网络首发时间: 2019-12-19 11:05
白钨矿捕收剂FX-6的浮选作用机制研究
中南大学资源加工与生物工程学院
长沙矿冶研究院有限责任公司
摘 要:
以常规白钨矿捕收剂油酸钠(NaOL)作为参照,对白钨捕收剂FX-6的性能和作用机制进行研究。首先通过单矿物浮选试验和人工混合矿浮选分离试验分别考查FX-6对3种含钙矿物的捕收能力和选择性,然后对江西修水香炉山钨矿白钨矿浮选原矿进行浮选试验,对FX-6的实际使用效果进行研究。最后,通过红外光谱检测和药剂吸附量测定,对FX-6的作用机制进行初步的探讨。试验结果表明,在pH=9.5±0.1,捕收剂FX-6浓度(CFX-6)为150 mg·L-1的条件下,FX-6的捕收能力大小顺序为:白钨矿>萤石>方解石;在硅酸钠作抑制剂的浮选体系下,白钨矿与萤石可以实现高效的分离,混合矿中含有方解石时,分离效果一般。针对香炉山白钨矿,选用FX-6作捕收剂时,取得了最终白钨精矿WO3含量69.86%,回收率89.95%的良好指标。FX-6在白钨矿表面产生较强化学吸附,在较宽的pH值范围内,FX-6都能有效吸附在白钨矿表面;硅酸钠会影响捕收剂在矿物表面的吸附,从而强化3种含钙矿物的浮选分离。FX-6对原矿中萤石含量较高的白钨矿分选具有较大的潜力;同时,为香炉山白钨矿浮选提供了一种捕收剂选择。
关键词:
中图分类号: TD923.13;TD954
作者简介:张政权(1995-),男,河南新乡人,硕士,研究方向:矿物浮选工艺及药剂,E-mail:zzq0501@126.com;;*焦芬,副教授,电话:13549683403,E-mail:jfen0601@126.com;
收稿日期:2019-06-25
基金:中南大学研究生科研创新项目(2019zzts696);中南大学研究生科研创新项目(2018zzts224);湖南省战略含钙矿产资源清洁高效利用重点实验室项目(2018TP1002)资助;
Flotation Mechanism of Scheelite Collector FX-6
Zhang Zhengquan Jiao Fen Qin Wenqing Li Maolin Wang Xu Li Wei
School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering,Central South University
Changsha Research Institute of Mining and Metallurgy Co.,Ltd.
Abstract:
The flotation mechanism of the common collector FX-6 in scheelite has not been elucidated. In this paper,the flotation performance of the collector FX-6 and sodium oleate(NaOL)on scheelite,fluorite and calcite were