基于感应电机磁链观测器的速度辨识
曾谊晖1, 2,朱 浩2,朱有为3
(1.湖南大学 机械与运载工程学院,湖南 长沙,410082;
2. 湖南涉外经济学院 数控中心,湖南 长沙,410205;
3. 长沙大学 先进制造技术中心,湖南 长沙,410003)
摘 要:
摘 要:针对模型参考自适应速度辨识方法虽然其辨识精度高,但其数学模型复杂,而且在实时控制中需要高速控制器与之匹配等不足,提出一种结构简单且易于实现的感应电机直接转矩控制中转子磁链的观测方法,建立感应电机转子磁链及磁链转差理论模型,并对电机转速进行估算。仿真研究结果表明:该方法能够用于提高低速观测精度,并对电机参数的变化表现出良好的系统鲁棒性。
关键词:
中图分类号:TM464 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)06-1599-05
Induct motor speed identification based on flux observation
ZENG Yi-hui1, 2, ZHU Hao2, ZHU You-wei3
(1. College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. Computer Numberical Control Tooling Center, Hunan International Economics University, Changsha 410205, China;
3. Advancing Manufacturing Technology Centre, Changsha University, Changsha 410003, China)
Abstract: Based on the fact that the model reference adaptive speed identification method has identification with high precision, but its mathematical model is very complex, and it has to match high-speed controller in real-time control, an observation on the rotor flux of the induct machine direct torque control was presented, and the mathematics model of the rotor flux and flux slip was built to estimate the motor speed. The simulation results show that the low speed observation accuracy can be improved using this method, and robust characteristic of the system is enhanced when motor parameter changes.
Key words: flux observation; motor speed identification; direct torque control
在高性能异步电动机变频控制系统中,速度检测大多采用光电脉冲编码器[1-2]。但速度传感器的安装一方面增加了控制系统成本,降低了系统的可靠性,另一方面,在某种程度上使笼型电动机结构复杂,牢固性能变差。因此,无速度传感器技术成为目前交流传动的热门研究课题。国外在20世纪70年代就开始了无速度传感器的研究,如:Abbondanti等[3]报道了无速度传感器矢量控制的异步电机调速系统,它是从稳态电路获得,难以保证调速性能和精度;Onrani[4]提出了理论意义上的转速辨识方法。此后,Tamai等[5]引入了模型参考自适应方法(MRAS),用于解决速度辨识上的理论问题,得到了广泛应用。在此,本文作者提出一种基于磁链观测器的速度辨识,其速度观测精度比模型参考自适应方法的观测精度低,但其数学结构简单,无需运用复杂的控制理论和高速微控制器进行计算,容易实现。
1 基于磁链观测器的电机速度估计
直接转矩控制是基于定子磁链控制的,借助于离散式的2点调节,实现定子磁链的幅值和相位控制[6]。以定子磁链的观测值为基础,推算出转子磁链,再从转子磁链中估计出转子速度。这种推算方法是一种较好的速度估计方法[7],其速度估计的结果必定对定子参数表现出良好的鲁棒性。电动机的转子磁链yr是一个未知量,而对转子电压和电流的测量不方便,必需根据定子磁链值来进行估计。在该速度估计方法中,为了简化问题,减少计算量,采用电压模型来计算转子磁链[8-9]。电动机的励磁反电动势Em可以表示为:
![]()
则转子磁链的估算表达式如下:

从式(2)可以看出,转子磁链的估算与定子磁链相关,而与转子电阻Rr无关[10-11],因此,只要定子磁链的观测具有一定精度,则可满足转子磁链观测的精度要求。
2 电机速度的估计
异步电动机在静止两相α和β坐标上的电压方程可以表示成如下矩阵形式[12]:

则由上式可以得到转子磁链观测的2种不同模型:电压模型和电流模型。

由式(5)和(6)可见,电压模型不含电机速度ωr项,而电流模型包含ωr项。下面从转子磁链的电流模型出发,推算电机速度的估算公式。

由式(8)和(12),可以估算出电机速度ωr。由于式(8)中含有转子磁链的微分项,可以将该式转换成前向差分的形式[13],即:
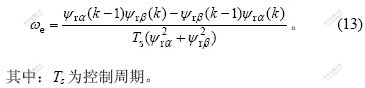
3 速度估计的仿真
跟据上述推出的转子磁链计算公式和转子速度计算公式,可以建立速度估计的仿真模型,如图1所示。模型的输入为定子磁链ys、定子电流is和电磁转矩Te,电磁转矩由DTC系统的转矩观测器提供。

