BP神经网络在地基土压缩指数预测中的应用
蒋建平1,章杨松2,阎长虹3,高广运4
(1. 上海海事大学 海洋环境与工程学院,上海,201306;
2. 南京理工大学 土木工程系,江苏 南京,210094;
3. 南京大学 地球科学系,江苏 南京,210093;
4. 同济大学 土木及地下工程教育部重点实验室,上海,200092)
摘 要:
摘 要:为了寻求基于多个常规物理参数间接得到土变形参数的途径,根据几个实际工程中的土工试验数据,利用BP神经网络方法对土压缩指数进行预测。选取土塑性指数、含水量、孔隙比、密度这4个常规物理参数作为影响土压缩指数的主要因素,得出土压缩指数的BP神经网络预测模型。结果表明:训练BP神经网络时,49组自变量数据中土压缩指数的BP神经网络拟合值与实测值的相对误差为-3.513 938 0%~1.570 422 5%,相对误差绝对值的平均值为0.915 48%;10组自变量数据中土压缩指数的BP神经网络预测值与实测值的相对误差为 -1.805 521 0%~6.012 417 3%,相对误差绝对值的平均值为3.329 40%。可见,本文建立的基于4个物理参数的土压缩指数BP神经网络预测模型是可行的。
关键词:
中图分类号:TU411 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)02-0722-06
Application of BP neural network in prediction of
compression index of soil
JIANG Jian-ping1, ZHANG Yang-song2, YAN Chang-hong3, GAO Guang-yun4
(1. College of Ocean Environment and Engineering, Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai 201306, China;
2. Department of Civil Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China;
3. Department of Earth Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China;
4. Key Laboratory of Geotechnical and Underground Engineering of Ministry of Education,
Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China)
Abstract: In order to acquire deformation parameters based on many routine physical parameters, a prediction of compression index was carried out with BP neural network based on the testing data of soil in several engineering sites. Taking plasticity index, water content, void ration and density of soil as primary influence factors, the prediction model of compression index based on BP neural network was obtained. The results show that the relative error of fitting value of compression index compared with the observed value for 49 groups of independent variables training BP neural network model is from -3.513 938 0% to 1.570 422 5%, and the average value of absolute value of relative error is 0.915 48%. And the relative error of fitting value of compression index compared with the observed value for 10 groups of independent variables validating BP neural network model is from -1.805 521 0% to 6.012 417 3%, and the average value of absolute value of relative error is 3.329 40%. Therefore, the prediction model of compression index with BP neural network based on 4 routine physical parameters is doable.
