网络首发时间: 2019-12-19 10:42
工业含铊废水处理研究现状与进展
付向辉 李立 杨国超 曾娟
中南大学冶金与环境学院
长沙矿冶研究院有限责任公司
摘 要:
铊是一种剧毒的稀散元素,微量的铊即可对动植物产生危害。由于当代对含铊矿物开采以及铊化合物应用的增加,工业含铊废水成了铊向环境进行迁移和释放的重要途径,导致近年来铊中毒及铊污染事件时有发生。铊在工业废水中的含量较低,大多在微克到不超过10 mg·L-1 的水平。但是铊在环境中的迁移性强,且有生物累积毒性,少量的铊即可对生态和环境产生危害。当前,我国制定了世界上最严格的工业废水铊排放标准(2~5μg·L-1 ),对生态环境的保护起到了积极作用,也对含铊工业废水的治理技术提出了更高的要求。本文分别对现有常用的氧化沉淀法、吸附法、离子交换法以及萃取法等方法进行了阐述,总结分析了不同方法的适用条件及处理效果。同时,针对不同浓度含铊废水的治理提出了相应的适用工艺路线,指出具有深度净化能力且污泥产生量少的单个或组合工艺是处理含铊工业废水的重要发展方向。
关键词:
铊 ;铊污染 ;工业废水 ;深度净化 ;吸附 ;氧化 ;
中图分类号: X703.1
作者简介: 付向辉(1977-),男,河北新河人,博士,教授级高级工程师,研究方向:复杂废水治理与深度净化;电话:13873183635;E-mail:fuxh@csu.edu.cn;
收稿日期: 2019-11-19
基金: “十三五”国家重点研发计划重点专项项目(2016YF0304105-03); 企业自主创新基金项目(2018HB-A5-01)资助;
Removal Thallium from Industrial Wastewater: A Review Fu Xianghui Li Li Yang Guochao Zeng Juan
School of Metallurgy and Environment,Central South University
Changsha Research Institute of Mining and Metallurgy Co.Ltd.
Abstract:
Thallium(Tl) is a highly toxic disperse element. Trace Tl can cause toxicity to animals and plants. Due to the increasing exploitation of Tl containing minerals and the application of Tl compounds, Tl-containing wastewater has become a primary medium for Tl migration and releasing to the environment, resulting in Tl poisoning and pollution incidents in recent years. The normal Tl concentration in industrial wastewater stays at a level of micrograms to less than 10 mg·L-1 . Nonetheless, even limited amount of Tl can be harmful due to its strong mobility and bioaccumulative toxicity. China has formulated the world's most stringent Tl emission standard for industrial wastewater(2~5 μg·L-1 ), which has played a positive role for the environment protection and designated higher requirements for processing technology of wastewater. By summarizing and analyzing current methods such as oxidation precipitation, adsorption, ion exchange and extraction, the corresponding applicable process routes were proposed for different Tl concentrations wastewater. The review highlighted the efforts to develop some single or combined processes which are capable of deep purification with less sludge.
