基于区域内一致性和区域间差异性的图像分割
周昌雄1,2, 于盛林1
(1. 南京航空航天大学 自动化学院,江苏 南京,210016;
2. 江苏科技大学 电子信息学院,江苏 镇江,212003)
摘要: 利用区域内方差描述区域内一致性,提出以区域间平均灰度值之差的平方来构建能量函数。运用梯度最陡下降法,推导出能量函数曲线演化方程,并应用于图像分割。研究结果表明:与仅基于区域内一致性或区域间差异性的图像分割算法相比,该算法的图像分割结果更符合实际情况;随着迭代次数增加,基于该算法的图像分割边界变得更平滑;当到达一定的迭代次数时,图像分割结果稳定。
关键词: 区域内一致性; 区域间差异性; 图像分割
中图分类号:TP391 文献标识码:A 文章编号: 1672-7207(2005)04-0668-05
Image segmentation based on intra-region similar and inter-region dissimilar properties
ZHOU Chang-xiong1,2, YU Sheng-lin1
(1. College of Automation Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautic, Nanjing 210016, China;
2. School of Electronics and Information, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang 212003, China)
Abstract: The energy function based on intra-region similar and inter-region dissimilar properties was constructed, and a novel algorithm for image segmentation was presented. The algorithm describes the similar property by intra-region variation and dissimilar property by squares of subtraction of regions mean value. Using gradient-descent methods the energy function is minimized and a curve evolution equation is obtained to segment the image. Compared to the previous method based on either intra-region similar property or inter-region dissimilar property, the experiments show that the results of image segmentation by the developed method tally with the facts. In addition, the segmented image edge is smoothed with increasing iteration number; furthermore, the result of segmentation is not changed until a certain iteration number.
Key words: intra-region similar property; inter-region dissimilar property; image segmentation
图像分割是指将图像分成各具特性的区域,并提取感兴趣目标的技术和过程[1],它是计算机视觉与高层图像处理的基础。图像分割技术通常可分为基于数据驱动和基于模型驱动两大类[2,3]。基于数据驱动的图像分割直接对当前图像数据进行操作,如微分算子、阈值化[4-6]和区域生长法[7]等。基于模型驱动的图像分割则是建立在先验知识基础上对图像进行分割,如目标几何、统计模型[8]和活动轮廓模型等[9,10]。
活动轮廓模型与水平集理论相结合的曲线演化方法,是目前广为关注的一种分割方法。该方法利用闭合曲线或曲面的几何特性,建立曲线变形的能量函数,将这个能量函数最小化,使闭合曲线逐渐逼近图像中目标边界[10]。曲线演化方法又可分为边界活动轮廓模型[11]、区域活动轮廓模型[12]和混合活动轮廓模型[13]3种。Mumford-shah模型是基于区域的活动轮廓模型,适用于模糊边界或不连续边界等场合,并且对初始曲线位置不敏感[14]。T.Chan等[14]提出的简化M-S模型,即C-V方法,假定图像中只有两类分片光滑的同质区域,即目标和背景区域。采用C-V方法建立最小化区域内方差的能量函数,该方法只考虑同质区域内像素的一致性。A.Tsai等[15]考虑到区域间像素的差异性,提出基于最大化区域间平均灰度值之差的平方建立能量函数。不同的曲线能量函数引导曲线演化,能得到不同的图像分割结果。如何设计有效的曲线能量函数,获得正确的或所需要的图像分割结果,是当前曲线演化方法研究的热点和难点。在此,本文作者综合考虑区域内一致性和区域间差异性,提出建立区域内方差加权区域间平均灰度值之差的平方为能量函数,基于区域一致性、区域间差异性、区域内一致性加权区域间差异性3种算法的图像分割方法。
1 简化的M-S模型