图1 基于磁链观测的速度估计仿真模型
Fig.1 Simulation model of speed estimation based on flux observation
将速度估算模型直接加入到DTC变频调速系统中,估计速度![]() 只用于进行速度观测,不作为速度反馈信号参加系统控制[14]。DTC调速系统的外环速度调节器的反馈信号仍为电机提供的真实转速。
只用于进行速度观测,不作为速度反馈信号参加系统控制[14]。DTC调速系统的外环速度调节器的反馈信号仍为电机提供的真实转速。
为了考察速度的估算精度,改变DTC调速系统的速度给定![]() ,将估计速度
,将估计速度![]() 与电动机实际输出的速度ωr进行对比。图2所示为估计速度不同时定时电机转速的估计波形;图3所示为电机速度ωr经历先升至120 rad/s—不变—下降到30 rad/s时不同运行状态下电机的估计速度和电磁转矩响应波形。
与电动机实际输出的速度ωr进行对比。图2所示为估计速度不同时定时电机转速的估计波形;图3所示为电机速度ωr经历先升至120 rad/s—不变—下降到30 rad/s时不同运行状态下电机的估计速度和电磁转矩响应波形。

(a) ![]() =100 rad/s; (b)
=100 rad/s; (b) ![]() =10 rad/s
=10 rad/s
图2 速度给定不同时电机转速的估计波形
Fig.2 Speed estimate waveforms for different speed settings
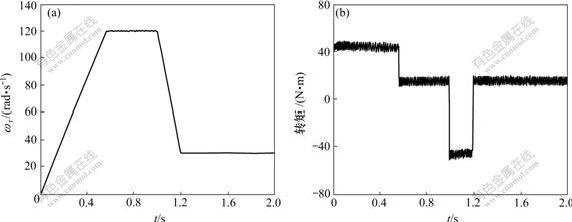
(a) 估计速度;(b) 电磁转矩
图3 电机速度变化的估计速度和电磁转矩的波形
Fig.3 Dynamic waveforms of estimate speed and electromagnetic torque
从图2和图3可以看出,这种速度估算器的估算精度较高,无论是在低速还是在高速,都能做到无静差,动态时跟踪效果好。只是在低速时存在一定的脉动和噪声。为了减少速度信号中的噪声,必须对速度信号进行低通滤波。滤波强度越大,其低速性能越好。但滤波强度过大会导致速度估算器的动态性能变差,必须在两者之间进行折衷选择。
电机参数的变化主要是定子电阻Rs和Rr的变化,这种变化可能会影响速度估计结果[15]。为了确定其对速度估计的影响程度,对实际定转子电阻变化对速度辨识的影响进行仿真,据文献[9]可知,电机电阻的最大变化范围为0~150%,对R′s=1.5Rs和R′r=1.5Rr 2种定转子电阻变化情况的速度估计结果与实际速度进行对比,结果如图4所示。从图4(a)可以看到,其估计速度比真实速度有0.2 s的收敛时延。这是因为定子观测磁链跟踪真实磁链时,Rs发生变化,便有一个收敛时延,致使速度的估计也存在收敛时延。实际上,定子电阻的变化是非常缓慢的,这种收敛时延并不存在,而速度估计的稳态精度并没有受Rs的影响。从图4(b)可以看到,估计速度与真实速度曲线几乎相同,这说明两者的误差非常小,即转子电阻Rr的变化对估计速度的精度影响很小。这是因为Rr本身很小,从式(12)可知,Rr只影响转差速度ωsl,而ωsl相对于ωe又很小,所以,Rr对速度估计的精度影响很小。

