DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.08.19
方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的协同抑制作用及机理
王纪镇1, 2,印万忠2,孙忠梅3
(1. 西安科技大学 化学与化工学院,西安 710054;
2. 东北大学 资源与土木工程学院,沈阳 110819;
3. 低品位难处理黄金资源综合利用国家重点实验室,上杭 364200)
摘 要:
通过浮选试验、离子浓度测定、动电位测定和理论计算等方法研究了方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的影响。结果表明:六偏磷酸钠与方解石存在协同作用,可强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用;方解石主要通过钙离子强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用,碳酸根离子不影响六偏磷酸钠的抑制性能,过量碳酸根离子的存在反而能够减弱方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的协同抑制作用。机理研究表明,方解石表面的钙离子在六偏磷酸钠的作用下可解吸至溶液中,增加溶液中的钙离子浓度,使六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的抑制作用增强。
关键词:
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-08-1645-08 中图分类号:TD91 文献标志码:A
白钨矿是钨的主要来源之一,经常与方解石、萤石等含钙脉石矿物共生。浮选是回收富集白钨矿重要方法[1-3]。白钨矿浮选主要的捕收剂为羧酸类捕收剂及其衍生物[4-5]。然而,由于白钨矿与含钙脉石矿物表面性质相近,导致难以实现这些矿物的分离。高效捕收剂以及选择性好的抑制剂是白钨矿浮选的研究重点[6-7]。白钨矿与含钙矿物捕收剂的研究已有较多报道,如阴离子型组合捕收剂[8],阴阳离子型组合捕收剂[9]以及新型阳离子捕收剂[10-11]。白钨矿与含钙脉石矿物分离的抑制剂为硅酸钠、水玻璃以及改性水玻璃[12-13],以及选择性较强的有机抑制剂,如腐殖酸钠[14]、聚丙烯酸钠[15]、海藻钠[16]等。
研究表明,六偏磷酸钠可强烈抑制方解石[17-20],且对方解石的抑制作用明显强于白钨矿[17]。然而,盐类矿物之间存在相互作用,溶解组分会影响药剂与矿物之间的作用,进而影响药剂的选择性[16, 19-22]。目前关于白钨矿与方解石之间的相互作用机制有以下两种观点:一种是认为方解石溶解的碳酸根离子与白钨矿表面的钨酸根离子发生置换反应,引起表面转化,导致分选困难[16, 23];另一种观点是认为方解石的溶解度较大,增加了溶液中钙离子浓度,进而影响白钨矿回收率[24] 。
如前所述,目前白钨矿浮选的研究主要集中于浮选药剂,但是矿物之间的作用影响浮选药剂性能,且关于该方面的研究报道较少,观点不一,开展该方面的研究不仅有利于实现白钨矿与方解石的浮选分离,而且对浮选药剂的研究起到互补作用。基于此,本文作者研究方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的抑制作用,通过研究方解石溶解所产生的钙离子和碳酸根离子对六偏磷酸钠抑制性能的影响,得出方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的协同抑制机制。该研究成果对白钨矿与方解石浮选分离研究具有一定指导意义。
1 实验
1.1 矿物与药剂
白钨矿单矿物样品取自云南省某白钨矿选矿厂,方解石单矿物样品取自湖南省长沙矿石粉厂,均为结晶良好的块状矿物,手捡出块状固体。取回的块矿样品经手碎后,手选出纯度较高、结晶形态较好的样品,经过再破碎、瓷球球磨后使用标准筛干筛至粒径小于106 μm,经去离子水冲洗并烘干后,置于磨口瓶中备用。两种矿物样品的X射线粉晶衍射分析与化学成分分析结果表明所有样品均为高纯度样品,符合单矿物试验的要求。
