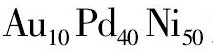网络首发时间: 2016-07-13 16:57
Pt基核壳结构质子交换膜燃料电池氧还原催化剂研究进展
李治应 曾蓉 蒋利军
北京有色金属研究总院能源材料与技术研究所北京市有色金属新能源基础制品工程技术研究中心
摘 要:
质子交换膜燃料电池在电动汽车动力电源上有广泛的应用前景, 其电催化剂的主要成分是Pt, Pt昂贵的价格限制了质子交换膜燃料电池的商业化应用。Pt与3d族过渡金属合金能显著提升Pt催化剂的催化活性, 但是活泼的过渡金属元素会在电化学过程和酸性环境下溶出, 从而降低燃料电池的整体性能, Pt合金催化剂的稳定尚需提高。Pt基核壳结构催化剂由于成分和结构可调, 在提高Pt基催化剂的Pt利用率、催化活性和稳定上有很大潜力, 是质子交换膜燃料电池催化剂的研究热点之一。本文按照Pt基核壳结构催化剂的成分划分, 从合成方法、结构设计与表征、催化活性、稳定性等方面综述了最近几年Pt基核壳结构催化剂的研究进展。已有研究显示通过控制催化剂纳米尺度的结构和成分分布, 包括控制Pt壳层厚度、核与壳的成分、催化剂尺寸和形貌, 设计多层核壳结构的催化剂和对催化剂进行后处理等途径, 可以制备出各种结构的Pt基核壳结构催化剂, 并对壳层Pt原子形成不同程度的电子转移效应和几何晶格应变, 提高了催化剂的催化活性和稳定性。
关键词:
质子交换膜燃料电池;Pt基核壳结构催化剂;结构和成分控制;电子转移效应;几何晶格应变;催化活性和稳定性;
中图分类号: O643.36;TM911.4
作者简介:李治应 (1990-) , 男, 新疆奎屯人, 硕士研究生, 研究方向:燃料电池氧还原催化剂;E-mail:lizyo313@163.com;;曾蓉, 高级工程师;电话:010-82241380;E-mail:zr_zengrong@163.com;
收稿日期:2016-03-07
基金:国家科技部院所基金项目 (2013EG11500);北京市有色金属研究总院院创新基金项目 (52218) 资助;
Pt-Based Core-Shell Catalyst for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
Li Zhiying Zeng Rong Jiang Lijun
Beijing Engineering Research Center of Nonferrous Metal Products for New Energy, Department of Energy Materials and Technology, General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals
Abstract:
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell has good prospects for automotive applications. The main component of its electrocatalysts is Pt, and the high cost of Pt has limited the commercial applications of proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) . Pt alloyed with the 3d transition metals is more active for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) compared to pure Pt catalysts, but the active3 d transition metals are prone to be dissolved by electrochemical or acid treatment, which leads to the performance degradation of PEMFCs. The stability of Pt alloy catalysts needs to be improved further. As the structure and composition of Pt-based core-shell catalyst can be tuned to improve the Pt utilization and stability, it is one kind of the highlighted catalysts for the proton exchange membrane fuel cells. In this paper, recent progress in the synthetic method, structure design and characterization, catalytic activity and