Keyword:
thallium; thallium pollution; industrial wastewater; deep purification; adsorption; oxidation;
Received: 2019-11-19
铊是一种高毒性的稀散元素, 对生物的毒害作用远超过As, Cr, Cd等常见重金属, 微量的铊就会导致人体中毒
[1 ,2 ,3 ]
。 目前, 铊被美国环境保护局和欧盟水框架公约列为需优先控制的污染物
[4 ,5 ]
, 我国在《重金属污染综合防治“十二五”规划》中也明确提出, 铊是需重点防护的重金属污染物之一
[6 ]
。
自然水体中铊的含量很低
[7 ,8 ]
, 但随着现代工业的发展, 大量的铊从矿山开采、 金属冶炼等途径进入环境
[9 ]
, 导致铊中毒及铊污染事件时有发生。 近年来, 在中国北江、 贺江等地分别爆发过铊污染事件
[10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ]
, 国外近年来也有类似的铊污染事件发生
[14 ]
, 对生态和生物健康造成了严重的负面影响。
由于铊的剧毒特性, 我国制定了当前世界上最严格的含铊废水排放标准(5 μg·L-1 , GB 31573-2015), 广东和江苏省进一步将铊的排放值限定在2 μg·L-1 (DB44/1989-2017, DB32/3431-2018), 对含铊工业废水的处理技术提出了更高的要求。 本文总结了含铊废水治理的研究现状, 对现行处理技术的优、 缺点进行了归纳。 同时, 面对当前严格的排放要求, 提出了对含铊工业废水进行深度净化的技术展望。
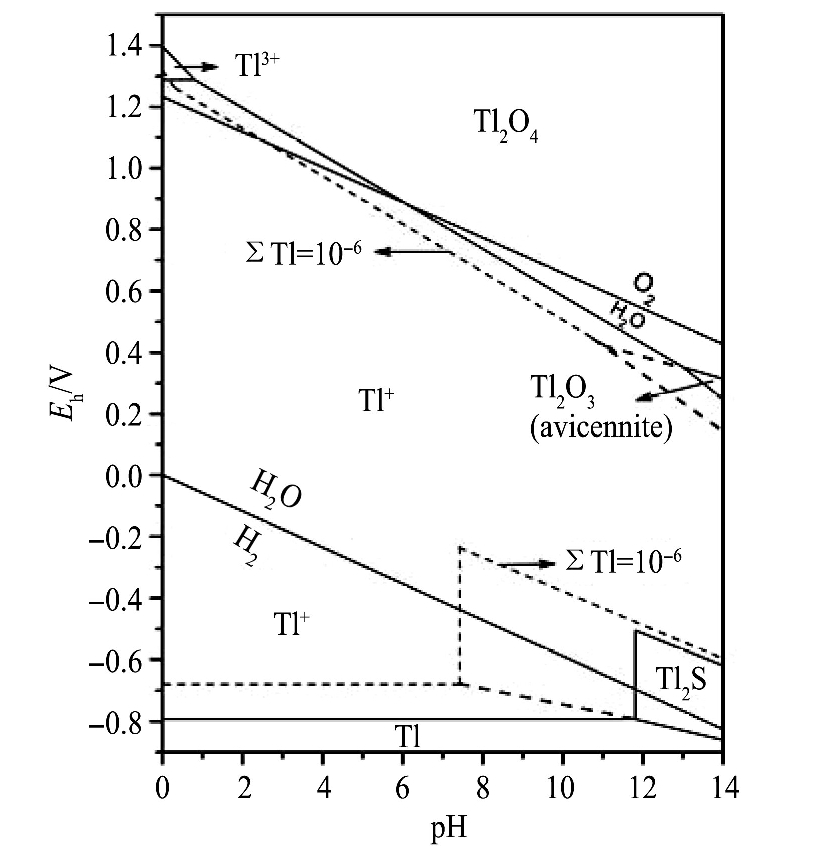
1 铊在溶液中的价态转换
铊在溶液中的无机形态主要以Tl(I)和Tl(III)的形式存在, 均具有很高的毒性
[15 ]
。 Tl-S-O-H体系E h -pH图(图1)显示
[16 ]
, Tl(I)占据了绝大部分空间。
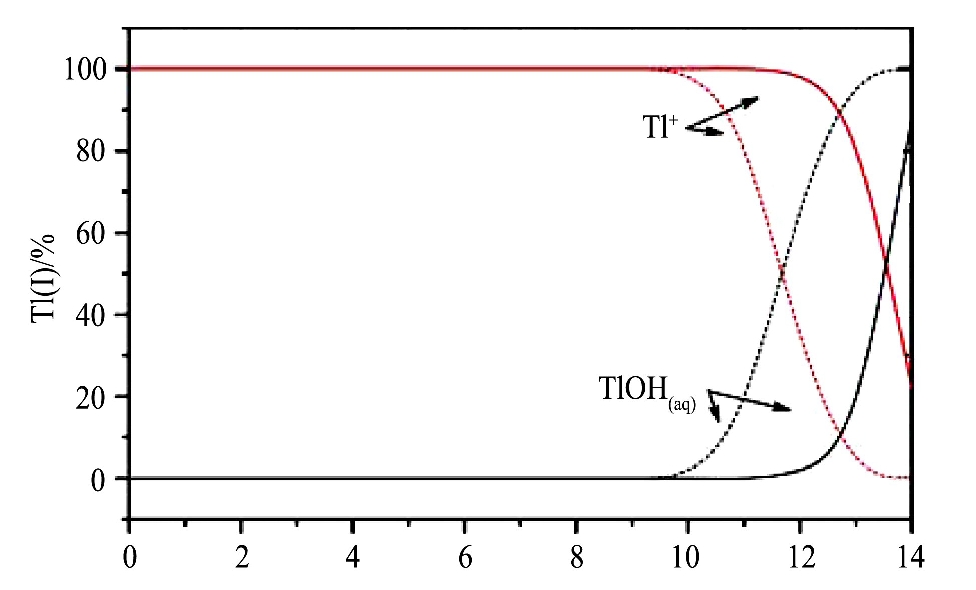
Tl(I)及其化合物在pH值0~14的广泛范围内是高度可溶的(图2)
[14 ]
, 水体中溶解性的铊主要以Tl(I)的形式存在
[17 ,18 ]
。 不同pH值下, 溶液中的Tl(III)分别以Tl3+ , TlOH+ 2 , Tl(OH)+ , Tl(OH)3 或Tl(OH)- 4 的形式存在
[19 ]
, 其中Tl(OH)3 的溶解度常数很小(K sp =10-45.2 )
[20 ]
, 表明Tl(III)可以通过调pH值的方法加以去除。 Tl(III)是热力学不稳定的
[21 ]
, Tl(III)能够稳定存在的区域很小(图1), 具有还原为Tl(I)的倾向
[22 ]
。 另外, Tl(III)可与包括有机质、 卤素(F- , Cl- , Br- 和I- )以及SO
4
2
-
等配体形成稳定的配合物
[19 ]
, 从而改变Tl(III)的溶解-沉淀行为
[14 ,22 ]
。 如在溶液中, Cl- 的存在会显著压缩Tl(III)氢氧化物种的不溶区间; 在富含胶体和有机质的湖泊、沼泽等自然水体中也可发现大量稳定存在的Tl(III)
[19 ]
,显示有机物配体的存在增大了Tl(III)的存在空间。
图1 Tl-S-O-H体系Eh-pH图
Fig.1 E h -pH diagram for system Tl-S-O-H areas
[16]
图2 pH值对Tl(I)在溶液中的物种分布影响
Fig.2 Distribution of Tl(I)(2 mg·L-1 )aqueous species as a function of p H at 25℃(solid lines and dotted lines are adapted from NIST
[27]
and Lin&Nriagu
[20]
,respectively)
[14]
2 含铊废水处理研究现状
2.1 化学沉淀法
化学沉淀法是一种常用重金属污染治理方法, 在废水处理中得到了广泛应用。 由于Tl(I)及其化合物大多是可溶的, 所以仅采用化学沉淀对Tl(I)的处理效果有限
[23 ]
。 虽然有报道通过添加硫化物
[24 ]
以及利用TlCl溶解度很小的特点
[25 ,26 ]
来沉淀Tl(I), 但存在会产生H2 S造成二次污染以及出水含盐量过高的缺点, 处理效果也难以达到我国现有排放标准。 因此, 鉴于Tl(OH)3 在水中较低的溶解度, 将Tl(I)预氧化为Tl(III)并沉淀是处理含铊废水的有效方法之一。