studied,and the real ore experiments on the scheelite was investigated. The flotation behavior of scheelite,fluorite and calcite using FX-6 as the collector was studied through single-mineral flotation tests and the artificial mixed flotation of three calcium-containing minerals. The results showed the collecting capacity and selectivity of the collector FX-6 and was compared with that of NaOL. Through infrared spectroscopy and according to the position of the characteristic peaks of the functional groups of each agent,the adsorption forms of FX-6 and NaOL on the surface of scheelite,fluorite,and calcite were characterized. And the physical adsorption or chemical adsorption was determined by the infrared spectroscopy. According to the Lambert-Beer law,the residual concentration method was used to determine the adsorption capacity on the surface of the mineral,and the adsorption capacity of FX-6 and NaOL on scheelite,fluorite and calcite under different pH conditions was calculated according to the standard curve. Finally,FX-6 and NaOL were used in the flotation separation test of Xianglushan tungsten mine in Xiushui,Jiangxi,and the application effect was investigated. The micro-flotation test showed that FX-6 had a stronger collecting capacity than NaOL without depressant,and the suitable pH for scheelite flotation was wider. However,it was difficult to effectively separate scheelite from fluorite and calcite in the absence of depressant. In the system of sodium silicate as the depressant,the inhibition effect of sodium silicate on fluorite was the strongest,followed by calcite,and the inhibition effect of scheelite was relatively weak at pH 9.5±0.1. Fluorite was almost completely inhibited,followed by calcite and scheelite when the concentration of sodium silicate was 6×10-3 mol·L-1 and the concentration of FX-6 was 150 mg·L-1. The flotation separation test of artificial mixed minerals showed that the flotation separation effect of NaOL and FX-6 was similar,and the flotation separation effect of FX-6 was slightly better in the system of scheelite-calcite. The scheelite and fluorite could be separated better whether NaOL or FX-6 was used,but the flotation separation effect of FX-6 was better than that of NaOL in the system of scheelite-fluorite. For artificial mixed minerals of containing three calcium-containing minerals at the same time,the collecting effect of FX-6 on scheelite was better than that of NaOL,but it made a certain amount of calcite float into the foam product. The infrared spectroscopy test results showed that the functional groups of collector FX-6 were carboxylic acid group