文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-03-0697-08
以Li2TiO3为原料合成Li4Ti5O12的机理和电化学性能
阚素荣,袁敏娟,刘 菲,卢世刚
(北京有色金属研究总院 动力电池研究中心,北京100088)
摘 要:
以偏钛酸锂(Li2TiO3)和二氧化钛(TiO2)为原料,采用固相法合成钛酸锂(Li4Ti5O12),通过XRD、SEM和电化学测试等方法对合成的钛酸锂材料的结构、形貌和电化学性能进行表征,同时研究一次颗粒长大规律和反应机理。结果表明:Li2TiO3是传统固相法合成Li4Ti5O12的中间产物,用Li2TiO3为原料在720、750 ℃保温10 h可合成纯的Li4Ti5O12,制备的一次颗粒粒径分别为270、278 nm,较用Li2CO3和TiO2为原料合成纯相的温度更低,一次颗粒粒径更小。反应期间,一次颗粒粒径随着反应分数的增大呈快速增长势头;反应结束后,一次颗粒粒径增长缓慢。750 ℃合成的Li4Ti5O12在充放电倍率为0.1C、1C、5C、9C时,比容量分别为170、164、149、126 mA·h/g,在0.1C时循环200次容量保持率大于97%,显示制备的Li4Ti5O12具有良好的电化学性能。
关键词:
中图分类号:0614.111;TM912.9 文献标志码:A
Mechanism and electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 prepared using Li2TiO3 as raw material
KAN Su-rong, YUAN Min-juan, LIU Fei, LU Shi-gang
(Research and Development Centre for Vechicle Battery and Energy Storage,
General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, Beijing 100088, China)
Abstract: The Li4Ti5O12 material was prepared by solid-state method with Li2TiO3 and TiO2 as the source of titanium and lithium. The crystalline structure,morphology and electrochemical performances of the samples were investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope and charge discharge test, and the growing regularity of primary particles and the reaction mechanism were studied at the same time. The results show that Li2TiO3 is an intermediate product for traditional method, pure Li4Ti5O12 materials are prepared at 720 and 750 ℃ for 10 h using Li2TiO3 as raw material, and the sizes of prepared fine primary particles are 270 and 278 nm, respectively, which are smaller than those using Li2CO3 and TiO2 as raw materials, and the temperature of pure phase Li4Ti5O12 obtained is lower. With increasing conversion of reaction, the size of primary particles increases rapidly, then increases slowly after the reaction finishes. The initial specific discharge capacities of Li4Ti5012 synthesized at 750 ℃ and the charge-discharge rate of 0.1C, 1C, 5C and 9C are 171, 164, 149 and 126.7 mA·h/g, respectively. After 200 cycles at 0.1C, it remains more than 97% of the initial specific discharge capacity, exhibiting excellent electrochemical performance.