Tl(III)具有较高的氧化还原电势
[28 ]
, 只有强氧化剂如MnO2 , KMnO4 , H2 O2 , 高铁酸盐以及过硫酸盐等可将Tl(I)氧化为Tl(Ⅲ)。 Huangpu等
[29 ]
报道了在中性条件下利用纳米二氧化锰快速氧化去除水溶液中Tl(I)的方法。 利用Fe0 -H2 O2 芬顿技术, 在碱性条件下对初始浓度为10.25 mg·L-1 Tl(I)的去除率可以达到99%以上
[30 ]
。 对于更低浓度的含铊废水, Davies等
[31 ]
利用KMnO4 氧化沉淀法可将水煤浆中的铊由1 mg·L-1 降到2 μg·L-1 。 高铁酸盐与过硫酸盐均具有强氧化性, 中性条件下利用K2 FeO4 处理痕量铊 (<1 μg·L-1 ), 5 min内去除率即可达到92%以上
[32 ]
。 对高浓度模拟含Tl(I)废水, 在Fe2+ -S2 O
8
2
-
这种类Fenton体系也展现了较好的去除效果
[33 ]
。
虽然Tl(III)可能受配体的影响改变其沉淀行为, 但从上述研究结果来看, 预氧化-沉淀法在应用于含铊废水处理时显示了良好的效果(表1)。 由于Tl(Ⅲ)的高氧化还原电位, 只有强氧化剂才能实现对Tl(I)的氧化, 这将导致废水处理成本居高不下, 不利于规模化工业应用。 因此, 在当前严格的排放标准下寻找经济有效的氧化手段
[34 ]
, 是氧化沉淀法除铊的重要发展方向。
2.2 吸附法
吸附是一种由液相到固相的传质过程, 污染因子从液相转移到吸附剂固体表面从而实现废水的净化
[35 ]
。 近年来吸附法已成为一种应用广泛的重金属废水处理技术。 目前针对含铊废水应用最广泛的吸附材料有金属氧化物、 炭基材料、 生物质吸附材料以及其他吸附材料等。
2.2.1 金属氧化物基材料
Fe, Mn, Al和Ti等金属氧化物对重金属具有良好的吸附性能。 Mn氧化物及Fe-Mn复合氧化物展现了对铊良好的亲和力, 自然环境中海底锰结核中也发现了铊的富集
[23 ]
。 这类吸附剂利用了MnO2 的强氧化性能, 对废水中Tl(I)的吸附往往伴随着铊的氧化沉淀过程。 Li等
[36 ]
利用合成的铁锰二元氧化物去除废水中的Tl(I), 在较宽的pH范围(3~12)和高离子强度(0.1~0.5 mol·L-1 )条件下平衡吸附量可达95%以上。 负载MnO2 的FeOOH材料应用于模拟废水时, Tl(I)的吸附速率快, 4 min即可达到吸附平衡, 且出水能达到饮用水的标准
[37 ]
。 Fe-Mn复合材料中MnO2 的氧化作用和FeOOH的吸附对Tl(I)的去除均起到了重要作用。 Gadde等
[38 ]
对铁锰水合氧化物的吸附作用机制研究也表明, 表面氧化还原作用是T1(I)在低pH值下吸附行为的主要原因。
纳米吸附剂具有更大的表面积和更高的界面反应活性, 展现出普通吸附材料不具备的优异性能。 纳米Al2 O3 材料在酸性水溶液中具有对Tl(III) 的良好吸附能力
[39 ]
。 通过与纳米过氧化钛表面羟基的离子交换形成Ti-O-Tl(I)表面络合物, 溶液中Tl(I)可得到有效去除
[40 ]
, 而且共存离子及有机质对吸附影响小, 表现出较高的吸附选择性。
2.2.2 炭基材料
活性炭及其纳米材料是在废水治理上应用最广的吸附材料之一。 Hanafi
[41 ]
的研究显示, 在pH值6.66~8.79间, Tl(I)在不同活性炭上表现出了相似的高吸附效率, 而且吸附效果受共存离子(Cl- , NO- 3 , S2 O
3
2
-
, CH3 COO- 及EDTA等)的影响较小。 Hoffman等
[42 ]
研究了活性炭等吸附Tl(I)的性能, 表明活性炭对Tl(I)有良好的吸附效果且受钾的影响较小, 在生理钾浓度下吸附容量基本保持不变。近年来,对于碳纳米材料的研究得到了普遍重视。Rehman等
[43 ]
研究了多壁碳纳米管对Tl(III)的吸附,显示经HNO3 处理的碳纳米管在p H值为中性时表现出对Tl(III)较强的吸附能力。在对Tl(I)的吸附效果上,经Na2 S2 O8 改性的多壁碳纳米管对初始浓度为100μg·L-1 的模拟废水可实现接近90%的去除率。但其处理效果尚无法满足当前的监管排放标准,且共存离子K+ 的存在对吸附效果有较大的负面作用
[44 ]
。
表1 氧化沉淀法从废水中去除铊
Table 1 Oxidation-precipitation on Tl removal from water/wastewater
Influent property
Oxidation
Operation
Max removal
Effect of coexisting ions
Ref.
