PtRuP/C催化剂的制备与表征
杨志宽1, 2,王要武2,谢晓峰2,郭建伟2,胡国荣1
(1. 中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 清华大学 核能与新能源技术研究院,北京,100084)
摘 要:
摘 要:以次磷酸钠为还原剂,采用浸渍法制备直接甲醇燃料电池用60% PtRuP/C(Pt与Ru的摩尔比为1?1)催化剂,并考察浸渍液pH值和P元素对催化剂活性的影响。采用X射线衍射、透射电镜、X射线能量分散谱和X射线光电子能谱等对催化剂进行结构、组成及形貌进行表征,通过线性扫描伏安法和计时电流曲线考察催化剂对甲醇氧化的电化学性能。研究结果表明:pH值对催化剂的结构和活性有很大影响,pH值为7时制备的催化剂分散均匀,平均粒径为2.8 nm,并且具有最高的对甲醇催化活性和抗毒化性能;与不含P的PtRu/C催化剂相比,PtRuP/C催化剂具有更高的催化活性,扫速为20 mV/s、电位为0.45 V时氧化甲醇的电流密度达到63 mA/cm2。
关键词:
中图分类号:TM911.4 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2008)03-0448-06
Preparation and characterization of PtRuP/C catalysts
YANG Zhi-kuan1, 2, WANG Yao-wu2, XIE Xiao-feng2, GUO Jian-wei2, HU Guo-rong1
(1. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Institute of Nuclear and New Energy Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China)
Abstract: A 60% PtRuP/C anode electrocatalyst for a direct methanol fuel cell(DMFC) was prepared by impregnation method using sodium hypophosphite as reductive agent. Effects of pH values and element P on the catalyst activities were studied. The structure, component and morphology were characterized by X-ray diffraction(XRD), transmission electron microscopy(TEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy(EDS) and X-ray photoelectron spectra(XPS). The electrocatalytic performances were examined by linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) and chronoamperometry. The results show that the structure and electrocatalytic properties are greatly influenced by the pH value of impregnating solution. The catalyst prepared at the pH value of 7 has high dispersion, the highest catalytic activity for methanol oxidation, good tolerance to poisoning species and the average particle size of 2.8 nm. Compared with the PtRu/C catalyst, the PtRuP/C catalyst possesses a higher catalytic activity producing current density of 63 mA/cm2 at 0.45 V (vs. SCE) with a scanning rate of 20 mV/s.