stability of Pt based core-shell catalysts based on composition of the catalyst was reviewed. Pt based catalysts with various structures could be prepared by controlling the nanoscale structure and composition of the catalyst, including Pt shell thickness, composition of the core and shell, particle size, and particle shape. These different structures showed different degrees of electron transfer effect and geometric lattice strain on Pt in shell, which might improve the ORR activity and stability of the catalyst.
Keyword:
proton exchange membrane fuel cell; Pt-based core-shell catalysts; structure and composition control; transferred-electron effect; geometric lattice strain; activity and durability;
Received: 2016-03-07
质子交换膜燃料电池 (proton exchange membrane fuel cell, PEMFC) 是一种清洁、高效和长寿命的动力电源, 目前PEMFC上采用的催化剂主要成分是Pt, 价格昂贵, 限制了PEMFC在实际应用。为了实现PEMFC商业化应用, 研究人员对Pt基氧还原催化剂进行了大量研究[1,2,3,4], 为了满足汽车公司的需求, Pt基催化剂的催化活性相比于Pt/C催化剂要有4~5倍的提升[5,6,7,8,9,10,11]。铂合金化是改善铂基催化剂催化活性最常用的方法, 尤其是Pt与3d族过渡金属合金化能显著提升催化活性[12,13,14,15]。但铂合金催化剂还存在稳定性差和铂利用率较低的缺点[16,17]。相比于铂合金催化剂, 核壳结构催化剂由于成分和结构的可调性, 在提高催化剂催化活性、提高Pt利用率、降低成本和提高催化剂稳定性等方面具有更大空间。
本文按照核成分划分, 主要介绍过渡金属@Pt类及贵金属@Pt类各类催化剂主要的合成方法、结构成分设计与表征, 性能对比等方面的研究进展。过渡金属核主要涉及3d族的Ni, Co, Cu, 贵金属核主要涉及Pd, Au, Ag。其他贵金属核如Ir[18], Ru[19,20], 或是氧化物如Fe2O3[21], 由于在ORR应用和研究较少, 不在此详细综述。
1 3d族过渡金属@Pt类催化剂
廉价的3d族过渡金属@Pt结构能显著降低催化剂成本, 3d族过渡金属对Pt壳层有明显的电子转移效应, 提升了Pt壳层的氧还原 (oxygen reduction reaction, ORR) 催化活性。目前报道的文献中, Ni@Pt核壳结构催化剂催化ORR的文献报道明显多于Co@Pt, Cu@Pt和Fe@Pt类核壳结构催化剂, 而且研究内容更深入和丰富。由于Ni与Co, Fe性能相似, Ni@Pt核壳结构催化剂的研究结果大多可以作为Co@Pt和Fe@Pt催化剂研究的模板, 也可以为其他过渡金属@Pt催化剂的研究提供参考。
1.1 Ni@Pt类催化剂
铂与过渡金属的合金在酸性环境和电化学循环过程中表面的过渡金属原子会溶出, 形成核壳结构[22,23,24]。对去合金化制备Ni@Pt催化剂的研究的代表是Gan等的工作[25,26], 结合HADDF和EELS结果 (图1 (a, b) ) , 发现D-Pt Ni3 (D代表去合金化) 具有最明显的核壳结构和ORR催化活性, 富铂层的厚度为0.8 nm。随后研究气氛对去合金化的影响, 发现N-D-Pt Ni3 (N代表在氮气气氛下去合金化, 与空气下对比) 具有更优的稳定性。最后, 他们对不同尺寸的D-Pt Ni3进行10000次CV循环 (图1 (c) ) , 发现当D-Pt Ni3小于10 nm时, 结构稳定性更好, 而当粒径大于10 nm后, 去合金化后会形成多孔的结构, 造成了内部Ni的流失。
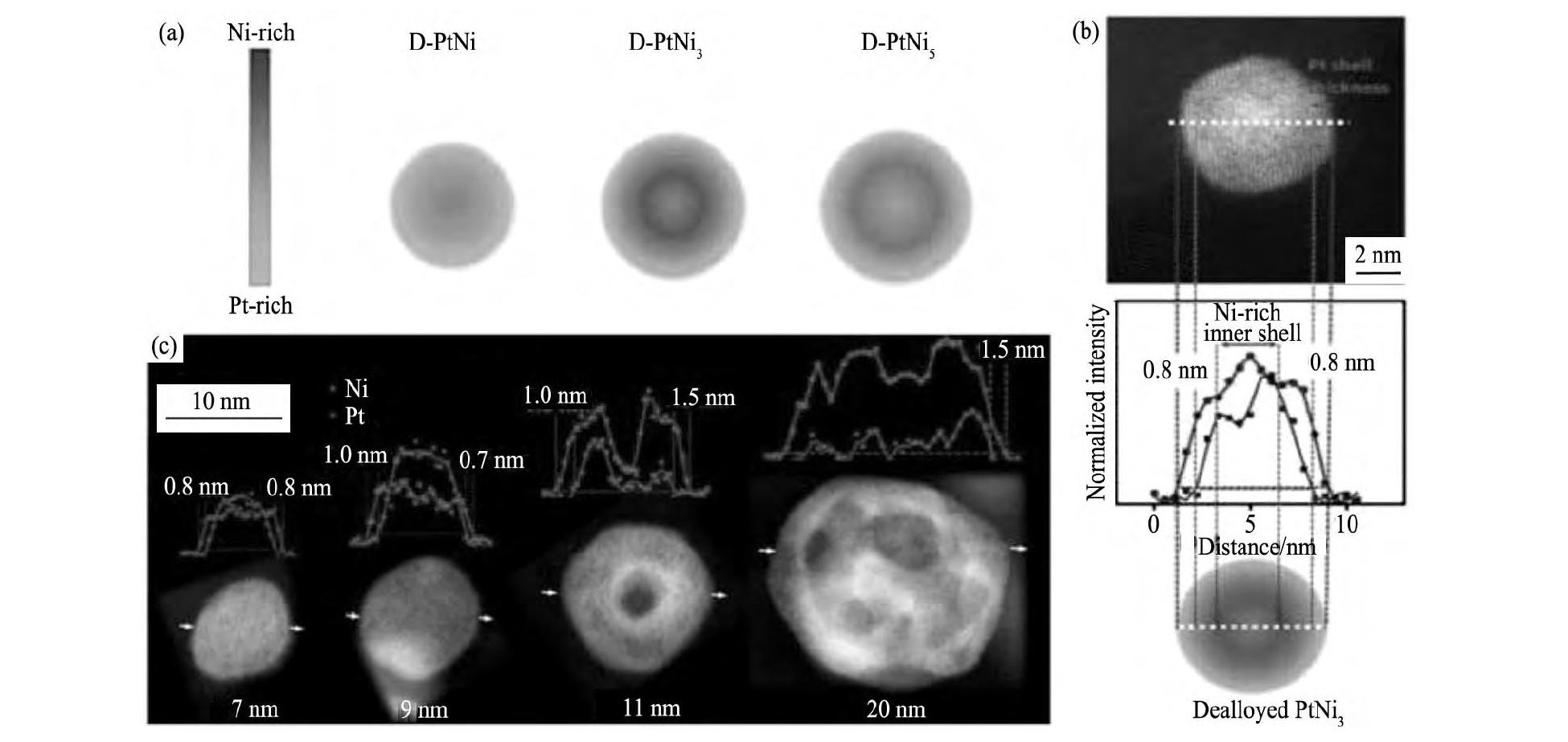