Key words: Li2TiO3; Li4Ti5O12; solid-state method; electrochemical performance
和传统的碳材料相比,尖晶石结构钛酸锂在锂离子嵌入-脱嵌过程中晶体结构能够保持高度的稳定性,体积变化很小(小于1%)[1-2],被称为“零应变”电极材料,因而具有良好的循环寿命;其平台电压为1.55 V(vs Li+/Li),有效避免了SEI膜的形成和金属锂沉积,而且充电结束时电位迅速上升,避免了过充电,因而具有较好的安全性;另外,锂离子在钛酸锂中的扩散系数比碳材料大一个数量级,为此尖晶石结构钛酸锂作为新型储能电池和动力电池的电极材料日益受到重视。然而,钛酸锂的导电性较差,电导率只有10-13 S/cm[3],大倍率环境下容量迅速衰减,制约了钛酸锂大规模应用。近年来,针对钛酸锂的研究主要集中在合成方法和提高钛酸锂材料倍率性能上[4-5],主要包括以下方面:1) 制备小粒径钛酸锂[6-7]。通过降低颗粒尺寸,缩短Li+扩散路径,减轻电极的极化,增大了与电解液的接触面积,提高材料的电化学性能;2) 制备含导电包覆层的钛酸锂 [8-10]。导电包覆层一方面可以阻止材料在烧结过程中颗粒团聚生长,降低颗粒尺寸,提高材料性能;另一方面,可以提供导电网络,有效地提高颗粒之间的导电能力,改善材料倍率性能;3) 制备添加AgCu等的钛酸锂复合物[11-14]。通过复合高导电率的金属,提高了材料的电子导电率,增强了其倍率性能;4) 制备掺杂的钛酸锂等[15-21],掺杂后不等价的离子部分占据Li位、Ti位、O位,通过电荷补偿,增加Ti3+在钛酸锂中的含量,从而提高钛酸锂本体电子导电性。以上改性研究都能不同程度提高钛酸锂的倍率性能,因此,制备方法才是决定产物的纯度、形貌粒度以及电化学性能的关键因素。常用合成方法包括传统的高温固相法[22-23]、溶胶-凝胶法[24-25]、水热合成法[26]等。高温固相法是钛酸锂合成常用的方法,该方法合成工艺简单,适合大规模生产。一般是采用二氧化钛和碳酸锂或者氢氧化锂为原料,在高温下合成钛酸锂。该方法常常造成产物颗粒粗大,而且目标产物常常存在偏钛酸锂等杂质相[27-28],而偏钛酸锂是电化学非活性物质,会造成材料电化学性能下降。因此,研究一种合成纯相温度低且一次颗粒尺寸小的固相合成方法是非常必要的。本文作者以纳米二氧化钛和碳酸锂为原料合成偏钛酸锂,研究偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛合成钛酸锂的机理以及产物的结构、形貌、电化学性能,探索了合金一次颗粒长大的规律。
1 实验
1.1 材料的制备
以纳米二氧化钛和碳酸锂为原料,按摩尔比为n(Li):n(Ti)=1.05:1的比例配料,以水作为溶剂棒磨机上球磨混合24 h左右,蒸干溶剂,得到前驱体。将前驱体放入高温炉中,以3 ℃/min速度升温到550 ℃保温10 h后随炉冷却,研磨、筛分后得到偏钛酸锂材料。
以合成的偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料,添加一定的乙炔黑,按照偏钛酸锂与二氧化钛的摩尔比为2:3配料,以无水乙醇为溶剂,在棒磨机上球磨混合24 h,蒸干溶剂,得到前驱体。将前驱体放入高温炉中,以3 ℃/min速度分别升温到620、650、680、700、720、750 ℃,保温10 h后随炉冷却,研磨、筛分后得到钛酸锂材料。
1.2 材料的表征
采用荷兰X’Pert PRO-MPD型X-射线衍射仪进行结构分析(Cu Kα靶。管电压为40 kV);采用日本HITACHI S-4800场发射扫描电子显微镜(5.0 kV)进行形貌测试;采用Nano measurer 软件对扫描电镜图中一次颗粒进行测试。
1.3 材料的电化学测试
用涂布法制备极片,将得到的钛酸锂、Super P、PVDF按照80:10:10的质量比进行混合搅拌,以N,N-二甲基甲酰胺为溶剂,混合成浆料,然后将浆料涂布在铜箔上,充分干燥后制成极片,以金属锂为负极、Celgard2400聚丙烯多孔膜为隔膜、1.0 mol LiPF6/EC-DMC(体积比为1:1)为电解液,在干燥室中组装2032型号扣式电池。将组装的电池在LAND电化学测试仪中进行电化学性能测试,充放电电压范围为1.0~2.5 V。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 XRD结构分析
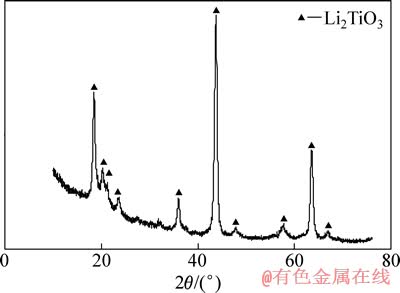