Key words: direct methanol fuel cell; PtRuP/C catalysts; electrocatalysis
直接甲醇燃料电池(direct methanol fuel cell,DMFC)使用液体燃料,具有结构简单、体积小、操作温度低、比能量高等优点,特别适用作笔记本电脑、数码相机、电动车等小型便携式电源[1-3]。然而,在低温条件下,阳极电催化剂活性不高、极化严重是阻碍DMFC商业化的突出问题,而且甲醇氧化产生的中间产物COads极易毒化催化剂[4]。因此,研究催化活性高、抗毒化性能好的催化剂对于DMFC的商业化至关重要。目前,人们对阳极催化剂的研究主要集中在碳载Pt基催化剂,其中PtRu/C催化剂通过双功能机理对甲醇的氧化具有很好的催化活性和抗中毒性能[5-6],成为研究最多的阳极催化剂之一。由于DMFC阳极极化严重,还不能像氢质子交换膜燃料电池那样采用低载量催化剂,所以,必须开发高载量PtRu/C催化剂,以减小催化层厚度,减小传质阻力,提高催化效率,降低极化程度[7]。但高载量催化剂的制备因团聚严重、粒径大、分散不均等问题而导致制备困难或催化活性不高。因此,制备出高载量、粒径小、分散均匀的PtRu/C催化剂就显得尤为重要。
PtRu/C催化剂的制备方法很多,其中浸渍还原法可以较好地控制粒径而被广泛研究,常用的还原剂有NaBH4、甲醛、水合肼以及乙二醇等[8-12],最近有报道在制备催化剂时加入NaH2PO2[13-14]或直接以NaH2PO2为还原剂,以Vulcan XC-72为载体在碱性条件下制备低载量(20%)PtRuP/C催化剂,具有较小的粒径和较高的分散度[15]。但是,低温下DMFC阳极电催化剂对甲醇的催化活性不高,极化严重,需要高载量催化剂来提高电池输出特性。
本文作者以NaH2PO2为还原剂,以XC-72R为载体,采用浸渍还原法制备60% PtRuP/C,考察浸渍液pH值对催化剂性能的影响,对比研究含P与不含P的PtRu/C催化剂对甲醇的催化性能。
1 实 验
1.1 催化剂的制备
称取一定量的XC-72R碳粉,加入去离子水,超声分散形成均匀黑色浆液后,加入适量氯铂酸溶液和氯化钌溶液,加热搅拌,浸渍一定时间后,使用1 mol/L HCl或1 mol/L NaOH溶液调节浸渍液pH值,然后,加入一定量NaH2PO2溶液进行还原,经过滤、洗涤、干燥等后处理得到催化剂样品。按照不同的浸渍液pH值(2,5,7,9和12)将所得样品分别标记为PtRuP/C-2,PtRuP/C-5,PtRuP/C-7,PtRuP/C-9和PtRuP/C-12。作为对比,按文献[11]以硼氢化钠为还原剂制备PtRu/C催化剂。碳粉在使用前经过前处理。所用药品均为分析纯。
1.2 催化剂的结构及形貌表征
XRD图谱表征在德国Bruker D8型粉末衍射仪上进行,Cu Kα靶,扫描速度为6 (?)/min;XPS能谱在PHI Quantera SXMX射线光电子能谱仪上测试,Al阳极靶,能量分辨率为0.5 eV;HRTEM照片在JEOL JEM-2000EX透射电子显微镜上拍摄;EDS能谱由自带的Oxford INCA-IET200分析仪完成。
1.3 催化剂的电催化活性评价
1.3.1 工作电极的制备
将直径为3 mm的玻碳电极用A12O3抛光粉抛光,去离子水清洗后自然晾干。取一定量的催化剂样品,按比例加入去离子水、Nafion溶液和无水乙醇,超声30 min后,取40 μL逐滴滴在玻碳电极表面,红外灯下缓慢烤干备用。电极上PtRu载量为0.8 mg/cm2。
