文章编号:1004-0609(2014)03-0808-06
高铁铝土矿与硫酸氢铵混合焙烧工艺
辛海霞,吴 艳,刘少名,翟玉春
(东北大学 材料与冶金学院,沈阳 110004)
摘 要:
摘 要:针对传统处理高铁铝土矿能耗高、金属提取率低等缺点,提出硫酸氢铵焙烧工艺。在分析广西高铁铝土矿热分解过程的基础上,研究硫酸氢铵加入量、焙烧温度和焙烧时间等工艺参数,采用XRD对反应产物物相进行表征。结果表明:在硫酸氢铵与铝土矿质量比为3.5:1、焙烧温度为450 ℃、焙烧时间60 min 的条件下,铝和铁的提取率分别为93%和95%以上;铝反应的产物为NH4Al(SO4)2,铁反应的中间产物为(NH4)3Fe(SO4)3,最终产物为NH4Fe(SO4)2。该工艺具有焙烧温度低、金属提取率高等特点,对广西高铁铝土矿的开发利用具有重要意义。
关键词:
中图分类号:TF821 文献标志码:A
Roasting process of mixture of high ferric bauxite and ammonium bisulfate
XIN Hai-xia, WU Yan, LIU Shao-ming, ZHAI Yu-chun
(School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China)
Abstract: A novel process of roasting high-iron bauxite using ammonium bisulfate was proposed to overcome the defects of traditional process, such as high power consumption and low extraction rates. First, the thermodynamics in decomposition process of high-iron gibbsitic bauxite resource in Guangxi was analyzed. Then, various parameters including ammonium bisulfate addition, roasting temperature and roasting time were investigated. The product was also characterized by XRD. The results show that extraction rates of over 93% and 95% respectively for aluminum and iron are obtained after roasting at 450 ℃ for 60 min and mass ratio of ammonium bisulfate to bauxite being 3.5:1. The phase of alumina-containing compounds is always NH4Al(SO4)2 in product. (NH4)3Fe(SO4)3 is produced as intermediate products, and it is replaced by NH4Fe(SO4)2 finally. The process is proved to be significant with the advantages of high extracting rates and low temperature.
Key words: high-iron bauxite; ammonium bisulfate; roasting technology
20世纪80年代,在我国广西中部地区发现了大规模的高铁三水铝石型铝土矿矿床[1],此类矿床规模和储量都很大,是我国铝、铁冶炼的重要潜在资源之一[2]。该类矿物具有高铁、高硅、低铝和低铝硅比的特点,成分和结构复杂,且矿物嵌布粒度细微,呈凝胶状态[3],是我国难处理复合矿石资源之一。