and hydroxyl group. After adding the collector NaOL and FX-6,the vibration absorption peaks of the functional groups of the two collectors had shifted. It showed that chemical adsorption occurred on the surface of scheelite. After NaOL reacted with fluorite and calcite,the functional groups of carboxylic acid group and hydroxyl group shifted to different degrees,indicating that NaOL chemically adsorbed on the surface of fluorite and calcite. After FX-6 interacted with fluorite and calcite separately,C-H stretching vibration peak appeared on the surface of the mineral,while the positions of the absorption peaks of the functional group carboxylic acid group and hydroxyl group did not change,which proved that NaOL was physically adsorbed on the surface of fluorite and calcite. The adsorption amount of the agent on the mineral surface showed that with the increase of pH,the adsorption amount of NaOL and FX-6 on the surface of scheelite,fluorite,and calcite gradually increased,and with the increase of sodium silicate concentration,the adsorption capacity of NaOL and FX-6 on the surface of the three minerals gradually decreased. The results indicated that the inhibiting effect of sodium silicate on scheelite,calcite,and fluorite increased in turn. From the results of the closed-circuit flotation test of scheelite ore,when NaOL was used as a collector,the final WO3 content of scheelite concentrate was 66.81%,and the recovery of WO3 was 89.09%;when FX-6 was used as a collector,the final WO3 content of scheelite concentrate was 69.86%,and the recovery was 89.95%. Compared with NaOL as a collector,the final concentrate obtained with FX-6 had a WO3 content of 3.05% higher and a WO3 recovery rate of 0.86% higher. In a wide pH range,the collecting capacity of FX-6 for scheelite was greater than that of fluorite and calcite. FX-6 had relatively similar collecting capacity for three calcium-containing minerals. Under the flotation system with sodium silicate as depressant,it could achieve efficient separation of scheelite and fluorite. When the mixed mineral contained calcite,the separation effect was poor. Compared with the conventional collector NaOL,FX-6 had stronger collecting ability and selectivity. Collector FX-6 was chemically adsorbed on the surface of scheelite,and it could be effectively adsorbed on the surface of scheelite in a wide range of pH of the slurry and make it float. Sodium silicate was added to expand the adsorption of the collector on the mineral surface. The difference of adsorption amount helped the flotation separation of the three minerals. In the flotation of scheelite,FX-6 had stronger collecting capacity and selectivity than NaOL,and the content and recovery of WO3 in the final scheelite concentrate were higher.