图1 在550 ℃合成偏钛酸锂的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of Li2TiO3 synthesized at 550 ℃
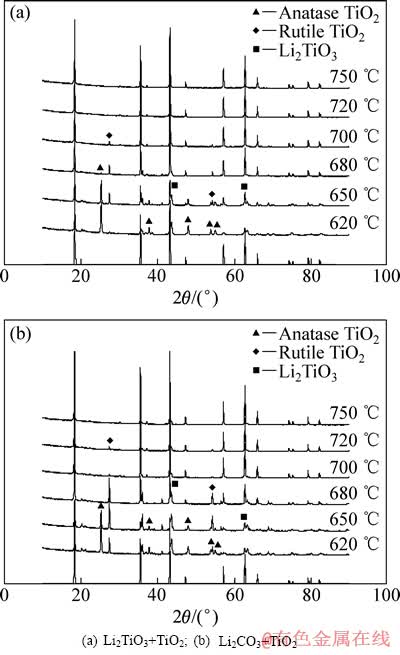
图2 不同温度下不同原料合成钛酸锂的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD images of Li4Ti5O12 synthesized using different raw materials at different temperatures
图1所示为在550 ℃下合成的偏钛酸锂的XRD谱,对照JCPDS00-033-0831标准谱线可知,550℃煅烧所得材料为单斜晶系的偏钛酸锂,在其XRD谱中没有出现明显其它的杂质峰,表明在此温度范围内保温10 h后,材料已经全部转化成偏钛酸锂。图2(a)所示为用550 ℃合成的偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在620~750 ℃不同温度下合成的钛酸锂的XRD谱,从图2(a)中可以看出,在620 ℃保温10 h合成的主要物相是锐钛型和金红石型的二氧化钛衍射峰,还存在偏钛酸锂,钛酸锂初步形成,衍射峰比较弱,从650到750 ℃合成的材料,其主要物相的衍射峰与JCPDS049-0207衍射峰相吻合,表现为2θ为18.33°、35.57°、43.24°、57.21°、62.84°、66.08°时出现几个强的特征峰,分别对应钛酸锂的(111)、(311)、(400)、(333)、(440)、(531)晶面,表明产物的主相均是具有尖晶石结构的钛酸锂。在650 ℃保温10 h后钛酸锂大量生成,但还存在明显的锐钛型和金红石型二氧化钛衍射峰,在680 ℃保温10 h钛酸锂合成反应基本完成,但还存在微量的金红石二氧化钛,在700 ℃保温10 h后,产物还能观察到有微弱的金红石二氧化钛衍射峰,在720和750 ℃合成10 h后,产物为单一钛酸锂相,其XRD谱的衍射峰尖锐,峰强较高,背底平整,表明在此温度范围内,由偏钛酸锂合成的钛酸锂材料具有较好的结晶性。图2(b)所示是用碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在620~750 ℃合成的钛酸锂的XRD谱。从图2(b)可以看出,在相同条件下采用碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在720 ℃保温10 h后合成的钛酸锂还存在二氧化钛相,在750 ℃才能合成纯相钛酸锂,表明采用偏钛酸锂为原料合成纯相钛酸锂的温度降低。为了进一步了解反应机理,分别测定了以碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料(未加乙炔黑)在不同反应时间下碳酸锂反应的摩尔数占原材料中碳酸锂总摩尔数的比例(碳酸锂的反应分数)和生成钛酸锂的摩尔数占完全反应生成钛酸锂的摩尔数的比例(钛酸锂的反应分数),其结果如图3所示。由图3可以看出,同一反应时间下,碳酸锂反应分数和生成的钛酸锂反应分数不一致,碳酸锂反应6 min就分解完全,而钛酸锂反应30 min后反应分数为0.8左右。将反应6 min的产物进行的XRD测试,其结果如图4所示,由图4可以看出,产物除了原料外还有偏钛酸锂生成,所以推测反应方程式如下:
TiO2+Li2CO3→Li2TiO3+CO2 (1)
2Li2TiO3+3TiO2→Li4Ti5O12 (2)
反应存在一个中间相偏钛酸锂。所以直接用偏钛酸锂为原料合成钛酸锂时,偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛均匀分散,有利于反应完全,合成纯相的温度会更低。
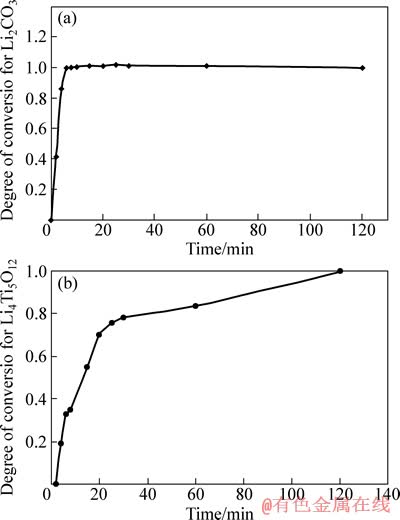
图3 Li2CO3和Li4Ti5O12的反应分数与反应时间的关系图
Fig. 3 Relationship between degree of conversion for Li2CO3 (a) and Li4Ti5O12 (b) and reaction time
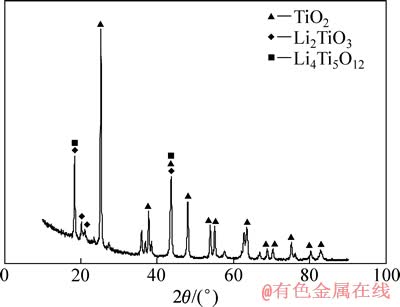
图4 钛酸锂反应6 min后产物的XRD谱
Fig. 4 XRD pattern of product of Li4Ti5O12 after reaction for 6 min
2.2 形貌分析
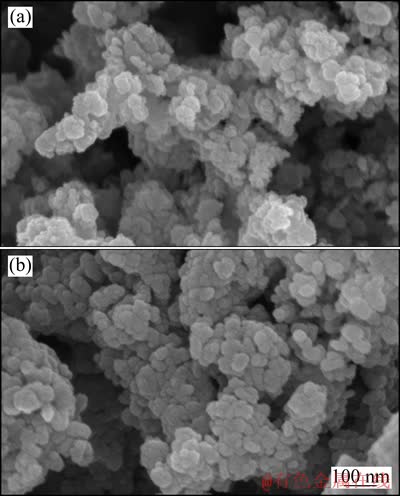
图5 二氧化钛和偏钛酸锂颗粒的SEM像
Fig. 5 SEM images of particles of TiO2 (a) and Li2TiO3 (b)
