DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.12.13
滚筒导热系数对外热式回转窑内物料传热的影响
张 喆1,刘义伦1,赵先琼1,肖友刚2,雷先明3
(1. 中南大学 机电工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 交通运输工程学院,长沙 410083;
3. 邵阳学院 机械与能源工程学院,邵阳 422004)
摘 要:
滚筒导热系数对物料在外热式回转窑内的传热特性影响巨大,将离散元方法与传热模型相结合,使用EDEM及C++等软件模拟外热式回转窑内物料的传热过程,研究滚筒导热系数对物料平均温度、物料温度标准差及物料总传热系数的影响规律,进而从微观上对回转窑内物料传热的两个步骤进行区分建模,并分别讨论滚筒导热系数在传热每一步骤中所起的作用。结果表明:在滚筒导热系数不断增大的过程中,回转窑内物料温度分布依次呈现出“整体缓慢加热-不规则冷核-规则冷核”特征;滚筒导热系数在一定范围内增大对物料传热有促进作用,超出一定范围后,继续增大对传热无显著影响;物料温度标准差增大阶段,滚筒导热系数越大,物料均匀性越差,随着加热进行,滚筒导热系数的增大对物料温度均匀性有促进作用;颗粒从筒壁吸收的总热量及相互接触颗粒间传递的总热量均随滚筒导热系数的增大而增大。
关键词:
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-12-2802-07 中图分类号:TK124 文献标志码:A
外热式回转窑是一种用于颗粒物料混合、干燥、分解、烧结、造粒等过程的回转类热工设备,广泛应用于冶金、化工、制药、食品加工等领域[1-2]。在实际工况中,滚筒旋转带动物料运动,运动过程中颗粒从高温筒壁吸收热量,同时热量也在颗粒间互相传递,以满足物料参与各种理化过程的温度要求[3-5]。
回转窑内物料传热过程复杂,影响传热的因素众多,可归纳为三个方面:一是滚筒设计参数[6-9],如滚筒尺寸、形状、内置扬料板等;二是颗粒物性参数[10-12],如颗粒尺寸、形状、密度、比热容、导热系数等;三是设备运行参数[13-17],如滚筒转速、物料填充率、有无倾角等。目前学者的研究重点主要集中在以上几方面,尤其是对滚筒部分的研究主要集中于设计参数上,对其自身的热物性研究很少,从直观上看,滚筒导热系数必然会影响物料传热状况,但该方面的研究目前尚未见报道。此外,颗粒在外热式回转窑内的传热机理有学者进行了相关描述[18],但并未被充分揭示,对传热的两个步骤通常也不做区分。本文将离散元方法[19-20]与CHAUDUURI等[11, 21]建立的传热模型相结合,使用EDEM、C++等软件对物料在外热式回转窑内的传热过程进行数值模拟,先从宏观上研究物料平均温度、物料温度标准差及总传热系数随滚筒导热系数的变化,进而从微观上对回转窑内物料传热的两个步骤进行区分建模,并分别讨论滚筒导热系数在每一步骤中所起的作用,可以为实际工况中设备节能运行提供理论依据。
1 接触传热模型
判定热传递是否产生,首先要判断是否发生了接触[21-23],颗粒-颗粒、颗粒-筒壁的接触模型如图1所示。半径分别为Ri和Rj的颗粒发生弹性接触,法向重叠量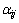 为
为
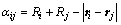 (1)
(1)
式中:ri和rj分别为颗粒i、j的球心位置矢量。当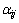 < 0时,判定颗粒i、j发生接触,发生接触即认为热量进行了传递。同理,当
< 0时,判定颗粒i、j发生接触,发生接触即认为热量进行了传递。同理,当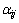 <0时,认为颗粒j与筒壁接触,即颗粒j与筒壁间有热量传递。
<0时,认为颗粒j与筒壁接触,即颗粒j与筒壁间有热量传递。
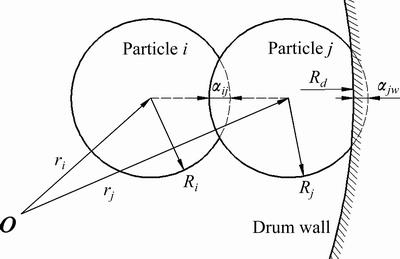
图1 颗粒-颗粒、颗粒-筒壁接触模型
Fig. 1 Contact model of particle-particle and particle-drum
除了颗粒-颗粒、颗粒-筒壁接触导热以外,在回转窑运行过程中还存在颗粒间隙气体的气膜导热、筒壁与表层裸露颗粒的辐射传热等辅助传热方式[24-25]。本文选取的壁面温度较低(400 K),基本可以忽略辐射影响;间隙气体导热率(0.0233 W/(m·K))远小于颗粒导热率时,颗粒-间隙气体导热与前两种传热机制相比也可忽略不计[6, 21]。本文所研究的传热方式为占据主导地位的颗粒-颗粒、颗粒-筒壁接触导热,颗粒相互接触后温度变化过程如下[21, 26]
