网络首发时间: 2016-05-12 12:43
超音速火焰喷涂FeCrBSi合金涂层的高温磨损性能
常州大学机械工程学院
常州大学江苏省材料表面科学与技术重点实验室
摘 要:
采用超音速火焰喷涂法在H13钢表面制备了FeCrBSi涂层,通过场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)、能谱仪(EDS)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)、分析了其表面的截面形貌、化学元素组成和物相。利用球/平面接触方式进行了涂层高温磨损试验,采用FESEM及其EDS分析了磨痕形貌和化学元素的变化,讨论了高温对涂层摩擦因数(COF)和磨损性能的影响。结果表明,FeCrBSi涂层表面涂覆性均匀,涂层厚度约为100μm,涂层截面无明显的层状结构;涂层磨痕处Fe,Cr,B和Si元素分布较均匀,没有发生富集现象;涂层在高温磨损后主要物相为α(Fe,Cr)固溶体,由摩擦产生FeSi相改善了涂层抗高温磨损性能;在200,300,400和500℃时涂层的摩擦因数平均值分别为0.29,0.70,0.63,0.54,氧化膜分布不均匀和磨损形式是摩擦因数发生变化的主要因素;在200℃时涂层主要发生氧化磨损,而在300,400和500℃时主要发生氧化磨损并伴有轻微的磨粒磨损,其中Cr和Si的化合物是涂层耐磨的主要因素。
关键词:
超音速火焰喷涂;FeCrBSi涂层;表面与截面;摩擦因数;磨损性能;
中图分类号: TG174.4
作者简介:宋瑞宏(1969-),男,江苏泗阳人,硕士,高级工程师,研究方向:机械设计制造及材料表面改性处理;E-mail:songrh929@163.com;;孔德军,教授;电话:0519-81169810;E-mail:kong-dejun@163.com;
收稿日期:2015-11-10
基金:江苏省科技支撑计划(工业)项目(BE2014818)资助;
High Temperature Wear Properties of FeCrBSi Alloy Coating by High Velocity Oxygen Fuel
Song Ruihong Zhao Benguo Liu Ming Kong Dejun
School of Mechanical Engineering,Changzhou University
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Materials Surface Science and Technology,Changzhou University
Abstract:
A layer of FeCrBSi coating was prepared on H13 hot worked die steel by high velocity oxygen fuel( HVOF),the surfacesection morphologies,chemical element compositions,and phases were analyzed with field emission scanning electron microscopy( FMSEM),energy dispersive spectroscopy( EDS) and X-ray diffraction( XRD),respectively. The friction and wear behaviors were investigated at high temperatures by the means of ball / plane contact,the wear scar morphologies and the changes of chemical elements on the coating surface after wear test were analyzed with SEM and EDS,respectively,and the influences of high temperature on coefficient of friction( COF) and wear performance were discussed. The results showed that the covering on the FeCrBSi coating surface was uniform,of which thickness was about 100 μm,and the coating section had no obvious layered structures. The distributions of Fe,Cr,B and Si elements on the coating worn scars were uniform,no obvious enrichment phenomenon. The main phase of the coating after high temperature wear was α-( Ni,Cr) solid solution,and the Fe Si phase produced by friction improved the high temperature wear resistance of the coating. At the temperatures of 200,300,400 and 500 ℃,the average COF values were 0. 29,0. 70,0. 63 and 0. 54,respectively,and the non-uniform distribution of oxide films and wear form were the main factors of COF change. The wear mechanism of FeCrBSi coating was an oxidative wear at 200 ℃,and the wear mechanism was mainly composed of oxidative wear,accompanied with abrasive wear at 300,400 and 500 ℃,in which the compounds of Cr and Si atoms were the main factors of increasing wear resistance of the coating.