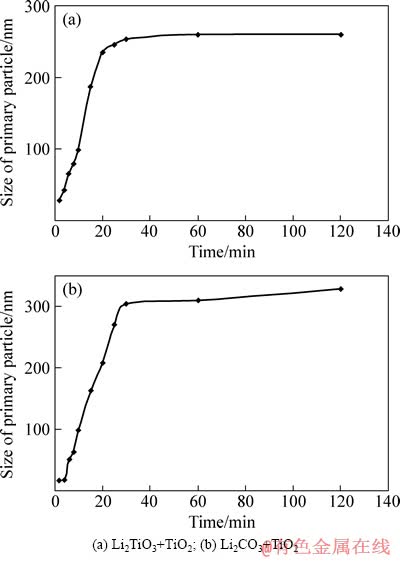
图6 在750 ℃采用不同原料合成钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径与反应时间的关系
Fig. 6 Relationships between primary particles and reaction time for Li4Ti5O12 prepared at 750 ℃ using different raw materials
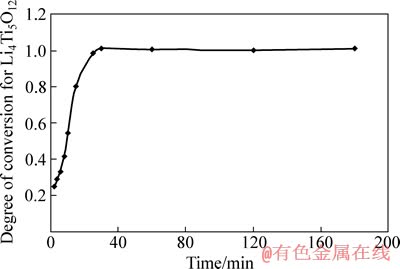
图7 钛酸锂反应分数与反应时间的关系曲线
Fig. 7 Relationship between degree of conversion of Li4Ti5O12 and reaction time
图5所示为实验所用二氧化钛原材料和在550 ℃合成的偏钛酸锂颗粒的SEM像。由图5可以看出,偏钛酸锂和原材料二氧化钛的形貌基本一致,即由几十纳米的一次颗粒团聚在一起,一次颗粒形态没有明显变化,一次颗粒尺寸大小由18 nm增大到54 nm。图6(a)和(b)所示分别是用偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料(未加乙炔黑)以及用碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料(未加乙炔黑)在750 ℃合成钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径和反应时间的关系。图7所示为用偏钛酸锂为原料时钛酸锂反应分数与反应时间的关系。从图6(a)和7中看出,一次颗粒粒径和反应分数随着反应时间的增加呈快速增长趋势,一次颗粒呈现异常长大的现象,反应进行30 min左右,反应分数接近1,反应基本完全,一次颗粒粒径基本稳定在250 nm左右,再继续反应,一次颗粒粒径缓慢增长。由此可见,刚开始反应速度和一次颗粒粒径增长很快,一次颗粒粒径增长趋势和反应分数的趋势一致,在反应完全后,一次颗粒粒径增长缓慢。从图6(b)可以看出,以碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在750 ℃合成钛酸锂的一次颗粒粒径首先随着反应时间的延长快速增长,当反应进行到30 min左右时,后一次颗粒粒径开始缓慢增长,反应完成后一次颗粒粒径达到了300 nm以上,反应的进行伴随着一次颗粒粒径的异常长大。图8所示是用偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料(加乙炔黑)在不同温度下保温10 h后的产物的SEM像。从图8可以看出,用偏钛酸锂合成的钛酸锂颗粒呈类球形,整体比较均匀,存在个别大颗粒,一次颗粒粒径相对较小。在620 ℃合成的钛酸锂一次颗粒没有明显长大,依然保持了二氧化钛和偏钛酸锂的形貌特征,在该温度下钛酸锂初步生成,大量二氧化钛结果和XRD测试结果一致。在650 ℃合成的钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径突然长大,达到了147 nm,XRD检测结果显示出现了较强的钛酸锂峰,表明在650 ℃下生成了大量的钛酸锂,一次颗粒粒径突然长大与生成大量钛酸锂有关。在680 ℃合成的钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径增大到266 nm,XRD检测结果显示钛酸锂衍射峰为主峰,只存在微弱的二氧化钛杂相峰,在此温度下保温10 h,生成钛酸锂的反应基本完成。在700、720、750 ℃合成的钛酸锂材料一次颗粒粒径分别为267、270、278 nm,在680~750 ℃合成的钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径稳定在266~278 nm,这表明在实验范围内,一次颗粒不再随着烧结温度的提高而明显长大,基本维持不变,这一规律使得钛酸锂的合成可以在较宽的温度范围内进行,有利于产品一致性和稳定性的提高。图9所示为两种不同方法合成钛酸锂的反应温度和一次颗粒粒径的关系图,用碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料时(加乙炔黑),在650 ℃时,一次颗粒开始长大;在650~750 ℃时,一次颗粒粒径持续增大,而且非常显著。