1.3.2 电化学测试
电化学测试在辰华CHI660B电化学工作站上进行。采用常规三电极体系,对电极为铂片(1 cm2),参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),电解液采用0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液。测试前,通高纯N2,以除去溶解氧。循环伏安测试时,工作电极先在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中扫描10次以达到稳定,电位范围为-0.2~0.45 V,然后,在0.5 mol/L CH3OH+0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中由-0.2 V线性扫描至0.45 V,扫速均为20 mV/s。计时电流曲线测试电位从-0.2 V阶跃到0.45 V,保持1 000 s。实验测试均在室温下进行。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 PtRuP/C催化剂的表征
以XC-72R碳粉作为载体,浸渍液pH值分别调至2,5,7,9和12制备PtRuP/C催化剂,其XRD图谱如图1所示。由图1可以看出,25?左右的峰为XC-72R碳粉的(002)晶面衍射峰。PtRuP/C-2,PtRuP/C-5和PtRuP/C-7 3个样品分别在39.8?,46.1?和67.8?出现衍射峰,分别对应Pt的(111),(200)和(220)特征峰,并且均较纯Pt的衍射峰稍向右移,说明有少量Ru与Pt形成的合金存在,没有出现Ru及Ru化合物的特征衍射峰。根据Sherrer公式:d=kλ/(βcos θ)(其中,d为晶粒尺寸,nm;k=0.89;λ为X射线的入射波长,![]() =0.154 06 nm;θ为衍射峰的角度;β为衍射峰的半峰宽),利用不受干扰的Pt(220)晶面计算PtRu催化剂粒径,三者粒径分别为2.3,2.4和2.1 nm,三者在数值上很接近。而PtRuP/C-9和PtRuP/C-12 2个样品的衍射峰与上述3个样品的不同,PtRuP/C-9仅在40.0?出现衍射峰,而PtRuP/C-12却在27.9?,35.0?和54.2?出现了RuO2的衍射峰,Pt的衍射峰很弱甚至消失,这可能是由于Ru3+与调节pH的OH-结合生成了Ru(OH)x沉淀,覆盖于Pt表面,使样品表现为非晶态。采用次磷酸钠为还原剂制备PtRuP/C催化剂,在当pH值为7时,制备了PtRuP/C催化剂。
=0.154 06 nm;θ为衍射峰的角度;β为衍射峰的半峰宽),利用不受干扰的Pt(220)晶面计算PtRu催化剂粒径,三者粒径分别为2.3,2.4和2.1 nm,三者在数值上很接近。而PtRuP/C-9和PtRuP/C-12 2个样品的衍射峰与上述3个样品的不同,PtRuP/C-9仅在40.0?出现衍射峰,而PtRuP/C-12却在27.9?,35.0?和54.2?出现了RuO2的衍射峰,Pt的衍射峰很弱甚至消失,这可能是由于Ru3+与调节pH的OH-结合生成了Ru(OH)x沉淀,覆盖于Pt表面,使样品表现为非晶态。采用次磷酸钠为还原剂制备PtRuP/C催化剂,在当pH值为7时,制备了PtRuP/C催化剂。
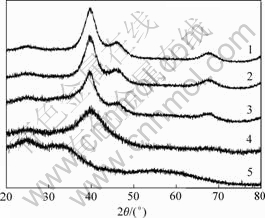
1—pH=2; 2—pH=5; 3—pH=7; 4—pH=9; 5—pH=12
图1 不同pH值下制备的PtRuP/C催化剂的XRD图谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of PtRuP/C catalysts prepared at different pH values
酸性和中性条件下制备的粒径较小,并且相当,而碱性条件下由于Ru发生沉淀,不能较好地制得所需的催化剂。