Keyword:
high velocity oxygen fuel(HVOF); FeCrBSi coating; surface and section; coefficient of friction(COF); wear performance;
Received: 2015-11-10
H13钢(4Cr5Mo Si V1)是热作模具使用的主要钢种之一
1实验
基体材料为H13钢热作模具钢,粉末材料为Fe基自熔合金。试样经丙酮清洗去除油污后,采用棕钢玉喷砂粗化处理。超音速喷涂试验在ZB-2700型高速火焰喷涂装置上进行,以航空煤油作燃料,O2作助燃气体,N2为送粉气体。喷涂工艺参数:送粉量为110 g·min-1,喷枪距离为250 mm,油压1.25 MPa,氧压1.58 MPa,水温40℃,喷枪压0.95 MPa。喷涂后涂层厚度约为300μm。制备的涂层试样经打磨抛光后,采用HT-1000型高温摩擦-磨损试验机考察Fe Cr BSi涂层高温摩擦-磨损特征,试验参数:温度分别为200,300,400和500℃;摩擦方式:旋转式,对磨副为Φ5 mm的Si3N4陶瓷球,加载载荷:10 N,摩擦副主轴转速:1000r·min-1,摩擦半径:4 mm,试验时间:40 min。磨损试验结束后,采用JSUPRA55型场发射扫描电镜(FESEM)及其配置的电子能谱仪(EDS)分析涂层高温磨损前后表面形貌和化学组成,并用D/max2500PC型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析高温磨损前后涂层物相组成,分析高温条件下Fe Cr BSi涂层磨损失效机制。
2结果与讨论
2.1表面与截面形貌
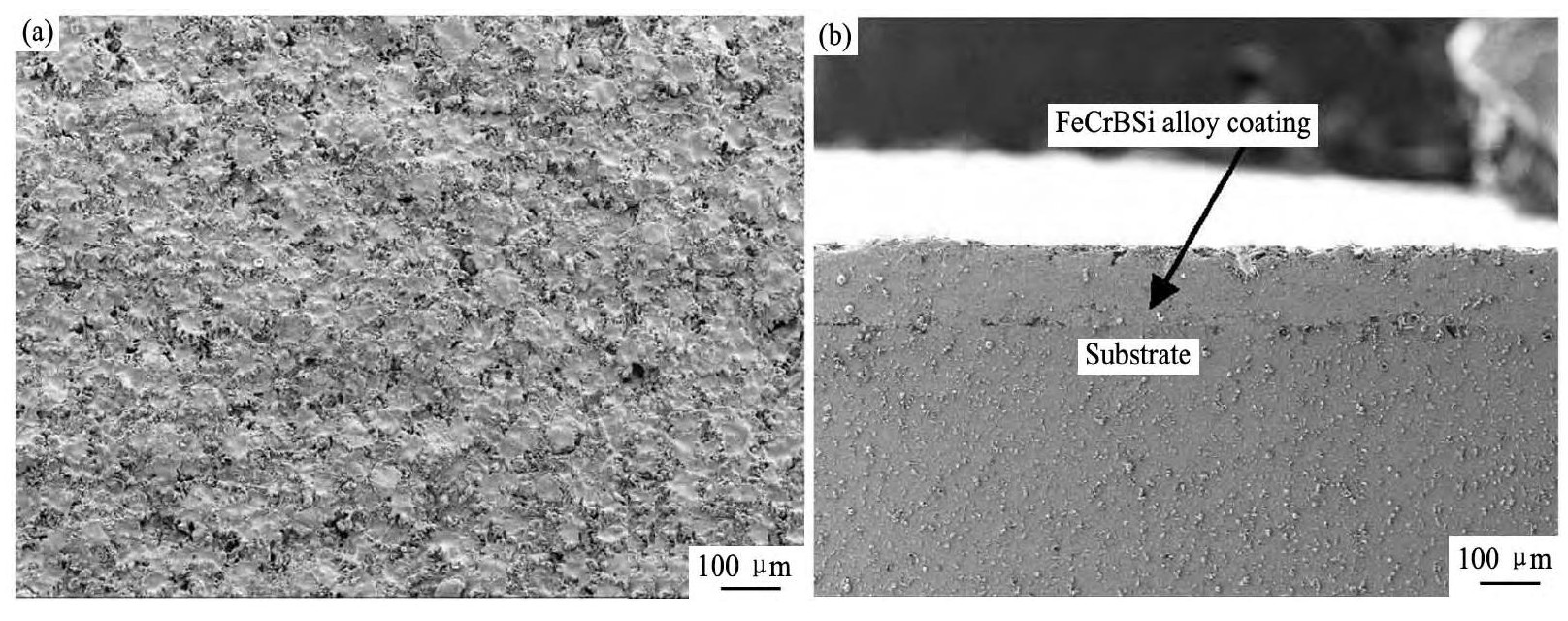
超音速喷涂Fe Cr BSi涂层表面形貌如图1(a)所示,平整度较好,粉末熔化情况良好,熔化后粉末颗粒在碰到基体后产生形变,弥散性较好。涂层表面覆盖了一层由细小氧化物颗粒组成的膜层,表面存在着少量微孔,分析认为是在喷涂过程中,粉末中Fe元素发生氧化。涂层截面形貌如图1(b)所示,厚度约为100μm,组织均匀,结构致密,无明显的裂纹及孔洞,只有少量的孔隙存在,涂层常有的层状结构不明显。
图1 Fe Cr BSi表面和截面形貌Fig.1 SEM images of surface(a)and section(b)morphologies of Fe Cr BSi coating
2.2 XRD分析
