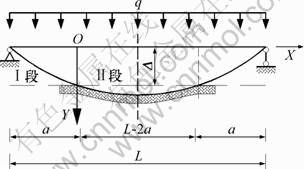
图2 局部悬空的两端简支弹性地基梁
Fig.2 Elastic foundation beam of local hang
3 Timoshenko深梁理论的退化
当梁的抗剪刚度C→∞时,Timoshenko深梁理论退化为不考虑剪切变形的Bernoulli-Euler梁理论,上述各计算公式相应退化为不考虑剪切变形的Bernoulli-Euler梁理论计算公式。
4 算例
地基梁抗弯刚度D=5.0×107 N/m2,抗剪刚度C=2.0×107 N/m2,基床系数K=1.8×107 N/m2,长度L=10.0 m。改变均布荷载q,当地基沉降Δ为0.01时,2种理论下悬空长度a与荷载q间的关系如图3所示(其中:TB代表Timoshenko梁理论,BEB代表Euler梁理论)。
从图3可以看出:不计剪切变形的影响,用弹性地基上Bernoulli-Euler梁理论计算的挠度比采用Timoshenko梁理论计算的挠度偏小,从而导致悬空长度a偏大。
为分析剪切变形对弹性地基梁的变形与内力的影响,取q=4.0×105 N,Δ=0.01 m,2种理论的挠度、转角、剪力、弯矩比较如图4~7所示。
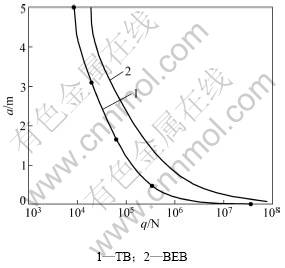
图3 地基沉降0.01 m时悬空长度a随荷载q的变化
Fig.3 Change of hang length with load for 0.01 m foundation settlement
从图4~7可以看出:不计剪切变形的影响,用弹性地基Bernoulli-Euler梁理论计算的悬空弹性地基梁的挠度、转角、剪力、弯矩都比相应的Timoshenko梁理论结果大,其中2种理论下的最大弯矩之比为2.455,最大剪力之比为1.772,可见2种理论间的差别较大。而且用考虑剪切变形的Timoshenko深梁理论计算的变形和内力变化平缓,没有集中现象,因此,地基沉降分析中用Timoshenko深梁理论更合适,计算中应考虑剪切变形的影响。
为分析地基逐步沉降时结构变形和内力的变化趋势,取q=4.0×105 N,沉降Δ为0,0.05,0.10,0.15和0.20 m 5种情况,2种理论计算的挠度、转角、剪力、弯矩变化如图8~11所示。
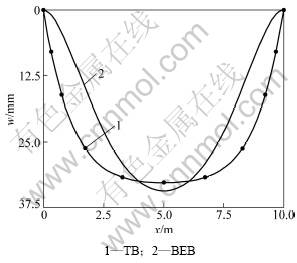
图4 地基沉降0.01 m时2种理论的挠度w比较
Fig.4 Comparison of deflection of different theories for 0.01 m foundation settlement
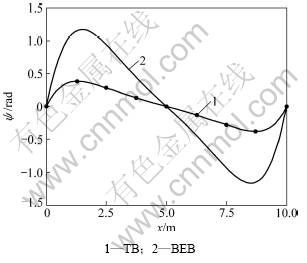
图5 地基沉降0.01 m时2种理论的转角ψ比较
Fig.5 Comparison of different theory angles for 0.01 m foundation settlement
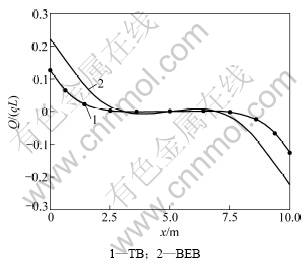
图6 地基沉降0.01 m时2种理论的剪力系数Q/(qL)比较
Fig.6 Comparison of shear force factor of different theories for 0.01 m foundation settlement
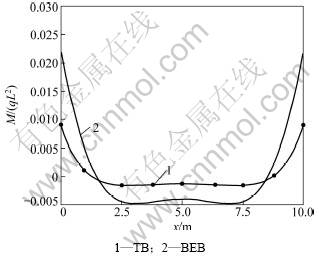
图7 地基沉降0.01 m时2种理论的弯矩系数M/(qL2)比较
Fig.7 Comparison of moment factor of different theory values for 0.01 m foundation settlement
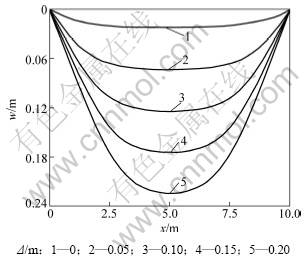
图8 不同地基沉降下的挠度w
Fig.8 Deformation of different foundation settlements
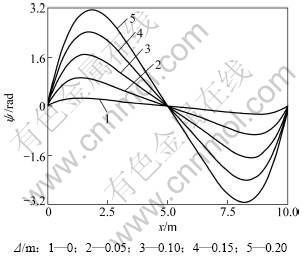
图9 不同地基沉降下的转角ψ变形
Fig.9 Rotating angel of different foundation settlements
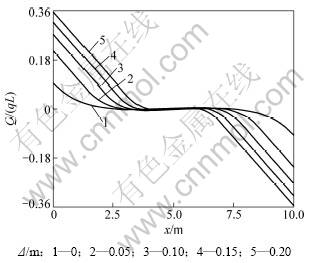
图10 不同地基沉降下的剪力系数Q/(qL)
Fig.10 Shear force factor of different foundation settlements
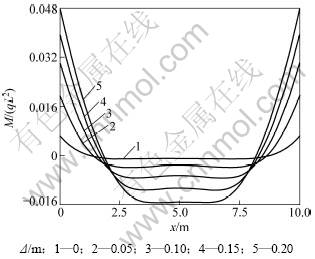
图11 不同地基沉降下的弯矩系数M/(qL2)
Fig.11 Moment factor of different foundation settlements
从图10和图11可以看出:不同沉降条件下,部分悬空的弹性地基梁中,悬空部分的梁段内力变化较大,而处于弹性地基上的梁段内力变化平缓,没有内力集中现象。
5 结论
(1) 对于局部悬空的弹性地基梁,采用不计剪切变形影响的Bernoulli-Euler梁理论计算的悬空长度偏大。
(2) 采用不计剪切变形影响的Bernoulli-Euler梁理论计算的局部悬空弹性地基梁的挠度、转角、剪力、弯矩都比相应的Timoshenko梁理论结果大。2种理论所得的最大弯矩之比为2.455,最大剪力之比为1.772,可见,这种理论间的差别较大。采用考虑剪切变形的Timoshenko深梁理论计算的变形和内力变化平缓,没有集中现象,因此地基沉降分析中用Timoshenko深梁理论更合适,计算中应考虑剪切变形的影响。
(3) 部分悬空的弹性地基梁中,悬空部分的梁段内力变化较大,而处于弹性地基上的梁段内力变化平缓,也没有内力集中现象。
参考文献:
[1] 龙驭球. 弹性地基梁的计算[M]. 北京: 人民教育出版社, 1981: 1-68.
LONG Yu-qiu. Calculation of beam on elastic foundation[M]. Beijing: People’s Education Press, 1981: 1-68.
[2] Selvadurai A P S. Elastic analysis of soil-foundation interaction[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co, 1979: 7-110.
[3] 文明才, 戴振东. 冲击荷载作用下Winkler地基上横观各向同性浅球壳的动力分析[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(3): 629-634.
