采用气相色谱-质谱法分析药对麻黄-羌活的挥发油
李国辉1, 2,李晓如1,邹 桥1,谭斌斌1
(1. 中南大学 化学化工学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湖南城市学院 化学与环境工程系,湖南 益阳,413000)
摘 要:
摘 要:采用气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)法分离测定了药对麻黄-羌活、单味药麻黄和羌活的挥发油,并对其重叠色谱峰采用化学计量学解析法进行了分辨,得到药对和各单味药的纯色谱曲线和质谱。药对麻黄-羌活、单味药麻黄和羌活分辨出的色谱峰,通过质谱库对其进行定性,分别得到58,51和52个定性结果,占总含量的83.75%, 88.70% 和80.79%。实验结果表明:药对麻黄-羌活中挥发油化学成分有40种来自羌活,13种来自麻黄,新产生了10种化合物。
关键词:
中图分类号:O657 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2007)05-0888-05
Determination of volatile components in Herba Ephedrae-Rhizoma seu Radix Notopeterygii by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
LI Guo-hui1, 2, LI Xiao-ru1, ZOU Qiao1, TAN Bin-bin1
(1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Chemistry and Environment Engineering, Hunan City College, Yiyang 413000, China)
Abstract: Determination of volatile components in drug pair (DP) Herba Ephedrae-Rhizoma seu Radix Notopeterygii (HE-RsRN), single drug HE and RsRN was performed using two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) data coupled with chemometric resolution method (CRM). With the help of CRM, the two-dimensional data obtained from GC-MS instruments were resolved into a pure chromatogram and a mass spectrum of each chemical compound. Using these methods to process two-dimensional data, 51, 52, and 58 volatile chemical components in essential oil of HE, RsRN, and DP HE-RsRN were respectively determined qualitatively and quantitatively, accounting for 88.70%, 80.79%, and 83.75% total contents of volatile oil of HE, RsRN, and DP HE-RsRN respectively. It is further demonstrated that 40 and 13 volatile components of DP HE-RsRN are from that of single drug RsRN and HE respectively, and 10 new volatile components in DP HE-RsRN are produced because of the chemical reactions and physical changes occurred in the process of decocting two single drugs.