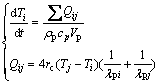 (2)
(2)
式中:Ti和Tj分别为颗粒i、j的温度;Qij为颗粒i、j之间传递的热量;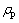 、cp、Vp分别为颗粒i、j的密度、比热容、体积;rc为接触面的有效半径;
、cp、Vp分别为颗粒i、j的密度、比热容、体积;rc为接触面的有效半径;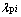 、
、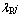 为颗粒i、j的导热系数,若颗粒与壁面接触,则分别为
为颗粒i、j的导热系数,若颗粒与壁面接触,则分别为 与
与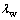 ,若颗粒与颗粒接触,则均为
,若颗粒与颗粒接触,则均为 。
。
2 数值模拟计算
为方便描述滚筒导热系数对传热的影响规律,此处引入一个无量纲的比值参数δ:
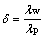 (3)
(3)
式中: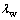 、
、 分别为滚筒导热系数和颗粒导热系数。
分别为滚筒导热系数和颗粒导热系数。
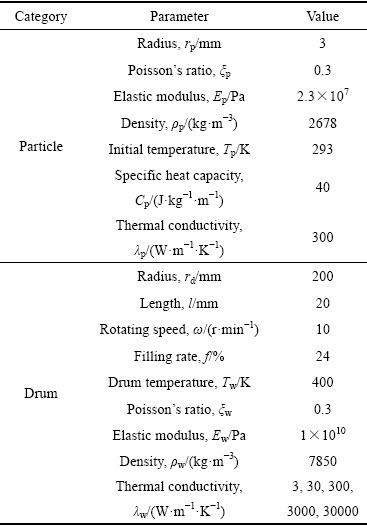
颗粒在外热式回转窑内的传热过程使用离散元软件EDEM以及二次开发工具C++进行数值计算。滚筒呈水平放置,筒壁为恒温热源,两端面绝热,单个颗粒内部不存在温度梯度。数值模拟参数设置如表1所列。
表1 数值计算参数设置
Table 1 Parameter setting for numerical calculation
3 结果与分析
3.1 物料传热过程
不同δ条件下物料在t=10s的温度分布如图2所示。其中,红色表示高温颗粒,蓝色表示低温颗粒,由图2可知,不同δ条件下物料在回转窑内的温度分布呈现三种状态。δ=0.01时,颗粒温度低且无明显差别,物料作为“整体”被缓慢加热,这是由于颗粒吸收热量过少,高温颗粒与低温颗粒温差很小,整体上看颗粒温度趋于一致。δ=0.1时,物料温度呈现“不规则冷核”分布,高温颗粒群与低温颗粒群在交界处相互夹杂,形成不规则边界,这是由于高温颗粒滚落后温度降低,但仍远高于周围低温颗粒,滚筒“加热”颗粒的能力有限,使得高温颗粒与低温颗粒出现夹杂。随着δ进一步增大,δ为1、10、100时,在贴壁运动高温颗粒群和沿斜面滚落高温颗粒群之间形成了“规则冷核”区域,不同温度的颗粒群随着与滚筒壁面远近呈现规则的分层现象,这是由于滚筒“加热”颗粒能力增强,高温颗粒滚落后迅速与周围低温颗粒一起再次被滚筒加热。
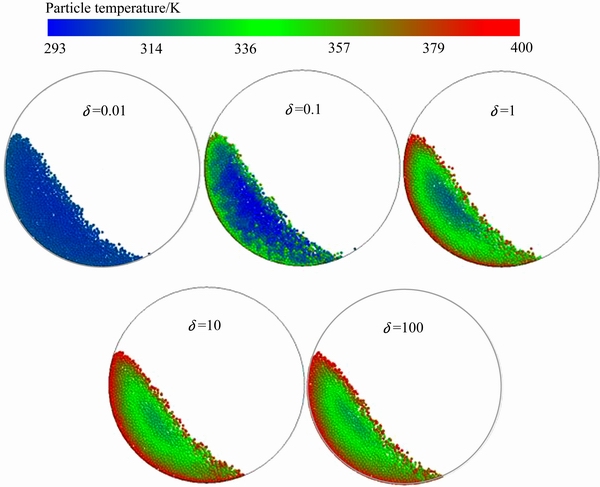
图2 不同δ条件下物料在t=10 s的温度分布
Fig. 2 Temperature distribution of particles at t=10 s under different δ
3.2 物料平均温度及温度标准差
为研究回转窑内物料传热快慢及传热均匀程度,引入物料平均温度(TAVG)及温度标准差(TSD)两个参数,表达式如下:
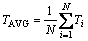 (4)
(4)
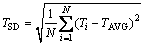 (5)
(5)
式中:i为颗粒;Ti为颗粒i的温度;N为颗粒总数。
不同δ下物料平均温度随时间的变化如图3所示。由图3可知,物料平均温度随着与高温筒壁持续接触而升高,但升温速率逐渐减小,这是颗粒平均温度与筒壁温度差逐渐减小导致;同一时刻下,物料平均温度随δ增大而增大,说明滚筒导热系数对物料传热有促进作用,但δ=10和δ=100时物料的温度变化曲线基本重合,说明当滚筒导热系数升到至一定数值时,进一步提高滚筒导热系数对传热无显著影响。
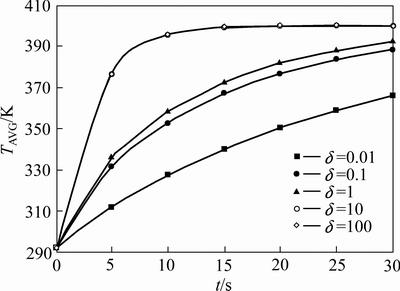
图3 不同δ条件下物料平均温度随时间的变化曲线
Fig. 3 Changing curves of TAVG with time under different δ
