文章编号:1004-0609(2007)06-1014-05
盐酸介质中异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜萃取Pd(Ⅱ)的机理
李耀威1,古国榜2
(1. 华南师范大学 化学与环境学院,广州 510006;
2. 华南理工大学 化学科学学院,广州 510640)
摘 要:
合成了异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜(ABSO),研究了盐酸介质中ABSO萃取Pd(Ⅱ)的机理。考察水相H+浓度和萃取剂浓度对钯萃取的影响, 采用斜率法、红外光谱和核磁共振H谱法确定了萃合物的组成及萃取平衡的机理。结果表明:低酸度条件下,H+浓度对钯的分配比无影响,ABSO以中性配位萃取机理萃取Pd(Ⅱ),并通过苯并噻唑环上的氮原子与Pd(Ⅱ)配位形成萃合物PdCl2(ABSO)2。
关键词:
中图分类号:TF 804.2 文献标识码:A
Mechanism of extraction of Pd(Ⅱ) with iso-amyl benzothiazolyl sulfoxide from hydrochloric acid media
LI Yao-wei1, GU Guo-bang2
(1. School of Chemistry and Environment, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China;
2. School of Chemistry Science, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China)
Abstract: Iso-amyl benzothiazolyl sulfoxide (ABSO) was synthesized and the mechanism of extraction of Pd(Ⅱ) with ABSO from hydrochloric acid media was studied. The effects of H+ and extractant concentration on the extraction of Pd(Ⅱ) were investigated. The composition of extracted complex and mechanism of extraction were determined by slope method, IR and H MNR spectra. The results show that the distribution ratio of Pd(Ⅱ) is independent on H+ concentration and ABSO acts as a neutral ligand coordinated with Pd(II) via thiazolyl N atom and forms Pd Cl2(ABSO)2 at low acidity.
Key words: palladium; iso-amyl benzothiazolyl sulfoxide; solvent extraction
钯是重要的贵金属元素,作为性能优越的催化剂,钯及其化合物广泛应用于石油化工、精细化工及电子工业等领域。含钯催化剂失效后,其中的金属数量并没有减少太多,因此含钯废催化剂是宝贵的二次资源,由于钯储量少、价格昂贵,加强钯二次资源的回收利用显得尤为重要。溶剂萃取技术已被广泛应用于回收和分离提纯贵金属[1?4]。在众多的萃取剂中,亚砜类萃取剂由于具有化学性能稳定,耐强酸、强碱作用,操作安全,萃取性能好等优点,被认为是贵金属萃取分离中很有前途的萃取剂。人们在亚砜萃取钯方面做了大量的研究工作[5?8],但多数文献仅局限于双烷基取代亚砜或石油亚砜的萃取研究报道。由于近年来石油亚砜资源供应缺乏,为了寻求新型的亚砜类萃取剂,本文作者合成了带杂环取代基的异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜并研究其萃取钯的机理。
1 实验
1.1 化学试剂与仪器
实验中所用主要试剂如下:促进剂-M,天津有机化工一厂,分析纯;溴代异戊烷,上海化学试剂一厂,分析纯;氢氧化钾,苯,广州化学试剂厂,分析纯;丙酮,汕头光华化学试剂厂,分析纯;双氧水,成都联合化工试剂研究所,分析纯。实验中的主要仪器有:VECTOR33红外光谱仪,德国Bruker公司生产;AVANCE核磁共振仪,400 MNz,德国Bruker公司生产; Finigan?2000 mass apparatus质谱仪;WFX?IB型原子吸收分光光度计,北京第二光学仪器厂生产;HY?4型调速电动定时振荡器。
1.2 异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜(ABSO)的合成
异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜按文献[9]合成,产物的表征数据如下:FT-IR(KBr):3 061(=CH), 2 952, 2 924, 2 913, 2 869(—CH2—, —CH3), 1 631(—C=N—), 1 555, 1 471, 1 455(C=C), 1 425, 1 385 (—C(CH3)2), 1 049 (S=O), 845(C—N), 767, 733 cm?1;1H-NMR(CDCl3):δ(ppm) 8.04~8.02(1H, =CH), 7.97~7.95(1H), 7.54~7.50(1H), 7.47~7.43(1H), 3.27~3.09(2H, CH2—C), 1.86~1.65(2H, C—CH2—C), 1.58~1.52(1H, —CH—), 0.91~0.88(6H, 2CH3);ESI-MS(M+1)/z: 254.064 2。
1.3 试液的配制
Pd(Ⅱ)储备液:精确称取纯钯粉250 mg,用王水加热溶解,小心蒸发近干,添加少量浓盐酸3次使硝酸分解挥发完全,再用0.1 mol/L盐酸配成250 mL浓度为1.0 g/L的Pd(Ⅱ)储备液。
有机相:取一定量的合成亚砜加入苯作为稀释剂,配成所需浓度的有机相,使用前用与水相酸度相同的HCl预平衡。
1.4 萃取实验
室温下,将等体积的有机相和水相置于分液漏斗中,在电动定时振荡器内振荡15 min(实验结果表明振荡15 min达到萃取平衡)。静置分相后,取萃余液分析。用原子吸收分光光度计测出萃余水相中钯的浓度,再用差减法求出有机相中钯的浓度,依此计算出分配比D。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 萃取机理的探讨
异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜是中性萃取剂,从水相中萃取钯有如下两种萃取方式[7]:
1) 配位取代机理