key words: drug pair Herba Ephedrae-Rhizoma seu Radix Notopeterygii; essential oil; gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; chemometric resolution method
药对是中药组方配伍的核心内容[1],是构成复方的基本单位。药对的研究将为中药复方的配伍研究提供最基本的依据,并揭示配伍理论的规律。麻黄-羌活是常用的解表药对之一。麻黄发汗解表,宣肺平喘,利水消肿;羌活散寒解表,祛风胜湿[2]。两药伍用,性味相同,羌活助麻黄发汗解表;麻黄协羌活祛风除湿,二者同奏散风寒、祛湿痛之功效。挥发油成分是解表药对的药效物质[3],而麻黄-羌活药对的挥发油成分未见报道。化学计量学解析方法(Chemometric resolution method, CRM)是一种对二维色谱-光谱矩阵数据进行解析的有效方法,其原理与解析方法见文献[4-5],该方法已成功应用于中药挥发油的分析[6-12]。在此,本文作者采用气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)和化学计量学解析法分析药对麻黄-羌活的挥发油成分,并比较、讨论了药对配伍前后挥发油成分变化。
1 实 验
1.1 仪器与材料
仪器为日本岛津QP2010型气相色谱仪/质谱仪。材料为麻黄(Herba Ephedrae,HE)、羌活(Rhizoma seu Radix Notopeterygii,RsRN),均购自河南南阳药材公司,经湖南中医药研究院中药研究所鉴定。
1.2 挥发油提取
药对挥发油的提取:称取干燥的麻黄,羌活各100克,混合,按中华人民共和国药典(2000年版)挥发油提取法提取[13]。
单味药挥发油的提取:分别称取干燥的麻黄和桂枝各100 g,按照文献[13]方法提取。
1.3 挥发油的测定条件
色谱条件:色谱柱OV-1(长度×直径为30 m×0.25 mm)。 程序升温如下:起始温度为40 ℃,以3 ℃/min升至160 ℃,再以8 ℃/min升至240 ℃,保温20 min。载气为He,流速为1.0 mL/min;进口温度为250 ℃,界面温度为280 ℃。EI源电子能量为70 eV,离子源温度为230 ℃。倍增电压为1.28 kV,扫描范围为20~600原子质量单位;扫描速率为3.8 次/s,溶剂延迟为2 min。
1.4 数据分析
数据分析在PentiumⅢ850(Intel)计算机上进行,程序用Metlab 6.1编写,所分辨的质谱在NIST107标准质谱库中检索。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 挥发油化学成分的定性分析
图1所示为麻黄、羌活和麻黄-羌活的挥发油的GC-MS总离子流图(TIC),采用GC-MS所附质谱库直接检索,发现其中有许多重叠色谱峰。图1(a)中A峰的保留时间为35.8~36.3 min,将A峰放大,其总离子流图如图2所示。
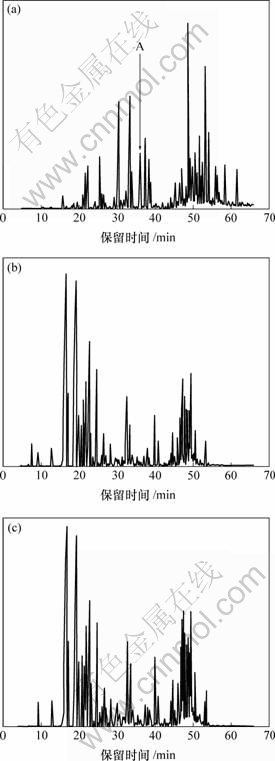
(a) 麻黄;(b) 羌活;(c) 麻黄-羌活
图1 麻黄、羌活和麻黄-羌活挥发油的总离子流图
Fig.1 TICs of volatile components of HE, RC and HP HE-RC
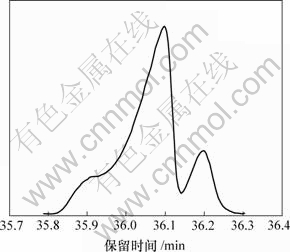
图2 图1(a)中A峰的总离子流图
Fig.2 TIC of peak cluster A in Fig.1(a)
由图2可见,A峰簇初看含2个色谱峰,但在左前部有1个凸起部分。若直接从色谱库中进行检索,A峰簇前半部分不同位置质谱变化很大,且检索结果与被测质谱相似程度都很低,其中1个为4-(1-甲基乙基)-苯甲醛,相似度仅为47%,而后半部分不同位置检索结果也不同,有的相似度较高,有的很低,如检索结果为2-甲基-3-苯基丙醛的化合物,相似度仅为53%。这样检索的定性结果其可靠程度和准确度都很低,同时由于色谱峰重叠,难以进行定量分析。
利用CRM[5-11]分析,结果表明A峰簇是一个三组分体系(见图3)。根据各组分的纯色谱曲线和质谱,再将它们与NIST标准库进行匹配,可检索到组分1,2和3分别为4-(1-甲基乙基)-苯甲醛,2-甲基-3-苯基丙醛和对-孟-4[8]-烯-3-酮,相似度分别为98%,98% 和95%,组分1,2和3相应的质谱图如图4~6所示。由于质谱是由纯组分得到的,故定性结果的准确性和可靠程度增加。