不同δ下物料温度标准差随时间的变化如图4所示,温度标准差表示物料温度分布的均匀程度,标准差越小,则物料温度分布均匀性越好。由图4可知,不同δ下物料温度标准差均呈现出先增大后减小的趋势。在温度标准差增大阶段,δ越大,则标准差的峰值也越大,标准差达到峰值的时间越短。δ增大过程中,标准差对应峰值依次为2.18、19.39、27.26、30.80和31.25,标准差增大时间依次为12.1、5.1、2.0、1.4和1.3 s。初始阶段,高温颗粒所占比例小,物料温度标准差呈现增大趋势;随后由于颗粒温度升高,颗粒与壁面及颗粒与颗粒间温度差逐渐减小,物料温度标准差逐渐下降,标准差随δ增大而减小。
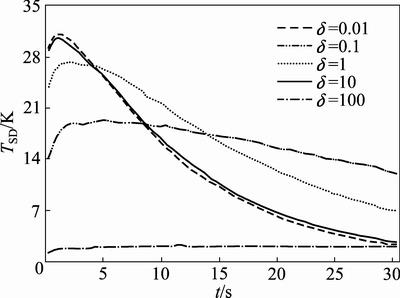
图4 不同δ条件下物料温度标准差随时间的变化曲线
Fig. 4 Changing curves of TSD with time under different δ
3.3 总传热系数
对物料传热方程进行求解可得
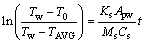 (6)
(6)
此方程中,物料在滚筒内运动时的传热面积Apw虽然随时间t略有波动,但这是由于颗粒运动的随机性造成的。其他条件(转速、填充率)不发生改变时,不同δ下Apw的波动范围均在3%以内,可作为常量处理。ln[(Tw-T0)/(Tw-TAVG)]随时间t的变化如图5所示。由图5可知,ln[(Tw-T0)/(Tw-TAVG)]随时间t的变化趋势近似于一次函数形式,对该曲线进行一次函数拟合
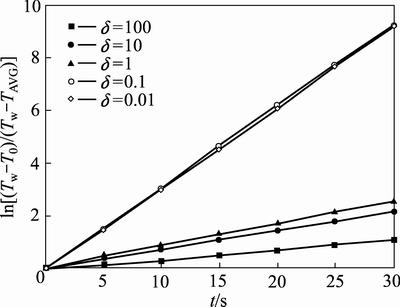
图5 不同δ条件下ln[(Tw-T0)/(Tw-TAVG)]随时间的变化曲线
Fig. 5 Changing curves of ln[(Tw-T0)/(Tw-TAVG)] with time under different δ
后得到一个斜率常量。因此,整体物料的传热效果就可以一个总体传热系数Ks来表征,Ks是一个宏观上表示整体物料传热快慢的物理量,Ks越大,表示传热效率越高。物料总传热系数Ks随lgδ的变化如图6所示。由图6可知,Ks在一定范围内随lgδ的增大而增大。
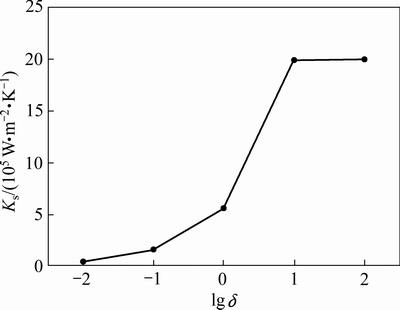
图6 物料在不同lg δ下的总传热系数
Fig. 6 Overall heat transfer coefficient of materials at different lg δ
3.4 传热机理模型构建
物料在外热式回转窑内的传热过程可以分为两部分。首先,与筒壁接触的颗粒从高温壁面吸收热量,然后随着滚筒旋转实现热量在物料内部的再次分配。物料平均温度Tavg、温度标准差TSD、总传热系数Ks均是从宏观上表征物料的传热特性,在分析其变化规律的基础上,从微观上对回转窑内物料传热的两个步骤进行区分,并讨论δ在每一步骤中所起的作用。
颗粒-筒壁传热过程中参与传热的仅有贴壁运动的单层颗粒,由傅里叶定理可推导出影响热量在颗粒- 筒壁间传递的因素为等效导热系数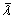 、贴壁运动颗粒与筒壁接触面积Apw及贴壁运动颗粒与筒壁间的温度差均值
、贴壁运动颗粒与筒壁接触面积Apw及贴壁运动颗粒与筒壁间的温度差均值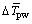 。此处将贴壁运动颗粒群看做整体,构建一个“平均化”的颗粒从筒壁吸热模型:
。此处将贴壁运动颗粒群看做整体,构建一个“平均化”的颗粒从筒壁吸热模型:
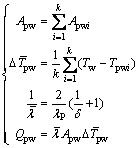 (7)
(7)
式中:k为与筒壁接触的颗粒个数;Tw为筒壁温度;Tpwi为与筒壁接触的颗粒i的温度;Qpw为滚筒传递给颗粒的总热量;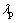 颗粒导热系数;δ为导热系数比。
颗粒导热系数;δ为导热系数比。
在颗粒从筒壁吸热过程中,Apw保持不变。δ越大则等效导热系数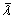 变大,对传热有促进作用。同时,δ越大则贴壁运动颗粒从高温筒壁吸收的热量越多,其本身温度也越高,导致
变大,对传热有促进作用。同时,δ越大则贴壁运动颗粒从高温筒壁吸收的热量越多,其本身温度也越高,导致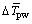 下降,不利于传热。δ增大的过程中,