2) 酸性离子缔合机理

分析两种萃取机理的特点可知,第一种机理氢离子不参加萃取反应,分配比D应与H+浓度无关,而按第二种机理萃取时,分配比D应与H+浓度m次方成正比(控制其它条件不变)。因此通过考察H+浓度对分配比的影响可知ABSO萃取钯的机理。
2.1.1 H+浓度对分配比的影响
固定Pd(Ⅱ)的起始浓度为100 mg/L,ABSO的浓度分别为0.25和0.5 mol/L,用NaCl调节溶液离子浓度,考察lgD—lg[H+]的关系(见图1)。由图1结果可知,在实验酸度范围内([H+]≤3 mol/L),lgD—lg[H+]是一条斜率近似为零的直线,说明H+浓度对钯分配比无影响,ABSO萃取钯是配位取代机理。文献[7]曾报道在低酸度条件下,亚砜萃取钯属配位取代机理;在高酸度条件下,亚砜萃取钯属离子缔合机理。对于高酸度条件下ABSO萃取钯的机理将在另文探讨。

图1 lg[H+]对lgD的影响
Fig.1 Effect of lg[H+] on lgD
2.1.2 n值的确定
在萃合物中,金属离子与萃取剂的比例可以由lgD—lg[萃取剂]的关系图得到[10?11]。固定Pd(Ⅱ)的起始浓度为100 mg/L,盐酸浓度为0.1 mol/L,亚砜ABSO的浓度由0.05至1.0 mol/L变化。lgD与lg[ABSO]的关系如图2所示。由图可见,lgD—lg[ABSO]的关系为两条直线,斜率分别为2.13和1.97,取整数n值为2,说明萃合物中钯与ABSO的配比为1?2。
由此可以确定ABSO萃取钯的反应机理为:

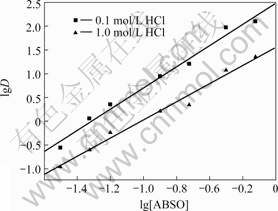
图2 lg[ABSO]对lgD的影响
Fig.2 Effect of lg[ABSO] on lgD
2.2 萃合物的红外光谱分析
用浓度为0.5 mol/L的ABSO多次萃取盐酸浓度为0.1 mol/L、浓度为1.0 g/L的Pd(Ⅱ)溶液制备饱和萃合物,待溶剂挥发后得到固体萃合物做红外光谱。
由文献[12?13]可知,亚砜基—S=O的硫、氧原子都有孤对电子,因此硫、氧原子均有可能与被萃金属形成配位键。如果通过氧原子配位,则υS=O向低频方向移动;相反,如果通过硫原子配位,则υS=O向高频方向移动,且两种配位方式υS=O移动的波数较大。ABSO萃取钯前后的红外光谱如图3所示。由图可见,ABSO萃取钯前的S=O键特征峰在υ=1 049 cm?1处[14];萃取钯后,萃合物的S=O键特征峰出现在υ=1 063 cm?1处,向高频方向移动不大,且强度基本不变,说明ABSO没有通过S=O键的硫或氧原子与Pd(Ⅱ)配位。杂环C—S键的伸缩振动位于750~690 cm?1范围[14],苯并噻唑基上C—S—C键伸缩振动在733 cm?1处,形成萃合物后出现在726 cm?1,位移及强度变化不大,说明杂环上的硫原子也没有参与配位。
文献[15?17]认为苯并噻唑?2?硫基的负电荷既可集中在硫原子上,又可完全离域到氮原子,使得配体上的硫原子和氮原子都可成为亲核加成反应的活性位。从图3的表征数据可知,苯并噻唑基上—C=N—键特征峰在萃取钯前后变化明显,υ—C=N—由萃钯前的1 631 cm?1向低频移动到1 613 cm?1处,且吸收强度减弱, 这与文献[18]报道的苯并噻唑基与金属配位的特性相似,说明杂环氮与Pd(Ⅱ)发生了配位反应。