在650、680、700、720、750 ℃合成的钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径分别为119、216、244、345、423 nm,表明用偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料比用碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料合成钛酸锂在一次颗粒粒径方面显示出明显的优势,钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径小而且在一定温度范围内变化不大。较小粒径的一次颗粒可以降低锂离子的迁移路径,有利于大电流充放电性能。通过观察材料形貌,发现用偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛合成钛酸锂时,晶粒之间有较多空隙,所以颗粒长大的几率要小一些。而采用碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料合成钛酸锂时,较多晶粒紧密堆积,合成温度的升高和合成时间的增加容易导致晶粒的长大,这可能是一次颗粒粒径比较大的原因。
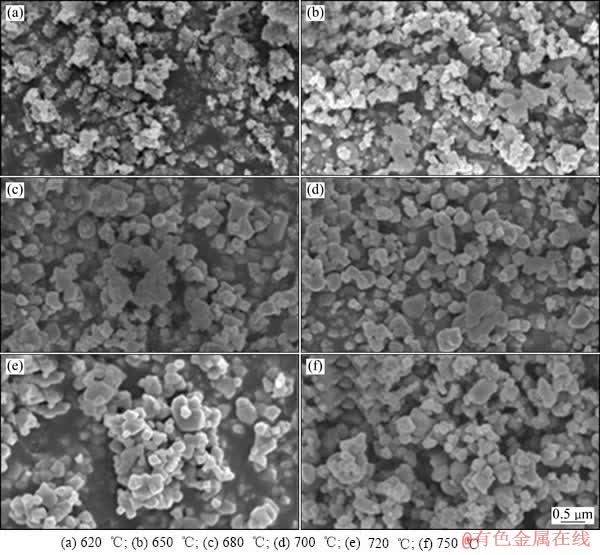
图8 在不同温度下保温10 h合成钛酸锂的SEM像
Fig. 8 SEM images of Li4Ti5O12 synthesized for 10 h at different temperatures
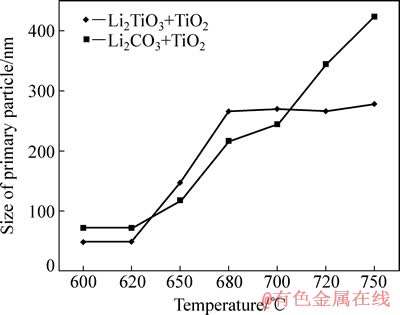
图9 采用不同原料保温10 h合成的钛酸锂一次颗粒粒径与温度的关系
Fig. 9 Relationship between size of primary particles and temperatures for synthesizing Li4Ti5O12 using different raw materials for 10 h
2.3 钛酸锂的电化学性能
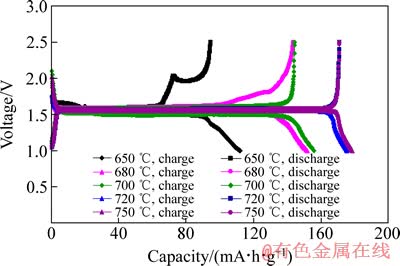
图10 在不同温度下合成的钛酸锂在0.1C时的充放电性能
Fig. 10 Electrochemical charge-discharge performances of Li4Ti5O12 synthesized at different temperatures at 0.1C
图10所示为以偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在不同温度下保温10 h合成的钛酸锂首次充放电曲线,可以看出,650、680、700 ℃合成的钛酸锂比容量较低,这和XRD分析显示有杂质的结果一致,成分和结构不单一使得材料的电化学性能下降,尤其650 ℃合成的钛酸锂容量很低,在2 V左右存在一个不可逆平台,这一现象可能和存在大量二氧化钛有关。在720和750 ℃合成的钛酸锂首次充放电曲线显示较长的充放电平台,充放电曲线呈L形,具有典型的两相反应特征,充放电电位差较小,显示出较小的极化,预示材料具有较好的可逆性,电化学性能测试在充放电倍率为0.1C时的比容量为170 mA·h/g左右,显示较好的容量特性。这和XRD测试为纯相的结果一致。图11所示为以偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在750 ℃保温10 h合成的钛酸锂的倍率性能,从图11中可以看出,0.1C、1C、5C、9C时的比容量分别为171.4、164.4、149、126 mA·h/g,5C时的容量是0.1C时容量的87%,9C时容量是0.1C时的容量的73.5%,显示出较好的倍率性能。较小的一次颗粒可能是较好倍率性能的关键,一次颗粒较小时,由于Li+嵌脱路径较短,阻力较小,极化相对较小,大电流时极化小,倍率性能较好。图12所示为以偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在750 ℃保温10 h合成的钛酸锂为正极,金属锂为负极制作的扣式电池的循环性能,可以看出,以0.1C循环200次后容量保持率大于97%,显示出优异的循环稳定性,表明用此方法合成的钛酸锂结晶性好、晶格完整、结构稳定。
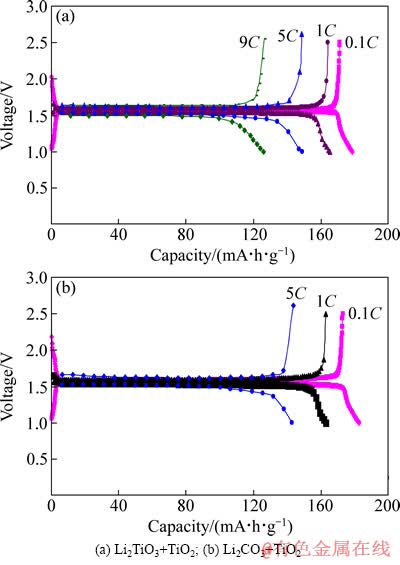
图11 采用不同原料制备的钛酸锂的倍率性能
Fig. 11 Rate performances for Li4Ti5O12 prepared using different raw materials
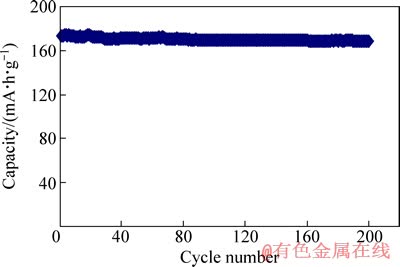
图12 以钛酸锂为正极的电池的循环性能
Fig. 12 Cycle performance of battery using Li4Ti5O12 as anode
3 结论