试验所用pH调整剂为HCl和NaOH,油酸钠(NaOL)、六偏磷酸钠、碳酸钠以及氯化钙为化学纯,实验用水为一次蒸馏水。
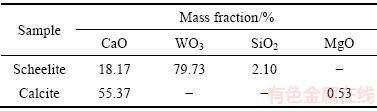
表1 白钨矿与方解石的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of scheelite and calcite
1.2 浮选试验
纯矿物浮选试验在40 mL的XFG型挂槽式浮选机(转速为1900 r/min)中进行,每次取2.0 g矿样,加入30 mL去离子水,调浆1 min后,用HCl或NaOH调节pH值,搅拌2 min并记录pH值,然后依次加入调整剂,加入调整剂后用HCl/NaOH调节矿浆pH值,确保调整剂对矿浆pH值影响不明显,最后加入捕收剂以及起泡剂,若pH值变化明显,用HCl/NaOH调节矿浆pH值至未加捕收剂之前的pH值,搅拌2 min,浮选5 min,泡沫产品和槽内产品分别烘干、称量、化验、计算回收率。
1.3 动电位测定和溶解度测定
将矿样磨至粒度小于5 μm,每次取100 mg置于烧杯中,加50 mL去离子水,加入相应药剂后,用HCl或NaOH调节pH值,用玻璃棒搅拌一定时间后,吸取少量均匀溶液采用Nano ZS-90 Zeta分析仪测量矿物表面动电位,每个结果取3次动电位值的平均值。
试验采用型号为Prodigy XP的电感耦合等离子光谱发生仪(ICP)测定溶液中的钙离子的浓度。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 方解石与六偏磷酸钠的协同抑制作用对白钨矿浮选的影响
六偏磷酸钠(SH)对白钨矿浮选回收率的影响如图1所示。由图1可知,随着矿浆pH值增加,六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用作用减弱,当pH=11.0时,六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用消失,然而当方解石和六偏磷酸钠同时存在时,白钨矿回收率均较低。
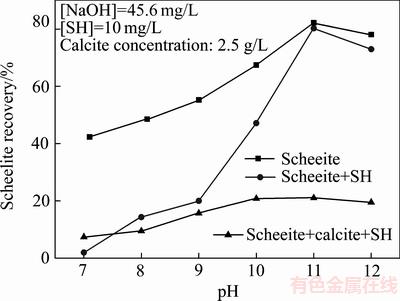
图1 不同矿浆pH值时六偏磷酸钠(SH)对白钨矿回收率的影响
Fig. 1 Effect of SH on flotation recovery of scheelite with different pH values
油酸钠用量对白钨矿回收率的影响如图2所示。由图2可知,随着油酸钠用量增加,白钨矿回收率逐渐增加;当油酸钠用量小于90 mg/L时,在相同的油酸钠用量下,方解石与六偏磷酸钠共同添加时白钨矿回收率下降最明显,方解石单独添加时白钨矿回收率降低程度次之,六偏磷酸钠单独添加时下降最不明显,且基本不影响白钨矿回收率。
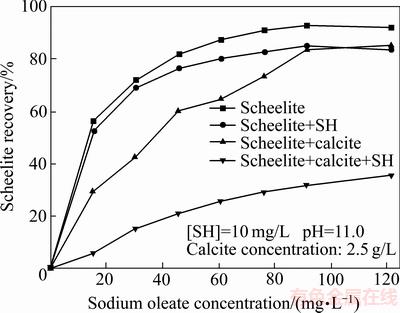
图2 油酸钠用量对白钨矿回收率的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of sodium oleate dosage on flotation recovery of scheelite
方解石含量和六偏磷酸钠含量对白钨矿回收率的影响分别如图3和4所示。由图3可知,当六偏磷酸钠不存在时,白钨矿回收率随方解石含量的增加为先降低后增加,然后趋于平衡,且回收率均在60%以上;当浮选体系中同时存在六偏磷酸钠与方解石时,白钨矿回收率随方解石含量的增加急剧降低,然后趋于平衡,且回收率均在26%以下,说明方解石可强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用。图4所示则进一步证明方解石可强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用。
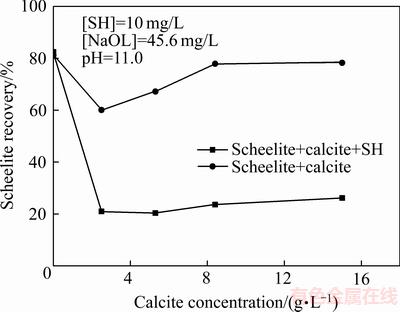
图3 方解石含量对白钨矿回收率的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of calcite dosage on flotation recovery of scheelite