图3 ABSO萃取剂和Pd-ABSO萃合物的红外光谱图
Fig.3 IR spectra of ABSO (a) and Pd-ABSO complex (b)
2.3 萃合物的核磁共振氢谱分析
图4所示是ABSO萃取剂(a)和Pd(Ⅱ)-ABSO萃合物(b)的核磁共振1H谱。从图4可知,1H NMR测得ABSO苯环上4个氢的δ值分别为8.04×10?6、7.97×10?6、7.54×10?6、7.47×10?6,异戊基上氢的δ值为(3.27~3.09)×10?6(2H, CH2—C)、(1.86~1.65)× 10?6(2H, C—CH2—C)、(1.58~1.52)×10?6 (1H, —CH—)、(0.91~0.88)×10?6(6H, 2CH3)。比较图4(a)和(b)可以看出,当萃取剂ABSO萃取Pd(Ⅱ)后,萃合物的1H峰向低场移动,萃合物苯环上4个氢原子的δ值分别为 9.37×10?6、9.25×10?6、7.99×10?6、7.87×10?6,异戊基上氢的δ值为(4.22~3.71)×10?6(2H, CH2—C)、(2.13~2.08)×10?6(2H, C—CH2—C)、(1.86~ 1.174)× 10?6(1H, —CH—)、(1.01~0.92)×10?6 (6H, 2CH3),原因是杂环氮与Pd(Ⅱ)发生配位后,苯并噻唑基与亚砜的共轭系统受到影响,从而使苯环及异戊基上的氢化学位移向低场移动[19]。

图4 ABSO萃取剂(a)和Pd(Ⅱ)-ABSO萃合物(b)的核磁共振1H谱(CDCl3)
Fig.4 1H NMR spectra of ABSO (a) and Pd(Ⅱ)-ABSO complex (b) (CDCl3)
结合萃合物的组成与红外光谱、核磁共振氢谱分析推断,萃合物的可能结构为:

3 结论
合成的异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜对盐酸介质中的Pd(Ⅱ)有很好的萃取性能,在实验酸度范围内([H+]≤3 mol/L),溶液H+浓度对钯的分配比无影响,ABSO以中性配位萃取机理萃取钯。萃取反应为