1) 以偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料合成尖晶石结构钛酸锂,在相同合成条件下合成纯相的温度较以碳酸锂和二氧化钛为原料的合成温度更低,一次颗粒粒径更小。
2) 以偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料在750 ℃合成尖晶石结构钛酸锂,刚开始随着反应分数的增大,一次颗粒粒径快速长大,在30 min左右时,反应基本完全,一次颗粒粒径达到250 nm;继续延长反应时间,一次颗粒粒径增长逐渐缓慢。
3) 以偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料,在680~750 ℃保温10 h合成尖晶石结构钛酸锂,一次颗粒粒径变化不大。
4) 以偏钛酸锂和二氧化钛为原料合成的钛酸锂具有两相反应特征,极化小、平台宽、比容量高、倍率性能和循环性能较佳。
REFERENCES
[1] 贺 慧, 程 璇, 张 颖. 锂离子电池负极材料Li4Ti5O12的结构和性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2007, 21(1): 82-86.
HE Hui, CHENG Xuan, ZHANG Ying. Structure and performance of lithium battery anode material Li4Ti5O12[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2007, 21(1): 82-86.
[2] 张 欢, 其 鲁, 高学平, 杨 坤, 张 鼎. 离子交换法合成纳米级锂离子电池负极材料Li4Ti5O12[J]. 无极化学学报, 2010, 26(9): 1539-1543.
ZHANG Huan, QI Lu, GAO Xue-ping, YANG Kun, ZHANG Ding. Preparation of nanosized Li4Ti5O12 as anode material for lithium-ion batteries via ion-exchange method[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2010, 26(9): 1539-1543.
[3] NI Jiang-feng, YANG Liu-xiang, WANG Hai-bo, GAO Li-jun. A high performance hybrid supercapacitor with Li4Ti5O12-C nano-composite prepared by in situ and ex situ carbon modification[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2012, 16(8): 2791-2796.
[4] 付安安, 张庆武, 高 剑, 王 莉, 何向明. 锂离子电池负极材料Li4Ti5O12的研究进展[J]. 电源技术, 2013, 37(12): 2239-2242.
FU An-an, ZHANG Qing-wu, GAO Jian, WANG Li, HE Xiang-ming. Review of anode material Li4Ti5O12 for lithium ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 37(12): 2239-2242.
[5] 李 星, 唐水花, 瞿美臻, 于作龙, 黄朋肖, 康毅力. 尖晶石型钛酸锂负极材料的研究现状[J]. 合成化学, 2013, 21(1): 119-123.
LI Xing, TANG Shui-hua, QU Mei-zhen, HUANG Peng-xiao, KANG Yi-li. Present status on research of spinel Li4Ti5O12 as the anode material for lithium ion batteried[J]. Chinese Journal of Synthetic Chemistry, 2013, 21(1): 119-123.
[6] SHAO Dan, HE Jia-rong, LUO Ying, LIU Wei, YU Xiao-yuan, FANG Yue-ping. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of nanoporous Li4Ti5O12 anode material for Lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2012, 16: 2047-2053.