20世纪80年代出现了M-S模型,该模型通过利用目标边界曲线特定规律实现图像分割。采用分片光滑函数表示强度变化很小的同质区域,短的光滑曲线并集表示强度变化非常大的边界区域,建立能量函数,令其最小化,将原图像分割成同质的连通区域,不连续点集逼近目标边界。M-S模型实质上是一种变分问题。
T.Chan等[14]提出了一种简化的M-S模型,认为图像中只有两类分片光滑区域:目标和背景。设区域为Ω的图像I(x,y)被闭合边界C分割为目标Ωo(C的内部)和背景Ωb(C的外部)2个同质区域,2个区域的平均灰度值分别为co和cb,建立如下能量函数:
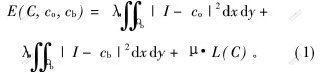
其中:λo>0,λb>0,μ≥0,分别为各项加权系数。式(1)中第1项和第2项为保真项,当闭合轮廓线C位于目标的边界时,此2项和为最小值;L(C)为闭合轮廓线C的长度;第3项为正则项约束,使演化曲线平滑。
2 算法
2.1 引理
若
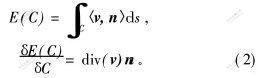
则
其中:v为矢量;n为闭合曲线C的单位外法线方向;s为任意参数;div为散度;〈·〉表示括号内前、后两者做内积[16]。
命题
设
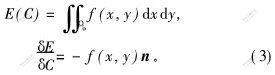
则
其中:n={ys,-xs};f(x,y)为区域Ωo上的函数。
证明 假定有两函数P(x,y)和Q(x,y)[17],且
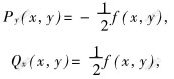
则f(x,y)=Qx(x,y)-Py(x,y)。
由格林公式得:
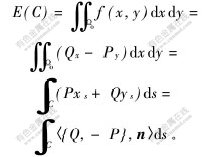
由引理可知:
![]()
证毕。
2.2 区域内一致加权区域间差异性
区域内一致性由区域内方差描述,区域间差异性由目标平均灰度值co与背景平均灰度值cb之差的平方描述,2个能量函数分别定义如下:

式(4)为式(1)中的保真项;λo,λb和μ为加权系数,在此取λo=λb=[SX(]1[]2[SX)]。
为了得到最优分割,式(4)应取最小值,式(5)应取最大值。联合式(4)和式(5),得:
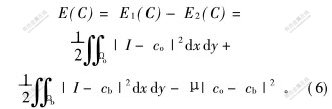
取式(6)的最小值得最优分割。μ为大于或等于零的常数,取代式(1)中正则项约束,对式(6)求变分得:

考虑算法稳定性,用Pb代替 ![]() ,Po代替
,Po代替 ![]() ,则有:
,则有:
![]()
将式(8)和式(11)合并,则有:

由其梯度最陡下降法:
![]()
则有:
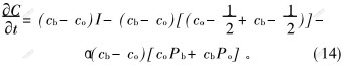
由曲线演化方程 ![]() ,对应的隐式水平集方程为
,对应的隐式水平集方程为 ![]() 。式(14)水平集方程为:
。式(14)水平集方程为:

其中:为符号距离函数。
3 实验结果及讨论
基于区域内一致性图像分割的结果如图1所示。图1(a)为原始图像,目标为手写的阿拉伯数字9,叠加在图像上的黑色圆周曲线为解方程时迭代的初始曲线(初始条件);图1(b)所示为迭代2次后的分割结果;图1(c)所示为迭代5次后的分割结果。在基于区域内一致性图像分割实验中,随着迭代次数的增加,目标手写的阿拉伯数字9内部的小圆圈已无法分割,分割结果与实际情况不符。
图2所示为基于区域间差异性图像分割结果,其初始曲线仍为图1(a)所示的黑色圆周曲线。随着迭代次数增加,虽然能分割出手写的阿拉伯数字9内部的小圆圈,但是分割出的区域面积较小。
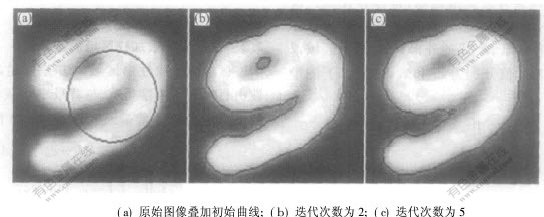
图 1 基于区域内一致性图像分割
Fig. 1 Image segmentations based on intra-region similar property
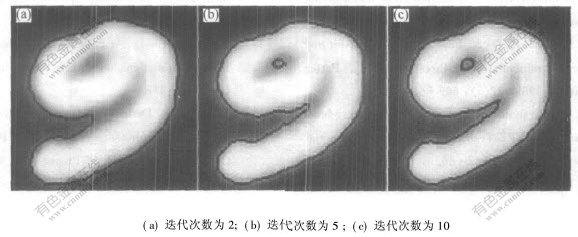
图 2 基于区域间差异性图像分割
Fig. 2 Image segmentations based on inter-region dissimilar property
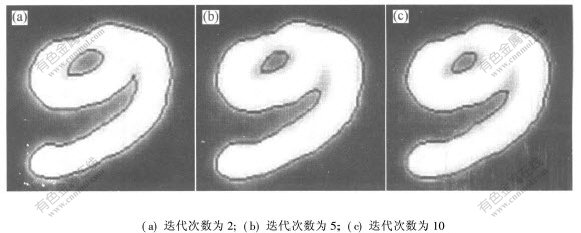
图 3 改进算法图像分割(α=0.2)
Fig. 3 Image segmentations based on improved method
图3所示为本文作者提出的算法图像分割结果。其中,区域间差异性加权系数α=0.2,其初始曲线仍为图1(a)所示的黑色圆周曲线。所用软件为Matlab6.5,每迭代1次的运行时间为2.8750 s。从实验结果可以看出,作者所提出的算法能有效地分割出手写阿拉伯数字9中的小圆圈,分割结果与实际情况相符;随着迭代次数增加,分割出阿拉伯数字9中的小圆圈平滑;当达到一定迭代次数时,图像分割结果稳定。
4 结 论
图像分割应使同一区域中的像素具有某些相同特性, 不同的子区域具有不同的特性, 区域内一致性和区域间的差异性是图像分割的必然要求。 本文作者提出以区域内方差加权区域间平均灰度值之差的平方为能量函数, 利用变分原理建立了曲线演化方程, 分别研究了基于区域内一致性、 区域间差异性、区域内一致性加权区域间差异性3种算法的图像分割方法。 与仅基于区域内或区域间信息的图像分割算法相比, 该算法的分割结果更符合实际情况; 随着迭代次数增加, 基于该算法图像分割结果平滑而稳定。
参考文献:
[1]章毓晋. 图像分割[M].北京:科学出版社,2001.