图2所示为pH值为7时,PtRuP/C催化剂的EDS图。可见,样品中不含Cl和Na等杂质元素,但存在少量P元素,Pt与Ru的摩尔比近似为1?1,说明PtRu已经完全沉淀,几乎全部在碳粉表面发生成核生 长,这与制备过程中滤液为无色相一致。PtRuP/C催化剂的XPS谱如图3所示。分别对Pt 4f和Ru 3d+C 1s的XPS谱图进行分峰拟合,结果表明,Pt主要以0价和2价存在,同时还有少量的4价,而Ru全部以4价的水合氧化钌(RuO2·xH2O或HxRuOy)存在,C元素除了单质C外,还有少量的羰基碳和羧酸根,这可能是载体表面本身所含的活性基团。HxRuOy具有很好的质子和电子传导性,容易分解H2O产生Ru—OH活性物种,通过双功能机理解除CO对Pt的毒化[16],使得催化剂具有很好的抗中毒性能。P 2p的XPS谱图如图3(c)所示,可见,结合能为132.9 eV处出现很强的峰,说明催化剂表面存在的磷主要为氧化态[13]。
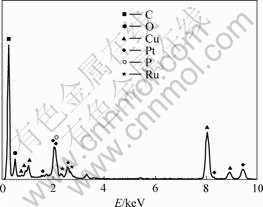
图2 PtRuP/C催化剂的EDS图谱
Fig.2 EDS spectrum of PtRuP/C catalyst
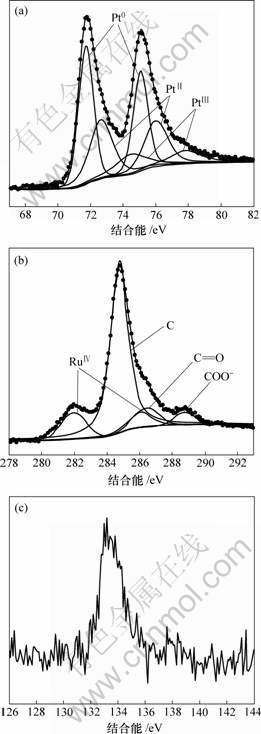
(a) Pt 4f; (b) Ru 3d+C 1s; (c) P 2p
图3 PtRuP/C催化剂的XPS谱
Fig.3 XPS spectra of PtRuP/C catalyst
图4所示为PtRuP/C催化剂的低倍和高倍TEM照片。图中灰黑色的阴影为XC-72R碳载体,黑色颗粒为PtRu催化剂粒子。从图4可以看出,催化剂粒子均匀地分散于载体上,且粒径分布较窄,没有出现明显的团聚现象。经计算得催化剂的平均粒径为2.8 nm,与XRD估算结果2.1 nm比较吻合,这也许是催化剂表面非金属元素P的存在,减弱了PtRu间金属键,避免了团聚,使得催化剂粒径减小,而分散度提高之故[13, 15]。

(a) 低放大倍数;(b) 高放大倍数
图4 PtRuP/C催化剂的TEM照片
Fig.4 TEM images of PtRuP/C catalyst
2.2 pH值对催化剂电催化性能的影响
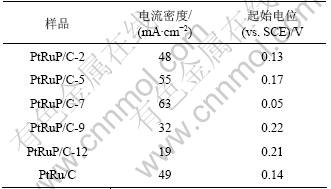
不同pH值下制备的PtRuP/C催化剂在0.5 mol/L CH3OH+0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的线性扫描曲线如图5所示。为了避免Ru在较高的电位下(>0.5 V)溶解而流失[11-12],电位扫描范围选择-0.2~0.45 V。由于起始电位较难判断,以电流密度为5 mA/cm2时的电位作为起始电位以便进行对比,电化学测试数据见表1。从表1可以看出,PtRuP/C催化剂对甲醇的催化活性与浸渍液pH值有很大关系,随着pH值的增大,催化活性先增大后减小,pH=7时催化活性最高,在0.45 V时氧化电流密度达到63 mA/cm2,起始电位为0.05 V,较其他催化剂样品的低,说明它具有较好的抗毒化性能。图6所示的计时电流曲线与图5所示的结果一致,PtRuP/C-7催化剂的电流密度始终保持最大,表明它具有最强的电催化活性和稳定性。
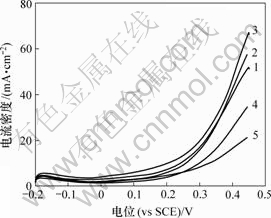
1—PtRuP/C-2; 2—PtRuP/C-5; 3—PtRuP/C-7;
4—PtRuP/C-9; 5—PtRuP/C-12
图5 不同pH值下制备的PtRuP/C催化剂对甲醇氧化的线性扫描伏安曲线
Fig.5 LSV curves of PtRuP/C catalysts with different pH values for methanol oxidation
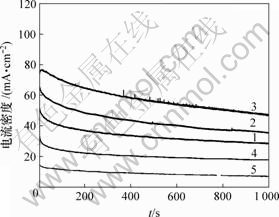
1—PtRuP/C-2; 2—PtRuP/C-5; 3—PtRuP/C-7;
4—PtRuP/C-9; 5—PtRuP/C-12