Key words: compression index; BP neural network; prediction; routine physical parameters
地基岩土变形参数是岩土工程中的重要指标,也是研究的热点问题之一[1-3]。土压缩指数是表征土体压缩性的重要变形参数,一般通过室内侧限压缩试验获得[4-6]。由于土压缩指数的试验费时费力,可考虑寻求间接方法。土的压缩性能是土体本身的物理特性所致,它与土的物理参数间应该存在一定的相关关系[4, 7-10]。如缪林昌等[4]在研究江苏海相软土压缩特性时发现软土压缩指数与含水量成正比。
土的一些常规物理参数的试验相对来说比土压缩指数的试验简单得多,因此,可利用土压缩指数与物理参数的相关关系,由多个常规物理参数来间接得到土的压缩指数。在岩土压缩指数与物理参数的多元关系方面的研究极少,张英魁等[11]研究了岩石压缩指数与压力、孔隙度的二元关系。目前,对土体方面研究还未发现有相关的报道。神经网络方法能很好地解决因变量与多个自变量的非线性关系问题,在岩土工程领域得到了初步应用[12-14]。因此,本文作者根据实际工程中的土工试验数据,基于多个物理参数建立土压缩指数的BP神经网络预测模型。
1 影响土压缩指数的主要因素及土工试验
经综合分析,选取影响土压缩指数的主要因素有塑性指数、含水量、孔隙比、密度。其中:孔隙比是表征土体中孔隙含量的指标,指孔隙体积与固体颗粒实体体积之比;密度为土单位体积的质量;含水量为土中水的质量与土粒质量之比;塑性指数指的是黏性土液态处于流动状态时的含水量与可塑性状态时含水量的差,其值越大,表明黏性土的可塑性越好。塑性指数综合反映了土的物质组成。
土的取样和土工试验严格按照《岩土工程勘察规范》(GB 50021—2001)、《土工试验方法标准》(GB/T 50123—1999)进行。原状土的取样采用钻孔过程中的薄壁取土器进行。
作者在承担的有关苏州—南通长江大桥工程、镇江—扬州(即润扬)长江大桥工程、南京地铁工程等项目中做了大量的第四纪土层的土工试验。压缩指数的试验是在压缩仪中进行。先用金属环刀从原状土样中切取试件,然后,将试件连同环刀侧限压缩仪的内环中,试件的上下各放1块透水石,再通过传压板施加竖向压力。密度用环刀法进行,含水量采用烘干法测定。塑性指数由液限、塑限获得,液限、塑限采用液、塑限联合测定法测定。试验结果如表1和表2所示。
2 土压缩指数的BP神经网络预测
2.1 BP神经网络的基本原理
人工神经网络[13](Artificial neural network,ANN)是近年来迅速发展的前沿性交叉学科,具有自组织、自学习、联想、容错、抗干扰、非线性动态处理等特征,可实现高度的网络输入因素与网络输出目标间的非线性映射关系。神经网络可揭示数据样本中蕴含的非线性关系,大量处理单元组成非线性自适应动态系统,在不同程度和层次上可模仿大脑的信息处理机 理,灵活方便地对多成因的、复杂的未知变量进行高度建模。
BP神经网络[15-16](Back propagation artificial neural network,即BPANN)是典型的多层前馈型网络,由输入层、隐含层和输出层组成,层与层之间多采用全部连接方式,同一层单元之间不存在相互连接。BP网络算法的基本思想是通过网络输出误差的反向传播,不断调整和修改网络的连接权值,从而使网络误差达到最小。BP神经网络的训练过程包括前向计算和误差反向传播2个过程。对于输入信号,先向前传播到隐含层,经过作用函数后,再把隐含层的输出信息传播到输出层,若在输出层得不到期望的输出,则转入反向传播,将误差信号沿原来通路返回,通过修改各层神经元的权值,使得误差信号最小。BP神经网络的节点作用函数一般为“S”型函数。
常用的激活作用函数f(x)为可导的Sigmoid函数:
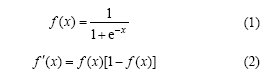
误差函数R为

式中:Yj为期望输出;Ymj为实际输出;n为样本长度。
BP算法权值修正公式可以统一表示为:

式中:![]() 为神经元的连接权值;
为神经元的连接权值;![]() 为网络学习率;opj为样本p的输出;
为网络学习率;opj为样本p的输出;![]() 为误差修正值。
为误差修正值。
表1 训练模型的实测数据及拟合值与实测值的比较
Table 1 Data of training model and fitting values by BP neural network

2.2 BP神经网络结构设计、学习与检验
2.2.1 BP神经网络结构设计
本文要建立的预测模型中,因变量为1个,自变量为4个,因此,可确定BP神经网络的输入层数为4个,输出层数为1个。可见,神经网络结构的确定主要是确定隐含层数及其节点数。
建立多层神经网络模型时,采用适当的隐层节点数是很重要的。经过反复试算,最终确定隐层数取3,每个隐含层的节点数都取10,BP神经网络结构示意图如图1所示。
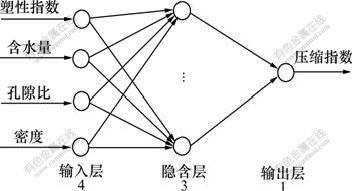
图1 BP神经网络结构示意图
Fig.1 Sketch map of framework of BPANN
2.2.2 BP神经网络学习训练
神经网络的学习,主要是通过样本的反复训练来实现。训练结果直接决定系统的质量。在本文的BP神经网络学习、训练时,先对原始的样本数据进行标准化转换,再设置最小训练速率为0.1,动态参数为0.6,Sigmoid函数为0.9,训练过程控制中,最大迭代次数为20 000。因不知迭代次数达20 000时的误差,故将误差设置为小于迭代次数为20 000时的误差,确定允许误差为0.000 001。