-1 n MnO2 n MnO2 0.05 mmol·L-1 /pH 7/15 min42.9% at pH of 7
Ca2+ , Mg2+ , SiO3 2- , PO
4
3
-
, CO
3
2
-
and hemic acid (HA); negative effect
[29]
-1 ; Real -1 Fe0 -based Fenton-like technique
Fe0 3.8 g·L-1 /[H2 O2 ]-Fe0 molar ratio 1.5/initial pH 2.9
99% at coagulation pH of 10.5 for model water; 80.3% and 96.7% for different real wastewater
Na+ , Mg2+ , and Ca2+ ; negative effect
[30]
-1 real -1 KMnO4 , oxidative precipitation
KMnO4 2.5 and 5 mg·L-1 /pH 9.3/30 min, and after 1 and 2 days, respectively
Dissolved Tl less than -1 at pH around 9
Al3+ , Ca2+ , Cu2+ , Fe3+ , Mg2+ , Na+ , Si4+ and Zn2+ ; Consume more KMnO4
[31]
-1 K2 FeO4 , oxidative precipitation
K2 FeO4 0.5~5 mg·L-1 /pH 4~11/30 min/20 ℃
92% of Tl removal within 5 min
Na+ , Ca2+ , HCO- 3 , less affected; HA; Significant negative effect
[32]
-1 Persulfate oxidation and iron coagulation
Fe2+ -S2 O
8
2
-
molar ratio: 0~1.6/initial pH 7, coagulation pH>10/25 ℃
96% Tl removal at coagulation pH>10
High concentration of Na+ , Mg2+ have negative effect, Ca2+ : Significant negative effect; HA: negative effect
[33]
2.2.3 生物质吸附材料
利用微生物或植物源的非活性生物物质对重金属进行生物吸附是一种可行的技术, 用以替代传统吸附剂具有一定的环保意义
[45 ]
。 吸附剂的来源多种多样, 有水稻壳
[46 ]
、 锯末
[47 ]
、 甜菜渣
[48 ]
、 巴拉圭茶渣
[49 ]
等农业废弃物材料, 以及绿藻
[50 ]
、 干燥生物膜
[51 ]
等微生物基材料。 这些生物质材料中含有大量的各种官能团(如羟基、 酰胺、 羧基、 乙酰氨基等), 可以通过氢置换或与金属离子络合的作用得以将其从废水中去除
[45 ,52 ]
。 这些天然生物材料对铊有一定的吸附作用, 但一般吸附量不高且容易受杂质离子的干扰, 须经改性或预处理提高其吸附性能
[53 ]
。 目前利用生物吸附材料吸附铊的研究大多处于研究阶段, 对反应机制、 共存效应以及回收方法的研究尚缺乏深入的探讨
[14 ]
。
2.2.4 其他吸附材料
Wick等
[54 ]
研究了微量Tl(I)在伊利石上的吸附行为, 建立了在伊利石上吸附Tl(I)的阳离子交换模型。 Sangvanich等
[26 ]
用亚铁氰化铜改性的介孔二氧化硅选择性吸附Tl(I), 表明这种材料在吸附亲和力、 吸附容量、 吸附速率和材料稳定性等方面优于普鲁士蓝, 在酸性条件下受pH值及共存金属离子的影响较小。
吸附剂的开发是吸附技术的关键。 目前已有金属氧化物基吸附工艺应用于工业含铊废水的治理。 但寻找吸附容量大、 吸附效率高、 循环性能好的吸附剂一直是吸附技术处理含铊废水的研究热点。 就目前研究结果来看, 普遍存在吸附容量不高, 受共存离子影响大等问题, 对吸附剂的再生和循环寿命的研究也有所不足。 另外, 当前多数研究利用高浓度含铊模拟废水开展相关实验, 针对工业含铊废水常规浓度范围(多为微克级, 一般小于10 mg·L-1 )的研究较少
[14 ,55 ]
, 展现的吸附效果可能会存在差异(表2)。 并且由于铊的毒性特征, 废弃含铊吸附剂作为危险废物,如何经济有效的处理也是一个棘手的问题。这些问题制约了吸附法在含铊废水处理上的应用,也为吸附法除铊的发展与改进提供了方向。
表2 吸附法从废水中去除铊
Table 2 Adsorption technology for Tl removal from water/wastewater
Influent property
Adsorbent
Operation conditions
MAC/Adsorption
Effect on adsorption capacity
Mechanism
Ref.
-1 Fe-Mn binary oxides
Adsorbent 0.1-2 g·L-1
8.28% in weight after adsorption/over 95%
Na+ , EDTA, DPTA;
Surface complexation, oxidation and precipitation
[36]
-1 FeOOH-loaded MnO2 nano-composite
Adsorbent 0.4 g·L-1
450 mg·g-1 -1 /NA
Na+ , no obvious affect; Ca2+ , Mg2+ ; decrease
Oxidation and adsorption
[37]
-1 Nano-Al2 O3
Adsorbent 3 g·L-1
6.28 mg·g-1 at 40 ℃/99.56%
NA
NA
[39]
-1 Titanium peroxide
Adsorbent 0.2 g·L-1
412 mg·g-1 at pH
Ca2+ , Mg2+ , K+ , Cu2+ , Zn2+ , organic acids; no significant affect
Ion-exchange reaction
[40]
-1 Multiwall carbon nanotubes
Adsorbent 0.1 g·L-1
NA/90% of Na2 S2 O8 -MWCNTs
Na+ , K+ ; decrease
Ion exchange or electrostatic interaction
[44]
-1 Yerba mate
Adsorbent 0.25 g·L-1
384.4 mg·g-1 of modified yerba mate/42.6~76.3% for real water
NA
NA
[49]
-1 Green
Adsorbent 0.2 g·L-1
830~1000 -1 /100%
NA
Ion exchange, coordination and/or complexation
[50]
-1 Copper ferrocyanide functionalized mesoporous silica
Adsorbent 1 g·L-1
28.3 mg·g-1 /85% of Tl(I) removal after 2 min
Cs+ , Na+ , Mg2+ , Ca2+ , K+ , Se4+ , Mn2+ , Fe3+ , Cu2+ , Zn2+ and Mo6+ ; no significant affect
NA
[26]