[7] SHEN Lai-fa, ZHANG Xiao-gang, EVAN Uchaker, YUAN Chang-zhou, CAO Guo-zhong. Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles embedded in a mesoporous carbon matrix as a superior anode material for high rate lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2012, 2: 691-698.
[8] 卢 海, 李艳红, 高宏权, 张治安, 赖延清, 李 劼, 刘业翔. Li4Ti5O12 /TiN复合材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(4): 1229-1234.
LU Hai, LI Yan-hong, GAO Hong-quan, ZHANG Zhi-an, LAI Yan-qing, LI Jie, LIU Ye-xiang. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 /TiN composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(4): 1229-1234.
[9] HU Xue-bu, LIN Zi-ji, YANG Ke-run, HUAI Yong-jian, DENG Zheng-hua. Effects of carbon source and carbon content on electrochemical performances of Li4Ti5O12/C prepared by one-step solid-state reaction[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56: 5046-5053.
[10] WANG Ru-ying, WANG Juan, QIU Tian, CHEN Li-peng, LIU Hai-mei, YANG Wen-sheng. Effect of different carbon sources on the electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5O12/C composites[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 70: 84-90.
[11] LIU Zhi-min, ZHANG Nai-qing, WANG Zhi-jun, SUN Ke-ning. Highly dispersed Ag nanoparticles (<10 nm) deposited on nano crystalline Li4Ti5O12 demonstrating high-rate charge-discharge capability for Lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 205: 479-482.
[12] HUANG Sha-hua, WEN Zhao-yin, ZHU Xiu-jian, YANG Xue-lin. Research on Li4Ti5O12/CuxO composite anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152(7): A1301-A1305.
[13] HUANG Sha-hua, WEN Zhao-yin, LIN Bin, HAN Jin-duo, XU Xiao-gang. The high-rate performance of the newly designed Li4Ti5O12/Cu composite anode for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 457: 400-403.
[14] HUANG Sha-hua, WEN Zhao-yin, ZHANG Jing-chao, GU Zhong-hua, XU Xiao-he. Li4Ti5O12 /Ag composite as electrode materials for lithium-ion battery[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2006, 177: 851-855.
[15] TIAN Bing-bing, XIANG Hong-fa, ZHANG Le, WANG Hai-hui. Effect of Nb-doping on electrochemical stability of Li4Ti5O12 discharged to 0V[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2012, 16: 205-211.
[16] LI Hong-sen, SHEN Lai-fa, ZHANG Xiao-gang, NIE Ping, CHEN Lin, XU Ke. Electrospun hierachical Li4Ti4.95Nb0.05O12 carbon composite nanofibers for high rate lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(4): A426-A430.
[17] CAI Rui, JIANG Si-min, YU Xing, ZHAO Bo-te, WANG Huan-ting, SHAO Zong-ping. A novel method to enhance rate performance of an Al-doped Li4Ti5O12 electrode by post-synthesis treatment in liquid formaldehyde at room temperature[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22: 8013-8021.
[18] YI Ting-feng, XIE Ying, JIANG Li-juan, SHU Jie, YUE Cai-bo, ZHOU An-na, YE Ming-fu. Advanced electrochemiscal properties of Mo-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material for power lithium ion battery[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2: 3541-3547.
[19] JHAN Yi-ruei, DUH Jeng-gong. Electrochemical performance and low discharge cut-off voltage behavior of ruthenium doped Li4Ti5O12 with improved energy density[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 63: 9-15.
[20] 熊训辉, 王志兴, 伍 凌, 李新海, 吴飞翔, 郭华军. Al掺杂对Li4Ti5O12结构及性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(9): 2146-2150.
XIONG Xun-hui, WANG Zhi-xing, WU Ling, LI Xin-hai, WU Fei-xiang, GUO Hua-jun. Effect of Al-doping on structure and electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(9): 2146-2150.
[21] 王 丹, 张春明, 吴晓燕, 何丹农. Co3+掺杂对Li4Ti5O12结构及性能的研究[J]. 电池, 2013, 43(2): 63-66.
WANG Dan, ZHANG Chun-ming, WU Xiao-yan, HE Dan-nong. The effect of Co+-doping on structure and performance of Li4Ti5O12[J]. Battery Bimonthly, 2013, 43(2): 63-66.
[22] 李 星, 瞿美臻, 于作龙. 锂离子电池负极材料Li4-xKxTi5O12结构和电化学性能[J]. 无机化学学报, 2010, 26(2): 233-239.
LI Xing, QU Mei-zhen, YU Zuo-long. Structural and electrochemical characteristics of Li4-xKxTi5O12 as anode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2010, 26(2): 233-239.