为了合理开发利用此类铝土矿,科研工作者进行了大量研究工作[4-6],先后提出了3种综合利用方案:“先选后冶”工艺、“先铝后铁”工艺和“先铁后铝”工艺[7]。“先选后冶”工艺是通过选矿的方法使含铝矿物与含铁矿物分离富集得到铝精矿与铁精矿,然后分别冶炼铝精矿和铁精矿。但此类铝土矿中铁、铝互相嵌布,密切共生,为选矿带来了极大的难度。“先铝后铁”工艺是利用三水铝石易于浸出的特点,先采用拜耳法将大部分铝溶出,再从溶出赤泥中回收铁。但由于铝土矿中存在的大量铝针铁矿和铝赤铁矿,因此氧化铝浸出率低,且赤泥附碱给进一步炼铁带来困难。“先铁后铝”工艺是先将铝土矿在高炉或电炉内冶炼提铁,再从炼铁炉渣中提取氧化铝。此种方法存在的最大问题是高炉炉料烧结过程能耗高。因此,探索合理利用此类铝土矿的新工艺具有实际意义。在酸法处理铝矿物工艺研究基础上[8-11],本文作者采用硫酸氢铵焙烧法提取铝土矿中的有价组元,研究整个焙烧反应过程及铝、铁反应提取率,以期为高铁铝土矿的合理利用提供参考。1 实验
1.1 实验原料
实验原料为广西某地铝土矿,将铝土矿磨细至粒度小于74 μm用于实验,其化学成分见表1。由表1可见,该矿属高铁、低铝硅比铝土矿。
表1 铝土矿的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of bauxite (mass fraction, %)

图1所示为铝土矿的XRD谱。图1表明:铝土矿结晶不完全,铝土矿中的铝主要以三水铝石形式存在,铁主要以赤铁矿和针铁矿形式存在,矿中含有石英和锐钛矿。
采用场发射扫描电镜对铝土矿形貌及组元分布进行分析,结果分别如图2和3所示。由图2可知,铝土矿呈豆状、鲕状和胶质形式存在,对图2(b)和(c)中鲕状和豆状颗粒进行铝、铁元素面扫描,结果如图3所示。由图3可以看出,铝、铁互相嵌布共生。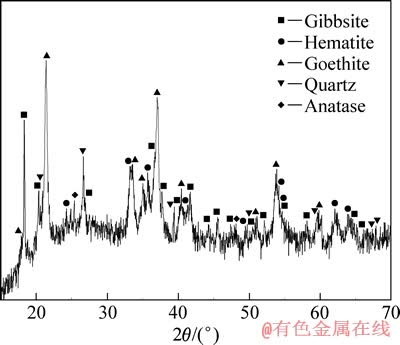
图1 铝土矿的XRD 谱
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of bauxite
实验所用硫酸氢铵为分析纯试剂,水为去离子水,分析检测用试剂均为天津科密欧公司生产,X射线衍射仪为Rigaku Ultima IV,扫描电镜为Ultra Plus场发射扫描电镜,热分析仪为SDT 2960(美国TA公司生产)型。1.2 实验方法

图2 铝土矿的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of bauxite

图3 铝土矿的元素面扫描谱
Fig. 3 Elemental mapping spectra of bauxite
将固体硫酸氢铵与铝土矿按一定比例混合均匀后,放入氧化铝坩埚中,置于电阻丝炉中焙烧,电阻丝炉以5 ℃/min的升温速率升至某一温度,保温一定时间后取出,冷却,加水搅拌溶出,溶出水量为熟料质量的3倍,溶出温度为60 ℃,溶出时间为30 min,溶出完毕后抽滤,滤渣洗涤两次,测定滤液中铝、铁的含量,计算铝、铁提取率。2 结果与讨论
2.1 铝土矿和硫酸氢铵热分解过程
硫酸氢铵是一种酸化剂,其熔点为146.9 ℃[12],在300 ℃左右开始分解,分解主要包括以下两个步骤[13]:

KIYOURA等[14]认为分解过程中产生中间产物(NH4)3H(SO4)2、NH2SO3H和(NH4)2S2O7 等,这些中间产物均为酸化剂。对本实验所用的硫酸氢铵进行热分析,所得的TG-DTA曲线如图4(a)所示。由图4(a) 可知硫酸氢铵在145 ℃左右开始熔化,在250~300 ℃开始分解,300~400 ℃为主要分解阶段,450 ℃时几乎分解完全。
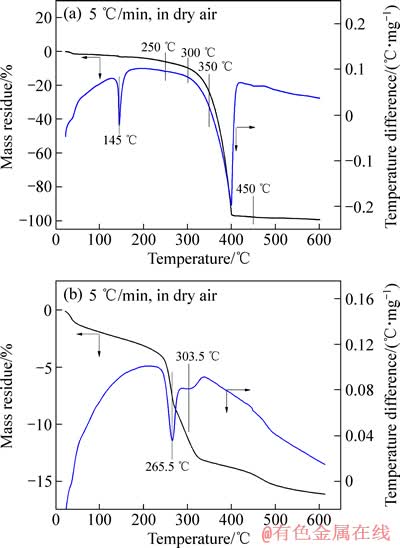
图4 硫酸氢铵和铝土矿的TG-DTA曲线
Fig. 4 TG-DTA curves of ammonium bisulfate (a) and bauxite (b)
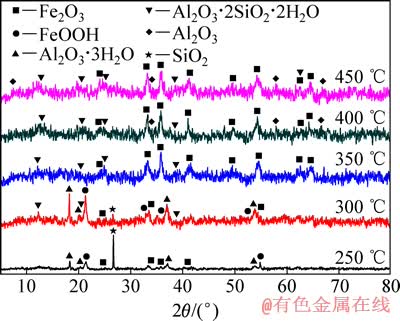
图5 铝土矿在不同温度下焙烧后的XRD谱
Fig. 5 XRD patterns of bauxite roasted at different temperatures
三水铝石在150~300 ℃下会逐渐脱水[15],针铁矿在200~350 ℃吸热脱水生成赤铁矿[16-17]。因此,对铝土矿进行差热分析,结果如图4(b)所示。同时将铝土矿在不同温度下进行烧结,对烧结后的铝土矿进行X射线衍射分析,结果如图5所示。由图5可以看出:在300 ℃时出现新物相Al2O3·2SiO2·2H2O,主要以埃洛石、高岭石和迪开石形式存在,说明温度低于300 ℃时无定形二氧化硅已与Al2O3·xH2O发生反应;在350 ℃时针铁矿消失,说明在300~350 ℃之间,针铁矿脱水形成赤铁矿。由图4(b)铝土矿热分析TG-DTA曲线可知:随着温度的升高,铝土矿质量不断减少,主要原因为:三水铝石与针铁矿不断脱水,且温度升高,埃洛石、高岭石和迪开石会吸热逐渐脱出结构水,形成莫来石和方石英。