图1 Pt Nix催化剂去合金化后不同的核壳结构模型, Pt Ni3催化剂去合金化后的HADDF高分辨图及对应的EELS成分剖面图和不同尺寸的Pt Ni3催化剂在空气中去合金化, 再经过10000次CV循环后的HADDF高分辨图及对应的EELS成分线扫图Fig.1 Structural model of distinctly different compositional core-shell fine structures of dealloyed Pt Nixcatalysts (a) , high resolution HAADF-STEM image and EELS line compositional profiles of dealloyed Pt Ni3 (b) and HAADF-STEM images and correspond-ing EELS line profiles of NPs with different sizes in air-dealloyed Pt Ni3catalyst after 10000 cycles of stability test (c)
除了铂合金催化剂去合金化制备Ni@Pt催化剂, 目前报道中比较常用的方法是合成单质Ni核, 然后再在Ni核表面包覆Pt壳层。Ni核的制备方法常用的方法是肼、Na BH4 (KBH4) 还原法和溶剂热法。
单纯的 还原法很难控制Ni核形貌, 制备Ni@Pt催化活性较差[27], Chen等[28,29]改进了Na BH4还原法, 在138℃下制备出粒径分布均匀的单质Ni, 并制备了不同Pt与Ni的原子比的Ni@Pt, 发现当Pt与Ni原子比为3∶10时, 催化剂的催化活性和稳定性最好。Zhang等[30]通过溶剂热法实现了Ni核粒径和Pt Fe合金厚度控制, 然后通过酸洗制备出Ni@Pt催化剂, 当Ni@Pt粒径为5.8 nm时催化活性最优。Sneed等[31]则通过肼还原法在不同粒径的Pd前驱体表面和较低温度下 (50℃) 实现了Ni与Pt的厚度控制, 得到不同尺寸的三文治型Pd-Ni-Pt纳米催化剂, 在未来的研究中可以通过调节Ni和Pt层的厚度继续优化三文治型Pd-Ni-Pt的催化活性。
还原法很难控制Ni核形貌, 制备Ni@Pt催化活性较差[27], Chen等[28,29]改进了Na BH4还原法, 在138℃下制备出粒径分布均匀的单质Ni, 并制备了不同Pt与Ni的原子比的Ni@Pt, 发现当Pt与Ni原子比为3∶10时, 催化剂的催化活性和稳定性最好。Zhang等[30]通过溶剂热法实现了Ni核粒径和Pt Fe合金厚度控制, 然后通过酸洗制备出Ni@Pt催化剂, 当Ni@Pt粒径为5.8 nm时催化活性最优。Sneed等[31]则通过肼还原法在不同粒径的Pd前驱体表面和较低温度下 (50℃) 实现了Ni与Pt的厚度控制, 得到不同尺寸的三文治型Pd-Ni-Pt纳米催化剂, 在未来的研究中可以通过调节Ni和Pt层的厚度继续优化三文治型Pd-Ni-Pt的催化活性。
Kuttiyiel等[32]将Pt-Ni/C在氨气中510℃处理2 h, 使Ni氮化为Ni4N, 然后酸洗, 制备出Ni4N@Pt/C催化剂。然后通过HADDF-STEM, 1D, 2D-EELS证明Ni4N@Pt/C结构的存在 (图2 (a~c) ) , ORR测试表明Ni4N@Pt/C相比于Pt/C催化剂面积比活性 (jS) 和质量比活性 (jm) 都有4.5~6.5倍的提升 (图2 (d) ) 。电化学和DFT计算结果表明Ni4N同时影响Pt壳层几何结构和电子d带中心位置, 使催化剂获得更优的催化活性和稳定性。这种过渡金属氮化物@Pt催化剂在ORR和其他化学催化反应上有广泛的应用前景。
1.2 Co@Pt类、Cu@Pt催化剂
Co@Pt, Cu@Pt类催化剂的制备主要通过两种方式, 一种是合成单质核, 然后通过置换法在核表面包覆Pt壳层, 根据单质核的合成方法, 又可以细分为氢气热还原法[33]、硼氢化钠还原法[34,35,36]、电沉积法[37]和溶剂热法[38]等。一种是Pt Co, Pt Cu合金通过电化学处理[39]、酸处理[40]和热处理[41,42,43], 形成内部富Co或Cu和表层富Pt核壳结构。
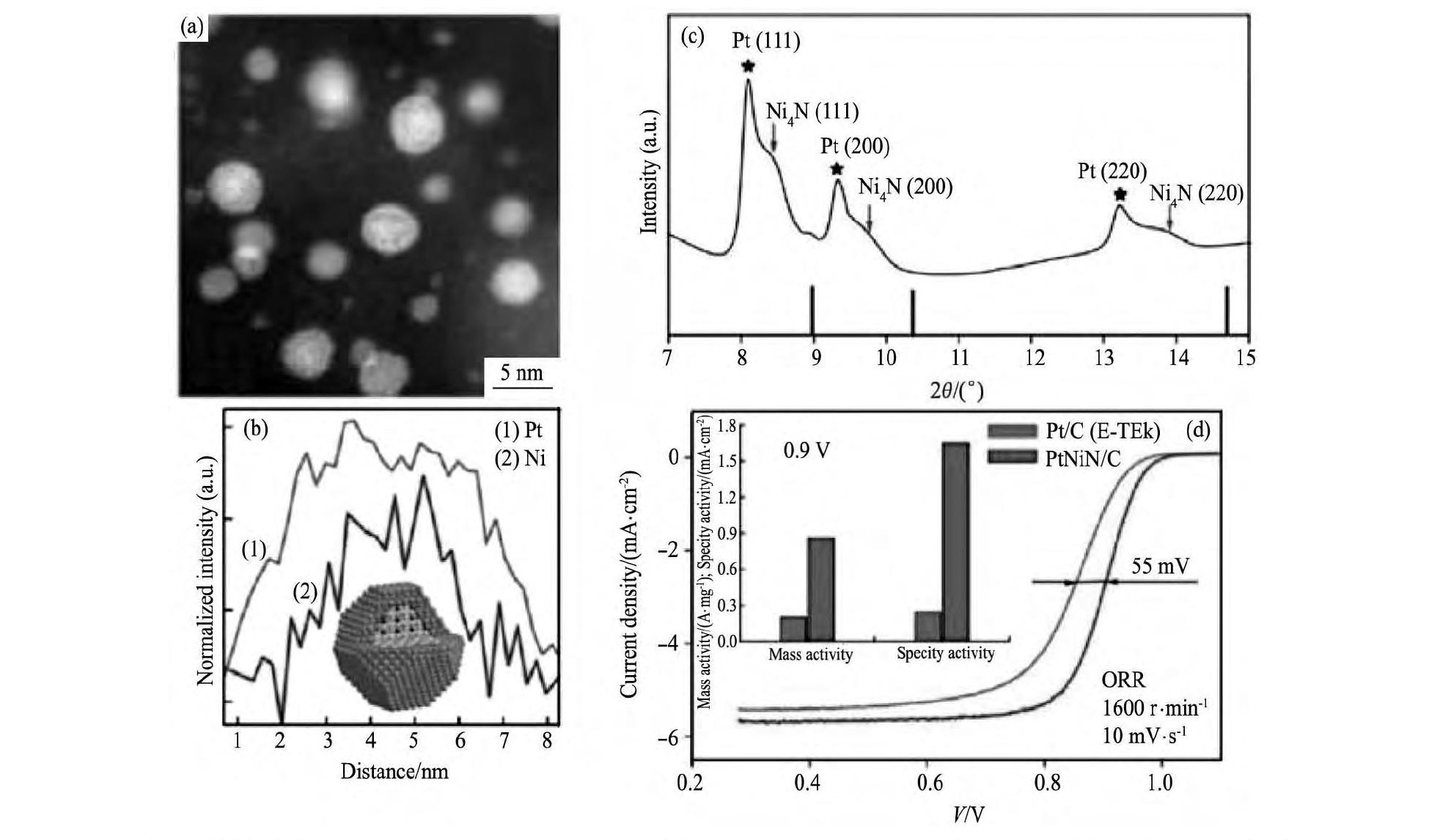
图2 Pt Ni N核壳结构纳米颗粒的STEM图和EELS线扫剖面图;Pt Ni N的同步辐射XRD衍结果表明催化剂中含有Pt和Ni4N相图和在旋转圆盘电极上测得的Pt Ni N/C与Pt/C催化剂的ORR极化曲线以及对应的质量比活性和面积比活性Fig.2 STEM image (a) and EELS line-scan profiles of Pt Ni N core-shell nanoparticles (b) ;synchrotron XRD pattern for Pt Ni N cata-lyst showing Pt and Ni4N phases (c) and polarization curves for ORR and (inset) mass and specific activities for Pt Ni N/C and Pt/C catalysts on a RDE electrode (d)
Pt Co合金主要通过表面Co原子溶解和Co与Pt之间的柯肯达尔效应 (kirkendall effect) 形成Co@Pt结构。目前, 文献报道的单纯的Co@Pt, Cu@Pt在催化活性和稳定性上并没有优势, 较高的是Cu3Pt/C催化剂, 在0.9 V (vs RHE) 的jS为0.75 A·mg-1[41]。