Note: MAC-Maximal adsorption capacity; EDTA-Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid; DPTA-Diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid; NA-Not available
2.3 离子交换法
离子交换方法具有操作简单、 选择性好, 不易产生二次污染以及有价金属易回收等优点, 在废水治理中得到了广泛应用
[56 ,57 ,58 ]
, 美国环境保护局曾推荐采用离子交换法处理受铊污染的饮用水
[59 ]
。 但该方法应用于含铊废水治理的研究较少。 Li等
[60 ]
研究了用改性阴离子交换树脂同时脱除高盐工业废水中的铊和氯。 在其实验条件下可实现97%以上的铊去除率。 其主要机制首先利用H2 O2 将Tl(I)氧化为Tl(III), 然后利用形成TlCl- 4 络合物的方式加以去除。 Albert等
[61 ]
提出用离子交换树脂从含有强无机酸盐的溶液中提取和回收铊, 但其母液铊浓度较高, 用于铊含量较低的废水治理时效果难以预测。 利用离子交换富集、 分离铊用于分析目的的文献较多, 如Lin等
[62 ]
利用离子交换法分析了五大湖区铊的化学形态和分布; 谢晓雁等
[63 ]
用溴水将Tl(I)氧化为Tl(III), 利用D401离子交换树脂提取Tl(III)后, 再用亚硫酸溶液将Tl(III)还原为Tl(I)后用于测定锰矿中的铊含量; Karatepe等
[64 ]
采用105色谱载体树脂选择性地交换络合态的Tl(I)和Tl(III), 提供了一种无机铊的选择性预富集方法。
工业废水中杂质离子种类复杂, 树脂的交换能力会受到其他离子的干扰造成交换容量和选择性的下降。 另外交换树脂易被废水中的有机物和其他悬浮物污染, 需要较严格的前处理。 当废水中污染因子含量较高时, 树脂需频繁再生, 导致处理效率下降。
2.4 萃取法
含三辛基氧化膦的正己烷
[65 ]
和仲辛基苯氧乙酸(CA-12)、 仲壬基苯氧乙酸(CA-100)以及环烷酸(NA)
[66 ]
在氯盐体系、 以甲苯溶解的三苯基胂氧化物在水杨酸盐体系
[67 ]
中均是铊的有效萃取剂。 Hasegawa等
[65 ]
的研究表明, TI(III)可以形成稳定的TlCl- 4 络合物是其易于萃取的主要原因。 Li等
[68 ]
的研究给出了相同的结论, 在 (丙醇和丁醇)-NaCl和乙醇-(NH4 )2 SO4 两相体系下对Tl(III)的提取效果较好而对Tl(I)较差, 将Tl(I)氧化则有助于提高萃取效率。 Yang等
[69 ]
开发了以2乙基己基磷酸-2乙基己基酯(P507)为载体的乳化液膜体系, 用于去除黑色金属冶炼烟气脱硫废水中的铊, 在15 min内萃取效率达到99.76%, 出水的铊含量可低于5 μg·L-1 。
萃取法具有高效、 选择性好的优点, 一般用于从高浓度含铊溶液中回收铊
[14 ]
。 另外, 萃取剂一般由有机物组成, 用于污水治理时, 在出水中不可避免地会有所夹带, 增加了二次污染的风险。
2.5 其他技术
利用硼掺杂金刚石(BDD)阳极在电化学氧化体系中, 在初始Tl(I)浓度为10 mg·L-1 , pH为2.0, 电流密度为5 mA·cm-2 的初始条件下, 15 min内99.2%的Tl(I)即被氧化成TI(III), 经絮凝沉淀后出水铊含量可达到2 μg·L-1
[70 ]
。 Tian等
[71 ]
利用单室微生物燃料电池的充气电化学反应器作为可再生能源能源用于去除地下水中的Tl(I), 在Tl(I)初始浓度为5 mg·L-1 , pH=2, 外加电压为600 mV的条件下, 4 h内可将80.5%的Tl(I)氧化成TI(III)。 然后经混凝沉淀可实现铊的去除。 其氧化机制主要是由原位生成的H2 O2 间接电化学氧化所致。 Wang等
[72 ]
利用微生物燃料电池将Tl(I)氧化为Tl(Ⅲ)后通过自然沉淀可去除地下水中的铊。 Mueller等
[73 ]
利用硫酸还原菌处理废弃金矿的含铊地下水, 可在微生物的诱导作用下形成Tl2 S沉淀, 从而实现铊的去除。 孙嘉龙等
[74 ]
、 龙建友等
[75 ]
分别从铊矿区土壤和沉积物以及含铊冶炼废水中筛选出了高耐受性菌株, 经培养后用于Tl(I)废水处理, 可分别达到70%和89.5%的去除率。 铊可发生光化学反应
[76 ]
, UVB和LED的照射可促进Tl(I)向Tl(Ⅲ) 的氧化, 进而通过控制pH值实现铊的去除。 以上相关研究为含铊废水的治理提供了不同的思路, 但进行规模化应用尚需进一步工作。
3 含铊废水处理技术进展
尽管工业废水中铊的浓度较低, 但由于铊及其化合物高毒性的特点, 当前我国对工业含铊废水排放限定为2~5 μg·L-1 有其现实意义。 根据Xu等
[14 ]
的统计, 目前单一技术仅有少数研究能达到这个排放标准。 因此, 利用复合处理技术提高铊去除效果以满足严格排放监管要求是一项可行的思路。
对较低浓度的含铊废水(微克级), 采用金属氧化物基吸附材料进行吸附是一项可行的解决方案。 其中铁基和铁锰基复合氢氧化物吸附剂是当前的研究热点, 这种吸附剂与铊的亲和力强, 去除效果好, 是一种有潜力的深度除铊吸附剂。 另外, 电化学技术在工业废水治理中已有广泛应用
[77 ,78 ,79 ]
。 其中电絮凝技术通过牺牲可溶性阳极, 可原位产生高活性的金属氢氧化物及其聚合物, 进而通过吸附、 混凝、 沉淀实现废水中污染因子的去除
[80 ]
。 电絮凝工艺可用于饮用水净化
[81 ]
, 表明该技术具有深度净化的能力, 有望成为在工业含铊废水深度净化上的潜在应用技术之一。
对含铊在毫克级的工业废水, 首先利用氧化-沉淀进行预处理, 然后与吸附、 离子交换或者电絮凝技术进行耦合的组合工艺路线具有较大的应用潜力。 通过氧化-沉淀将高可溶性的Tl(I)氧化为Tl(Ⅲ), 然后控制溶液pH首先去除废水中大部分铊, 再耦合具有深度处理能力的方法进一步深度处理可满足当前监管要求。
4 结 语
与其他常见重金属污染物如As, Cr, Cd, Pb等相比, 铊在污染物中的含量较低。 虽然对环境与生态的毒副作用很强, 但一方面受限于对铊及其化合物毒性的认知, 另一方面也受限于检测仪器的检测精度, 导致对含铊废水的治理长期没有得到足够的重视。 传统的重金属处理技术难以经济地达到我国现行铊排放标准的要求, 而且会产生大量毒性污泥, 造成二次污染。 因此, 开发具有深度净化能力且污泥产生量少的单个或组合工艺是含铊工业废水治理的重要发展方向。
参考文献
[1] Cheam V.Thallium contamination of water in canada [J].Water Quality Research Journal of Canada,2001,36(4):851.
[2] Rickwood C J,King M,Huntsman-Mapila P.Assessing the fate and toxicity of thallium I and thallium Ⅲ to three aquatic organisms [J].Ecotoxicology and Environment Safety,2015,115:300.
[3] Belzile N,Chen Y W.Thallium in the environment:A critical review focused on natural waters,soils,sediments and airborne particles [J].Applied Geochemistry,2017,84:218.