2.2 铝土矿与硫酸氢铵混合焙烧提取铝和铁
2.2.1 焙烧温度对铝、铁提取率的影响
当硫酸氢铵与铝土矿的质量比为3.5:1、恒温时间为60 min时,考察焙烧温度对铝、铁提取率的影响。实验结果如图6所示。由图6可知:焙烧温度对铝、铁提取率影响大,在450 ℃时铝、铁提取率达到最大值。温度高于450 ℃时,硫酸氢铵分解速度过快,导致还未与铝土矿发生反应便已分解完全,使得铝、铁提取率均明显下降。
对不同温度下所得熟料进行X射线衍射分析,结果如图7所示。 由图7可知:在150~250 ℃时三水铝石与硫酸氢铵反应产物为NH4Al(SO4)2,铁矿物与硫酸氢铵反应产物为(NH4)3Fe(SO4)3。300 ℃时(NH4)3Fe(SO4)3消失,出现新物相NH4Fe(SO4)2,证明(NH4)3Fe(SO4)3已经分解为NH4Fe(SO4)2。整个反应的最终产物为NH4Al(SO4)2和NH4Fe(SO4)2。
图6 焙烧温度对铝、铁提取率的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of roasting temperature on extracting rates of aluminum and iron

图7 不同温度下焙烧硫酸氢铵与铝土矿混合物所得熟料的XRD谱
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of mixture of bauxite and ammonium bisulfate roasted at different temperatures
2.2.2 恒温时间对铝、铁提取率的影响
当硫酸氢铵与铝土矿质量比为3.5:1,焙烧温度为450 ℃时,考察恒温时间对铝、铁提取率的影响,实验结果如图8所示。由图8可知,随着反应时间的延长,铝、铁反应率均增大,当反应时间多于45 min后,铝、铁提取率变化不大,说明在450 ℃下,90%以上的铝、铁反应在45 min内便已完成。
2.2.3 硫酸氢铵加入量对铝、铁提取率的影响
当焙烧温度为450 ℃和恒温时间为60 min时,考察硫酸氢铵加入量对铝、铁提取率的影响,实验结果如图9所示。由图9可以看出,随着硫酸氢铵量的增加,铝、铁提取率均有所增加。当硫酸氢铵与铝土矿的质量比大于3.5:1时,铝、铁提取率变化均不明显,说明此时硫酸氢铵量已足够。
对焙烧所得熟料溶出渣进行X射线衍射分析,结果如图10所示。由图10可知,渣中铝、铁晶相已消失,硅主要以石英和无定形二氧化硅形式存在,钛主要以锐钛矿和金红石形式存在。
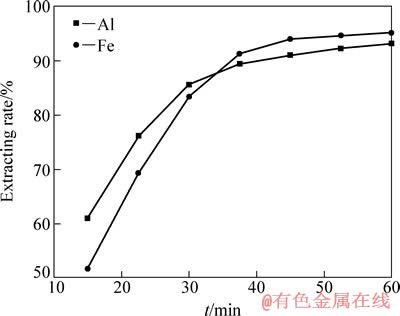
图8 恒温时间对铝、铁提取率的影响
Fig. 8 Effects of time on extracting rates of aluminum and iron

图9 硫酸氢铵加入量对铝、铁提取率的影响
Fig. 9 Effects of ammonium bisulfate addition on extracting rates of aluminum and iron

图10 溶出渣的XRD谱
Fig. 10 XRD pattern of leaching slag
3 结论
1) 铝土矿在煅烧过程中物相发生转变:三水铝石发生分解,同时出现新物相Al2O3·2SiO2·2H2O,针铁矿转变为赤铁矿。
2) 在铝土矿与硫酸氢铵混合焙烧过程中,铝矿物与硫酸氢铵反应生成 NH4Al(SO4)2,铁矿物与硫酸氢铵体系反应的中间产物为(NH4)3Fe(SO4)3,最终产物为NH4Fe(SO4)2。
3) 将铝土矿与硫酸氢铵进行混合焙烧,可达到将铝、铁提取的目的,当硫酸氢铵与铝土矿的质量比为3.5:1、450 ℃恒温焙烧60 min时,铝和铁的提取率分别可达到93%和95%以上。
REFERENCES
[1] 李殷泰, 毕诗文, 段振瀛, 杨毅宏, 张敬东. 关于广西贵港三水铝石型铝土矿综合利用工艺方案的探讨[J]. 轻金属, 1992(9): 6-14.
