文章编号:1004-0609(2008)03-0529-06
电磁软接触连铸高频磁场的数值模拟
夏小江1,王宏明1, 2,戴起勋1,李桂荣1,赵玉涛1
(1. 江苏大学 材料学院,镇江 212013;
2. 上海大学 材料学院,上海 200072)
摘 要:
以经典电磁场理论为依据,利用有限元软件ANSYS建立了电磁软接触连铸高频磁场计算的数学物理模型。用小线圈法实测了线圈内磁感应强度的分布,并将实测值与计算值进行比较,验证了模型的有效性。通过计算,分析了割缝结晶器内磁感应强度分布的不均匀性以及感应线圈匝间距对结晶器内磁感应强度分布的影响。结果表明:切缝对结晶器中半径小于25 mm范围的影响很小,使接近结晶器壁处圆周上磁感应强度分布的不均匀性较大;减小线圈匝间距可以提高结晶器内磁感应强度,线圈匝间距以5~10 mm为宜。
关键词:
中图分类号:TG 249.7;TG111.4 文献标识码:A
Numerical simulation of high frequency magnetic field for
electromagnetic soft-contact continuous casting
XIA Xiao-jiang1, WANG Hong-ming1, 2, DAI Qi-xun1, LI Gui-rong1, ZHAO Yu-tao1
(1. School of Materials, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China;
2. School of Materials, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China)
Abstract: Based on electromagnetism theory, a physical and mathematical model of electromagnetic continuous casting was developed through ANSYS software. The distribution of magnetic induction density (B) in the coil was measured through the little coil method. By comparing the measured value with the calculated results, the validity of calculating the electromagnetic field through the model was proved. The ununiformity of B distribution in slit mould was analyzed. The results show that the effect of slit on the B distribution in the area with radius smaller than 25 mm is unconspicuous, and the ununiformity of B distribution in the area close to the mould wall is much remarkable. The effect of distance between coil circles on the B distribution was also studied. The results show that the magnetic induction density increases by decreasing the distance between coil circles, and the better distance between cow circles is 5-10 mm.
Key words: electromagnetic soft contact continuous casting; high frequency electromagnetic field; numerical simulation
电磁软接触连铸技术是利用高频交变电磁场在结晶器内铸坯的初始凝固区施加电磁压力来减少液体金属与结晶器壁的接触压力,增强连铸保护渣的润滑效果,从而提高铸坯的表面质量和结晶器的寿命,最终实现高效连铸连轧[1-2]。该技术要求结晶器不仅具有很强的冷却能力,而且能够尽可能地使高频磁场透过结晶器壁作用在钢液上,理想的电磁连铸结晶器材质是一种冷却能力、机械性能、抗热振性能与Cu相当的绝缘材料,但目前很难找到此种材料,而是通过提高铜质结晶器的透磁率来实现该技术[3]。研究证明:电磁场在结晶器内的分布不仅影响结晶器内钢液的流动和凝固传热,而且影响结晶器内金属弯月面的形状和稳定性,从而决定了铸坯的质量及电磁软接触连铸的效果[4-5]。
近年来,针对电磁场分布的研究主要集中在磁场的频率、电源功率以及分瓣结晶器结构等参数上[6-7],而对线圈结构参数的研究还很少涉及。本文作者模拟计算了分瓣结晶器内磁感应强度的分布,分析了高频磁场线圈内磁感应强度的分布特性,并研究了线圈匝间距变化对磁场分布的影响,探讨如何优化磁场的分布,更好地实施该技术。