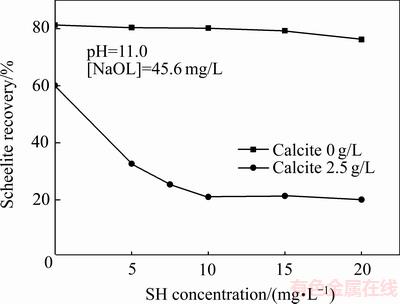
图4 SH用量对白钨矿回收率的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of SH dosage on flotation recovery of scheelite
综合分析图1~ 4可知,六偏磷酸钠和方解石对白钨矿回收率影响相对较小,但方解石与六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制具有协同作用,明显恶化了白钨矿浮选。
2.2 钙离子和碳酸根离子对六偏磷酸钠抑制性能的影响
六偏磷酸钠为抑制剂时,氯化钙和碳酸钠用量对白钨矿回收率的影响如图5和图6所示。
由图5可知,氯化钙可降低白钨矿回收率,当氯化钙和六偏磷酸钠同时存在时,白钨矿回收率下降更明显,说明钙离子可强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用。
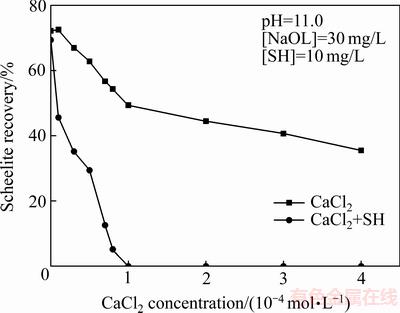
图5 氯化钙用量对白钨矿回收率的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of CaCl2 dosage on flotation recovery of scheelite
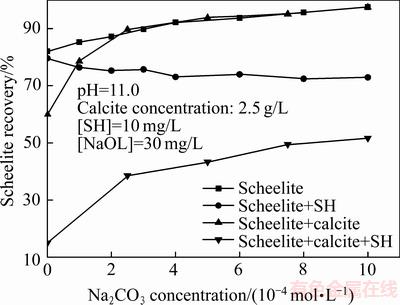
图6 碳酸钠用量对白钨矿回收率的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of Na2CO3 dosage on flotation recovery of scheelite
由图6可知,当方解石不存在时,碳酸钠不会强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用;当方解石存在时,在不添加六偏磷酸钠的条件下,白钨矿回收率随碳酸钠用量的增加而增加,且白钨矿回收率最高可达90%以上,基本消除了方解石对白钨矿回收率的影响,然而当方解石和六偏磷酸钠共同存在时,白钨矿回收率随碳酸钠用量增加而有所增加,但回收率仍然较低,进一步说明方解石和六偏磷酸钠存在协同效应,强化了对白钨矿的抑制作用。综合分析图5和6可知,方解石主要通过钙离子强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用,碳酸根离子不仅不强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用,反而可消弱方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的协同抑制作用。
2.3 机理分析
2.3.1 浮选溶液化学研究
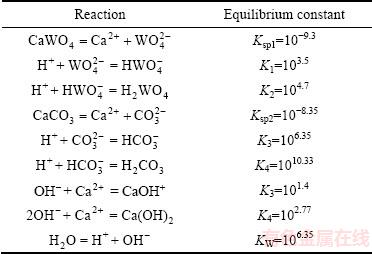
白钨矿和方解石在水溶液中的溶液化学反应及其平衡常数如表2所列。
表2 化学反应及其平衡常数[25]
Table 2 Chemical reactions and equilibrium constants[25]
设 ,
,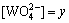 ,
,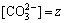 ,碳酸钠加入量为t,单位均为mol/L,那么,pH=11.0 时白钨矿-方解石-水体系中存在的化学平衡关系式及其对应的数学关系式如表3所列。
,碳酸钠加入量为t,单位均为mol/L,那么,pH=11.0 时白钨矿-方解石-水体系中存在的化学平衡关系式及其对应的数学关系式如表3所列。
根据表3所示的数学关系式,通过Matlab软件求解数学方程组,得到碳酸钠浓度与矿浆pH值以及白钨矿/方解石矿浆中钙离子浓度的关系,经计算,初始pH=11.0时,加入0~1.0×10-3 mol/L碳酸钠后矿浆pH值变化范围为11.00~11.06之间,因此可不考虑矿浆pH值对试验结果的影响。