[4] United States Environmental Protection Agency(US EPA).Effluent guidelines-toxic and priority pollutants under the clean water act[EB/OL].Agency E.P.https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/priority-pollutant-list-epa.pdf.2014-12/2019-10-17.
[5] European Parliament and of the Council.Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy.Official Journal of the European Communities.https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2000/60/oj.2000-12-22/2019-10-17.
[6] Ministry of Ecology and Enivronment,PRC(MEE,PRC).The 12th five-year plan for comprehensive prevention and control of heavy metals pollution [EB/OL].General office of the MEE,PRC.Beijing.http://www.hnep.gov.cn/Portals/0/fujian5/重金属污染综合防治"十二五"规划.pdf.2011/2019-10-17.(中华人民共和国生态环境部,重金属污染综合防治"十二五"规划 [EB/OL].生态环境部办公厅.http://www.hnep.gov.cn/Portals/0/fujian5/重金属污染综合防治"十二五"规划.pdf.2011/2019-10-17.)
[7] Cleven R,Fokkert L.Potentiometric stripping analysis of thallium in natural waters [J].Analytica Chimica Acta,1994,289(2):215.
[8] Banks D,Reimann C,R?yset O,Skarphagen H,Saether O M.Natural concentrations of major and trace elements in some norwegian bedrock groundwaters [J].Applied Geochemistry,1995,10(1):1.
[9] Liu J,Wang J,Chen Y,Shen C C,Jiang X,Xie X,Chen D,Lippold H,Wang C.Thallium dispersal and contamination in surface sediments from south china and its source identification [J].Environmental Pollution,2016,213:878.
[10] Chen Y H,Zhang P,Wu Y J,Qi J Y,Liu J,Wang J,Deng H M,Zhang H L,Su L X.The reasons and the control technology for thallium pollution in Beijiang,Guangdong Province [J].Journal of Guangzhou University(Natural Science Edition),2013,12(4):26.(陈永亨,张平,吴颖娟,齐剑英,刘娟,王津,邓红梅,张海龙,苏龙晓.广东北江铊污染的产生原因与污染控制对策 [J].广州大学学报(自然科学版),2013,12(4):26.)
[11] Jiang X L,Zhou L S.Thallium concentration exceeds the standard by 2.14 times in Hejiang river pollution event in Guangxi [N/OL].www.Chinanews.com.http://www.chinanews.com/gn/2013/07-06/5011289.shtml.2013-07-06/2019-10-25.(蒋雪林,周利朔.广西贺江水污染事件铊超标2.14倍 [N/OL].中国新闻网.http://www.chinanews.com/gn/2013/07-06/5011289.shtml.2013-07-06/2019-10-25.)
[12] Geng Z C,Zhang X.Preliminary investigation of thallium pollution in Jialing River:4 people from related enterprises were detained[N/OL].www.peoples.com.cn.http://js.people.com.cn/n2/2017/0511/c359574-30164508.html.2017-05-11/2019-10-25.(耿志超,张鑫.嘉陵江铊污染涉案企业初步查实 4人被拘[N/OL].人民网.http://js.people.com.cn/n2/2017/0511/c359574-30164508.html.2017-05-11/2019-10-25.)
[13] Li X,Diao F C.Liling section of Lujiang River in Hunan Province was polluted by thallium,two enterprises in Pingxiang,Jiangxi Province were shut down and renovated [N/OL].www.thepaper.cn.https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_2338432.2018-08-11/2019-10-25.(李珣,刁凡超.渌江湖南醴陵段遭跨省铊污染,上游江西萍乡两企业被停产整治[N/OL].澎湃新闻.https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_2338432.2018-08-11/2019-10-25.)
[14] Xu H,Luo Y,Wang P,Zhu J,Yang Z,Liu Z.Removal of thallium in water/wastewater:a review [J].Water Research,2019,165:114981.
[15] Kazantzis G.Thallium in the environment and health effects [J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2000,22(4):275.
[16] Vink B.The behaviour of thallium in the (sub) surface environment in terms of Eh and pH [J].Chemical Geology,1993,109(1-4):119.
[17] Xiong Y.The aqueous geochemistry of thallium:Speciation and solubility of thallium in low temperature systems [J].Environmental Chemistry,2009,6(5):441.
[18] Ospina-Alvarez N,Burakiewicz P,Sadowska M,Krasnodebska-Ostrega B.Tl I and Tl Ⅲ presence in suspended particulate matter:speciation analysis of thallium in wastewater [J].Environmental Chemistry,2015,12(3):374.
[19] Kaplan D I,Mattigod S V.Aqueous geochemistry of thallium [J].Advances in Environmental Science and Technology,1998,29:15.
[20] Lin T S,Nriagu J.Revised hydrolysis constants for thallium(I) and thallium(Ⅲ) and the environmental implications [J].Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association,1998,48(2):151.
[21] Jia Y L,Xiao T F,Zhou G Z,Ning Z P.Advance on the chemical speciation of thallium in water,soil and sediment [J].Environmental Chemistry,2013,32(6):917.(贾彦龙,肖唐付,周广柱,宁增平.水体,土壤和沉积物中铊的化学形态研究进展 [J].环境化学,2013,32(6):917.)
[22] Delvalls T,Saenz V,Arias A M,Blasco J.Thallium in the marine environment:first ecotoxicological assessments in the guadalquivir estuary and its potential adverse effect on the doňana european natural reserve after the aznalcóllar mining spill (sw spain) [J].Ciencias Marinas,1999,25(2):161.
[23] Matthews A D,Riley J P.The occurrence of thallium in sea water and marine sediments [J].Chemical Geology,1970,6:149.
[24] Williams-Beam C,Twidwell L G.Removal of thallium from wastewater [J].Electrometallurgy and Environmental Hydrometallurgy,2003,2:1717.
[25] Khoo K H,Fernando K.Solubility and activity coefficient of thallium (I) chloride in the system TlCl+HCl+NaCl+H2 O at 25 ℃ [J].Journal of Solution Chemistry,1991,20(12):1199.