图2为在高温磨损后Fe Cr BSi涂层XRD分析。通过对4种温度下涂层的物相分析,可知:(1)在200,300,400和500℃时磨损后涂层主要物相均为α(Fe,Cr)固溶体。(2)在4种温度下,磨损后涂层表面均产生Fe Si,其熔点在1410℃左右,可提高涂层抗高温性能,在500℃时磨损后Fe Si在冷却过程中向Fe Si2转化,Fe Si2熔点在1220℃左右。由于涂层中Fe Si2含量较少,因此,对涂层的抗高温性能影响较小。(3)涂层在400和500℃时磨损后涂层中Fe发生氧化,产生的Fe2O3在高温时分解产生Fe3O4,而在200和300℃时涂层磨损后氧化程度较小。
2.3摩擦因数
图3为在载荷为10 N时不同的温度对Fe Cr B-Si涂层摩擦因数影响关系曲线。由图3可知:(1)摩擦磨损试验初期,由于受到硬质膜层和表面小颗粒影响,涂层摩擦因数波动较大。随磨损试验进行,涂层中Cr和Si元素发生氧化反应,产生的氧化物在摩擦表面形成氧化膜,起到减摩作用,使摩擦因数降低,然后趋于平缓。(2)在整个磨损试验阶段(0~30 min),200℃时涂层摩擦因数平均值最小,为0.29,但200℃时涂层摩擦因数一直随时间增加而增加,平稳性能较差;300℃时涂层摩擦因数平均值最大,为0.70,同时在12~22 min时,出现摩擦因数突然下降的变化,这可能和涂层表面小颗粒出现剥落有关;400℃时涂层摩擦因数平均值较大,为0.63;500℃时涂层摩擦因数平均值较小,为0.54。在不同温度磨损时,涂层中O原子含量随着温度增加而增大,如表1所示,导致涂层摩擦因数平均值不同。涂层中氧化物含量在300~500℃时最小,此时摩擦因数最大,这表明摩擦因数与涂层中O原子含量有关,随着O原子含量增加而减小。(3)摩擦因数的波动与图4(f),图5(f)和图6(f)中O原子含量分布均匀性有关,在300℃时涂层中O原子含量分布均匀性较差,此时涂层摩擦因数波动最大;在400和500℃时涂层中O原子含量分布较均匀,其摩擦因数波动趋向平缓,磨损过程较为稳定,因此,氧化膜的均匀性是影响摩擦因数波动的一个重要因素。
图2 Fe Cr BSi涂层不同高温磨损后表面XRD分析Fig.2 XRD patterns of Fe Cr BSi coating after wear under dif-ferent temperatures
图3 在不同高温时摩擦因数与磨损时间关系Fig.3 COF vs wear-time at different high temperatures
2.4磨痕表面形貌与面扫描分析
在200℃时涂层磨损后的磨痕形貌深度较浅、宽度较窄,如图4(a)所示,采用能谱仪对磨损后涂层表面元素进行面能谱分析,可见涂层磨痕处Fe,Cr,B和Si元素分布均匀,没有发生富集现象,如图4(b~e)所示。磨痕处O元素出现完整连续的亮带,说明O元素发生富集现象,如图4(f)所示。这是由于在高温磨损过程中涂层中Fe发生氧化产生氧化膜,而且氧化膜没有发生破裂,保持完好,这表明涂层在200℃时磨损机制主要是氧化磨损。