2 贵金属@Pt催化剂
贵金属@Pt催化剂中贵金属核主要有Pd, Au, Ag, Ru, Ir等, 其中以Pd和Au为核的贵金属@Pt催化剂的研究报道最多。
2.1 Pd@Pt类催化剂
相比于3d族过渡金属, Pd更容易被还原制备, 制备过程中, 不需要考虑氧化问题, 形貌更容易控制。最近几年文献报道的有关Pd@Pt的研究首先关注的是催化剂的形貌、尺寸控制和Pt壳层厚度调节, 其次是通过合金化进一步提高催化活性。
用欠电位沉积-置换法可以在不同形貌的Pd表面包覆单层Pt壳层, 如Pd纳米立方体[44]、纳米线[45]等。对比不同的直径的纳米线状Pd@Pt催化剂, 直径为 (2.5±0.5) nm[45] (图3) 的催化活性优于直径为7~9 nm[46], 在0.9 V (vs RHE) 时的jS和jm分别为0.77 A·cm-2和1.83 A·mg-1[45]。以上3种情况下的Pd@Pt在多次CV循环后, 催化活性都有一定提升, 很可能是在电化学过程中, Pd与Pt合金化而提升了性能[47]。欠电位沉积法只能得到单层Pt, 直接置换法Pd核会部分溶解形成缺陷, 两种方法都不能很好的控制Pt壳层厚度。
Pt壳层厚度的控制, 多采用同样的Pd核, 通过溶剂热法和还原法包覆Pt壳层, 还原剂多是AA (抗坏血酸) [47]、多元醇[48]等弱还原剂。通过调节Pd/Pt原子比可以粗略地调节Pt壳层厚度[47,48,49], 但最优的jm和面积比活性jS并不是在同一Pd/Pt原子比获得:Choi等[48]的研究结果表明, Pd@Pt0.5具有最佳的jm (0.21 A·mg-1在0.9 V下) , Pd@Pt1.5具有最佳的jS (0.58 m A·cm-2) 。Xie等[49]认为Pt在Pd纳米颗粒表面沉积的形貌主要取决于Pt的沉积速度和Pt在Pd颗粒表面的扩散速度, 如图4 (a) 。Xie通过减慢Pt前驱体的加入速度, 即减慢Pt生成速率, 使vdeposition<vdiffusion, 在Pd立方体表面逐层包覆均匀的Pt壳层, 壳层厚度为1~6层, 如图4 (b~g) 所示。同时发现单层Pt壳层具有最佳的jm, 而2~3层Pt壳层具有最佳的jS和稳定性, 与控制Pd/Pt原子比得到的结果类似。
通过不同方式控制Pt, Pd的沉积速率, 可以获得不同形貌的Pd@Pt核壳结构纳米颗粒。Kim等[50]通过加入能与Pt4+发生特异性吸附的添加剂, 减慢了Pt4+还原速率, 实现了一步制备具有树枝状Pt壳层的Pd@Pt催化剂 (图5 (a~ (c) 。Wang等[51]则在Pd十面体纳米方块表面, 不减慢Pt沉积速度, 得到了凹面Pd@Pt纳米十面体催化剂 (图5 (d~f) ) , 由于该催化剂中存在孪晶界和高指数晶面, 催化活性相对于Pt/C催化剂显著提升。
Pd核与其他元素合金化, 如与Au合金化, 会同时对Pt产生电子转移效应和横向拉升效应 (几何效应) , Liu等研究[52]制备出PdxAu@Pty催化剂, 其中Pd3Au@Pt0.5表现出最佳催化活性, jm提高至0.939 A·mg-1。另一方面, Pt合金化能提升Pt的催化活性, 主要是因为电子效应[12,13]。以Pt M合金为壳层 (M代表3d过度金属) 能显著提升催化活性, 如Pt Fe[53], Pt Ni[54,55]等, 其中Choi等[55]采用两性溶剂转移Pd核至疏水溶液中, 从而避免了Ni氧化, 合成了Pd@Pt Ni0.55/C催化剂, 通过醋酸酸洗, 其面积比活性和质量比活性分别为2.7 m A·cm-2和2.5 A·mg-1, 在目前文献报道的该类催化剂中最高。
图3 不同Pd@Pt纳米线催化剂的催化活性和稳定性对比Fig.3Comparison of ORR catalytic activity and stability for different kinds of Pd@Pt NWs catalysts
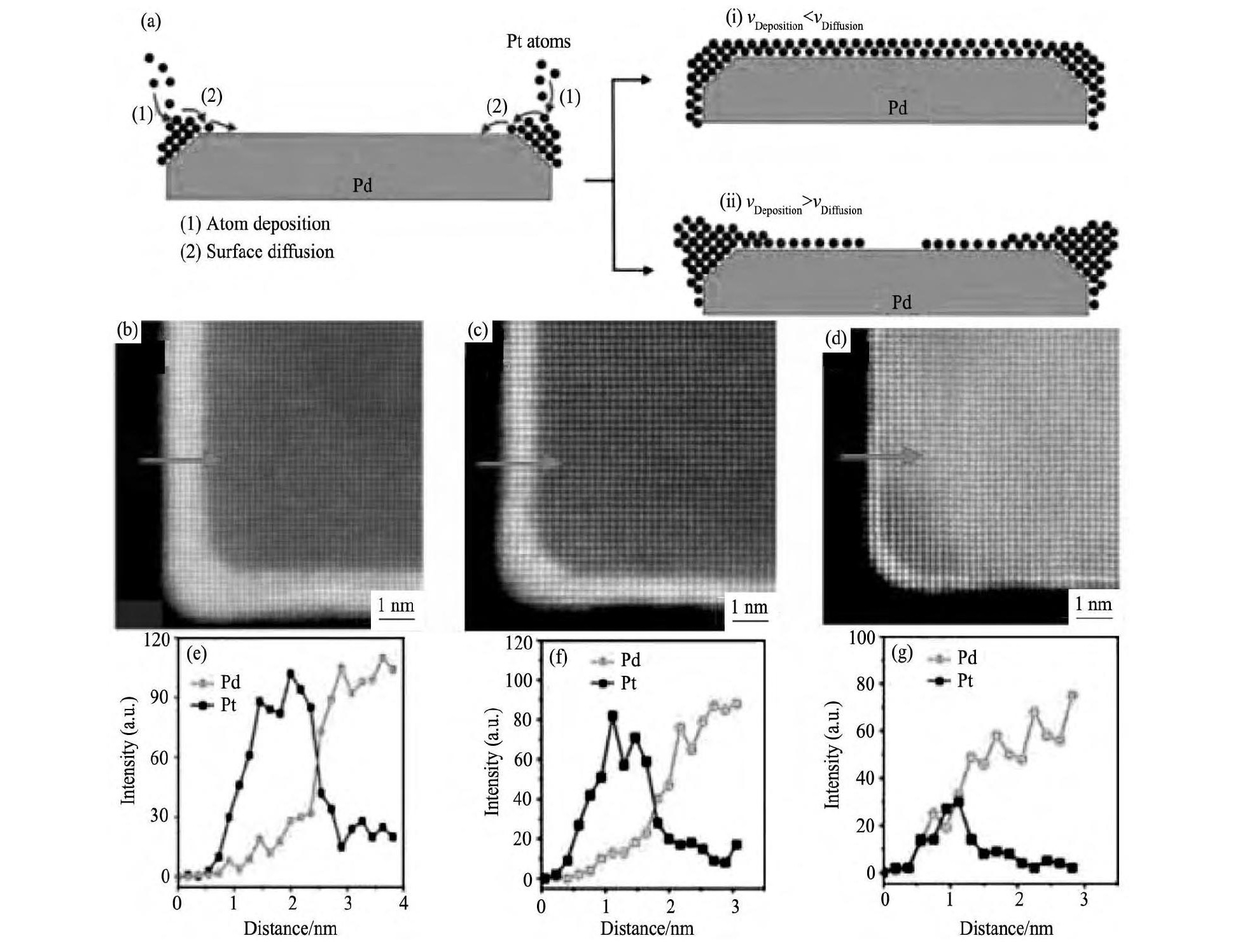
图4 Pt原子在Pd立方体表面的沉积的示意图 (a) ; (b, e) , (c, f) , (d, g) 分别是6, 4和1层Pt原子层的Pd@Pt的HAD-DF-STEM图和EELS线扫图Fig.4Schematic illustration showing deposition of Pt atoms on Pd cubic seeds (a) , low-magnification HAADF-STEM images and EDX line scan analyses of Pd@Pt6L (b, e) , Pd@Pt4L (c, f) and Pd@Pt1L nanocubes (d, g)
2.2 Au@Pt类催化剂