[26] Sangvanich T,Sukwarotwat V,Wiacek R J,Grudzien R M,Fryxell G E,Addleman R S,Timchalk C,Yantasee W.Selective capture of cesium and thallium from natural waters and simulated wastes with copper ferrocyanide functionalized mesoporous silica [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,182(1-3):225.
[27] Martell A E,Smith R M,Motekaitis R J.NIST Critically selected stability constants of metal complexes database,Version 8.0 [DB].Ghaitersburg,MD,USA:NIST,2004.
[28] Downs A J.Chemistry of Aluminium,Gallium,Indium and Thallium [M].Springer Science & Business Media,1993.216.
[29] Huangfu X,Jiang J,Lu X,Wang Y,Liu Y,Pang S Y,Cheng H,Zhang X,Ma J.Adsorption and oxidation of thallium(I) by a nanosized manganese dioxide [J].Water,Air,& Soil Pollution,2015,226(1):2272.
[30] Li H,Li X,Long J,Li K,Chen Y,Jiang J,Chen X,Zhang P.Oxidation and removal of thallium and organics from wastewater using a zero-valent-iron-based fenton-like technique [J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,221:89.
[31] Davies M,Figueroa L,Wildeman T,Bucknam C.The oxidative precipitation of thallium at alkaline pH for treatment of mining influenced water [J].Mine Water and the Environment,2016,35(1):77.
[32] Liu Y,Wang L,Wang X,Huang Z,Xu C,Yang T,Zhao X,Qi J,Ma J.Highly efficient removal of trace thallium from contaminated source waters with ferrate:role of in situ formed ferric nanoparticle [J].Water Research,2017,124:149.
[33] Li K,Li H,Xiao T,Zhang G,Long J,Luo D,Zhang H,Xiong J,Wang Q.Removal of thallium from wastewater by a combination of persulfate oxidation and iron coagulation [J].Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2018,119:340.
[34] Liu J,Luo X,Sun Y,Tsang D C W,Qi J,Zhang W,Li N,Yin M,Wang J,Lippold H,Chen Y,Sheng G.Thallium pollution in China and removal technologies for waters:a review [J].Environment International,2019,126:771.
[35] Crini G,Lichtfouse E,Wilson L D,Morin-Crini N.Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment [J].Environmental Chemistry Letters,2018,17(1):195.
[36] Li H,Chen Y,Long J,Li X,Jiang D,Zhang P,Qi J,Huang X,Liu J,Xu R,Gong J.Removal of thallium from aqueous solutions using Fe-Mn binary oxides [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2017,338:296.
[37] Chen M,Wu P,Yu L,Liu S,Ruan B,Hu H,Zhu N,Lin Z.FeOOH-loaded MnO2 nano-composite:an efficient emergency material for thallium pollution incident [J].Journal of Environmental Management,2017,192:31.
[38] Gadde R R,Laitinen H A.Heavy metal adsorption by hydrous iron and manganese oxides [J].Analytical Chemistry,1974,46(13):2022.
[39] Zhang L,Huang T,Zhang M,Guo X,Yuan Z.Studies on the capability and behavior of adsorption of thallium on nano-Al2 O3 [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2008,157(2-3):352.
[40] Zhang G,Fan F,Li X,Qi J,Chen Y.Superior adsorption of thallium(I) on titanium peroxide:performance and mechanism [J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,331:471.
[41] Hanafi H A.Adsorption of cesium,thallium,strontium and cobalt radionuclides using activated carbon [J].Journal of Atomic and Molecular Sciences,2010,1(4):292.
[42] Hoffman R S,Hoffman R,Stringer J A,Feinberg R S,Goldfrank L R.Comparative efficacy of thallium adsorption by activated charcoal,prussian blue,and sodium polystyrene sulfonate [J].Journal of Toxicology:Clinical Toxicology,1999,37(7):833.
[43] ur Rehman S,Ullah N,Kamali A R,Ali K,Yerlikaya C,ur Rehman H.Study of thallium(Ⅲ) adsorption onto multiwall carbon nanotubes [J].New Carbon Materials,2012,27(6):409.
[44] Pu Y,Yang X,Zheng H,Wang D,Su Y,He J.Adsorption and desorption of thallium(I) on multiwalled carbon nanotubes [J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,219:403.
[45] Ahluwalia S S,Goyal D.Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater [J].Bioresource Technology,2007,98(12):2243.
[46] Alalwan H A,Abbas M N,Abudi Z N,Alminshid A H.Adsorption of thallium ion (Tl+3 ) from aqueous solutions by rice husk in a fixed-bed column:Experiment and prediction of breakthrough curves [J].Environmental Technology & Innovation,2018,12:1.
[47] Memon S Q,Memon N,Solangi A R.Sawdust:a green and economical sorbent for thallium removal [J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2008,140(1-3):235.
[48] Zolgharnein J,Asanjarani N,Shariatmanesh T.Removal of thallium(I) from aqueous solution using modified sugar beet pulp [J].Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry,2011,93(2):207.
[49] Quintas P Y,Dotto G L,Da Silva S M,Escudero L B.Removal of thallium from environmental samples using a raw and chemically modified biosorbent derived from domestic wastes [J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2019,26:32285.
[50] Birungi Z S,Chirwa E M.The adsorption potential and recovery of thallium using green micro-algae from eutrophic water sources [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,299:67.
[51] Yin Z,Zhang D,Pan X.Biosorption of thallium by dry biofilm biomass collected from a eutrophic lake [J].International Journal of Environment and Pollution,2009,37(2-3):349.
[52] Carolin C F,Kumar P S,Saravanan A,Joshiba G J,Naushad M.Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment:a review [J].Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2017,5(3):2782.
[53] Wan Ngah W S,Hanafiah M A.Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents:a review [J].Bioresource Technology,2008,99(10):3935.
[54] Wick S,Baeyens B,Marques Fernandes M,Voegelin A.Thallium adsorption onto illite [J].Environmental Science and Technology,2018,52(2):571.