WEN Ming-cai, DAI Zhen-dong. Dynamic analysis of transversely isotropic shallow spherical shell of Winkler foundation subjected to impact force[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2008, 39(3): 629-634.
[4] 楼梦麟, 沈霞. 弹性地基梁振动特性的近似分析方法[J]. 应用力学学报, 2004, 21(3): 149-152.
LOU Meng-lin, SHEN Xia. An approach for analyzing dynamic characteristic of reinforced concrete beam on elastic foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2004, 21(3): 149-152.
[5] 刘小兵, 陈宇. 溶槽地段双跨连拱隧道的结构计算与分析[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 36(3): 517-521.
LIU Xiao-bing, CHEN Yu. Structural calculation and analysis for double-arch tunnel in water-eroded groove[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2005, 36(3): 517-521.
[6] 刘人通. 局部塌陷的Winkler地基上的梁和板的计算[J]. 西安公路交通大学学报, 1999, 19(增刊): 45-47.
LIU Ren-tong. The calculation of beam and plate on Winkler foundation in partial collapse[J]. Journal of Xi’an Highway University, 1999, 19(S): 45-47.
[7] Essenburg F. Shear deformation in beams on elastic foundations[J]. ASME: Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1962, 29(3): 313-317.
[8] Aydogan M. Stiffness-matrix formulation of beams with shear effect on elastic foundation[J]. ASCE: Journal of Structural Engineering,1995, 121(9): 1265-1270.
[9] Onu G. Shear effect in beam finite element on two-parameter elastic foundation[J]. ASCE: Journal of Structural Engineering, 2000, 126(9): 1104-1107.
[10] Shirima L M, Giger M W. Timoshenko beam element resting on two-parameter elastic foundation[J]. ASCE: Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1992, 118(2): 280-295.
[11] Chen Y H. General dynamic stiffness matrix of a Timoshenko beam for transverse vibration[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 1987, 15(3): 391-402.
[12] Yokoyama T. Vibrations of Timoshenko beam-columns on two-parameter elastic foundations[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 1991, 20(3): 355-370.
[13] 胡海昌. 弹性力学的变分原理及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981: 139-156.
HU Hai-chang. Variational principles of elasticity mechanics and their applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1981: 139-156.
[14] 袁聚云, 孙洋波, 王美云. 传递矩阵法分析中心荷载下对称刚性板地基沉降及反力[J]. 力学季刊, 2005, 26(2): 316-321.
YUAN Ju-yun, SUN Yang-bo, WANG Mei-yun. Analysis of settlement and contact pressure of symmetric rigid plate on subgrade under central concentrated load with method of transferring matrix[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2005, 26(2): 316-321.
[15] 夏桂云, 李传习. 考虑剪切变形影响的杆系结构理论与应用[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2008: 120-124.
XIA Gui-yun, LI Chuan-xi. Frame structure theory including shear deformation effect and its applications[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2008: 120-124.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2010-06-15;修回日期:2010-08-28
基金项目:中国博士后基金资助项目(20080441177);长沙理工大学桥隧重点学科创新基金资助项目(2010-01)
通信作者:夏桂云(1972-),男,湖南湘阴人,博士,副教授,从事桥梁与结构工程研究;电话:13974885367;E-mail:xiagy72@163.com