Au@Pt类催化剂一般都具有良好的催化活性和结构稳定性, 如Au@Pt[56,57], Au@Pt3Fe[58] (图6 (a, b) ) 和Au Cu@Pt[59] (图6 (e, f) ) 催化剂在10000次CV循环后, 催化活性衰减量都不足10%。对Au@Pt3Fe[58]和Au Cu@Pt[59]催化剂循环前后进行形貌表征, 发现催化剂形貌没有明显变化 (图6 (c, d, g, h) ) 。其中的Au@Pt3Fe[58]和Au Cu@Pt[59]催化剂, 在保持良好的稳定同时, 通过合金化, 分别对Pt壳层形成一定的电子转移效应和几何晶格应变 (压缩应变效应) , 相比于Au@Pt催化剂, 进一步提升了催化活性 (图6 (b, f) ) 。
Au@Pt中Au质量分数若高, 催化剂成本则高。Kuttiyiel等[60]在以较为廉价和稳定的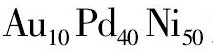 为核, 采用Cu欠电位沉积-置换法制备Au10Pd40Ni50@Pt ML催化剂, 相比于Pd Ni@Pt ML催化剂进一步提升了催化活性和稳定性。说明Au对于含大量Ni的不稳定核有一定的稳定作用。另一方面, Kang等[61]在不稳定的Ni核与Pt Ni壳层之间加入Au元素, 发现Ni@Au@Pt Ni的催化活性与Au@Pt Ni相当, 逐渐降低Au原子比至5%左右, 仍能保持Au@Pt Ni催化活性的90%以上 (图7 (a) ) 。经过10000次CV循环后, Au质量分数为5%的Ni@Au@Pt Ni质量比活性下降低于10%, 仍具有良好的稳定性 (图7 (b, c, d) ) 。Ni@Au@Pt Ni催化活性和稳定性优于Ni@Pt Ni和Pt Ni@Pt类催化剂, 是因为少量的Au插入Ni与Pt Ni之间, 限制了Ni向Pt Ni中扩散, 保持了Ni@Au@Pt Ni稳定性, 使Ni对Pt Ni壳层的影响能长时间保持。这种核/中间层/壳层结构设计可以广泛应用在平衡ORR催化剂的催化活性和稳定性上。
为核, 采用Cu欠电位沉积-置换法制备Au10Pd40Ni50@Pt ML催化剂, 相比于Pd Ni@Pt ML催化剂进一步提升了催化活性和稳定性。说明Au对于含大量Ni的不稳定核有一定的稳定作用。另一方面, Kang等[61]在不稳定的Ni核与Pt Ni壳层之间加入Au元素, 发现Ni@Au@Pt Ni的催化活性与Au@Pt Ni相当, 逐渐降低Au原子比至5%左右, 仍能保持Au@Pt Ni催化活性的90%以上 (图7 (a) ) 。经过10000次CV循环后, Au质量分数为5%的Ni@Au@Pt Ni质量比活性下降低于10%, 仍具有良好的稳定性 (图7 (b, c, d) ) 。Ni@Au@Pt Ni催化活性和稳定性优于Ni@Pt Ni和Pt Ni@Pt类催化剂, 是因为少量的Au插入Ni与Pt Ni之间, 限制了Ni向Pt Ni中扩散, 保持了Ni@Au@Pt Ni稳定性, 使Ni对Pt Ni壳层的影响能长时间保持。这种核/中间层/壳层结构设计可以广泛应用在平衡ORR催化剂的催化活性和稳定性上。
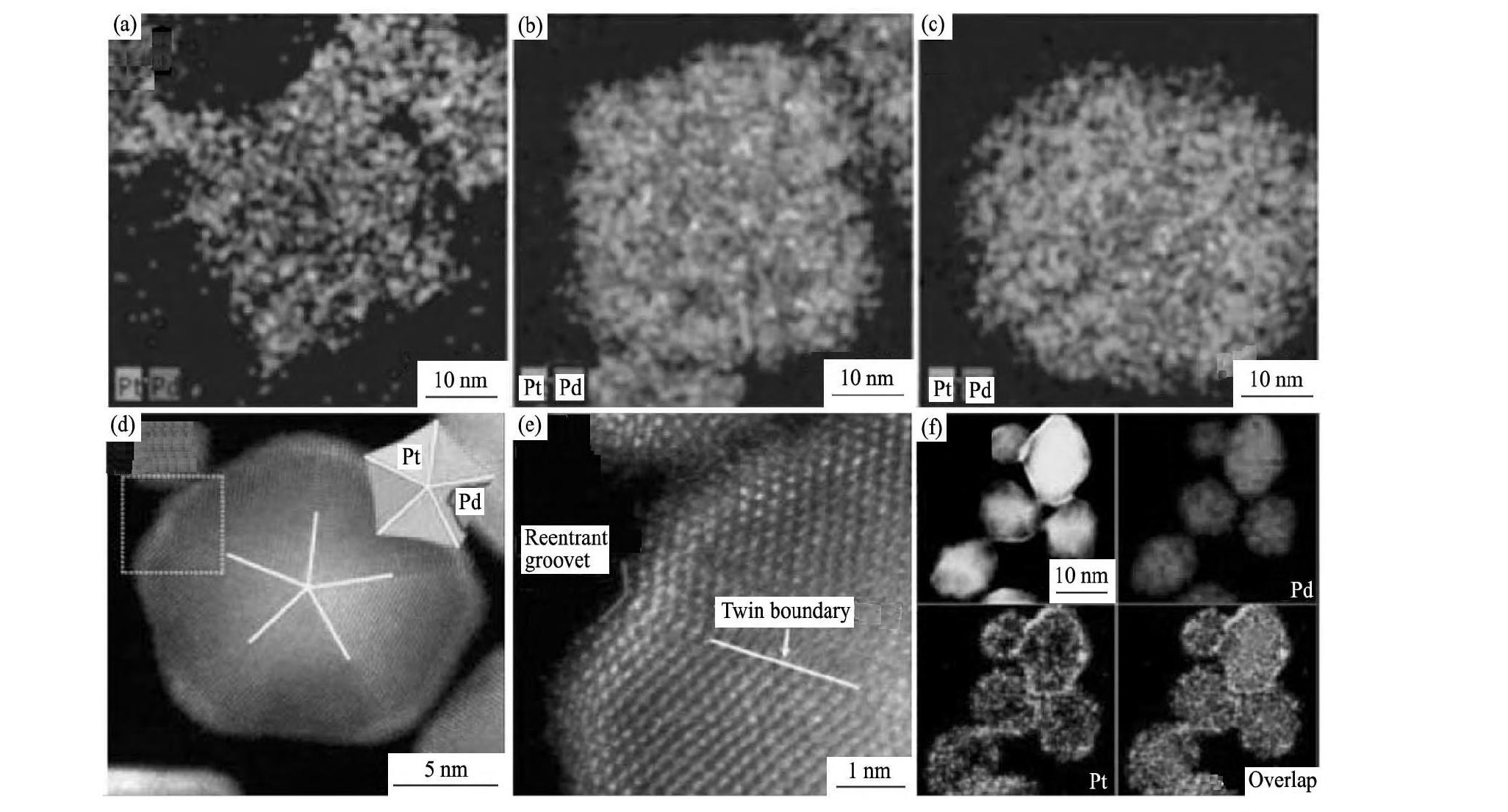
图5 Pd3@Pt1, Pd1@Pt1, and Pd1@Pt3催化剂的HADDF-STEM-EDS成分面扫图;凹面Pd@Pt纳米十面体的HAADF和HADDF高分辨图, 以及HADDF-STEM-EDS成分面扫图Fig.5 HAADF-STEM-EDS elemental mapping images of Pd3@Pt1 (a) , Pd1@Pt1 (b) , and Pd1@Pt3 (c) NC;structural and compositional analyses of Pd@Pt core-shell concave decahedra:HAADF-STEM image (d) , atomic-resolution HAADF=STEM image (e) , HAADF-STEM image and corresponding EDX mapping (f)
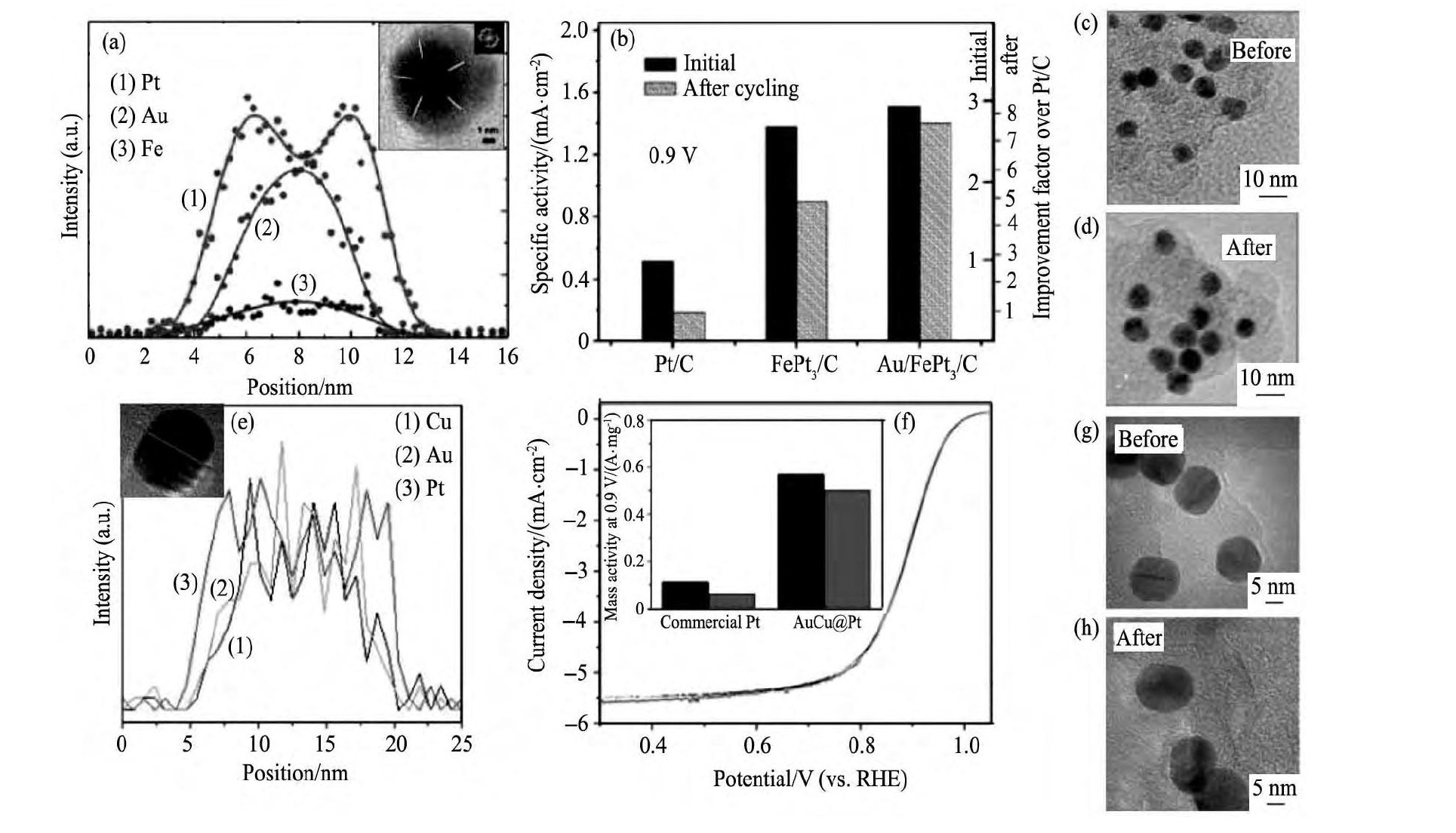
图6 Au@Fe Pt3和Au Cu@Pt催化剂循环前后的EELS线扫剖面图、稳定性对比和TEM图Fig.6 TEM, EELS line profiles and stability characterization of Au/Fe Pt3/C (a~d) and Au Cu@Pt/C (e~h) catalysts before and after potential cycles

图7 Ni@Au@Pt Ni催化剂催化活性与中间层中Au的含量之间的关系;优化的Ni@Au@Pt Ni催化剂10000次CV循环前后的ORR极化曲线和TEM图Fig.7Correlation between catalytic activity and Au content in subsurface of Ni@Au@Pt Ni nanoparticles (a) ;ORR polarization curves (b) , TEM images (c~d) of optimized Ni@Au@Pt Ni/C electrocatalysts