下降,不利于传热。δ增大的过程中,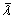 与
与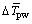 相互抑制的关系共同影响了颗粒从筒壁吸热总热量。
相互抑制的关系共同影响了颗粒从筒壁吸热总热量。
热量在物料内部再次分配过程中,影响热量在高温颗粒和低温颗粒间传递的因素为颗粒导热系数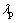 、颗粒间总接触面积App以及相互接触颗粒间的温度差均值
、颗粒间总接触面积App以及相互接触颗粒间的温度差均值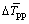 。此处仍构建一个“平均化”的物料内部热量再分配模型:
。此处仍构建一个“平均化”的物料内部热量再分配模型:
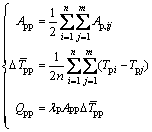 (8)
(8)
式中: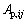 为颗粒i与j的接触面积;m为与颗粒i接触的颗粒个数;n为总颗粒数;Tpi , Tpj分别为颗粒i、j的温度;Qpp为相互接触颗粒间传递的总热量。
为颗粒i与j的接触面积;m为与颗粒i接触的颗粒个数;n为总颗粒数;Tpi , Tpj分别为颗粒i、j的温度;Qpp为相互接触颗粒间传递的总热量。
在物料内部热量再分配过程中,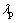 、App均为定值。δ越大则贴壁运动颗粒温度越高,随滚筒运动后与低温颗粒接触,则温度差均值
、App均为定值。δ越大则贴壁运动颗粒温度越高,随滚筒运动后与低温颗粒接触,则温度差均值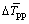 越大,对传热越有利。
越大,对传热越有利。
4 结论
1) 滚筒导热系数不断增大的过程中,回转窑内物料温度分布依次呈现出“整体缓慢加热-不规则冷核-规则冷核”特征。
2) 从传热效率看,滚筒导热系数在一定程度上能促进传热,超出一定范围后,继续增大对传热无显著影响。从传热均匀性看,物料温度标准差均呈现先增大后减小趋势;标准差增大阶段,滚筒导热系数越大,物料温度均匀性越差;随着加热进行,滚筒导热系数对物料温度均匀性有促进作用。
3) 颗粒从筒壁吸热过程中,滚筒导热系数对等效导热系数及贴壁运动颗粒与筒壁间的温度差均值产生影响,使得颗粒从筒壁吸收的总热量随滚筒导热系数 的增大而增大;在物料内部热量再分配过程中,滚筒导热系数对相互接触颗粒间的温度差均值产生影响,使得相互接触颗粒间传递的总热量随滚筒导热系数的增大而增大。
REFERENCES
[1] 吴 静, 李选友, 陈宝明, 高 玲, 王瑞雪, 赵改菊, 王成运. 大颗粒低填充率外热式回转窑传热系数模型的构建[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(13): 256-262.
WU Jing, LI Xuan-you, CHEN Bao-ming, GAO Ling, WANG Rui-xue, ZHAO Gai-ju, WANG Cheng-yun. Development of heat transfer coefficient model for external heated rotary kiln with low filling large particles[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(13): 256-262.
[2] 朱立平, 秦 霞, 袁竹林, 闫亚明, 罗登山, 李 斌. 丝状颗粒在滚筒横向截面中的传热传质特性[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(4): 756-763.
ZHU Li-ping, QIN Xia, YUAN Zhu-lin, YAN Ya-ming, LUO Deng-shan, LI Bin. Heat and mass transfer characteristics of filamentous particles in transverse section of rotary dryer[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 44(4): 756-763.