pH=6~11.5时白钨矿的溶液中钙离子浓度为1.0×10-5 ~2.2×10-5mol/L,当pH=11.0时钙离子浓度大约为1.0×10-5 mol/L [26]。由图7可知,钙离子浓度随碳酸钠浓度增加而明显降低,且钙离子浓度-碳酸钠浓度的关系与图6中的白钨矿回收率-碳酸钠浓度关系一致。根据浮选溶液化学计算结果可知,当碳酸钠浓度由0增加到1.0×10-3 mol/L时钙离子浓度由8×10-5 mol/L降至0.5×10-5 mol/L,即1.0×10-3 mol/L碳酸钠完全消除了方解石对白钨矿浮选溶液中钙离子浓度的影响,因此,当六偏磷酸钠不存在时碳酸钠可消除方解石对白钨矿浮选的影响,而图6表明,即使1.0×10-3 mol/L碳酸钠存在时六偏磷酸钠仍能够强烈抑制白钨矿,由此可见,方解石与六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿具有协同抑制作用,但不是由于方解石溶解产生钙离子消耗油酸钠所致,而是由于六偏磷酸钠与方解石可发生相互作用,且作用产物可强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用。
由图8可知,六偏磷酸钠提高了方解石溶解度,且碳酸钠不能消除六偏磷酸钠对方解石溶解度的影响,由此可见,六偏磷酸钠在方解石表面生成的化合物(记为SH-Ca)并不完全滞留在方解石表面,而是溶解于溶液中增加了钙离子浓度。
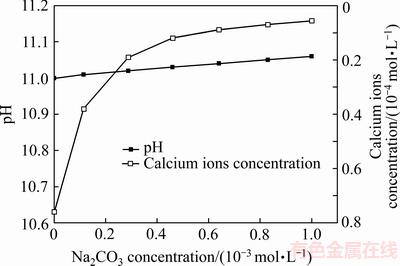
图7 碳酸钠用量对白钨矿/方解石混合矿溶液中钙离子浓度的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of sodium carbonate on calcium ions concentration in solution of mixed scheelite/calcite
表3 白钨矿-方解石-水溶液中离子化学守恒式及其对应的数学关系式
Table 3 Balanced chemical equations and mathematical relationship for scheelite-calcite-water system

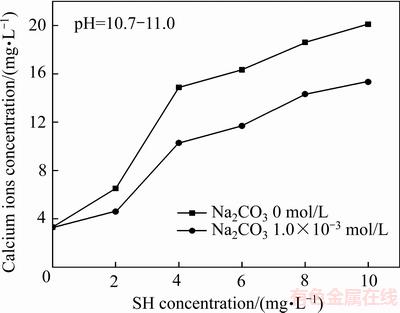
图8 SH对方解石溶解度的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of SH on solubility of calcite
2.3.2 矿物-药剂作用机制研究
药剂作用前后白钨矿动电位如图9所示,白钨矿和方解石解理面结构如图10所示。由图9可知,当pH>9时,六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿动电位的影响程度随pH的增加而逐渐降低,这可能是因为随着pH值的升高,白钨矿动电位值急剧降低、六偏磷酸钠解离程度增加,导致白钨矿与六偏磷酸钠的静电斥力增加,阻止了六偏磷酸钠在白钨矿表面的吸附。当pH=11时,单独添加六偏磷酸钠时白钨矿动电位变化不明显,而同时添加钙离子和六偏磷酸钠时白钨矿动电位具有更明显,说明钙离子促进了六偏磷酸钠在白钨矿表面的吸附。
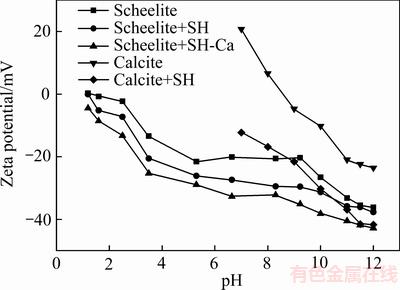
图9 药剂对白钨矿与方解石动电位的影响
Fig. 9 Effect of reagents on zeta potential of scheelite and calcite
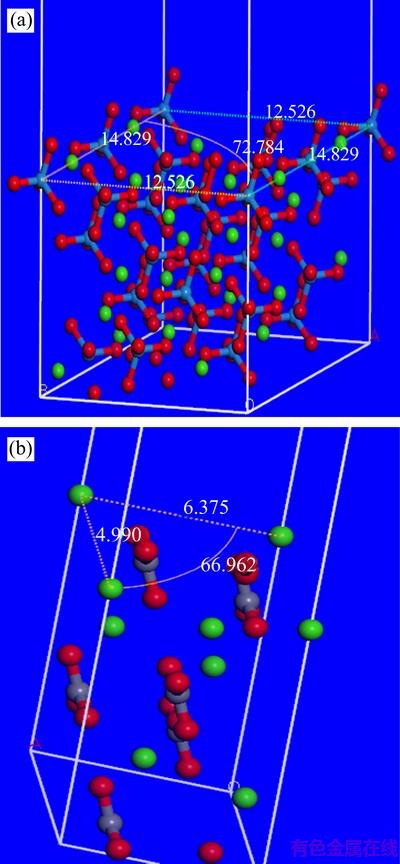
图10 白钨矿与方解石的解理面
Fig. 10 Cleavage surface of scheelite (a) and calcite (b)
由图10可知,白钨矿解理面最外层是由钨酸根离子的氧组成,钨酸根中心原子的钨与钙离子处于同一平面。方解石解理面的最外层是由钙和氧组成,碳酸根的氧几乎与钙离子处于同一平面。矿物解理面单位面积Ca数目(NCa)如下:
NCa(Sch) =2/[1.2526×1.4829×sin(72.784°)]= 1.127/nm2 (1)
NCa(Cal) =1/[0.6375×0.4990×sin(66.962°)]= 3.416/nm2 (2)
与方解石相比,白钨矿表面的阴离子基团较多,钙离子含量较少,因此,白钨矿电位更低。矿物单体解离时阴离子基团的化学键难以断裂,钨酸根、碳酸根以及磷酸根离子基团电负性的计算以如下计算公式所得:
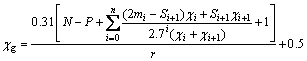 (3)
(3)
式中:r为亲固原子的共价半径;N为亲固原子的价电子数;P为亲固原子被相邻原子键合的电子数;mi为与亲固原子间隔为i的二电子数;Si +1为与亲固原子相隔i键的原子未成键电子数。
离子基团电负性计算结果如表4所列。表4中的数据表明,六偏磷酸钠的基团电负性介于碳酸根和钨酸根之间。基团电负性越大,越容易与钙离子形成离子键,作用能力也就越强,因此,六偏磷酸钠与钙离子的作用介于碳酸根和钨酸跟离子之间,同时,白钨矿表面的钨酸根离子的氧更靠近表面,对六偏磷酸钠的排斥力强,且钙离子含量少,因此难以与六偏磷酸钠作用,而方解石表面的钙离子含量大于白钨矿,且六偏磷酸钠与方解石间的静电斥力小于白钨矿,因此六偏磷酸钠更易与方解石作用。溶解度测定表明六偏磷酸钠与方解石作用后所产生的化合物并不停留于方解石表面,而是溶液溶液中,增加溶液中钙离子浓度,由于钙离子浓度增加有利于强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用(见图5和9),由此可见,方解石能够强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿抑制作用的原因是由于方解石表面的钙离子在六偏磷酸的作用下能够解吸至溶液中,增加溶液中钙离子浓度,进而强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用。碳酸根离子与钙离子的作用弱于六偏磷酸钠的,难以消除方解石与六偏磷酸钠的相互作用,因而难以消除方解石与六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的协同抑制作用。
表4 离子基团电负性计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of group electronegativity of ions

3 结论
1) 六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用随矿浆pH值的增加而逐渐减弱,矿浆pH=11.0时六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿基本无抑制作用,然而在方解石的作用下,六偏磷酸钠可强烈抑制白钨矿浮选。
2) 方解石主要通过钙离子强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用,碳酸根离子不仅不影响六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制行为,反而可消除方解石对白钨矿回收率的影响以及削弱方解石与六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的协同抑制作用。
3) 六偏磷酸钠难以抑制白钨矿浮选,但钙离子可强化白钨矿六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的抑制作用。方解石在六偏磷酸钠的作用下可增加溶液中的钙离子浓度,进而能够强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的抑制作用。pH=11.0时碳酸钠可消除方解石溶解产生的大量钙离子对白钨矿浮选行为的影响,但难以消除六偏磷酸钠对方解石表面钙离子的解吸作用,因而难以消除方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的协同抑制作用。
REFERENCES
[1] HU Yue-hua, GAO Zhi-yong, SUN Wei, LIU Xiao-wen. Anisotropic surface energies and adsorption behaviors of scheelite crystal[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2012, 415: 439-448.