[23] GUERFI A, EVIGNY S, LAGACE M, HOVINGTON P, KINOSHITA K, ZZGHIB K. Nano-particle Li4Ti5O12 spinel as electrode for electrochemical generators[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 119/121: 88-94.
[24] MOSA J, VELEZ J F, LORITE I, ARCONADA N, APRICIO M. Film-shaped sol-gel Li4Ti5O12 electrode for Lithium-ion microbatteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 205: 491-494.
[25] WANG Jin, LIU Xiao-min, YANG Hui. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of highly dispersed Li4Ti5O12 nanocrystalline for lithium secondary batteries[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 613-620.
[26] WU Fei-xiang, LI Xin-hai, WANG Zhi-xing, GUO Hua-jun, HE Zhen-jiang, ZHANG Qian, XIONG Xun-hui, YUE Peng. Low-temperature synthesis of nano-micron Li4Ti5O12 by an aqueous mixing technique and its excellent electrochemical performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 202: 374-379.
[27] 李 劼, 王娇丽, 张治安, 赖延清. 煅烧制度对Li4Ti5O12材料结构与电化学性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(2): 294-299.
LI Jie, WANG Jiao-li, ZHANG Zhi-an, LAI Yan-qing. Effect of calcined system on Li4Ti5O12 material structure and electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(2): 294-299.
[28] 唐定国, 雷 嘉, 张玉良, 张 宇. 纯相Li4Ti5O12负极材料的制备[J]. 中南民族大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 29(4): 1-4.
TANG Ding-guo, LEI Jia, ZHANG Yu-liang, ZHANG Yu. Synthesis of pure-phased Li4Ti5O12 as anode material for lithium ion battery through high-temperature solid state routine[J]. Journal of South-Central University for Nationalities: Natural Science Edition, 2010, 29(4): 1-4.
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2012AA110102)
收稿日期:2014-07-13;修订日期:2014-11-26
通信作者:阚素荣,教授;电话:010-82241333-8182;E-mail:ksr8065@163.com
摘 要:以偏钛酸锂(Li2TiO3)和二氧化钛(TiO2)为原料,采用固相法合成钛酸锂(Li4Ti5O12),通过XRD、SEM和电化学测试等方法对合成的钛酸锂材料的结构、形貌和电化学性能进行表征,同时研究一次颗粒长大规律和反应机理。结果表明:Li2TiO3是传统固相法合成Li4Ti5O12的中间产物,用Li2TiO3为原料在720、750 ℃保温10 h可合成纯的Li4Ti5O12,制备的一次颗粒粒径分别为270、278 nm,较用Li2CO3和TiO2为原料合成纯相的温度更低,一次颗粒粒径更小。反应期间,一次颗粒粒径随着反应分数的增大呈快速增长势头;反应结束后,一次颗粒粒径增长缓慢。750 ℃合成的Li4Ti5O12在充放电倍率为0.1C、1C、5C、9C时,比容量分别为170、164、149、126 mA·h/g,在0.1C时循环200次容量保持率大于97%,显示制备的Li4Ti5O12具有良好的电化学性能。
[1] 贺 慧, 程 璇, 张 颖. 锂离子电池负极材料Li4Ti5O12的结构和性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2007, 21(1): 82-86.
[2] 张 欢, 其 鲁, 高学平, 杨 坤, 张 鼎. 离子交换法合成纳米级锂离子电池负极材料Li4Ti5O12[J]. 无极化学学报, 2010, 26(9): 1539-1543.
[4] 付安安, 张庆武, 高 剑, 王 莉, 何向明. 锂离子电池负极材料Li4Ti5O12的研究进展[J]. 电源技术, 2013, 37(12): 2239-2242.
[5] 李 星, 唐水花, 瞿美臻, 于作龙, 黄朋肖, 康毅力. 尖晶石型钛酸锂负极材料的研究现状[J]. 合成化学, 2013, 21(1): 119-123.
[20] 熊训辉, 王志兴, 伍 凌, 李新海, 吴飞翔, 郭华军. Al掺杂对Li4Ti5O12结构及性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(9): 2146-2150.
[21] 王 丹, 张春明, 吴晓燕, 何丹农. Co3+掺杂对Li4Ti5O12结构及性能的研究[J]. 电池, 2013, 43(2): 63-66.
[22] 李 星, 瞿美臻, 于作龙. 锂离子电池负极材料Li4-xKxTi5O12结构和电化学性能[J]. 无机化学学报, 2010, 26(2): 233-239.
[27] 李 劼, 王娇丽, 张治安, 赖延清. 煅烧制度对Li4Ti5O12材料结构与电化学性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(2): 294-299.
[28] 唐定国, 雷 嘉, 张玉良, 张 宇. 纯相Li4Ti5O12负极材料的制备[J]. 中南民族大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 29(4): 1-4.