图6 不同pH值下制备的PtRuP/C催化剂对甲醇氧化的计时电流曲线
Fig.6 Chronoamperometry curves of PtRuP/C catalysts with different pH values for methanol oxidation
表1 不同pH值下制备的催化剂对甲醇氧化的电化学性能
Table 1 Electrochemical performance of methanol oxidation of catalysts prepared at different pH values
XRD和电化学测试表明,浸渍液pH值对催化剂电催化活性有很大影响。![]() 的电极反应和标准电极电势为:
的电极反应和标准电极电势为:
![]()
可见,在碱性条件下,![]() 的还原性更强,反应的推动力最大。但实验结果表明,pH值较高时,Ru3+与OH-结合生成Ru(OH)x沉淀,不能很好地制备催化剂;酸性条件减弱了
的还原性更强,反应的推动力最大。但实验结果表明,pH值较高时,Ru3+与OH-结合生成Ru(OH)x沉淀,不能很好地制备催化剂;酸性条件减弱了![]() 的还原能力,虽然较好地制备了PtRuP/C催化剂,但活性比中性条件下制备的催化剂活性低;当pH=7时,既可避免Ru3+的沉淀,又没有减弱NaH2PO2还原反应的推动力,制备的催化剂对甲醇具有更强的催化活性和稳定性。
的还原能力,虽然较好地制备了PtRuP/C催化剂,但活性比中性条件下制备的催化剂活性低;当pH=7时,既可避免Ru3+的沉淀,又没有减弱NaH2PO2还原反应的推动力,制备的催化剂对甲醇具有更强的催化活性和稳定性。
2.3 PtRuP/C与PtRu/C催化剂的电催化性能比较
作为对比,以硼氢化钠为还原剂制备了PtRu/C催化剂。PtRuP/C和PtRu/C催化剂的线性扫描伏安曲线和计时电流曲线如图7和图8所示。可见,PtRuP/C催化剂在0.45 V时对甲醇的氧化电流密度为63 mA/cm2,高于PtRu/C催化剂的电流密度49 mA/cm2,结合计时电流曲线,表明含有P元素的PtRuP/C催化剂较不含P的催化剂有更强的催化活性和稳定性。
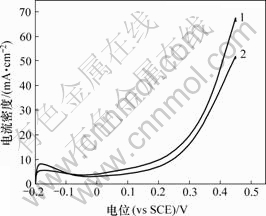
1—PtRuP/C; 2—PtRu/C
图7 PtRuP/C与PtRu/C催化剂对甲醇氧化的线性扫描伏安曲线
Fig.7 LSV curves of PtRuP/C catalyst and PtRu/C catalyst for methanol oxidation
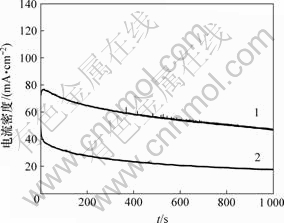
1—PtRuP/C; 2—PtRu/C
图8 PtRuP/C与PtRu/C催化剂对甲醇氧化的计时电流曲线
Fig.8 Chronoamperometry curves of PtRuP/C catalyst and PtRu/C catalyst for methanol oxidation
3 结 论
a. 采用浸渍还原法,以次磷酸钠为还原剂制备了60% PtRuP/C催化剂。浸渍液pH值对催化剂的结构和活性有很大影响,在酸性和中性条件下可以较好地制备催化剂。在碱性条件下,由于Ru发生沉淀而不能制得所需催化剂。
b. 制备的催化剂中含有非金属元素P,并主要以氧化态存在于催化剂表面,P的存在使得催化剂分散均匀,平均粒径为2.8 nm。
c. 浸渍液在pH=7时制备的催化剂对甲醇催化活性最高,稳定性最强;当扫描速率为20 mV/s,电位为0.45 V时,氧化甲醇的电流密度达到63 mA/cm2。
d. PtRuP/C催化剂较不含P元素的PtRu/C催化剂有更强的甲醇催化氧化活性和稳定性。但是,P对直接甲醇燃料电池输出性能的影响还需进行进一步研究。
参考文献:
[1] 谢晓峰, 范星河. 燃料电池技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004.