[2] YIN Wan-zhong, WANG Ji-zhen. Effects of particle size and particle interactions on Scheelite flotation[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(11): 3682-3687.
[3] SHEPETA E D, SAMATOVA L A, KONDRAT’EV S A. Kinetics of calcium minerals flotation from scheelite-carbonate ores[J]. J Min Sci, 2012, 48 (4): 746-753.
[4] 朱海玲, 覃文庆, 陈 臣, 刘瑞增. 阴-非离子复配表面活性剂对白钨矿的低温捕收性能及其应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(10): 2188-2196.
ZHU Hai-ling, QIN Wen-qing, CHEN Chen, LIU Rui-zeng. Low-temperature collecting performance of mixed anionic-nonionic surfactants for scheelite flotation and its application[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(10): 2188-2196.
[5] LI CH-gen,Lü Yong-xin. Selective flotation of scheelite from calcium minerals with sodium oleate as a collector and phosphates as modifiers. I. Selective flotation of scheelite[J]. Int J Miner Process, 1983, 10(3): 205-218.
[6] 孙 伟, 胡岳华, 覃文庆, 徐 竟. 钨矿浮选药剂研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与用, 2000(3): 42-46.
SUN Wei, HU Yue-hua, QIN Wen-qing, XU Jing. The status abuot research of flotation reagent for solfram-mineral- flotation[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2000(3): 42-46.
[7] SHIN B S, CHOI K S. Adsorption of sodium metasilicate on calcium minerals[J]. Minerals and Metallurgical Processing, 1987, 2(4): 223-226.
[8] GAO Zhi-yong, BAI Ding, SUN Wei, CAO Xue-feng, HU Yue-hua. Selective flotation ofscheelitefrom calcite and fluoriteusing a collector mixture[J]. Minerals Engieneering, 2015, 72(1): 23-26.
[9] FILIPPOV L O, DUVERGER A, FILIPPOVA I V, KASAINI H, THIRY J. Selective flotation of silicates and Ca-bearing minerals: The role of non-ionic reagent on cationic flotation[J]. Minerals Engieneering, 2012: 36/38: 314-323.
[10] ARNOLD R, BROWNBILL E E, IHLE S W. Hallimond tube flotation of scheelite and calcite with amines[J]. Int J Miner Process, 1978, 5(2): 143-152.
[11] HU Yue-hua, YANG Fan, SUN Wei. The flotation separation of scheelite from calcite using a quaternary ammonium salt as collector[J].Minerals Engineering, 2011,24(1): 82-84.
[12] 张 英, 胡岳华, 王毓华, 文书明. 硅酸钠对含钙矿物浮选行为的影响及作用机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(9): 2366-2372.
ZHANG Ying, HU Yue-hua, WANG Yu-hua, WEN Shu-ming. Effects of sodium silicate on flotation behavior of calcium-bearing minerals and its mechanism[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(9): 2366-2372.
[13] 孙 伟, 宋韶博. 水玻璃及其在白钨矿浮选中的应用和分析[J]. 中国钨业, 2013, 28(4): 22-25.