1 电磁场分布数学模型
电磁软接触连铸示意图如图1所示。
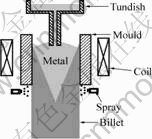
图1 电磁软接触连铸示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of electromagnetic soft-contact continuous casting
激励电流为正弦交流电,频率20 kHz,该交变电磁场满足似稳条件,位移电流可忽略[8]。根据Maxwell方程组在此问题中的简化,电磁软接触连铸工艺中的电磁场分布满足下列方程[9]:

2 有效性验证及模型的前处理
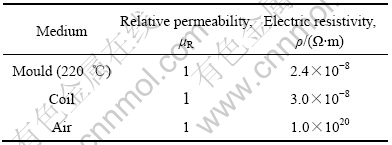
利用ANSYS软件对结晶器内三维磁场分布进行计算,实体模型物性参数如表1所列。
表1 实体模型物性参数
Table 1 Electromagnetic parameters of solid model
由于计算区域的对称性,取整体区域的1/4作为实际计算区域,包括线圈及其周围的空气,并在对称面上加载平行边界条件(见图2)。为满足狄利克莱边界条件,通常取达到相对激励源(线圈)直径3~4倍远处为无穷远[10],本文作者取线圈半径5倍处为无穷远来加载边界条件。
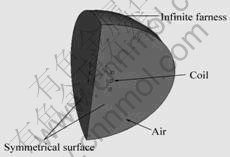
图2 电磁场计算区域示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of simulation area of magnetic field
为确定计算结果的有效性,用小线圈法[11]实测了磁感应强度的分布,并与计算结果作比较。实验所选测定点分布如图3所示(r为线圈的内半径,50 mm)。
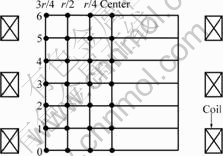
图3 线圈内磁场测定点位置示意图
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of position of magnetic induction density measurement
图4所示为线圈内各点处的磁感应强度的计算值与实测值。从图4可看出,磁感应强度的计算值与实测值基本相符,且变化规律完全一致,从而证明本模型计算结果的有效性。
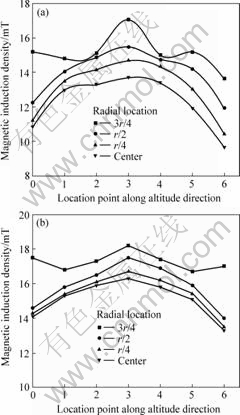
图4 线圈内各点磁感应强度的计算值与实测值的比较
Fig.4 Comparison of measured and calculated results of magnetic induction density: (a) Calculated results; (b) Measured results
在线圈中放入结晶器,由于交变载荷的存在,在结晶器中产生涡流,从而对其内部的磁场产生屏蔽作用,为了减小结晶器壁的屏蔽程度,对结晶器壁进行分瓣[9],分瓣数为4,切缝宽度为1 mm。图5所示为结晶器与线圈的结构示意图。
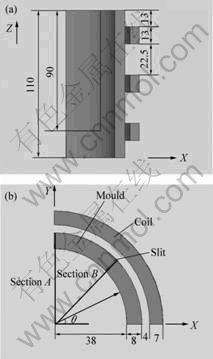
图5 结晶器与线圈的结构示意图(mm)
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of mold and coil: (a) Elevation; (b) Planform
根据集肤效应,涡流主要分布在导体表面,因此,在网格剖分时须在透入深度范围内沿导体表面的厚度方向加密网格(集肤效应厚度δ内至少要有一个单元),否则会使金属熔体表面以内的各层网格的感应电流出现正负交替的现象。根据以下公式[12-13]计算δ:

图6所示为线圈与结晶器模型网格的划分,在结晶器壁厚度方向上,网格宽度由内到外逐渐减小,在最外层处达到0.2 mm。
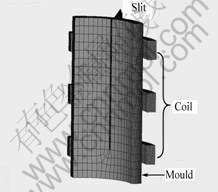
图6 线圈与结晶器模型网格
Fig.6 Meshes of coil and mould
3 结果与讨论
3.1 分瓣结晶器内磁场分布
图7所示为竖直方向A、B两个剖面上磁感应强度的分布(A剖面为分瓣中心线与线圈中心线对应的剖面,B剖面为切缝中心线与线圈中心线对应的剖面,见图5(b))。比较图4和7可知,放入结晶器后,对应点的磁感应强度都有所减小,而在上下两端减小的幅度较小,由于部分磁力线绕过结晶器并没有受到结晶器壁的屏蔽作用。由图7可知,B剖面上的磁感应强度相对较大,特别是在3r/4处,靠近结晶器壁的点磁感应强度小,而靠近切缝处磁感应强度比较大(B中0点水平面所对应的结晶器处无切缝)。
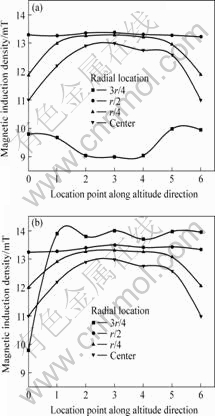
图7 竖直方向磁感应强度分布
Fig.7 Magnetic induction density distribution of B at vertical direction: (a) Section A; (b) Section B