Keyword:
FX-6; scheelite; calcium mineral; flotation;
Received: 2019-06-25
中国的钨资源储量丰富,占据世界总储量的66%以上,远高于其他国家和地区
随着优质白钨资源的减少,白钨资源开发利用的技术要求逐步提高。白钨捕收剂是白钨矿浮选的一项重要研究内容
1实验
1.1试样制备
试验所用白钨矿、萤石和方解石分别产自四川省、湖南省、湖南省,单矿物样品由块矿经锤碎、人工挑选、陶瓷球磨机磨矿后制得,筛分得到的-0.074~+0.038 mm粒级的矿样供单矿物试验使用,-0.038 mm粒级的矿样供分析测试使用。所有单矿物化学分析结果如表1所示,单矿物样品纯度能够达到试验要求。
表1 单矿物化学分析结果 下载原图
Table 1 Chemical analysis results of single minerals(%,mass fraction)
1.2研究方法
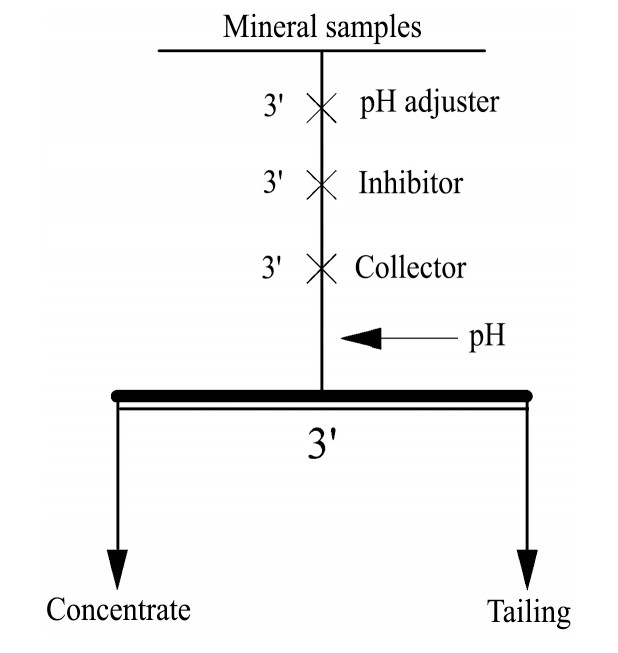
1.单矿物浮选试验。在室温下,选用XFG型挂槽式浮选机进行单矿物浮选试验,浮选机转数定为1800 r·min-1。称量2.0 g单矿物样品放进80 ml浮选槽内,加入75 ml去离子水调浆,用Na OH或H2SO4调整矿浆p H值,根据需要添加抑制剂水玻璃,加捕收剂后测定矿浆p H值,刮泡3 min。将浮选得到的泡沫产品和槽内产品分别烘干、称重并计算其回收率。试验流程见图1。
2. 人工混合矿浮选分离试验。人工混合矿同样采用XFG挂槽式浮选机进行浮选试验,浮选温度及浮选机参数不变。人工混合矿由各种单矿物样品按照不同比例混合,称取2.0 g人工混合矿放进80 ml浮选槽内,加入75 ml去离子水调浆,用H2SO4或Na OH调节矿浆p H值,按顺序依次加入抑制剂、捕收剂,加捕收剂后测定矿浆p H值,刮泡3min。将浮选得到的泡沫产品和槽内产品分别烘干、称重、化验并计算其回收率。试验流程见图1。
3.红外光谱分析。主要依据样品表面对不同波长红外光的吸收程度的差异,来分析和研究物质的分子组成和分子结构。红外光谱测试矿物样品的处理方式:取-0.038 mm粒级的单矿物样品2.0 g,经三头玛瑙研磨机研磨至-2μm,用H2SO4或Na OH调整矿浆p H值,加入相应的药剂后强烈搅拌20 min,使矿物与药剂充分作用后进行过滤,并用同样p H值的蒸馏水洗涤若干次,在真空干燥箱中40℃恒温干燥后进行红外光谱测定。