SUN Wei, SONG Shao-bo. The application and analysis of water glass in the scheelite flotation[J]. China Tungsten Industry, 2013, 28(4): 22-25.
[14] 邱廷省, 宋宜富, 邱仙辉, 李晓波. 白钨矿浮选体系中大分子有机抑制剂的抑制性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(7): 1527-1534.
QIU Ting-sheng,SONG Yi-fu,QIU Xian-hui,LI Xiao-bo. Performance of organic depressants in scheelite flotation system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(7): 1527-1534.
[15] 张 英. 白钨矿与含钙脉石矿物浮选分离抑制剂的性能与作用机理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
ZHANG Ying. Research on the performance and mechanisms of depressants for separating scheelite from calcareous gangue minerals by flotation[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
[16] CHEN Wei, FENG Qi-ming, ZHANG Guo-fan, YANG Qun, ZHANG Cheng. The effect of sodium alginate on the flotation separation of scheelite from calcite and fluorite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 113: 1-7.
[17] 于 洋, 孙传尧, 卢烁十. 白钨矿与含钙矿物可浮性研究及晶体化学分析[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2013, 42(2): 278-283, 313.
YU Yang, SUN Chuan-yao, LU Shuo-shi. Study of floatability and crystal chemistry analysis of scheelite and calcium minerals[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2013, 42(2): 278-283, 313.
[18] 冯其明, 周清波, 张国范, 卢毅屏, 杨少燕. 六偏磷酸钠对方解石的抑制机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(2): 436-441.
FENG Qi-ming, ZHOU Qing-bo, ZHANG Guo-fan, LU Yi-ping, YANG Shao-yan. Inhibition mechanism of sodium hexametaphosphate on calcite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(2): 436-441.
[19] SHI Qing, ZHANG Guo-fan, FENG Qi-ming, DENG Hong. Effect of solution chemistry on the flotation system of smithsonite and calcite[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 119: 34-39.
[20] 罗 娜, 张国范, 朱阳戈, 崔萌萌. 六偏磷酸钠对菱锰矿与方解石浮选分离的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(11): 3214-3220.
LUO Na, ZHANG guo-fan, ZHU yang-ge, CUI meng-meng. Effect of sodium hexametaphosphate on the separation of rhodochrosite from calcite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(11): 3214-3220.
[21] HELLE UGILT S, DiEKE P, RASMUS J, FLEMMING L. Sorption of phosphate onto calcite; results from batch experiments and surface complexation modeling[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2011, 75: 2911-2923.
[22] 朱玉霜, 朱建光. 浮选药剂的化学原理[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1996: 55-84.
ZHU Yu-shuang, ZHU Jian-guang. Chemical Principle of flotation reagents[M]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology Press, 1996: 55-84.
[23] 邱冠周, 胡岳华, 王淀佐. 颗粒间相互作用与细粒浮选[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1993: 1-434.
QIU Guan-zhou, HU Yue-hua, WANG Dian-zuo. Interactions between partilces and flotation of fine particles[M]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology Press, 1993: 1-434.
[24] 沈慧庭, 宫中贵. 白钨矿浮选中方解石的影响及消除影响的方法和机理研究[J]. 湖南有色金属, 1996, 12(2): 32-36.
SHEN Hui-ting, GONG Zhong-gui. The mechanism and method to eliminate the influence of calcite on scheelite flotation[J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 1996, 12(2): 32-36.
[25] 王淀佐, 胡岳华. 浮选溶液化学[M]. 长沙: 湖南科技出版社, 1987: 1-260.
WANG Dian-zuo, HU Yue-hua. Flotation solution chemistry[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1987: 1-260.
[26] ATADEMIR M R, KITCGEBER J A, SHERGOLD H L.The surface chemistry and flotation of scheelite I. Solubility and surface characteristics of precipitated calcium tungstate[J]. Jounal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1979, 71(3): 466-476.