图8所示为高度方向位置点3所在水平面不同半径的圆弧上磁感应强度的分布。由图8可见,在结晶器内,周向上越靠近结晶器,磁场分布的不均匀性就越大。在半径为12.5 mm和25 mm处,磁感应强度已经很接近,说明切缝对半径小于25 mm范围的影响已经很小。
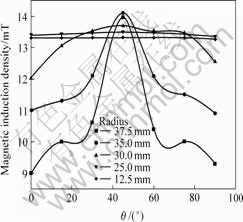
图8 水平面上磁感应强度分布
Fig.8 Magnetic induction density distribution of B in horizontal plane
`3.2 线圈匝间距对磁场分布的影响
图9所示为在高度方向位置点3水平面上线圈匝间距不同时磁感应强度的分布。由图9可看出,线圈匝间距对磁感应强度的分布有重要影响。当线圈匝间距为15 mm时,磁感应强度分布明显较小,在r<35 mm的圆周上,随着线圈匝间距的减小,磁感应强度有所增大,但变化不是很明显;当线圈匝间距为5 mm和10 mm时,磁感应强度分布较为接近,靠近切缝处的值远大于靠近分瓣中心处的值;当线圈匝间距为2 mm时,在r≥35 mm的圆周上磁感应强度有所减小。因此,线圈匝间距取5~10 mm为宜。
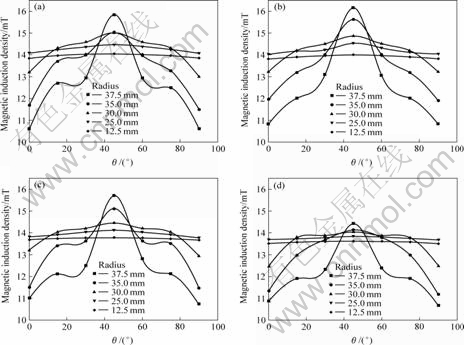
图9 不同线圈匝间距对磁感应强度分布的影响
Fig.9 Effect of different space between coil circles on B distribution: (a) 2 mm; (b) 5 mm; (c) 10 mm; (d) 15 mm
然而,在线圈匝数一定的条件下,减小匝间距,必然会使线圈长度减小,从而减小磁场在竖直方向的有效作用范围,使得竖直方向磁场强度分布的不均匀性增大。由公式[14] 知:在电磁软接触连铸过程中,结晶器内沿拉坯方向作用于液态金属及初生坯壳上的电磁压力分布的不均匀性表现得更加显 著[15-16]。因此,在减小线圈匝间距时,为增大磁场的有效作用范围,可以适当增加线圈匝数。
知:在电磁软接触连铸过程中,结晶器内沿拉坯方向作用于液态金属及初生坯壳上的电磁压力分布的不均匀性表现得更加显 著[15-16]。因此,在减小线圈匝间距时,为增大磁场的有效作用范围,可以适当增加线圈匝数。
4 结论
1) 建立了电磁软接触连铸高频磁场计算的数学物理模型,用ANSYS有限元法进行模拟计算,模拟计算出线圈内磁感应强度分布与实际测量结果吻合,证明模型及计算方法的正确性。
2) 结晶器割缝引起了结晶器内磁感应强度分布的不均匀性,主要体现在同一高度的圆周上,割缝处和远离割缝处,磁感应强度差别明显。特别是在靠近结晶器壁位置,由于无割缝处磁屏蔽现象显著,导致磁感应强度的不均匀性增加,这是电磁软接触连铸使用分瓣结晶器要注意的问题。
3) 减小感应线圈匝间距,可以增大结晶器内的磁感应强度,匝间距小于5 mm对提高磁感应强度作用不大,但线圈匝间距减小,需适当增加线圈匝数以保证高频磁场的作用区域长度。
REFERENCES
[1] 张林涛, 邓安元, 张兴武, 王恩刚, 赫冀成. 矩形电磁软接触连铸结晶器内弯月面行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(8): 1405-1410.
ZHANG Lin-tao, DENG An-yuan, ZHANG Xing-wu, WANG En-gang, HE Ji-cheng. Behavior of meniscus in soft-contact electromagnetic continuous casting (EMCC) rectangular mold[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(8): 1405-1410.
[2] KIM H, PARK J, JEONG H, KIM J. Continuous casting of billet with high frequency electromagnetic field[J]. ISIJ International, 2002, 42(2): 171-177.
[3] 那贤昭, 张兴中, 仇圣桃, 干 勇. 方坯软接触电磁连铸结晶器内三维电磁场的数值模拟[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(9): 944-951.
NA Xian-zhao, ZHANG Xing-zhong, QIU Sheng-tao, GAN Yong. 3-D numerical simulation of high frequency electromagnetic field in soft continuous casting mold[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2002, 38(9): 944-951.
[4] 王宏明, 柏立庆, 李桂荣, 夏小江, 戴起勋, 任忠鸣, 邓 康, 雷作胜. 高频调幅磁场分布和液面波动行为研究[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2006, 27(8): 468-470.