ZHANG Yu-jin. Image segmentation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001.
[2]王爱民,沈兰荪.图像分割研究综述 [J]. 测控技术,2000, 19(5): 1-6.
WANG Ai-min, SHEN Lan-sun. Study review on image segmentation[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2000, 19(5): 1-6.
[3]李俊.基于曲线演化的图像分割方法及应用[D].上海: 上海交通大学图像处理与模式识别研究所, 2001.
LI Jun. Curve evolution based image segmentation and applications[D]. Shanghai: Institute of Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2001.
[4]Kittler J, Illingworthv I. Minimum error thresholding[J]. Patter Recognition, 1986, 19(1): 41-47.
[5]Cho S, Haralick R, Yi S. Improvement of Kittler and Illingworths minimum error thresholding[J]. Patter Recognition, 1989, 22(5): 609-617.
[6]Ostu N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histogram[J]. IEEE Transactions on System Man and Cybernet, 1978, 8(1): 62-66.
[7]Sandor T, Metcalf D, Kim Y J. Segmentation of brain CT images using the concept of region growing[J]. Biomed Comput, 1991(29): 133-147.
[8]Levitt T S, Hedgcock M W, Dye J W, et al. Bayesian inference for model-based segmentation of computed radiographs of the hand[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 1993, 5(4): 365-387.
[9]Kass M, Witkin A, Terzopoulos D. Snake: Active contour models [J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1988, 1(4): 321-331.
[10]李俊. 基于Mumford-Shah模型的快速水平集图像分割方法[J].计算机学报,2002,25(11):1175-1183.
LI Jun. A fast level set approach to image segmentation based on Mumford-Shah model[J]. Chinese J Computers, 2002, 25(11): 1176-1184.
[11]Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G. Geodesic active contours[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1997, 22(1): 61-79.
[12]Chan T, Vese L. Active contours without edges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(2): 266-277.
[13]Paragios N, Deriche R. Geodesic active regions for supervised texture segmentation[A]. Proc IEEE ICCV[C]. Kerkyra: IEEE Press,1999: 926-932.
[14]Chan T, Vese L. An efficient variation multiphase motion for the Mumford-Shah segmentation model[A]. Processing of Asiomar Conference Signals, Systems, and Computers[C]. Pacific Grove: IEEE Press, 2000: 490-494.
[15]Tsai A, Yezzi A, Willsky A. A statistical approach to snake for bimodal and trimodal imagery[A]. Proc IEEE ICCV[C]. Kerkyra: IEEE Press, 1999: 898-903.
[16]Stanley O, Ronald P. Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag Press, 2003.
[17]Zhu S, Lee T, Yuille A. Region competition: unifying snake, region growing energy/bayes/ MDL for multi-band image segmentation[A]. Proc IEEE ICCV[C]. Boston: IEEE Press, 1995: 416-423.
收稿日期: 2004-10-25
作者简介:周昌雄(1965- ),男,湖北汉川人,博士研究生, 副教授,从事图像处理研究
论文联系人: 周昌雄,男,博士研究生;电话:0511-8829660(H);E-mail:handzhou@sina.com
[1]章毓晋. 图像分割[M].北京:科学出版社,2001.
[2]王爱民,沈兰荪.图像分割研究综述 [J]. 测控技术,2000, 19(5): 1-6.
[3]李俊.基于曲线演化的图像分割方法及应用[D].上海: 上海交通大学图像处理与模式识别研究所, 2001.
[4]Kittler J, Illingworthv I. Minimum error thresholding[J]. Patter Recognition, 1986, 19(1): 41-47.
[10]李俊. 基于Mumford-Shah模型的快速水平集图像分割方法[J].计算机学报,2002,25(11):1175-1183.