LI Yin-tai, BI Shi-wen, DUAN Zhen-ying, YANG Yi-hong, ZHANG Jing-dong. Reviews on the comprehensive utilization technology of bauxite in Guigang, Guangxi, China[J]. Light Metals, 1992(9): 6-14.
[2] 李小斌, 孔莲莲, 齐天贵, 周秋生, 彭志宏, 刘桂华. 高铁三水铝石矿拜耳法溶出过程中铝针铁矿的行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(2): 543-548.
LI Xiao-bin, KONG Lian-lian, QI Tian-gui, ZHOU Qiu-sheng, PENG Zhi-hong, LIU Gui-hua. Effect of alumogoethite in Bayer digestion process of high-iron gibbsitic bauxite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(2): 543-548.
[3] 赵恒勤, 赵新奋, 胡四春, 马化龙. 我国三水铝石铝土矿的矿物学特征研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2008(6): 40-44.
ZHAO Heng-qin, ZHAO Xin-fen, HU Si-chun, MA Hua-long. Study on the mineralogical characteristics of gibbsite bauxite in China[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2008(6): 40-44.
[4] 李光辉, 刘牡丹, 姜 涛, 周太华, 范晓慧. 高铝铁矿石工艺矿物学特征及铝铁分离技术[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 40(5): 1165-1171.
LI Guang-hui, LIU Mu-dan, JIANG Tao, ZHOU Tai-hua, FAN Xiao-hui. Mineralogy characteristics and separation of aluminum and iron of high-aluminum iron ores[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2009, 40(5): 1165-1171.
[5] 陈怀杰, 刘志强, 朱 薇, 郭秋松. 贵港式铝土矿综合利用工艺研究[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2012, 6(1): 65-68.
CHEN Huai-jie, LIU Zhi-qiang, ZHU Wei, GUO Qiu-song. Study on the comprehensive utilization technology of bauxite of Guigang[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2012, 6(1): 65-68.
[6] 李光辉, 董海刚, 肖春梅, 范晓慧, 郭宇峰, 姜 涛. 高铁铝土矿的工艺矿物学及铝铁分离技术[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 37(2): 235-240.
LI Guang-hui, DONG Hai-gang, XIAO Chun-mei, FAN Xiao-hui, GUO Yu-feng, JIANG Tao. Mineralogy and separation of aluminum and iron from high ferrous bauxite[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(2): 235-240.
[7] 唐向琪, 陈谦德. 贵港式三水铝石矿综合利用方案比较[J]. 轻金属, 1995(2): 1-6.
TANG Xiang-qi, CHEN Qian-de. Comparisons on the comprehensive utilization technology of bauxite in Guigang[J]. Light Metals, 1995(2): 1-6.
[8] OZDEMIR M, CETISLI H. Extraction kinetics of alunite in sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2005, 76: 217-224.
[9] BAZIN C, EL-OUASSITI K, OUELLET V. Sequential leaching for the recovery of alumina from a Canadian clay[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 88: 196-201.
[10] REDDY B R, MISHRA S K, BANERJEE G N. Kinetics of leaching of a gibbsitic bauxite with hydrochloric acid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1999, 51: 131-138.