土压缩指数的神经网络的训练样本由如下4维矢量构成:X=[x1, x2, x3, x4],x1, x2, x3, x4分别代表塑性指数、含水量、孔隙比、密度。
将表1中的第2~第6列数据代入神经网络进行训练。在训练过程中,当迭代次数为20 000时,拟合残差为0.000 144 575,结果如图2所示。
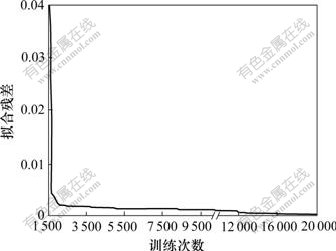
图2 误差与训练次数的关系曲线
Fig.2 Error after calculation
训练结束后,可得到第1~3隐含层各个节点的权重矩阵及输出层各个节点的权重矩阵。
2.2.3 BP神经网络检验及误差分析
训练好的网络已经具有计算土压缩指数的能力。为了验证训练效果,对神经网络进行检验,检验结果如表2、图3和图4所示。
表2 BP神经网络预测值与实测值的比较
Table 2 Comparison between prediction value by BP neural network and measurement value

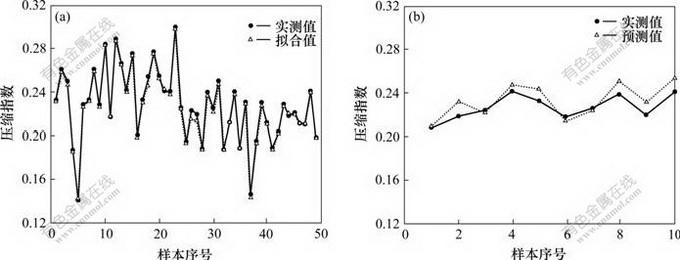
(a) 拟合值与实测值的比较;(b) 预测值与实测值的比较
图3 拟合值和预测值与实测值的比较
Fig.3 Comparison of fitting values and prediction values with actual values
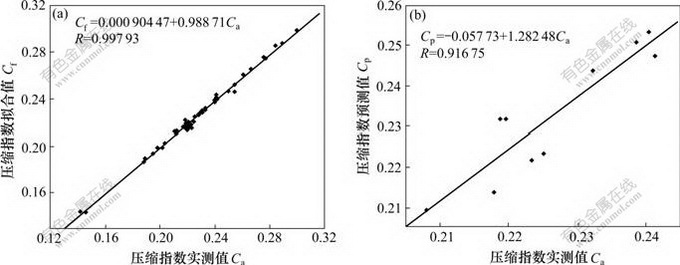
(a) 拟合值与实测值的比较;(b) 预测值与实测值的比较
图4 拟合值、预测值与实测值的关系曲线
Fig.4 Correlativity curves among fitting value, prediction value and actual value
基于本文的BP模型,由训练数据得出的结果是拟合值(表1),由检验数据得出的结果是预测值(表2)。从图3可看出:拟合值与实测值几乎重合,预测值与实测值较吻合。从图4可见:拟合值、预测值与实测值的相关曲线(相关系数R都达0.916 75以上)几乎都过原点,并与坐标轴几乎都呈45?的直线;49组自变量数据的土压缩指数的BP神经网络拟合值与实测值的相对误差为-3.513 938 0%~1.570 422 5%,相对误差绝对值的平均值为0.915 48%;10组自变量数据的土压缩指数的BP神经网络预测值与实测值的相对误差为-1.805 521 0%~6.012 417 3%,相对误差绝对值的平均值为3.329 40%。
3 结论
(1) 训练BP神经网络时,土压缩指数的BP神经网络拟合值与实测值的相对误差为-3.513 938 0%~ 1.570 422 5%,相对误差绝对值的平均值为0.915 48%。
(2) 验证BP神经网络时,土压缩指数的BP神经网络预测值与实测值的相对误差为-1.805 521 0%~ 6.012 417 3%,相对误差绝对值的平均值为3.329 40%。
(3) 基于BP神经网络对土压缩指数进行计算和预估是完全可行的。
参考文献:
[1] 杨坪, 唐益群, 周念清, 等. 上海充填土自重固结沉降离心模型试验[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(4): 862-867.
YANG Ping, TANG Yi-qun, ZHOU Nian-qing, et al. Consolidation settlement of Shanghai dredger fill under self-weight using centrifuge modeling test[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2008, 39(4): 862-867.
[2] ZHANG Ping, XU Jian-guang, LI Ning. Fatigue properties analysis of cracked rock based on fracture evolution process[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(1): 95-99.
[3] 刘松玉, 经绯. 软土地基上分期施工的路堤沉降预测方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2003, 25(2): 228-232.
LIU Song-yu, JING Fei. Settlement prediction of embankments with stage construction on soft ground[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2003, 25(2): 228-232.
[4] 缪林昌, 张军辉, 陈艺南. 江苏海相软土压缩特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(11): 1171-1174.