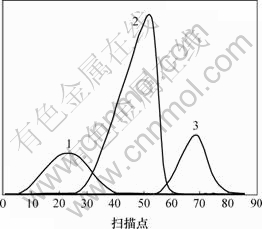
1—4-(1-甲基乙基)-苯甲醛; 2—2-甲基-3-苯基丙醛; 3—对-孟-4[8]-烯-3-酮
图3 A峰解析后的色谱图
Fig.3 Resolved chromatograms of peak cluster A
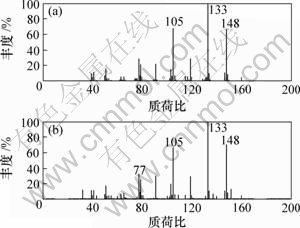
(a) 解析质谱图; (b) 标准质谱图
图4 4-(1-甲基乙基)-苯甲醛的解析质谱图和标准质谱图
Fig.4 Resolved mass spectrum and standard mass spectrum of 4-[1-methylethyl]-benzaldehyde
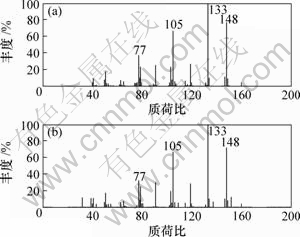
(a) 解析质谱图; (b) 标准质谱图
图5 2-甲基-3-苯基丙醛的解析质谱图和标准质谱图
Fig.5 Resolved mass spectrum and standard mass spectrum of 2-methyl-3-phenyl-propanal
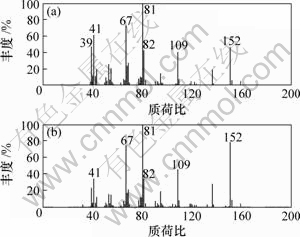
(a) 解析质谱图; (b) 标准质谱图
图6 对-孟-4[8]-烯-3-酮的解析质谱图和标准质谱图
Fig.6 Resolved mass spectrum and standard mass spectrum of p-menth-4[8]-en-3-one
与解析A峰簇过程相似,对麻黄TIC图中其他保留时间段的组分和羌活、麻黄-羌活TIC图,利用CRM逐步进行分辨,可得到组分的纯质谱,再用质谱库对分辨出的组分进行质谱定性检索,得到组分定性结果。麻黄、羌活和药对麻黄-羌活挥发油定性鉴定的组分分别为51,52和58个,它们的主要成分见表1。
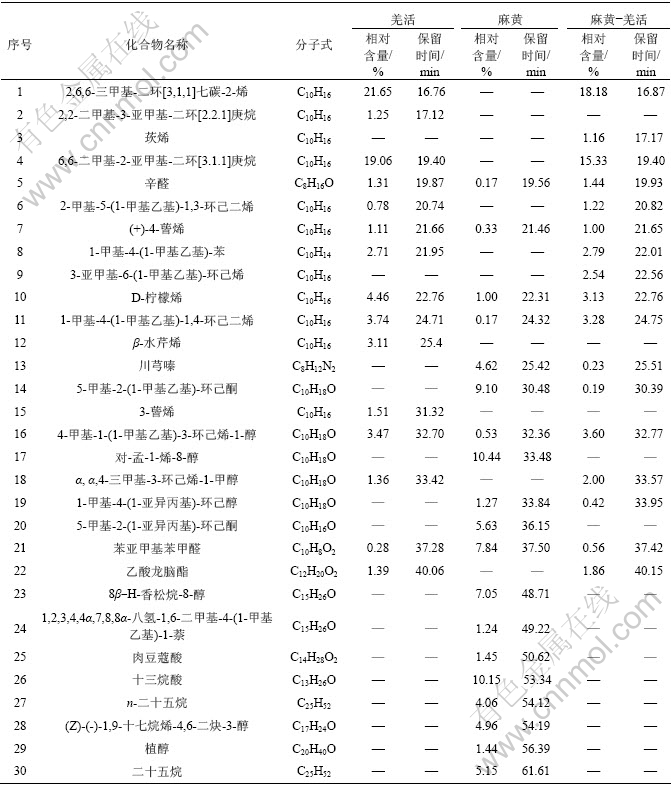
表1 麻黄、羌活和麻黄-羌活挥发油主要化学成分
Table 1 Main chemical components of volatile oils from HE, RsRN and drug pair HE-RsRN
2.2 挥发油化学成分的定量分析
对解析后的所有色谱采用总体积积分法积分,可得到各个组分的定量分析结果,麻黄、羌活和药对麻黄-羌活定性组分含量分别占总含量的88.70%, 80.79%和83.75%,三者的挥发油主要化学成分见表1。
2.3 药对与单味药之间挥发性成分的比较与分析
从表1可见,麻黄挥发油主要成分是对-孟-1-烯-8-醇, 十三烷酸, 5-甲基-2-(1-异丙基)-环己酮, 苯亚甲基苯甲醛, 8β-H-柏木烷醇, 5-甲基-2-(1-甲基-亚乙烯基)-环己酮, 二十五烷, (Z)-(-)-1,9-七癸二烯-4,6-二炔-3-镰叶芹醇; 羌活挥发油主要成分是2,6,6-三甲基-二环[3.1.1]庚-2-烯, 6,6-二甲基-2-亚甲基-二环[3.1.1]庚烷, D-柠檬烯, 1-甲基-4-异丙基-1,4-环己二烯,4-甲基-1-(异丙基)-3-环己-1-醇, β-水芹烯, 1-甲基-4-(1-异丙基)-苯, 3-蒈烯; 药对麻黄-羌活挥发油主要成分是2,6,6-三甲基-二环[3.1.1]庚-2-烯,6,6-二甲基-2-亚甲基-二环[3.1.1]庚烷, 4-甲基-1-(异丙基)-3-环己-1-醇, 1-甲基-4-异丙基-1,4-环己二烯,D-柠檬烯,1-甲基-4-(1-异丙基)-苯, 3-亚甲基-6-(1-异丙基)-环己烯, α,α,4-三甲基环己烯-3-甲醇。
药对麻黄-羌活挥发油化学成分有40种来自羌活,13种来自麻黄,该药对的挥发油化学成分主要来自羌活。药对麻黄-羌活挥发油化学成分新产生了10种化合物,推测其原因在于合煎中的化学反应(如氧化反应,水解反应等)与物理变化(如增溶作用等)。
3 结 论
a. 麻黄、羌活和药对麻黄-羌活挥发油定性鉴定的组分分别为51,52和58个, 含量分别占总含量的88.70%, 80.79和83.75%。
b. 药对麻黄-羌活挥发油化学成分有40种来自羌活,13种来自麻黄,还产生了10种新化合物。
参考文献:
[1] 胥庆华, 刘丽云, 赵瑞华, 等. 中药药对大全[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 1996: 367.