[55] MEE,PRC.Explanation on compilation of amendment list of “Emission standare of pollutantss for lead and zinc industry” (GB 25466-2010) (Draft for comment) [EB/OL].General office of MEE.http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/stbgth/201809/W020180926341528139268.pdf.2018-09-20/2019-10-11.(中华人民共和国生态环境部.关于编制《铅锌工业污染物排放标准修订清单》(GB 25466-2010)(征求意见稿)的说明 [EB/OL].生态环境部办公厅,http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/stbgth/201809/W020180926341528139268.pdf.2018-09-20/2019-10-11.
[56] Lee C G,Alvarez P J J,Nam A,Park S J,Do T,Choi U S,Lee S H.Arsenic(Ⅴ) removal using an amine-doped acrylic ion exchange fiber:Kinetic,equilibrium,and regeneration studies [J].Journal of Hazardous Mterials,2017,325:223.
[57] Ma A,Abushaikha A,Allen S J,McKay G.Ion exchange homogeneous surface diffusion modelling by binary site resin for the removal of nickel ions from wastewater in fixed beds [J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,358:1.
[58] Zhao W,Zhou M,Yan B,Sun X,Liu Y,Wang Y,Xu T,Zhang Y.Waste conversion and resource recovery from wastewater by ion exchange membranes:state-of-the-art and perspective [J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(18):6025.
[59] Pontius F W.Update on USEPA's drinking water regulations [J].Journal-American Water Works Association,2003,95(3):57.
[60] Li H,Chen Y,Long J,Jiang D,Liu J,Li S,Qi J,Zhang P,Wang J,Gong J,Wu Q,Chen D.Simultaneous removal of thallium and chloride from a highly saline industrial wastewater using modified anion exchange resins [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2017,333:179.
[61] Albert L,Elancourt,Masson H,Marly M.Thallium extraction process [P].USA,US 5296204A,1994.
[62] Lin T S,Nriagu J.Thallium speciation in the great lakes [J].Environmental science & technology,1999,33(19):3394.
[63] Xie X Y,Wu W Q,Li F,Liao H M,Liu Y Y.Determination of thallium in manganese ore by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry after ion exchange separation [J].Metallurgical Analysis,2015,35(8):61.(谢晓雁,吴文启,李奋,廖红梅,刘媛媛.离子交换分离_电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定锰矿中铊 [J].冶金分析,2015,35(8):61.)
[64] Karatepe A,Soylak M,El?i L.Selective preconcentration of thallium species as chloro and iodo complexes on chromosorb 105 resin prior to electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry [J].Talanta,2011,85(4):1974.
[65] Hasegawa Y,Shimada T,Niitsu M.Solvent extraction of 3b group metal ions from hydrochloric acid with trioctylphosphine oxide [J].Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry,1980,42(10):1487.
[66] Zhang X,Yin G,Hu Z.Extraction and separation of gallium,indium and thallium with several carboxylic acids from chloride media [J].Talanta,2003,59(5):905.
[67] Vartak S V,Shinde V M.An extraction study of gallium,indium and thallium using tpaso as an extractant [J].Talanta,1998,45(5):925.
[68] Li H,Long J,Li X,Li K,Xu L,Lai J,Chen Y,Zhang P.Aqueous biphasic separation of thallium from aqueous solution using alcohols and salts [J].Desalination and Water Treatment,2018,123:330.
[69] Yang L,Xiao J,Shen Y,Liu X,Li W,Wang W,Yang Y.The efficient removal of thallium from sintering flue gas desulfurization wastewater in ferrous metallurgy using emulsion liquid membrane [J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2017,24(31):24214.
[70] Li Y,Zhang B,Borthwick A G L,Long Y.Efficient electrochemical oxidation of thallium(I) in groundwater using boron-doped diamond anode [J].Electrochimica Acta,2016,222:1137.
[71] Tian C,Zhang B,Borthwick A G,Li Y,Liu W.Electrochemical oxidation of thallium(I) in groundwater by employing single-chamber microbial fuel cells as renewable power sources [J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2017,42(49):29454.
[72] Wang Z,Zhang B,Jiang Y,Li Y,He C.Spontaneous thallium(I) oxidation with electricity generation in single-chamber microbial fuel cells [J].Applied Energy,2018,209:33.
[73] Mueller R F.Microbially mediated thallium immobilization in bench scale systems [J].Mine Water and the Environment,2001,20(1):17.
[74] Sun J L,Xiao T F,Ning Z P,Jia Y L,Yang F,Peng J Q.Adsorption of thallium by microbes:a case study of fungus [J].Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemisry,2011,30(3):341.(孙嘉龙,肖唐付,宁增平,贾彦龙,杨菲,彭景权.几株真菌对铊吸附作用的初步研究 [J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2011,30(3):341.)
[75] Long J Y,Luo D G,Chen Y H.Identification and biosorption characterization of a thallium-resistant strain [J].Chinese Journal of Appled and Environmental Biology,2014,20(3):426.(龙建友,罗定贵,陈永亨.一株Tl抗性菌株的鉴定及吸附特性 [J].应用与环境生物学报,2014,20(3):426.)
[76] Li D,Gao Z,Zhu Y,Yu Y,Wang H.Photochemical reaction of Tl in aqueous solution and its environmental significance [J].Geochemical Journal,2005,39(2):113.
[77] Dura A,Breslin C B.Electrocoagulation using stainless steel anodes:simultaneous removal of phosphates,orange II and zinc ions [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,374:152.
[78] Ilhan F,Ulucan-Altuntas K,Avsar Y,Kurt U,Saral A.Electrocoagulation process for the treatment of metal-plating wastewater:kinetic modeling and energy consumption [J].Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering,2019,13(5):73.
[79] Wang D J,Yi H H,Tang X L,Zhou K H,Li J T,Chang C.Experimental study on treating the simulated ammonium chloride wastewater with electrolysis [J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2018,42(4):415.(王东杰,易红宏,唐晓龙,周凯红,李建亭,常诚.电解法处理模拟氯化铵废水的试验研究 [J].稀有金属,2018,42(4):415.)
[80] Mollah M Y A,Schennach R,Parga J R,Cocke D L.Electrocoagulation (EC)-science and applications [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2001,84(1):29.
[81] Das D,Nandi B K.Defluoridization of drinking water by electrocoagulation (EC):process optimization and kinetic study [J].Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology,2019,40(8):1136.