采用斜率法、红外光谱和核磁共振氢谱法确定了萃合物的组成。结果表明,在低酸度条件下,ABSO通过苯并噻唑环上的氮原子与Pd(Ⅱ)配位形成萃和物PdCl2(ABSO)2。
[1] Lokhande, T N, Anuse M A, Chavan M B. Liquid–liquid extraction of palladium(Ⅱ) with N-n-octylaniline from hydrochloric acid media[J]. Talanta, 1998, 46: 163?169.
[2] Szczepanska I, Borowiak-Resterna A, Wisniewski M. New pyridinecarboxamides for rapid extraction of palladium from acidic chloride media [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 68: 159?170.
[3] Wisniewski M. Palladium(Ⅱ) extraction by pyridine carboxylic acid esters[J]. J Radioanal Nucl Chem, 2000, 256: 693?696.
[4] Uheida A, Zhang Y, Muhammed M. Selective extraction of palladium(Ⅱ) from chloride solutions with nonylthiourea dissolved in chloroform[J]. Solv Extr Ion Exch,2002, 20(6): 717?733.
[5] 张邦劳. 不对称二烷基亚砜的合成及其对Au(Ⅲ)、Pd(Ⅱ)、Pt(Ⅳ)的萃取性能研究[J]. 陕西师范大学学报:自然科学版, 1998, 26(2): 70?73.
ZHANG Bang-lao. Synthesis of asymmetric dialkyl sulfoxides and structure-reactivity and extraction of Au(Ⅲ), Pd(Ⅱ) and Pt(Ⅳ)[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 1998, 26(2): 70?73.
[6] 程 飞,龙惕吾. 石油亚砜的极性与萃取钯铂性能的关系[J]. 贵金属, 1992, 13(1): 10?13.
CHENG Fei, LONG Ti-wu. Relation between petroleum sulfoxide polarity and extraction properties for palladium and platinum[J]. Precious Metals, 1992, 13(1): 10?13.
[7] 陈 景. 钯(Ⅱ)氯配离子在一些化学反应中的两种反应现象与机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(3): 327?333.
CHEN Jing. Two different phenomena and mechanisms of Pdcl2-4 in some chemical reactions [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(3): 327?333.
[8] Preston J S, du Preez A C. Solvent extraction of platinum group metals from hydrochloric acid solutions by dialkyl sulphoxides[J]. Solvent Extr Ion Exch, 2002, 20(3): 359?374.
[9] 李耀威,古国榜,李立平,徐志广. 烃基?苯并噻唑亚砜从硫脲介质中萃取金的性能研究[J]. 贵金属, 2004, 25(4): 1?5.
LI Yao-wei, GU Guo-bang, LI Li-ping, XU Zhi-guang. Solvent extraction of Au(I) from gold-thiourea leaching solution by alkyl benzothiazole sulphoxides[J]. Precious Metals, 2004, 25(4): 1?5.
[10] Gholivand M B, Nozari N. Extraction and spectrophotometric determination of trace amount of Pd(Ⅱ) with 2, 2′-dithiodianiline[J]. Talanta, 2000, 52: 1055?1060.
[11] Lokhande T N, Anuse M A, Chavan M B. Liquid-liquid extraction of palladium(Ⅱ) with N-n-octylaniline from hydrochloric acid media[J]. Talanta, 1998, 46: 163?169.
[12] Lewis P A, Morris D F C, Short E L, Waters D N. Application of solvent extraction to the refining of precious metals Ⅳ. Practical and structural aspects of the separation of rhodium, palladium, iridium and platinum with organic sulphoxides[J]. J Less-Common Met, 1976, 45: 193?214.
[13] Price J H, Williamson A N, Schramm R F, Wanyland B B. Palladium(II) and platinum(II) alkyl sulfoxide complexes. Examples of sulfur-bonded, mixed sulfur- and oxygen- bonded, and totally oxygen-bonded complexes[J]. Inorg Chem, 1972, 11(6): 1280?1284.
[14] 宁永成. 有机化合物结构鉴定与有机波谱学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2000: 485?497.
NING Yong-cheng. Structure identification of organic compound and organic spectroscopy[M]. Beijing: Science Publishing Company, 2000: 485?497.
[15] Ciriano M A, Sebastián S, Oro L A, Tiripcchio A, Lahoz F J. Tetranuclear complexes as intermediates in transannular oxidative-addition reactions. Structure of the first tetrairidium linear cluster[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng, 1988, 27(3): 402?403.
[16] Ciriano M A, López J, Oro L A, Pérez-Torrente J J, Canfranchi M, Tiripicchio A. Oxidation of substrates by an iridium dioxygen complexes: intramolecular oxidation of carbon monoxide and activation of a carbonyl group by attack of a heterocyclic nitrogen[J]. Organometallics, 1995, 14: 4764?4775.
[17] Zhang L X, Zhou X G, Huang Z E, Cai R F, Fluang X Y. Synthesis and characterization of biscyclopentadienyllanthanide benzothiazole-2-thiolates. X-ray crystal structures of Cp2Ln(SBT)(THF)(Ln=Yb, Dy)[J]. Polyhedron, 1999, 18: 1533?1537.
[18] Ito M, Furuhashi A, Shimoi M. Crystal and molecular structures of bis[2-(2-benzoxazoly)phenol-N] dichloropalladium(Ⅱ)[J]. Polyhedron, 1997, 16(11): 1889?1893.
[19] 孟令芝,龚淑玲,何永炳. 有机波普分析(第二版)[M]. 武汉:武汉大学出版社, 2003: 66?120.
MENG Ling-zhi, GONG Shu-ling, HE Yong-bing. Analysis of organic spectroscopy[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Publishing Company, 2003: 66?120.
收稿日期:2006-10-26;修订日期:2007-04-02
通讯作者:李耀威,博士;电话: 020-39310250;E-mail: liyaowei@scnu.edu.cn
摘 要:合成了异戊基苯并噻唑亚砜(ABSO),研究了盐酸介质中ABSO萃取Pd(Ⅱ)的机理。考察水相H+浓度和萃取剂浓度对钯萃取的影响, 采用斜率法、红外光谱和核磁共振H谱法确定了萃合物的组成及萃取平衡的机理。结果表明:低酸度条件下,H+浓度对钯的分配比无影响,ABSO以中性配位萃取机理萃取Pd(Ⅱ),并通过苯并噻唑环上的氮原子与Pd(Ⅱ)配位形成萃合物PdCl2(ABSO)2。