2.3 Ag@Pt催化剂
目前Ag@Pt类催化剂的研究较少, 主要集中在Ag Pt合金去合金化和Ag@Pt合成方法两方面。Ag Pt合金去合金化最常用的是电化学法, 只需采用数十个CV循环, 就能有效溶解掉Ag。Peng等[62]研究发现通过控制CV循环的电压范围, 能选择性溶解Ag Pt中的Ag, 如果将Ag完全溶解, 则可以得到空心结构[63,64]。相对于Ni, Co等活泼金属, Ag更容易通过化学还原法制备, 大多采用Na BH4作为还原剂[63,65], 也有文献中采用常用的溶剂热法[62,63]。由于Ag易溶解, 同时对Pt壳层的电子效应没有Ni, Co等金属明显, 所以Ag@Pt的催化活性较差, 即使是性能较好的去合金化的AgPt[64]在0.9 V (vs RHE) 的质量比活性也仅仅在0.2A·mg Pt-1左右。
3 结论
Pt基核壳结构催化剂仍然是PEMFC氧还原催化剂的研究热点, 由于Pt核壳结构催化剂成分和结构可调节, 相比Pt合金催化剂, 在提高催化活性和稳定方面具有更大潜力。HAADF-STEM、EELS、EELS-mapping等检测方法成为表征核壳结构的重要方法。近年来Pt基核壳结构催化剂取得了一系列研究成果。在制备方法上, 通过硼氢化物、AA、多元醇法、肼等化学还原法, 与置换法等方法结合使用, 实现了核和壳层厚度的精确控制, 这是调节催化剂尺寸、结构, 改善催化性能的基础。在核壳结构的设计上, M@Pt, MN@Pt, M@Pt N, MN@Pt X, M@N@Pt X等结构被成功设计和制备出来 (其中M, X指不同的3d过渡金属, N指Au, Pd等贵金属) , 尤其是M@N@Pt X类催化剂, 可以利用Pt X的高催化活性、M对Pt的电子效应和中间层N对整体结构的稳定作用, 同时保持了催化剂高催化活性和稳定性, 平衡了二者之间的矛盾。在后处理方法上, 通过一定的后处理也可以提升催化剂的活性和稳定性, 常用的方法有化学、电化学法去合金化, 臭氧、酸处理、热处理去除有机杂质及增加催化剂有序结构等, 是提高核壳结构催化剂性能的辅助手段。
参考文献
[1] Wagner F T, Lakshmanan B, Mathias M F.Electrochemistry and the future of the automobile[J].Phys.Chem.Lett., 2010, 1 (14) :2204.
[2] Gasteiger H, Kocha S, Sompalli B, Wagner F.Activity benchmarks and requirements for Pt, Pt-alloy, and non-Pt oxygen reduction catalysts for PEMFCs[J].Appl.Catal.B, 2005, 56 (1-2) :9.
[3] Markovic N, Schmidt T, Stamenkovic V, Ross P.Oxygen reduction reaction on Pt and Pt bimetallic surfaces:a selective review[J].Fuel Cells, 2001, 1 (2) :105.
[4] Nrskov J K, Bligaard T, Rossmeisl J, Christensen C H.Towards the computational design of solid catalysts[J].Nature.Chem., 2009, 1 (1) :37.
[5] Debe M K.Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells[J].Nature, 2012, 486 (7401) :43.
[6] Rabis A, Rodriguez P, Schmidt T J.Electrocatalysis for polymer electrolyte fuel cells:recent achievements and future challenges[J].ACS Catal., 2012, 2 (5) :864.
[7] Chorkendorff I, Stephens I E L, Bondarenko A S, Andersen U G, Rossmeisl J.Under standing the electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction on platinum and its alloys[J].Energy Environ Sci., 2012, 5 (5) :6744.
[8] Swider-Lyons K E, Campbell S A.Physical chemistry research toward proton exchange membrane fuel cell advance-ment[J].J.Phys.Chem.Lett., 2013, 4 (3) :393.