(a) R′s=1.5Rs; (b) R′r=1.5Rr
1—真实速度; 2—估计速度
图4 Rs和Rr偏离真实值时速度估计与真实速度对比曲线
Fig.4 Contrast curves between estimated speed and actual speed when Rs and Rr are away from its actual values
4 结 论
a. 所提出的速度估算器算法简单、直观,实现较容易。结合高性能的定子磁链观测器,能获得较高的稳态估计精度和动态性能。
b. 将速度估计算法与磁链观测器相结合,高性能定子磁链观测器可以消除积分器的积累误差,对电机参数的变化表现出良好的鲁棒性,通过定子磁链值推算出转子磁链,并基于转子磁链,可实现对电机转速的估计。
c. 这种速度估算器虽然受转子电阻的影响,但仿真结果证实其影响非常小。该速度估算器具有较高的观测精度,特别是在较低的转速范围内仍能保持优良的性能。
参考文献:
[1] Swamy M, Kume T, Maemura A, et al. Extended high speed operation via electronic winding change method for ac motors[C]// 2004 39th IAS Annual Industry Applications Conference. Seattle, 2004: 608-614.
[2] 崔纳新, 张承惠, 杜春水. 变频调速异步电动机效率优化控制的研究进展[J]. 电工技术学报, 2004, 19(5): 36-42.
CUI Na-xin, ZHANG Cheng-hui, DU Chun-shui. Advances in efficiency optimization control of inverter-fed induction motor driver[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2004, 19(5): 36-42.
[3] Abbondanti A, Brennen M. variable speed induction motor drives use electronic slip calculator based on motor voltages and currents[J]. IEEE Trans on Industry Application, 1975(11): 483-488.
[4] Ontani T. A new method of torque control free from motor parameter variation in induction motor drives[C]//Proceedings of IEEE-IAS Annual Meeting Conf, 1986: 203-229.
[5] Tamai S, Sugimoto H, Yano M. Speed sensorless vector control of induction motor with model reference adaption system[C]// Proceedings of IEEE-IAS Annual Meeting Conf, 1987: 189-195.
[6] Klumpner C, Nielsen P, Boldea I, et al. A new matrix converter motor(mcm) for industry applications[J]. IEEE Trans Ind Electronics, 2002, 49(2): 325-335.
[7] 宋文祥. 基于状态观测器的异步电机定子磁链观测和速度辨识[J]. 上海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 59(4): 349-354.
SONG Wen-xiang.Stator flux linkage and speed estimation of induction motor based on full-order state observer[J]. Journal of Shanghai University: Natural Science Edition, 2008, 59(4): 349-354.
[8] 孙 丹, 贺益康. 基于转子磁链观测的无速度传感器PMSM DTC[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2006, 35(7): 1276-1280.
SUN Dan, HE Yi-kang. Rotor flux observation based sensorless PMSM DTC[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering Science, 2006, 35(7): 1276-1280.
[9] 沈天珉. 直接转矩控制全阶磁链观测器的设计及离散仿真[J]. 变频器世界, 2008, 36(5): 53-55, 62.
SHEN Tian-min. The design and emulation of full-order stator flux observer[J]. The World of Inverters, 2008, 36(5): 53-55, 62.
[10] YANG Cheng-feng, LIN He-yun, GUO Jian. Magnetic field analysis of hybrid excitation brushless claw-pole motor with three-dimensional finite element method[C]//The Eighth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems. Nanjing, 2005: 213-219.
[11] Asher O, Sumnerm G. Comparative analysis of experimental performance and stability of sensorless induction motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2006, 53(1): 178-186.
[12] Surapong S, Somboon S. Design strategy of an adaptive full-order observer for speed sensorless induction-motor drives-tracking performance and stabilization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2006, 53(8): 96-119.
[13] Kim J P, Yoon T, Kim J M, et al. Design of an ultra wide2band printed monopole antenna using FDTD and Genetic Algorithm[J]. Microw Opt Tech Lett, 2005, 15(6): 395-397.
[14] 安 姣. 全数字交流永磁同步电机伺服系统设计[J]. 机床与液压, 2009, 58(1): 4-9.
AN Jiao. Design of PMSM digital servo system[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2009, 58(1): 4-9.
[15] 祝龙记. 基于直接转矩控制的高性能磁链观测与速度观测[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2004, 37(8): 209-213, 292.
ZHU Long-ji. High performance flux observer and speed observer of direct torque control[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2004, 37(8): 209-213, 292.
收稿日期:2009-01-25;修回日期:2009-04-09
基金项目:湖南省教育厅优秀青年基金资助项目(08B042)
通信作者:曾谊晖(1972-),男,湖南湘潭人,副教授,从事数控、材料和自动控制的研究;电话:0731-88118922;E-mail: 774158154@qq.com