4.药剂吸附量测定。本试验根据朗伯-比尔定律,采用剩余浓度法测量药剂吸附量。使用紫外分光光度计,在特征波长下,测出不同药剂浓度溶液的吸光度,测定3次取平均值,绘制药剂浓度与吸光度的标准曲线。每次称取2 g单矿物样品,置于75 ml去离子水中,依次添加相应药剂,通过磁力搅拌器搅拌15 min后静置,待单矿物样品沉淀,抽取少量上层清液,使用高速离心机离心10 min,测定相同波长条件下离心后上清液的吸光度,对照标准曲线计算得到药剂在矿物表面的吸附量。
图1 浮选试验流程图
Fig.1 Flowsheet of flotation experiment
2结果与讨论
2.1 FX-6的捕收性能
捕收剂的捕收性能主要包括其对矿物的捕收能力和选择性。选择常用的白钨矿捕收剂Na OL作为对比,分别进行有无抑制剂硅酸钠存在条件下的单矿物试验以及人工混合矿浮选分离试验,研究FX-6对白钨矿、萤石和方解石的捕收能力及选择性。
2.1.1 无抑制剂体系单矿物浮选试验
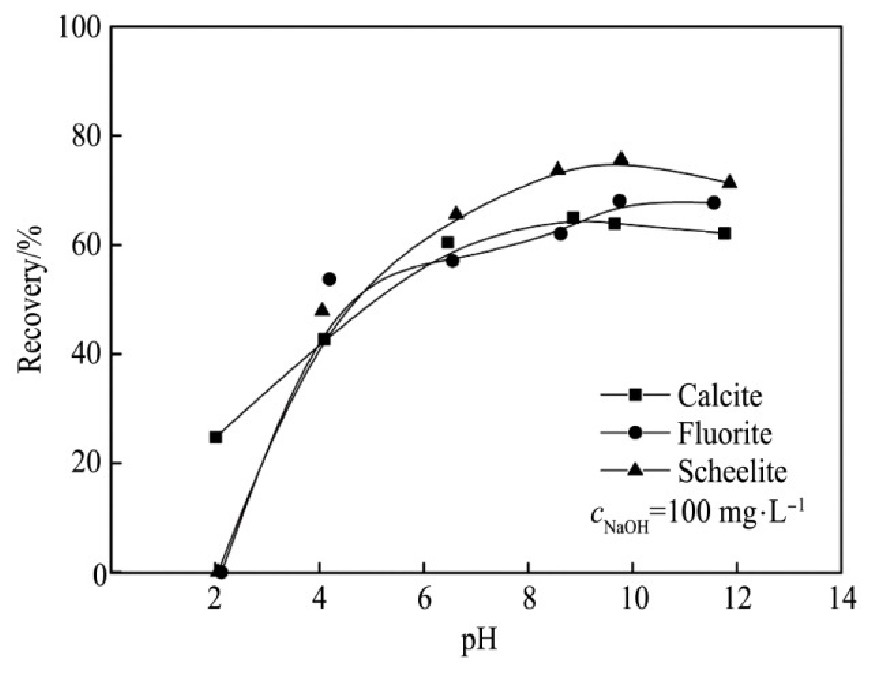
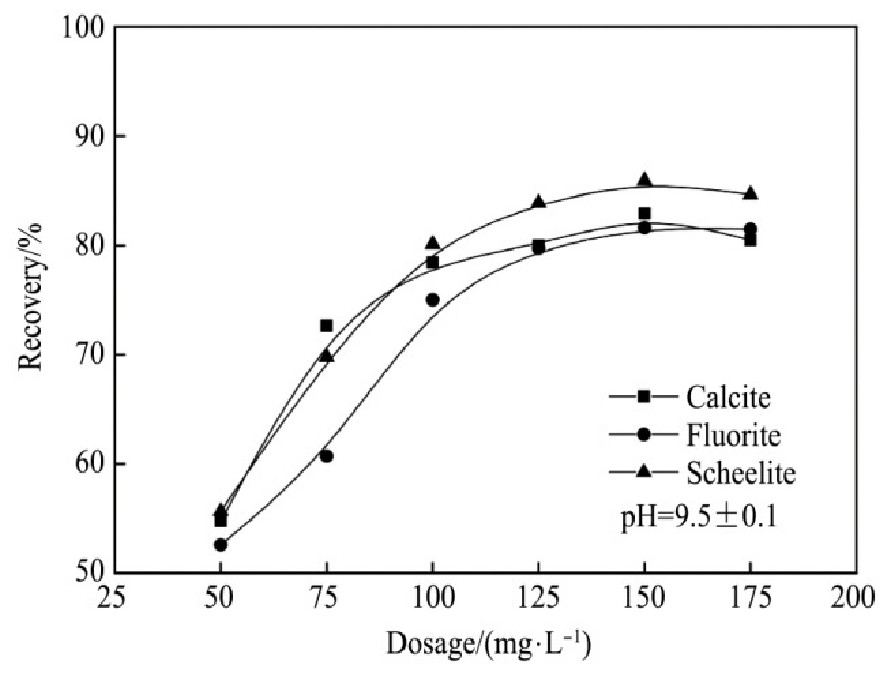
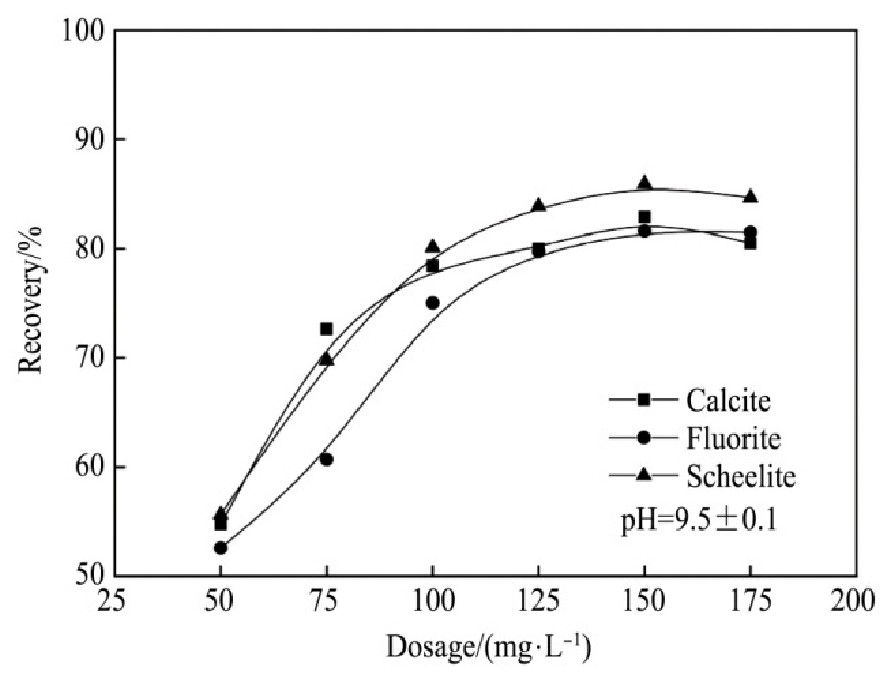
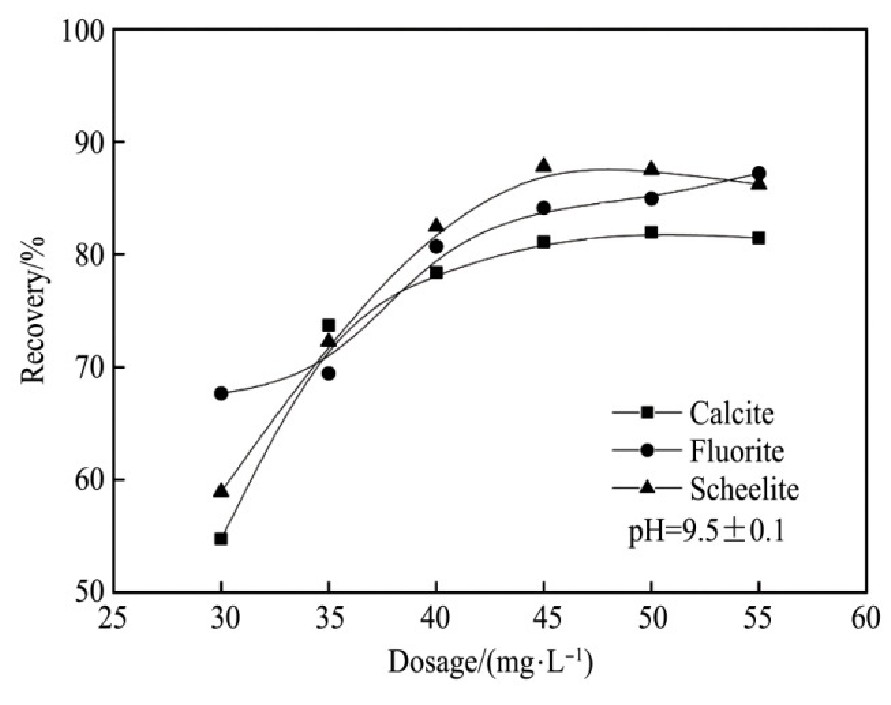
不添加抑制剂时,FX-6与Na OL对3种单矿物的捕收能力与矿浆p H值以及药剂用量的关系见图2~5。
由试验结果可知:
1.当p H值在2左右时,FX-6和Na OL对白钨矿和萤石未表现出捕收能力。FX-6对方解石的捕收能力在p H=7.5~8.5时较好,Na OL对方解石的捕收能力在p H=8~9时较强。FX-6和Na OL对萤石的捕收能力在p H>10时较强。Na OL对白钨矿的捕收能力在p H=9~11较强,FX-6对白钨矿的捕收能力在p H=8~11时较好,浮选适宜p H值范围较Na OL广。
图2 p H对Na OL捕收能力的影响
Fig.2 Effects of p H on collecting capability of Na OL
图3 Na OL用量对捕收能力的影响
Fig.3 Effects of dosage on collecting capability of Na OL
图4 p H对FX-6捕收能力的影响
Fig.4 Effects of p H on collecting capability of FX-6
图5 FX-6用量对捕收能力的影响
Fig.5 Effects of dosage on collecting capability of FX-6
2.当Na OL用量为150 mg·L-1时,对白钨矿的捕收能力达到较大值,此时白钨矿的回收率为85.93%,继续增加用量,白钨矿回收率没有明显上升趋势;当FX-6用量大于125 mg·L-1后,白钨矿的回收率达到较大值为87.80%,继续增加用量,白钨矿回收率无明显上升趋势。
3.与Na OL相比,FX-6的捕收能力相对较强。两种捕收剂对3种含钙矿物都有一定的捕收能力,若仅采用Na OL或FX-6作捕收剂,难以将白钨矿与另外两种含钙矿物进行有效地浮选分离,须添加适量的抑制剂。
2.1.2 硅酸钠体系单矿物浮选试验