[3] DUAN L F, QI C G, LING X, PENG H.The contact heat transfer between the heating plate and granular materials in rotary heat exchanger under overloaded condition[J]. Results in Physics, 2018, 28: 600-609.
[4] FANTOZZI F, ALESSANDRO B D, BIDINI G. IPRP (Integrated-Pyrolysis Regenerated Plant): Gas turbine and externally heated rotary-kiln pyrolysis as a biomass and waste energy conversion system. Influence of thermodynamic parameters[J]. Journal of Power and Energy, 2003, 217(5): 519-527.
[5] NJENG A S B, VITU S, CLAUSSE M, DIRION J L, DEBACQ M. Wall-to-solid heat transfer coefficient in flighted rotary kilns: Experimental determination and modeling[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 91: 197-213.
[6] XIE Q, CHEN Z B, HOU Q F, Yu A B, YANG R Y. DEM investigation of heat transfer in a drum mixer with lifters[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 314: 175-181.
[7] XIE Q, CHEN Z B, MAO Y, CHEN G, SHEN W Q. Case studies of heat conduction in rotary drums with L-shaped lifters via DEM[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2018, 11: 145-152.
[8] 王 擎, 李 建, 王智超, 张立栋. 回转干馏炉内颗粒间传热特性的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(11): 4137-4146.
WANG Qing, LI Jian, WANG Zhi-chao, ZHANG Li-dong. Numerical simulation on characteristics of heat transfer between particles in rotary retorting[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(11): 4137-4146.
[9] 葛 良, 桂 南, 徐文凯, 闫 洁. 波形滚筒内颗粒混合和导热分布形态特性的研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2014, 44: 62-70.
GE Liang, GUI Nan, XU Wen-kai, YAN Jie.Numerical study of the distribution characteristics on particle mixing and thermal conduction in wavy drum[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Technologica, 2014, 44: 62–70.
[10] NGUYEN H T, COSSON B, LACRAMPE M F, KRAWCZAK P. Numerical simulation on the flow and heat transfer of polymer powder in rotational molding[J]. International Journal of Material Forming, 2015,8(3): 423-438.