XU Qing-hua, LIU Li-yun, ZHAO Rui-hua, et al. Collection of herbal pairs in traditional Chinese medicine[M]. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1996: 367.
[2] 田代华. 实用中药辞典[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2000: 984-985, 1820-1821.
TIAN Dai-hua. Practical dictionary of traditional Chinese herbs[M]. Beijing: People’s Healthy Press, 2000: 984-985, 1820-1821.
[3] 沈映君. 中药解表方药研究[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2005: 198-199.
SHEN Ying-jun . Study on exterior-releasing drugs and prescriptions in traditional Chinese medicine[M]. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2005: 198-199.
[4] Kvalheim O M, LIANG Yi-zeng. Heuristic evolving latent projections-resolving 2-way multicomponent data.1. Selectivity, latent-projective graph, datascope, local rank and unique resolution[J]. Anal Chem, 1992, 64(8): 936-946.
[5] LIANG Yi-zeng, Kvalheim O M, Keller H R, et al. Heuristic evolving latent projections-resolving 2-way multicomponent data. 2. Detection and resolution of minor constituents[J]. Anal Chem, 1992, 64(8): 946-953.
[6] GONG Fan, LIANG Yi-zeng, CUI Hui, et al. Determination of volatile components in peptic power by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and chemometric resolution[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2001, 909: 237-247.
[7] GONG Fan, LIANG Yi-zeng, XU Qing-song, et al. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and chemometric resolution applied to the determination of essential oils in Cortex Cinnamomi[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2001, 905: 193-205.
[8] LI Xiao-ru, LIANG Yi-zeng, GUO Fang-qiu. Analysis of volatile oil in rhizoma ligustici chuanxiong-radix paeoniae rubra by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and chemometric resolution[J]. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2006, 27(4): 491-498.
[9] GONG Fan, LIANG Yi-zeng, FUNG Ying-sing. Analysis of volatile components from Cortex cinnamomi with hyphenated chromatography and chemometric resolution[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2004, 34(5): 1029-1047.
[10] WU Ming-jian, SUN Xian-jun, DAI Yuan-hui, et al. Determination of essential oil form angelica sinensis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2005, 12(4): 430-436.
[11] LI Xiao-ru, LAN Zheng-gang, LIANG Yi-zeng. Analysis of the volatile chemical constituents of Radix Paeoniae Rubra by GC-MS and chemometric resolution[J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2007, 14(1): 57-61.
[12] GONG Fan, LIANG Yi-zeng, CHOU Fou-tian. Combination of GC-MS with local resolution for determining volatile components in si-wu decoction[J]. J Sep Sci, 2003, 26: 112-122.
[13] 中华人民共和国卫生部药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(一部)[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2000: 附录64.
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese pharmacopoeia (Part Ⅰ)[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000: Appendix 64.
收稿日期:2007-03-20;修回日期:2007-04-25
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(20235020)
作者简介:李国辉(1964-),男,湖南益阳人,副教授,从事有机化学教学与研究
通信作者:李晓如,男,教授;电话:0731-8836376; E-mail: xrli@mail.csu.edu.cn