XIE Xiao-feng, FAN Xing-he. Fuel cells technologies[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004.
[2] Liu Y, Xie X F, Shang Y M, et al. Power characteristics and fluid transfer in 40W direct methanol fuel cell stack[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2007, 164(1): 322-327.
[3] 齐 亮, 谢晓峰, 徐景明, 等. 直接甲醇燃料电池中的涉水传递现象及数值模拟[J]. 化学进展, 2006, 12(18): 1725-1734.
QI Liang, XIE Xiao-feng, XU Jing-ming, et al. Transport phenomena and numerical simulation related to water in direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2006, 12(18): 1725-1734.
[4] Liu H S, Song C J, Zhang L, et al. A review of anode catalysis in the direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 155(2): 95-110.
[5] Gojkovi? S L, Vidakovi? T R, ?urovi? D R. Kinetic study of methanol oxidation on carbon-supported PtRu electrocatalyst[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2003, 48(24): 3607-3614.
[6] Lee C H, Lee C W, Kim D I, et al. Characteristics of methanol on Pt-Ru catalysts supported By HOPG in sulfuric acid[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2002, 27(4): 445-450.
[7] Han K, Lee J, Kim H. Preparation and characterization of high metal content Pt-Ru alloy catalysts on various carbon blacks for DMFCs[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2006, 52(4): 1697-1702.
[8] Guo J S, Sun G Q, Sun S G, et al. Polyol-synthesized PtRu/C and PtRu black for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2007,168(2): 299-306.
[9] 王振波, 尹鸽平, 史鹏飞. 制备过程中缓冲溶液对Pt-Ru/C电催化剂性能的影响[J]. 催化学报, 2005, 26(10): 923-928.
WANG Zhen-bo, YIN Ge-ping, SHI Peng-fei. Influence of buffer solution on the performance of anodic catalyst Pt-Ru/C during preparation[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 26(10): 923-928.
[10] Colmenares L, Wang H, Jusys Z, et al. Ethanol oxidation on novel, carbon supported Pt alloy catalysts—Model studies under defined diffusion conditions[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2006, 52(1): 221-233.
[11] Xu Y Q, Xie X F, Guo J W, et al. Effects of annealing treatment and pH on preparation of citrate-stabilized PtRu/C catalyst[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 162(1): 132-140.
[12] Guo J W, Zhao T S, Prabhuram J, et al. Preparation and characterization of a PtRu/C nanocatalyst for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 51(4): 754-763.
[13] Daimon H, Kurobe Y. Size reduction of PtRu catalyst particle deposited on carbon support by addition of non-metallic elements[J].Catalysis Today, 2006 111(3/4): 182-187.
[14] King W D, Corn J D, Murphy O J, et al. Pt-Ru and Pt-Ru-P/carbon nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization, and unexpected performance as direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) anode catalysts[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2003, 107(23): 5467-5474.
[15] Xue X Z, Ge J J, Liu C P, et al. Novel chemical synthesis of Pt-Ru-P electrocatalysts by hypophosphite deposition for enhanced methanol oxidation and CO tolerance in direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2006, 8(8): 1280-1286.
Rolison D R, Hagans P L, Swider K E, et al. Role of hydrous ruthenium oxide in Pt-Ru direct methanol fuel cell anode electrocatalysts: the importance of mixed electron/proton conductivity[J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15(3): 774-779.
收稿日期:2007-08-25;修回日期:2007-11-01
基金项目:图家“863”计划项目(2006AA05Z128,2007AA05Z146);国家自然科学基金资助项目(5057341)
通信作者;谢晓峰(1960-),女,湖南长沙人,博士,副教授,从事质子换膜燃料电池研究,电话:010-627827;E-mail:xiexf@tsinghua.edu.cn