[11] CHAUDHURI B, MUZZIO F J, TOMASSONE M S. Modeling of heat transfer in granular flow in rotating vessels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(19): 6348-6360.
[12] 张立栋, 韦庆文, 秦 宏, 王 擎. 柱状生物质颗粒在回转干馏炉中的运动及导热特性[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(11): 3993-3999.
ZHANG Li-dong, WEI Qing-wen, QIN Hong, WANG Qing. Motion and heat conduction in rotary retorting filled with cylindrical biomass particles[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(11): 3993-3999.
[13] 张 喆, 刘义伦, 赵先琼, 肖友刚, 雷先明. 外热式回转窑横截面内散体物料的传热特性[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(9): 2178-2183.
ZHANG Zhe, LIU Yi-lun, ZHAO Xian-qiong, XIAO You-gang, LEI Xian-ming. Heat transfer characteristics of granular materials in cross section of externally heated rotary kiln[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2018, 49(9): 2178-2183.
[14] KOMOSSA H, WIRTZ S, SCHERER V, HERZ F, SPECHT E. Heat transfer in indirect heated rotary drums filled with monodisperse spheres: Comparison of experiments with DEM simulations[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 286: 722-731.
[15] EMADY H N, ANDERSON K V, BORGHARD W G, MUZZIO F J, GLASSER B J, CUITINO A. Prediction of conductive heating time scales of particles in a rotary drum[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 152: 45-54.
[16] GUI N, YAN J, XU W K, GE L, WU D L, JI Z L, GAO J S, JIANG S Y, YANG X T. DEM simulation and analysis of particle mixing and heat conduction in a rotating drum[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 97: 225-234.
[17] SCHMIDT R, NIKRITYUK P A. Numerical simulation of the transient temperature distribution inside moving particles[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 90(2): 246-262.
[18] FIGUEROA I, VARGAS W L, MCCARTHY J J. Mixing and heat conduction in rotating tumblers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(2): 1045-1054.
[19] ZHU H P, ZHOU Z Y, YANG R Y, YU A B. Discrete particle simulation of particulate systems: Theoretical developments[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(13): 3378-3396.
[20] ZHU H P, ZHOU Z Y, YANG R Y, YU A B. Discrete particle simulation of particulate systems: A review of major applications and findings[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(23): 5278-5770.
[21] CHAUDHURI B, MUZZIO F J, TOMASSONE M S. Experimentally validated computations of heat transfer in granular materials in rotary calciners[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 198: 6-15.
[22] 陈 辉, 刘义伦, 赵先琼, 肖友刚, 刘 颖. 一元散体颗粒物料在回转窑截面上的运动与混合[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(5): 2575-2581.
CHEN Hui, LIU Yi-lun, ZHAO Xian-qiong, XIAO You-gang, LIU Ying. Motion and mixing of mono-disperse granular material in cross section of rotary kiln[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(5): 2575-2581.
[23] 王瑞芳, 李占勇, 窦如彪, 郭建忠. 水平转筒内大豆颗粒随机运动与混合特性模拟[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(6): 93-99.
WANG Rui-fang, LI Zhan-yong, DOU Ru-biao, GUO Jian-zhong. Simulation on random motion and mixing characteristic for Soybean in rotary drum[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(6): 93-99.
[24] 陈 辉, 肖友刚, 赵先琼, 刘 颖, 刘义伦. 回转窑内二元颗粒物料的径向混合[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016, 38(2): 194-199.
CHEN Hui, XIAO You-gang, ZHAO Xian-qiong, LIU Ying, LIU Yi-lun. Transverse mixing of binary solid materials in a rotating kiln[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, 38(2): 194-199.
[25] SHI D, VARGAS W L, MCCARTHY J J. Heat transfer in rotary kilns with interstitial gases[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(18): 4506-4516.
[26] CHENG G J, YU A B, ZULLI P. Evaluation of elective thermal conductivity from the structure of a packed bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1999, 54: 4199-4209.