[9] Oezaslan M, HaschéF, Strasser P.Pt-based coreshell catalyst architectures for oxygen fuel cell electrodes[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 4 (19) :3273.
[10] Wang C, Chi M, Li D, Vliet V D, Wang G F, Lin Q Y, Mitchell J F, More K L, Markovic N M, Stamenkovic V R.Synthesis of homogeneous Pt-bimetallic nanoparticles as highly efficient electrocatalysts[J].Acs Catalysis, 2011, 1 (10) :1355.
[11] Choi S I, Lee S U, Kim W Y, Choi R, Hong K, Nam K M, Han S W, Park J T.Composition-controlled Pt Co alloy nanocubes with tuned electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction[J].Acs Applied Materials&Interfaces, 2012, 4 (11) :6228.
[12] Chen C.Highly crystalline multimetallic nanoframes with three-dimensional electrocatalytic surfaces[J].Science, 2014, 343 (6177) :1339.
[13] Su L, Jia W, Li C M, Li Y.Chem Inform abstract:mechanisms for enhanced performance of platinum-based electrocatalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J].Chemsuschem, 2014, 7 (18) :361.
[14] Wang C, Vliet D V D, Chang K C, You H, Strmcnik D, Schlueter J A, Markovic N M, Stamenkovic V R.Monodisperse Pt3Co nanoparticles as a catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction:size-dependent activity[J].J.Phys.Chem.Lett., 2009, 113 (45) :19365.
[15] Yang Y, Yang B, Hao X Y, Peng J C.Structure and catalytic performance of Pt Cu-Ce Oxmembrane electrode with acid etching[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2015, 39 (5) :435. (杨勇, 杨滨, 郝鑫禹, 彭进才.酸蚀处理对Pt Cu-Ce Ox膜电极结构与催化性能的影响[J].稀有金属, 2015, 39 (5) :435.)
[16] Dubau L, Lopez-Haro M, Castanheira L, Dursta J, Chateneta M, Bayle-Guillemaudb P, Guétazc L, Caquéd N, Rossinotd E, Maillard F.Probing the structure, the composition and the ORR activity of Pt3Co/C nanocrystallites during a 3422 h PEMFC aging test[J].Scientiae Studia, 2013, 142-143 (10) :801.
[17] Dubau L, Durst J, Maillard F, Guétazb L, Chateneta M, Andréc J, Rossinot E.Further insights into the durability of Pt3Co/C electrocatalysts:formation of“hollow”Pt nanoparticles induced by the Kirkendall effect[J].Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56 (28) :10658.
[18] Chen D, Chen R, Dang D, Shu T, Peng H L, Liao S J.High performance of core-shell structured Ir@Pt/C catalyst prepared by a facile pulse electrochemical deposition[J].Electrochemistry Communications, 2014, 46 (9) :115.
[19] Javaheri M.Investigating the influence of Pd situation (as core or shell) in synthesized catalyst for ORR in PEMFC[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40 (20) :6661.
[20] Yang L, Vukmirovic M B, Su D, Sasaki K, Herron J A, Mavrikakis M, Liao S J, Adzic R R.Tuning the catalytic activity of Ru@Pt core-shell nanoparticles for the oxygen reduction reaction by varying the shell thickness[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 117 (4) :1748.
[21] Dhavale V M, Kurungot S.Tuning the performance of low-Pt polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell electrodes derived from Fe2O3@Pt/C core-shell catalyst prepared by an in situ anchoring strategy[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116 (116) :7318.
[22] Wang C, Chi M, Li D, Vliet D V D, Wang G, Komanicky V, Chang K C, Paulikas A P, Tripkovic D, Pearson J, More K L, Markovic N M, Stamenkovic V R.Design and synthesis of bimetallic electrocatalyst with multilayered Pt-skin surfaces[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133 (36) :14396.
[23] Lai F J, Su W N, Subramanyam S L, Liu D G, Hsieh C A, Lee J, Hwang B J.Chemical dealloying mechanism of bimetallic Pt-Co nanoparticles and enhancement of catalytic activity toward oxygen reduction[J].Chemistry-AEuropean Journal, 2010, 16 (15) :4602.
[24] Wang C, Chi M F, Wang G F, Vliet D V D, Li D G, More K, Wang H H, Schlueter J A, Markovic N M, Stamenkovic V R.Correlation between surface chemistry and electrocatalytic properties of monodisperse Pt{sub x Ni{sub 1-x nanoparticles[J].Adv.Funct.Mater., 2011, 21 (1) :147.
[25] Gan L, Cui C, Rudi S, Strasser P.Core-shell and nanoporous particle architectures and their effect on the activity and stability of Pt ORR electrocatalysts[J].Topics in Catalysis, 2014, 57 (1-4) :236.
[26] Lin G, Heggen M, Rudi S P.Core-shell compositional fine structures of dealloyed PtxNi1-xnanoparticles and their impact on oxygen reduction catalysis[J].Nano Letters, 2012, 12 (10) :5423.
[27] Hielscher M.Enhanced electroactivity for the oxygen reduction on Ni@Pt core-shell nanocatalysts[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37 (19) :14902.
[28] Chen Y, Yang F, Dai Y, Chen S.Ni@Pt core-shell nanoparticles:synthesis, structural and electrochemical properties[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112 (5) :1645.
[29] Chen Y M, Liang Z X, Yang F, Liu Y W, Chen S L.Ni-Pt core-shell nanoparticles as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts:effect of Pt shell coverage[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115 (49) :24073.
[30] Zhang S, Hao Y Z, Su D, Vicky V T, Doan N, Wu Y T, Li J, Sun S H, Christopher B.Murray monodisperse core/shell Ni/Fe Pt nanoparticles and their conversion to Ni/Pt to catalyze oxygen reduction[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136 (45) :15921.
[31] Sneed B T, Young A P, Jalalpoor D, Golden M C, Mao S, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Tsung C K.Shaped Pd-Ni-Pt core-sandwich-shell nanoparticles:influence of Ni sandwich layers on catalytic electrooxidations[J].Acs Nano, 2014, 8 (7) :7239.
[32] Kuttiyiel K A, Sasaki K, Choi Y M, Su D, Liu P, Radoslav R.Adzic Nitride stabilized Pt Ni core-shell nanocatalyst for high oxygen reduction activity[J].Nano Letters, 2012, 12 (12) :6266.
[33] Lia Z, Hea C, Caib M, Kanga S, Shen P K.A strategy for easy synthesis of carbon supported Co@Pt coreeshell configuration as highly active catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37 (19) :14152.
[34] Reyes-Rodríguez J L, Godínez-Salomón F, Leyva M A, Solorza-Feria O.RRDE study on Co@Pt/C core-shell nanocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38 (28) :12634.
[35] Lin R, Cao C H, Zhao T T, Huang Z, Li B.Wieckowski A, Ma J X.Synthesis and application of core-shell Co@Pt electrocatalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J].Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 223 (223) :190.
[36] Sarkar A, Manthiram A.Synthesis of Pt@Cu coreshell nanoparticles by galvanic displacement of Cu by Pt4+ions and their application as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells[J].J.Phys.Chem.C, 2010, 114 (10) :4725.
[37] Kulp C, Gillmeister K, Widdra W, Bron M.Synthesis of Cu core Pt shell nanoparticles as model structures for core-shell electrocatalysts by direct platinum electrodeposition on copper[J].Chemphyschem, 2013, 14 (6) :1205.
[38] Zhu H.Synthesis and characterization of Cu@Pt/C core-shell structured catalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J].Fuel&Energy Abstracts, 2011, 36 (15) :9151.