Effect and mechanism of co-depressant of calcite and sodium hexametaphosphate on scheelite flotation
WANG Ji-zhen1, 2, YIN Wan-zhong2, SUN Zhong-mei3
(1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an 710054, China;
2. School of Resource and Civil Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Comprehensive Utilization of Low Grade Refractory Gold Resources, Shanghang 364200, China)
Abstract: The depressing effect of sodium hexametaphosphate and calcite on scheelite recovery was studied by flotation tests, dissolution measurements and theoretical calculation. The results indicate that the synergistic effect existed between sodium hexametaphosphate and calcite has significant depressing effect on the scheelite flotation. Calcite will enhance the depression of sodium hexametaphosphate with the action of calcium ions on its surface. The carbonate ions have little effect on the depressing effect of sodium hexametaphosphate, instead, the presence of excess carbonate ions can decrease the synergistic depressing effect of calcite and sodium hexametaphosphate on scheelite flotation. The sodium hexametaphosphate can not only react with the scheelite, but also it will deadsorb the calcium ions of calcite, thus increases the calcium ions concentration in solution, which is benefit to the depression of scheelite flotation.
Key words: scheelite; calcite; sodium hexametaphosphate; calcium ions; flotation
Foundation item: Project(51374079) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2017JQ5090) supported by Basic Research Plan of Shanxi Natural Science, China; Project(201624) supported by the Xi’an University of Science and Technology Foundation for Fostering, China
Received date: 2017-08-24; Accepted date: 2018-01-16
Corresponding author: WANG Ji-zhen; Tel: +86-13201871689; E-mail: jizhenwang@126.com
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51374079);陕西省自然科学基础研究计划(2017JQ5090);西安科技大学校级培育基金项目(201624)
收稿日期:2017-08-24;修订日期:2018-01-16
通信作者:王纪镇,讲师,博士;电话:13201871689;E-mail: jizhenwang@126.com
摘 要:通过浮选试验、离子浓度测定、动电位测定和理论计算等方法研究了方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的影响。结果表明:六偏磷酸钠与方解石存在协同作用,可强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用;方解石主要通过钙离子强化六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的抑制作用,碳酸根离子不影响六偏磷酸钠的抑制性能,过量碳酸根离子的存在反而能够减弱方解石和六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿的协同抑制作用。机理研究表明,方解石表面的钙离子在六偏磷酸钠的作用下可解吸至溶液中,增加溶液中的钙离子浓度,使六偏磷酸钠对白钨矿浮选的抑制作用增强。
[4] 朱海玲, 覃文庆, 陈 臣, 刘瑞增. 阴-非离子复配表面活性剂对白钨矿的低温捕收性能及其应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(10): 2188-2196.
[6] 孙 伟, 胡岳华, 覃文庆, 徐 竟. 钨矿浮选药剂研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与用, 2000(3): 42-46.
[12] 张 英, 胡岳华, 王毓华, 文书明. 硅酸钠对含钙矿物浮选行为的影响及作用机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(9): 2366-2372.
[13] 孙 伟, 宋韶博. 水玻璃及其在白钨矿浮选中的应用和分析[J]. 中国钨业, 2013, 28(4): 22-25.
[14] 邱廷省, 宋宜富, 邱仙辉, 李晓波. 白钨矿浮选体系中大分子有机抑制剂的抑制性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(7): 1527-1534.
[15] 张 英. 白钨矿与含钙脉石矿物浮选分离抑制剂的性能与作用机理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
[17] 于 洋, 孙传尧, 卢烁十. 白钨矿与含钙矿物可浮性研究及晶体化学分析[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2013, 42(2): 278-283, 313.
[18] 冯其明, 周清波, 张国范, 卢毅屏, 杨少燕. 六偏磷酸钠对方解石的抑制机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(2): 436-441.
[20] 罗 娜, 张国范, 朱阳戈, 崔萌萌. 六偏磷酸钠对菱锰矿与方解石浮选分离的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(11): 3214-3220.
[22] 朱玉霜, 朱建光. 浮选药剂的化学原理[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1996: 55-84.
[23] 邱冠周, 胡岳华, 王淀佐. 颗粒间相互作用与细粒浮选[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1993: 1-434.
[24] 沈慧庭, 宫中贵. 白钨矿浮选中方解石的影响及消除影响的方法和机理研究[J]. 湖南有色金属, 1996, 12(2): 32-36.