Effect of drum thermal conductivity on heat transfer of solids in externally heated rotary kiln
ZHANG Zhe1, LIU Yi-lun1, ZHAO Xian-qiong1, XIAO You-gang2, LEI Xian-ming3
(1 College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. College of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. College of Mechanical and Energy Engineering, Shaoyang University, Shaoyang 422004, China)
Abstract: The drum thermal conductivity has a great influence on the heat transfer characteristics of the solids in the externally heated rotary kiln. The discrete element method was combined with heat transfer model, and EDEM and C++ were used to simulate the heat transfer process of the solids in the externally heated rotary kiln. The effects of drum thermal conductivity on the solids average temperature, standard deviation of temperature and the overall heat transfer coefficient were studied. The two steps of the solids heat transfer in the rotary kiln were modeled separately, and the roles of drum thermal conductivity in each step of heat transfer were discussed. The results show that during the process of increasing drum thermal conductivity, the solids temperature distribution in the rotary kiln presents the characteristics of “integral slow heating-irregular cold core-regular cold core”. In a certain range, the increase of drum thermal conductivity promotes the heat transfer of the solids. After exceeding a certain range, it continues to increase without significant effect on heat transfer. When the solids standard deviation of temperature increases, the greater the drum thermal conductivity is, the worse the uniformity of the solids becomes. With the heating, the increase of drum thermal conductivity promotes the uniformity of the solids temperature. The total heat absorbed by the particles from the drum and the total heat transferred between the particles in contact with each other increase with the increase of drum thermal conductivity.
Key words: rotary kiln; externally heated; particles; heat transfer; thermal conductivity; discrete element method
Foundation item: Projects(51374241, 51275531) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(17A194) supported by the Key Projects in Hunan Province Department of Education, China
Received date: 2018-11-12; Accepted date: 2019-06-24
Corresponding author: LIU Yi-lun; Tel: +86-731-88876734; E-mail: ylliu@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51374241,51275531);湖南省教育厅重点研究项目(17A194)
收稿日期:2018-11-12;修订日期:2019-06-24
通信作者:刘义伦,教授,博士;电话:0731-88876734;E-mail:ylliu@csu.edu.cn
摘 要:滚筒导热系数对物料在外热式回转窑内的传热特性影响巨大,将离散元方法与传热模型相结合,使用EDEM及C++等软件模拟外热式回转窑内物料的传热过程,研究滚筒导热系数对物料平均温度、物料温度标准差及物料总传热系数的影响规律,进而从微观上对回转窑内物料传热的两个步骤进行区分建模,并分别讨论滚筒导热系数在传热每一步骤中所起的作用。结果表明:在滚筒导热系数不断增大的过程中,回转窑内物料温度分布依次呈现出“整体缓慢加热-不规则冷核-规则冷核”特征;滚筒导热系数在一定范围内增大对物料传热有促进作用,超出一定范围后,继续增大对传热无显著影响;物料温度标准差增大阶段,滚筒导热系数越大,物料均匀性越差,随着加热进行,滚筒导热系数的增大对物料温度均匀性有促进作用;颗粒从筒壁吸收的总热量及相互接触颗粒间传递的总热量均随滚筒导热系数的增大而增大。
[1] 吴 静, 李选友, 陈宝明, 高 玲, 王瑞雪, 赵改菊, 王成运. 大颗粒低填充率外热式回转窑传热系数模型的构建[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(13): 256-262.
[2] 朱立平, 秦 霞, 袁竹林, 闫亚明, 罗登山, 李 斌. 丝状颗粒在滚筒横向截面中的传热传质特性[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(4): 756-763.
[8] 王 擎, 李 建, 王智超, 张立栋. 回转干馏炉内颗粒间传热特性的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(11): 4137-4146.
[9] 葛 良, 桂 南, 徐文凯, 闫 洁. 波形滚筒内颗粒混合和导热分布形态特性的研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2014, 44: 62-70.
[12] 张立栋, 韦庆文, 秦 宏, 王 擎. 柱状生物质颗粒在回转干馏炉中的运动及导热特性[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(11): 3993-3999.
[13] 张 喆, 刘义伦, 赵先琼, 肖友刚, 雷先明. 外热式回转窑横截面内散体物料的传热特性[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(9): 2178-2183.
[22] 陈 辉, 刘义伦, 赵先琼, 肖友刚, 刘 颖. 一元散体颗粒物料在回转窑截面上的运动与混合[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(5): 2575-2581.
[23] 王瑞芳, 李占勇, 窦如彪, 郭建忠. 水平转筒内大豆颗粒随机运动与混合特性模拟[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(6): 93-99.
[24] 陈 辉, 肖友刚, 赵先琼, 刘 颖, 刘义伦. 回转窑内二元颗粒物料的径向混合[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016, 38(2): 194-199.