[39] O'Reilly M, Edrisinha C, Sigafoos J, Lancioni G, Machalicek W, Antonucci M.Formation and analysis of core-shell fine structures in Pt bimetallic nanoparticle fuel cell electrocatalysts[J].Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 2012, 116 (36) :19073.
[40] Luo M, Wei L, Wang F, Zhu H.Gram-level synthesis of core-shell structured catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J].Dalton Transactions, 2014, 270 (3) :34.
[41] Wang D, Xin H L, Hovden R, Wang H, Yu Y C, Muller D A, Di Salvo F J, Abruna H D.Structurally ordered intermetallic platinum-cobalt core-shell nanoparticles with enhanced activity and stability as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts[J].Nature Materials, 2013, 12 (1) :81.
[42] Mani P, Srivastava R, Strasser P.Dealloyed Pt-Cu core-shell nanoparticle electrocatalysts for use in PEM fuel cell cathodes[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112 (7) :2770.
[43] Guo H Z, Liu X, Bai C D, Chen Y Z, Wang L S, Zheng M S, Dong Q F, Peng D L.Effect of component distribution and nanoporosity in Cu Pt nanotubes on electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction[J].Chemsuschem, 2015, 8 (3) :486.
[44] Taufany F, Pan C, Rick J, Chou H, Tsai M, Hwang B, Liu D, Lee J, Tang M, Lee Y C, Chen C.Kinetically controlled autocatalytic chemical process for bulk production of bimetallic core-shell structured nanoparticles[J].Acs.Nano., 2011, 5 (12) :9370.
[45] Mullan F, Frehywot S, Omaswa F, Buch E, Chen C, Greysen S R, Wassermann T, El Gaili D E A, Awases M, Boelen C, Isidore M J, Delanyo D, Josefo D, Abraham F, Jehu H, Marian I, Karim J, KoumaréAbdel, Mipando M, Monekosso L G, Olapade-Olaopa E O, Rugarabamu P, Sewankambo N K, Ross H, Ayas H, Chale S B, Cyprien S, Cohen J, Haile-Mariam T, Hamburger E, Jolley L, Kolars J C, Kombe G, Neusy A.Enhanced electrocatalytic performance of processed, ultrathin, supported Pd-Pt core-shell nanowire catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction[J].J.Am.Chem.Soc, 2011, 133 (25) :9783.
[46] Li H H, Ma S Y, Fu Q Q, Liu X J, Wu L, Yu S H.Scalable bromide-triggered synthesis of Pd@Pt core-shell ultrathin nanowires with enhanced electrocatalytic performance toward oxygen reduction reaction[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137 (24) :7862.
[47] Zhang G, Shao Z G, Lu W, Xie F, Xiao H, Qin X P, Yi B L.Core-shell Pt modified Pd/C as an active and durable electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in PEMFCs[J].Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2013, s132-133 (12) :183.
[48] Choi R, Choi S I, Choi C H, Nam K M, Woo S I, Park J T, Han S W.Designed synthesis of well-defined Pd@Pt core-shell nanoparticles with controlled shell thickness as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts[J].Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) , 2013, 19 (25) :8190.
[49] Xie S, Choi S I, Lu N, Roling L T, Herron J A, Zhang L, Park J, Wang J, Kim M J, Xie Z, Mavrikakis M, Xia Y.Atomic layer-by-layer deposition of Pt on Pd nanocubes for catalysts with enhanced activity and durability toward oxygen reduction[J].Nano Letters, 2014, 14 (6) :3570.
[50] Kim Y, Lee Y W, Kim M, Han S W.One-pot synthesis and electrocatalytic properties of Pd@Pt core-shell nanocrystals with tailored morphologies[J].Chemistry, 2014, 20 (26) :7901.
[51] Wang X, Vara M, Luo M, Huang H W, Ruditskiy A, Park J, Bao S X, Liu J Y, Howe J, Chi M F, Xie Z X, Xia Y N.Pd@Pt core-shell concave decahedra:a class of catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction with enhanced activity and durability[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137 (47) :15036.
[52] Liu H Q, Yao R, Wang D, He J F, Li M R, Song Y J.Facile synthesis of carbon supported Pd3Au@super-thin Pt core/shell electrocatalyst with a remarkable activity for oxygen reduction[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119 (8) :4052.
[53] Mazumder V, Chi M F, More L K, Sun S H.Core/shell Pd/Fe Pt nanoparticles as an active and durable catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132 (23) :7848.
[54] Zhao X, Chen S, Fang Z C, Ding J, Sang W, Wang Y C, Zhao J, Peng Z M, Zeng J.Octahedral Pd@Pt1.8Ni core-shell nanocrystals with ultrathin Pt Ni alloy shells as active catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137 (8) :2804.
[55] Choi S, Shao M, Lu N, Ruditskiy A, Wang J, Xia Y.Synthesis and characterization of Pd@Pt Ni core shell octahedra with high activity toward oxygen reduction[J].Acs Nano, 2014, 8 (10) :10363.
[56] Bian T, Zhang H, Jiang Y Y, Jin C H, Wu J B, Yang H, Yang D R.Epitaxial growth of twinned Au-Pt coreshell star-shaped decahedra as highly durable electrocatalysts[J].Nano Letters, 2015, 15 (12) :7808.
[57] Higuchi E, Okada K, Chiku M, Inoue H.Electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction of Au core/Pt shell nanoparticle-loaded carbon black catalyst with different core sizes[J].Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 3 (179) :100.
[58] Wang C, Vliet D V D, More K L, Zaluzec N J, Peng S, Sun S H, Daimon H, Wang G F, Greeley J, Pearso J, Paulikas A P, Karapetrov G, Strmcnik D, Markovic N M, Stamenkovic V R.Multimetallic Au/Fe Pt3nanoparticles as highly durable electrocatalyst[J].Nano Letters, 2011, 11 (3) :919.
[59] Yang J, Chen X, Yang X, Ying J Y.Stabilization and compressive strain effect of Au Cu core on Pt shell for ox-ygen reduction reaction[J].Energy Environ.Sci., 2012, 5 (10) :8976.
[60] Kuttiyiel K A, Sasaki K, Dong S, Su D, Vukmirovica M B, Marinkovicc N S, Adzic R R.Pt monolayer on Austabilized Pd Ni core-shell nanoparticles for oxygen reduction reaction[J].Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 110 (6) :267.
[61] Kang Y J, Snyder J H, Chi M F, Li D G, More K L, Markovic N M, Stamenkovic V R.Multimetallic core/interlayer/shell nanostructures as advanced electrocatalysts[J].Nano Letters, 2014, 14 (11) :6361.
[62] Peng Z, You H, Yang H.An electrochemical approach to Pt Ag alloy nanostructures rich in Pt at the surface[J].Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20 (21) :3734.
[63] Tsai Y L, Huang K L, Yang C C, Ye J S, Pan L S, Lee C L.Preparation and cyclic voltammetric dissolution of core-shell-shell Ag-Pt-Ag nanocubes and their comparison in oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39 (39) :5528.
[64] Peng Z, Wu J, Yang H.Synthesis and oxygen reduction electrocatalytic property of platinum hollow and platinum-on-silver nanoparticles?[J].Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 22 (3) :1098.
[65] Pech-Pech I E, Gervasio D F, Godínez-Garcia A, Solorza-Feria O, Pérez-Robles J F.Nanoparticles of Ag with a Pt and Pd rich surface supported on carbon as a new catalyst for the oxygen electroreduction reaction (ORR) in acid electrolytes:part 1[J].Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 276 (15) :365.