表1 不同高温时涂层表面EDS分析结果Table 1 EDS analysis results of coating surface at differ-ent temperatures 下载原图
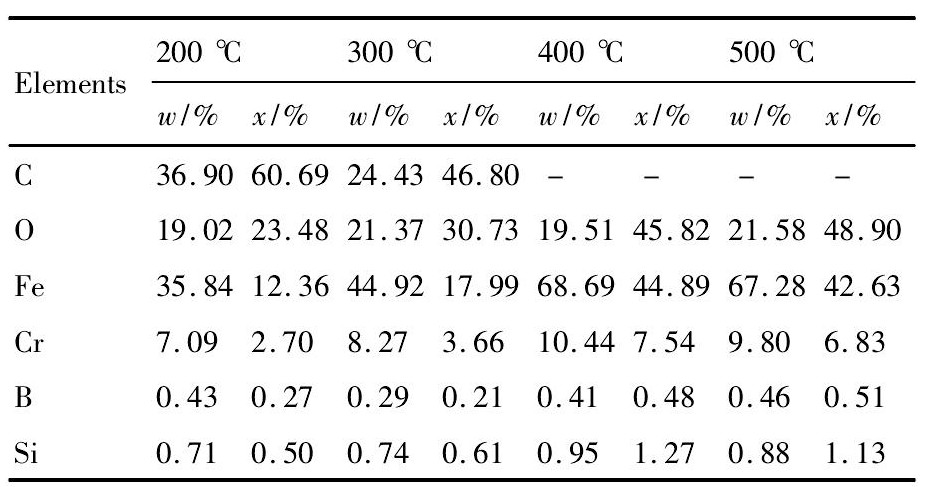
表1 不同高温时涂层表面EDS分析结果Table 1 EDS analysis results of coating surface at differ-ent temperatures
图4 200℃时磨痕表面形貌与面能谱分析Fig.4 Worn morphology and plane scans of worn scar at 200℃
(a)SEM image of worn surface morphology;(b)Fe distribution;(c)Cr distribution;(d)B distribution;(e)Si distribution;(f)O distribution
在300℃时涂层磨损后磨痕形貌深度也较浅、宽度较宽,如图5(a)所示。采用能谱仪进行面能谱分析磨损后涂层元素面分布,可知涂层磨痕处Fe和B元素分布均匀,没有发生富集现象,如图5(b)和(d)所示。涂层中Cr和Si都出现不同程度的贫瘠,如图5(c)和(e)所示,O元素出现富集现象,如图5(f)所示。涂层中Cr和Si元素发生氧化反应,形成氧化膜。在磨损过程中部分氧化膜被碾碎、剥落,形成片状剥落坑,导致摩擦因数产生波动,这表明涂层在300℃时的磨损机制主要为氧化磨损和磨粒磨损。
图5 300℃时磨痕表面形貌与面能谱分析Fig.5 Worn morphology and plane scans of worn scar at 300℃
(a)SEM image of worn surface morphology;(b)Fe distribution;(c)Cr distribution;(d)B distribution;(e)Si distribution;(f)O distribution
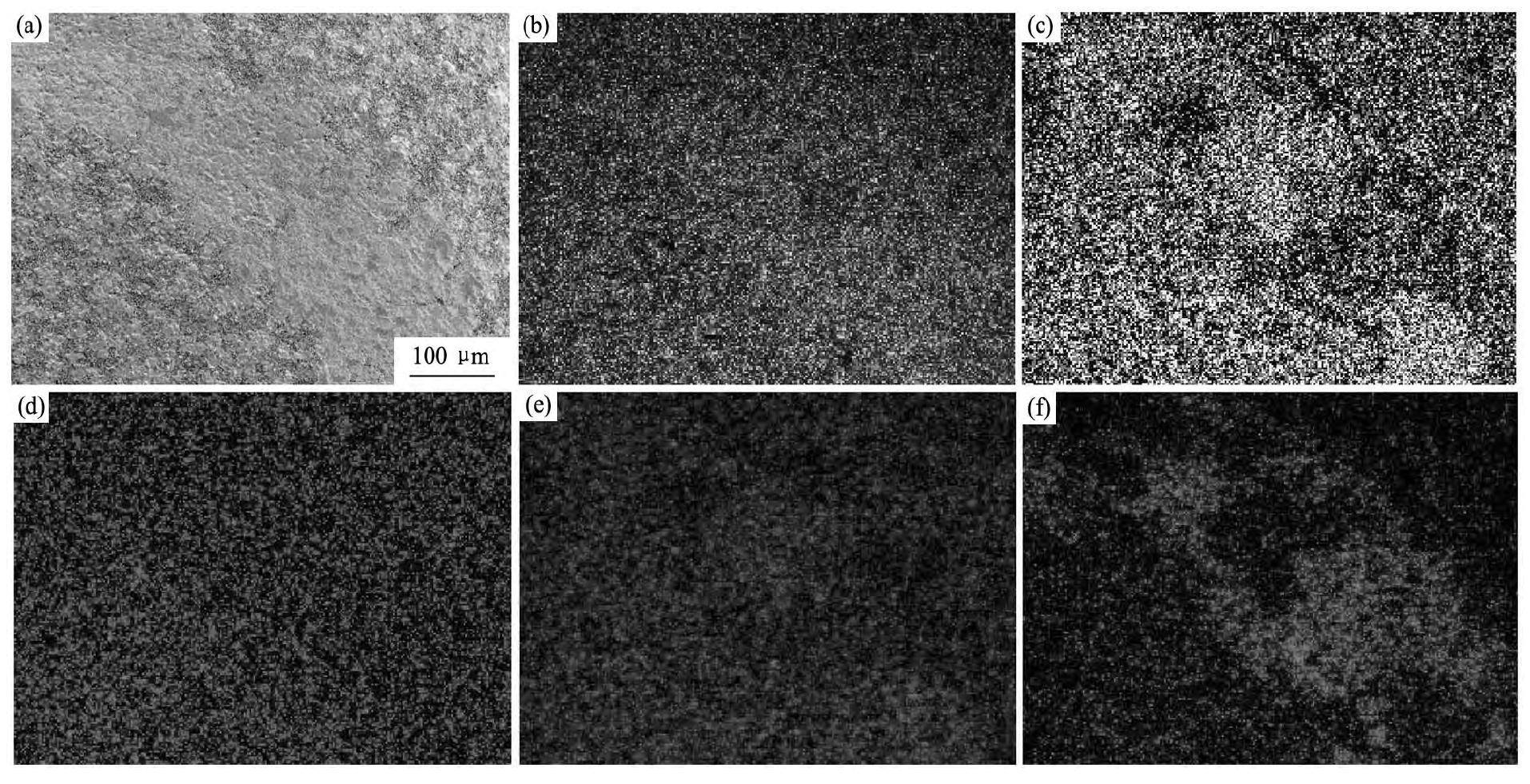
在400℃时涂层磨损后磨痕深度较深、宽度较宽,并产生一条轻微的犁沟,如图6(a)所示。采用能谱仪进行面能谱分析磨损后涂层元素面分布,可知涂层磨痕面中B元素分布均匀,没有发生富集现象,如图6(d)所示。在涂层中犁沟处,Fe元素出现富集现象,如图6(b)所示。Cr和Si元素出现不同程度的贫瘠,面分布不均匀,如图6(c)和(e)所示。在磨痕处O元素出现富集现象,如图6(f)所示。