MIU Lin-chang, ZHANG Jun-hui, CHEN Yi-nan. Study on compressibility of Jiangsu marine clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(11): 1171-1174.
[5] 张振营, 杨云芳, 陈云敏. 城市生活垃圾的应力压缩曲线及压缩参数[J]. 浙江理工大学学报, 2008, 25(1): 119-122.
ZHANG Zhen-ying, YANG Yun-fang, CHEN Yun-min. Study on the properties of stress compression for municipal solid waste[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-tech University, 2008, 25(1): 119-122.
[6] 徐庆华, 徐庆飞. 地基沉降计算中压缩指数法修正系数研究[J]. 大坝与安全, 2004(4): 40-43.
XU Qing-hua, XU Qing-fei. Study on correction factor of compression index method in settlement calculation[J]. Dam and Safety, 2004(4): 40-43.
[7] 肖军华, 刘建坤, 彭丽云, 等. 黄河冲积粉土的密实度及含水率对力学性质影响[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(2): 409-414.
XIAO Jun-hua, LIU Jian-kun, PENG Li-yun, et al. Effects of compactness and water Yellow-River alluvial silt content on its mechanical behaviors[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(2): 409-414.
[8] 蒋建平, 章杨松, 高广运, 等. 长江下游水下地基土两类参数相关关系试验研究[J]. 四川大学学报: 工程科学版, 2008, 40(3): 13-19.
JIANG Jian-ping, ZHANG Yang-song, GAO Guang-yun, et al. Experimental study on correlativity of testing parameters and educing parameters of foundation soil under water in the lower reaches of Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Sichuan University: Engineering Science Edition, 2008, 40(3): 13-19.
[9] 蒋建平, 罗国煜. 苏通大桥地基粉质粘土物性指标相关关系试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(6): 1669-1674.
JIANG Jian-ping, LUO Guo-yu. Experimental investigation on correlativity between liquidity index and other parameters of silty clay in Su-Tong bridge subgrade[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(6): 1669-1674.
[10] 蒋建平, 罗国煜, 高广运. 粘性土变形和强度参数分析[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2007, 7(6): 76-79.
JIANG Jian-ping, LUO Guo-yu, GAO Guang-yun. Analysis of deformation and strength parameters for cohesive clay[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2007, 7(6): 76-79.
[11] 张英魁, 刘斌, 古武, 等. 利用多元回归方法确定岩石压缩指数[J]. 油气井测试, 2003, 10(1): 7-10.
ZHANG Ying-kui, LIU Bin, GU Wu, et al. Determine the rock compressibility by the multiple regression analysis method[J]. Well Testing, 2003, 10(1): 7-10.
[12] 张孟喜, 李钢, 冯建龙, 等. 双连拱隧道围岩变形有限元与BP神经网络耦合分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(5): 1243-1248.
ZHANG Meng-xi, LI Gang, FENG Jian-long, et al. Coupling analysis of surrounding rocks in double-arch tunnel by FE and BP neural networks[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(5): 1243-1248.
[13] 高浪, 谢康和. 人工神经网络在岩土工程中的应用[J]. 土木工程学报, 2002, 35(4): 77-81.
GAO Lang, XIE Kang-he. Application of artificial neural network to geotechnical engineering[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(4): 77-81.
[14] 常斌, 李宁, 马玉扩. 神经网络方法在洞室施工期应力及变形预测中的应用及其改进[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(7): 1132-1135.
CHANG Bin, LI Ning, MA Yu-kuo. Improvement and application of ANN method in stress and deformation predictions during tunnel excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(7): 1132-1135.
[15] 邵拥军, 贺辉, 张贻舟, 等. 基于BP神经网络的湘西金矿成矿预测[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(6): 1192-1198.
SHAO Yong-jun, HE Hui, ZHANG Yi-zhou, et al. Metallogenic prediction of Xiangxi gold deposit based on BP neural networks[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(6): 1192-1198.
[16] 唐启义, 冯明光. DPS数据处理系统: 实验设计、统计分析及数据挖掘[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007.
TANG Qi-yi, FENG Ming-guang. DPS data processing system: Experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007.
收稿日期:2009-06-02;修回日期:2009-10-12
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50678128);上海市教委科研创新项目(09YZ250);上海海事大学科研基金资助项目(2009160);洪口、海岸及近海工程校重点学科项目(2009445878)
通信作者:蒋建平(1966-),男,湖南邵阳人,副教授,从事岩土工程、港航工程的教学和研究工作;电话:13917926638;E-mail: jjpwx@163.com