[11] ZHAO Ai-chun, LIU Yan, ZHANG Ting-an,  Guo-zhi, DOU Zhi-he. Thermodynamics study on leaching process of gibbsitic bauxite by hydrochloric acid[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 266-270.
Guo-zhi, DOU Zhi-he. Thermodynamics study on leaching process of gibbsitic bauxite by hydrochloric acid[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 266-270.
[12] 刘科伟, 陈天朗. 硫酸铵的热分解[J]. 化学应用与研究, 2002, 14(6): 737-738.
LIU Ke-wei, CHEN Tian-lang. Studies on the thermal decomposition of ammonium sulfate[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2002, 14(6): 737-738.
[13] 范芸珠, 曹发海. 硫酸铵热分解反应动力学研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2011, 25(2): 341-346.
FAN Yun-zhu, CAO Fa-hai. Thermal decomposition kinetics of ammonium sulfate[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2011, 25(2): 341-346.
[14] KIYOURA R, URANO K. Mechanism, kinetics, and equilibrium of thermal decomposition of ammonium sulfate[J]. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Develop, 1970, 9(4): 489-494.
[15] 杨重愚. 氧化铝生产工艺学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1993: 141.
YANG Zhong-yu. Process technology of alumina[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1993: 141.
[16] 邹雪华, 陈天虎, 刘海波, 陈 冬, 张 萍, 谢巧勤. 热处理针铁矿的结构与色度演化[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2013, 41: 669-673.
ZOU Xue-hua, CHEN Tian-hu, LIU Hai-bo, CHEN Dong, ZHANG Ping, XIE Qiao-qin. Structural and chromatic evolution of goethite by thermal treatment[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 41(5): 669-673.
[17] 阮华达, 吉波博, 贺纪正. 铝代换针铁矿及其加热形成的赤铁矿的矿物学特性[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 1997, 16(6): 562-570.
RUAN Hua-da, JI Bo-bo, HE Ji-zheng. The mineralogical properties of Al-substituted goethite and its resultant hematite formed from thermal dehydroxylation[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 1997, 16(6): 562-570.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51204034)
收稿日期:2013-06-27;修订日期:2013-09-21
通信作者:翟玉春,教授,博士;电话:13304048096;E-mail:zhaiyc@smm.neu.edu.cn[1] 李殷泰, 毕诗文, 段振瀛, 杨毅宏, 张敬东. 关于广西贵港三水铝石型铝土矿综合利用工艺方案的探讨[J]. 轻金属, 1992(9): 6-14.
[2] 李小斌, 孔莲莲, 齐天贵, 周秋生, 彭志宏, 刘桂华. 高铁三水铝石矿拜耳法溶出过程中铝针铁矿的行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(2): 543-548.
[3] 赵恒勤, 赵新奋, 胡四春, 马化龙. 我国三水铝石铝土矿的矿物学特征研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2008(6): 40-44.
[4] 李光辉, 刘牡丹, 姜 涛, 周太华, 范晓慧. 高铝铁矿石工艺矿物学特征及铝铁分离技术[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 40(5): 1165-1171.
[5] 陈怀杰, 刘志强, 朱 薇, 郭秋松. 贵港式铝土矿综合利用工艺研究[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2012, 6(1): 65-68.
[6] 李光辉, 董海刚, 肖春梅, 范晓慧, 郭宇峰, 姜 涛. 高铁铝土矿的工艺矿物学及铝铁分离技术[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 37(2): 235-240.
[7] 唐向琪, 陈谦德. 贵港式三水铝石矿综合利用方案比较[J]. 轻金属, 1995(2): 1-6.
[12] 刘科伟, 陈天朗. 硫酸铵的热分解[J]. 化学应用与研究, 2002, 14(6): 737-738.
[13] 范芸珠, 曹发海. 硫酸铵热分解反应动力学研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2011, 25(2): 341-346.
[15] 杨重愚. 氧化铝生产工艺学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1993: 141.
YANG Zhong-yu. Process technology of alumina[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1993: 141.
[16] 邹雪华, 陈天虎, 刘海波, 陈 冬, 张 萍, 谢巧勤. 热处理针铁矿的结构与色度演化[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2013, 41: 669-673.
[17] 阮华达, 吉波博, 贺纪正. 铝代换针铁矿及其加热形成的赤铁矿的矿物学特性[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 1997, 16(6): 562-570.