分析认为在磨损过程中涂层表面原子键产生断裂,形成大量松脱的磨粒。在随后的摩擦过程中,这些硬质的磨粒(主要是Cr和Si元素的化合物)不断压入摩擦副表面,进行切削时会产生犁沟,从而致使摩擦磨损增强,表现为磨粒磨损现象,这表明涂层在400℃时的磨损机制主要为氧化磨损(图7(a))和磨粒磨损(图7(b))。
在500℃时涂层磨损后磨痕痕貌较宽,磨痕表面存在剥落坑(图8(a))。采用能谱仪分析磨损后涂层的化学元素分布,在500℃时涂层磨痕面中Fe元素发生氧化,其元素面分布如图8(b)所示,在磨损过程中Fe元素的氧化膜破裂与剥落,导致磨痕处Fe元素含量减少。Cr和B元素面分布均匀,没有发生富集现象,如图8(c)和(d)所示。在涂层磨痕中Si和O元素产生富集,如图8(e)和(f)所示。
图6 在400℃时磨痕表面形貌与面能谱分析Fig.6 Worn morphology and plane scans of worn scar at 400℃
(a)SEM image of worn surface morphology;(b)Fe distribution;(c)Cr distribution;(d)B distribution;(e)Si distribution;(f)O distribution
图7 Fe Cr BSi涂层在400℃时磨损形貌Fig.7 SEM images of worn morphologies of Fe Cr BSi coating at 400℃
(a)Oxidation wear;(b)Abrasive wear
图8 500℃时磨痕表面形貌与面能谱分析Fig.8 Worn morphology and plane scans of worn scar at 500℃
(a)SEM image of worn surface morphology;(b)Fe distribution;(c)Cr distribution;(d)B distribution;(e)Si distribution;(f)O distribution
由上述分析可知,涂层在300℃时耐磨性能较差,而在200,400和500℃时磨损形貌均具有较好的完整性,同时表现出良好的耐磨性能,涂层中Cr和Si元素产生的化合物是涂层耐磨的主要机制。
3结论
1.经过高温磨损后,涂层的主要物相为α(Fe,Cr)固溶体,由摩擦产生Fe Si相改善了涂层抗高温磨损性能。
2.在200~500℃时涂层的摩擦因数平均值为0.29,0.70,0.63,0.54,涂层中氧化膜分布不均匀和磨损形式是摩擦因数发生变化的主要因素,其中磨粒磨损使得摩擦因数有所增大。
3.涂层在200℃时主要发生氧化磨损,而在300,400和500℃时主要发生氧化磨损和轻微的磨粒磨损。
4.在200~500℃时涂层具有良好的耐磨性能,可以保持完整性,其中Cr和Si形成的化合物改善了涂层磨损性能。
参考文献