WANG Hong-ming, BO Li-qing, LI Gui-rong, XIA Xiao-jiang, DAI Qi-xun, REN Zhong-ming, DENG Kang, LEI Zuo-sheng. High frequency amplitude-modulated magnetic field and behavior of meniscus fluctuation[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloys, 2006, 26(8): 468-470.
[5] DENG An-yuan, WANG En-gang, HE Ji-cheng. Meniscus behavior in electromagnetic soft-contact continuous casting round billet mold[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2006, 13(4): 13-16.
[6] PARK J, JEONG H, KIM H, KIM J. Laboratory scale continuous casting of steel billet with high frequency magnetic field[J]. ISIJ Int, 2002, 42(4): 385-391.
[7] NAKATA H, INOUE T, MORI H, AYATA K, MURAKAMI T, KOMINAMI T. Improvement of billet surface quality by ultra-high-frequency electromagnetic casting[J]. ISIJ Int, 2002, 42(3): 264-272.
[8] 冯慈章. 电磁场[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1986: 302.
FENG Ci-zhang. Electromagnetic field[M]. Beijing: Advanced Education Press, 1986: 302.
[9] TANAKA T, KURITA K, KURODA A. Mathematical modeling for electromagnetic field and shaping of melts in cold crucible[J]. ISIJ International, 1991, 31(4): 350-357.
[10] 金百刚, 王 强, 刘 燕, 崔大伟, 吴成涛, 王恩刚, 赫冀成. 软接触电磁连铸结晶器内磁场分布与弯月面行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(11): 1931-1937.
JIN Bai-gang, WANG Qiang, LIU Yan, CUI Da-wei, WU Cheng-tao, WANG En-gang, HE Ji-cheng. Magnetic field distribution and molten metal meniscus behavior in soft contact electromagnetic continuous casting mold[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(11): 1931-1937.
[11] 王宏明, 陈国星, 任忠鸣, 雷作胜, 李桂荣, 夏小江, 戴起勋. 电磁连铸用高频磁场内磁感应强度的分布[J]. 铸造技术, 2006, 27(7): 737-739.
WANG Hong-ming, CHEN Guo-xing, REN Zhong-ming, LEI Zuo-sheng, LI Gui-rong, XIA Xiao-jiang, DAI Qi-xun. Magnetic induction density of high frequency magnetic field for electromagnetic continuous casting[J]. Foundry Technology, 2006, 27(7): 737-739.
[12] TAKATANI K. Effects of electromagnetic brake and meniscus electromagnetic stirrer on transient molten steel flow at meniscus in a continuous casting mold[J]. ISIJ Int, 2002, 43(6): 915-922.
[13] 邓安元, 王恩刚, 赫冀成, 孟广辉, 张永杰, 陈兆平, 周月明. 矩形软接触结晶器内磁场分布的实验研究[J]. 金属学报, 2003, 39(10): 1105-1109.
DENG An-yuan, WANG En-gang, HE Ji-cheng, MENG Guang-hui, ZHANG Yong-jie, CHEN Zhao-ping, ZHOU Yue-ming. Experimental study of distribution of magnetic flux in rectangular soft-contact mold[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2003, 39(10): 1105-1109.
[14] PARK J, SIM D, JEONG H, KIM H. Effect of high frequency electromagnetic field on continuously cast billet[J]. ISIJ International, 1999, 39(12): 57-60.
[15] PARK J, KIM H, JEONG H, KIM G, JONG M, CHUNG J, YOON M, KIM K, CHOI J. Initial solidification control of continuous casting using electromagnetic oscillation method[J]. ISIJ International, 2003, 43(6): 807-812.
[16] LI T J, LI X T, ZHANG Z F, LI Q L. Effect of multi-electromagnetic field on meniscus shape and quality of continuously cast metals[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2006, 33(1): 57-60.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50474037);江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK2006078);江苏省高校自然科学研究计划资助项目(05KJD450043)
收稿日期:2007-04-26;修订日期:2007-12-02
通讯作者:王宏明,讲师,博士研究生;电话:0511-88780191;E-mail: whmlgr@ujs.edu.cn
摘 要:以经典电磁场理论为依据,利用有限元软件ANSYS建立了电磁软接触连铸高频磁场计算的数学物理模型。用小线圈法实测了线圈内磁感应强度的分布,并将实测值与计算值进行比较,验证了模型的有效性。通过计算,分析了割缝结晶器内磁感应强度分布的不均匀性以及感应线圈匝间距对结晶器内磁感应强度分布的影响。结果表明:切缝对结晶器中半径小于25 mm范围的影响很小,使接近结晶器壁处圆周上磁感应强度分布的不均匀性较大;减小线圈匝间距可以提高结晶器内磁感应强度,线圈匝间距以5~10 mm为宜。