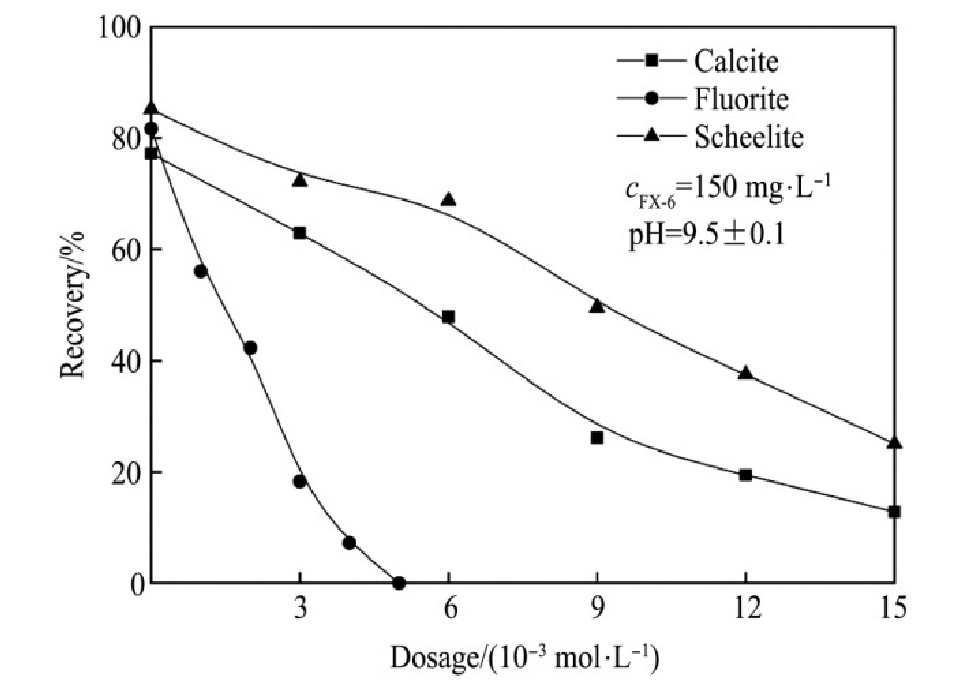
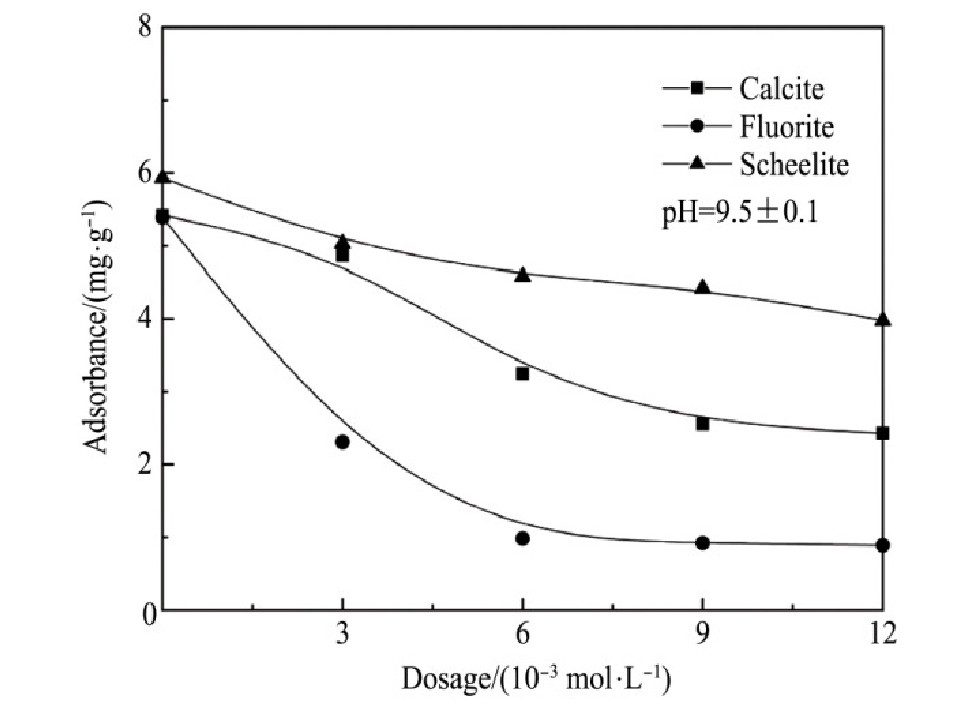
加入硅酸钠作为抑制剂,控制矿浆的p H值9.5±0.1,研究不同硅酸钠用量对两种捕收剂捕收能力的影响,见图6~7。由试验结果可知:
1.硅酸钠对萤石的抑制作用最强,其次是方解石,对白钨矿的抑制作用相对较弱。因此,可以通过加入硅酸钠强化3种含钙矿物的分离。
图6 硅酸钠用量对Na OL捕收能力的影响
Fig.6 Effects of dosage of sodium silicate on collecting capa-bility of Na OL
图7 硅酸钠用量对FX-6捕收能力的影响
Fig.7 Effects of dosage of sodium silicate on collecting capa-bility of FX-6
2.在p H值为9.5左右,硅酸钠用量为6×10-3mol·L-1,Na OL与FX-6用量在150 mg·L-1的情况下,萤石几乎完全受到抑制,其次是方解石,白钨矿受硅酸钠抑制作用最小。
2.1.3 人工混合矿浮选分离试验
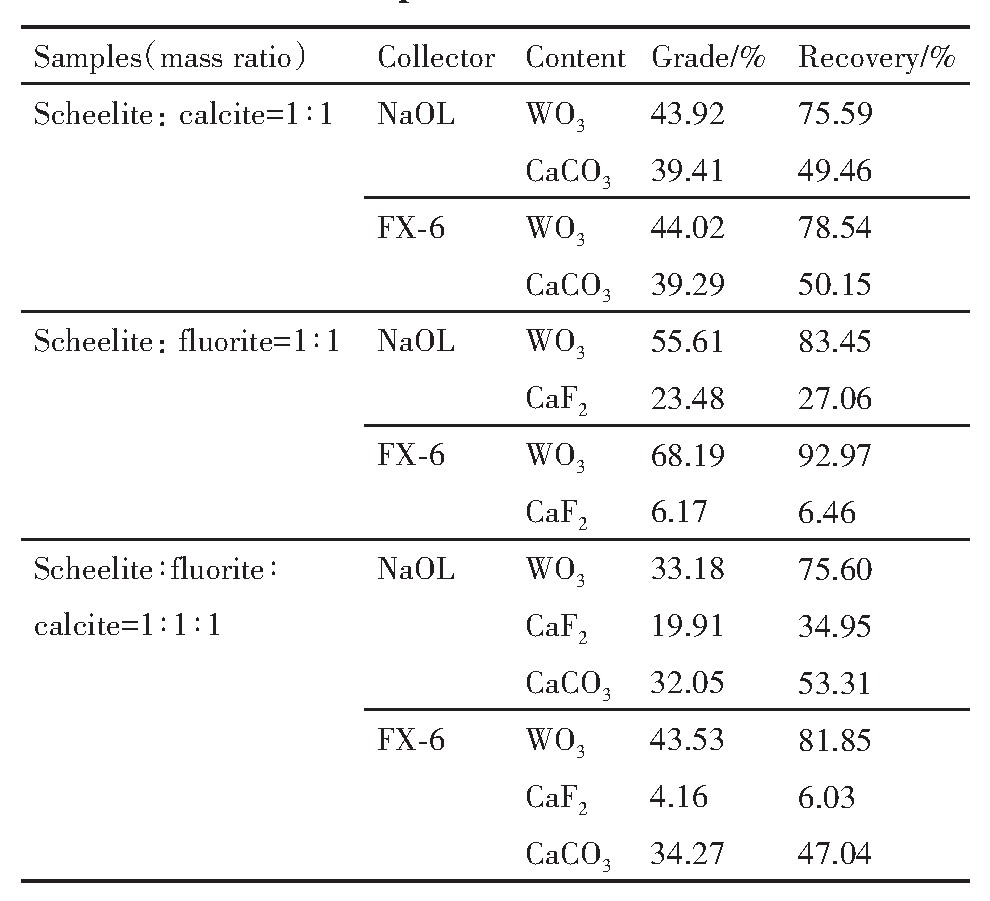
进行人工混合矿浮选分离试验,对FX-6的选择性进行研究。控制矿浆p H值在9.5±0.1,硅酸钠用量为6×10-3mol·L-1,捕收剂用量为150 mg·L-1。分别考察两种捕收剂对不同类型人工混合矿的浮选分离效果,对泡沫产品中WO3与Ca CO3的含量进行化学分析,并对其回收率进行了计算,结果见表2。
从表2可知,对于白钨矿-方解石类型的人工混合矿,Na OL与FX-6浮选分离白钨矿效果相当,FX-6分离效果略好。对于白钨矿-萤石类型的人工混合矿,无论使用Na OL还是FX-6都能使白钨矿和萤石实现相对较好的分离,但FX-6浮选分离效果优于Na OL。对于同时含有3种含钙矿物的人工混合矿,FX-6对白钨矿的捕收效果优于Na OL,但都使一定量的方解石上浮进入到泡沫产品中。总体来说,捕收剂FX-6浮选分离效果要优于Na OL,特别针对白钨-萤石型人工混合矿浮选分离效果最佳。同时可以看出,当人工混合矿中含有方解石时,分离难度较大。两种捕收剂在硅酸钠作抑制剂的体系下,FX-6对白钨矿的选择性略好于Na OL。
表2 人工混合矿浮选分离试验结果 下载原图
Table2 Results of experiments of artificial mixed miner-als flotation separation
2.2 捕收剂作用机制分析
通过红外光谱分析和药剂吸附量的测定等方法,对FX-6在3种含钙矿物表面的作用机制进行初步研究和探讨。
2.2.1 红外光谱分析
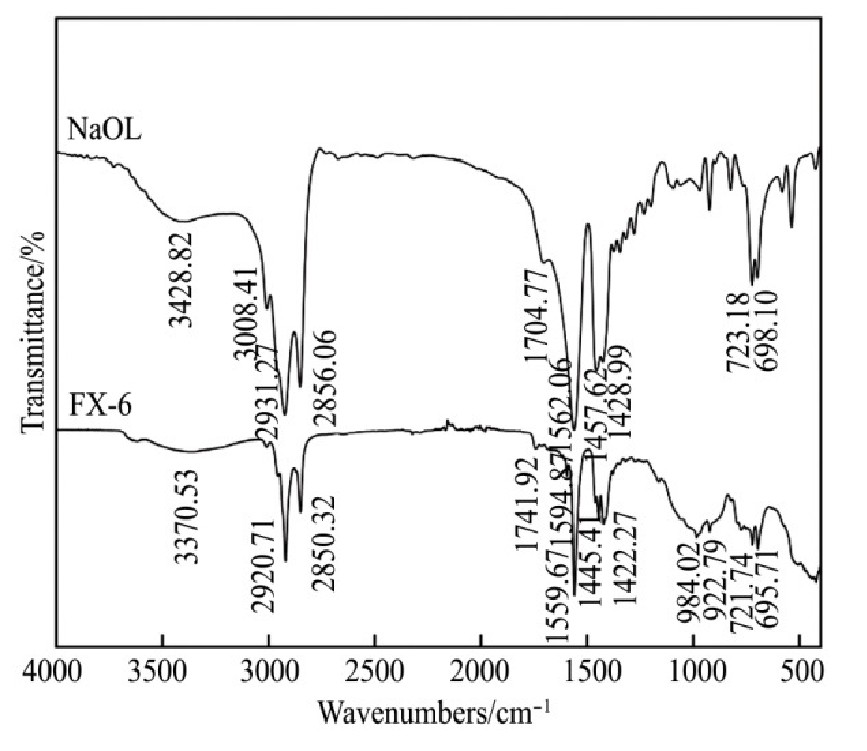
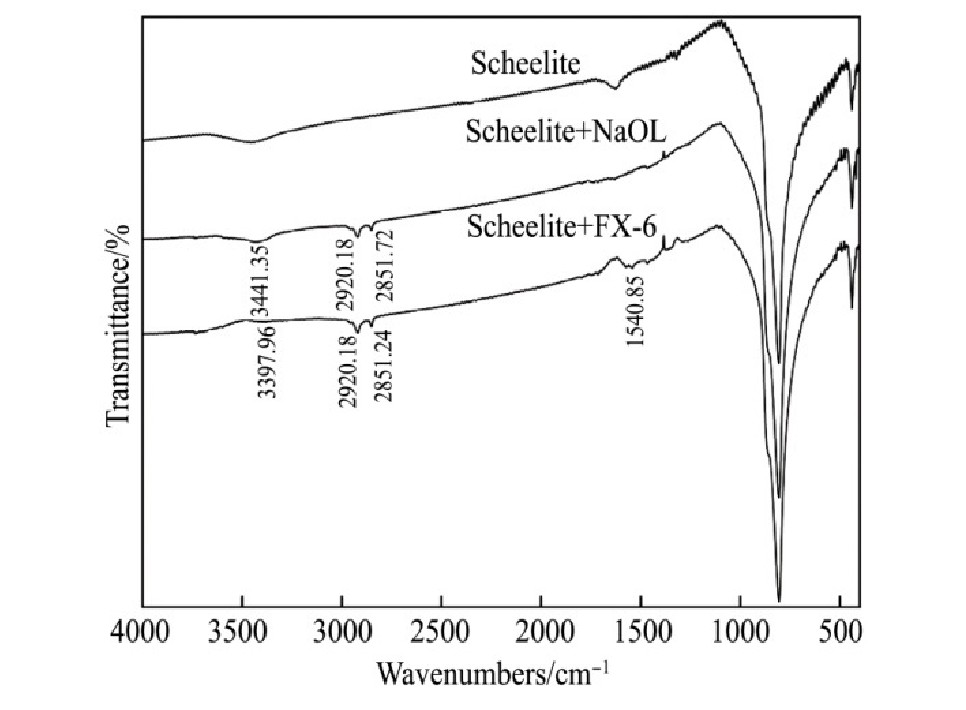
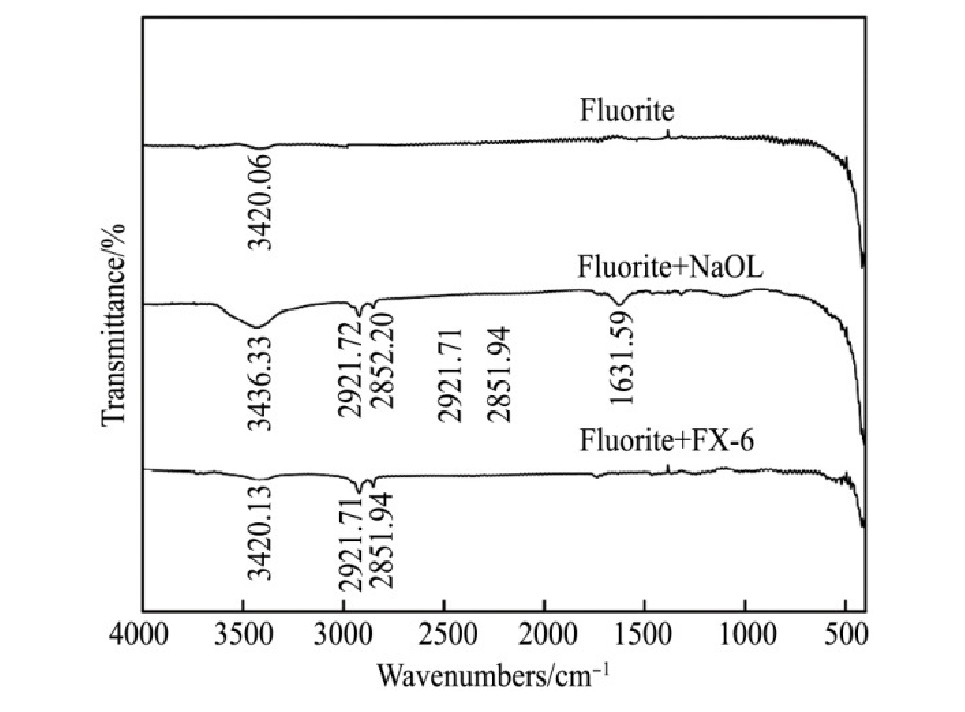
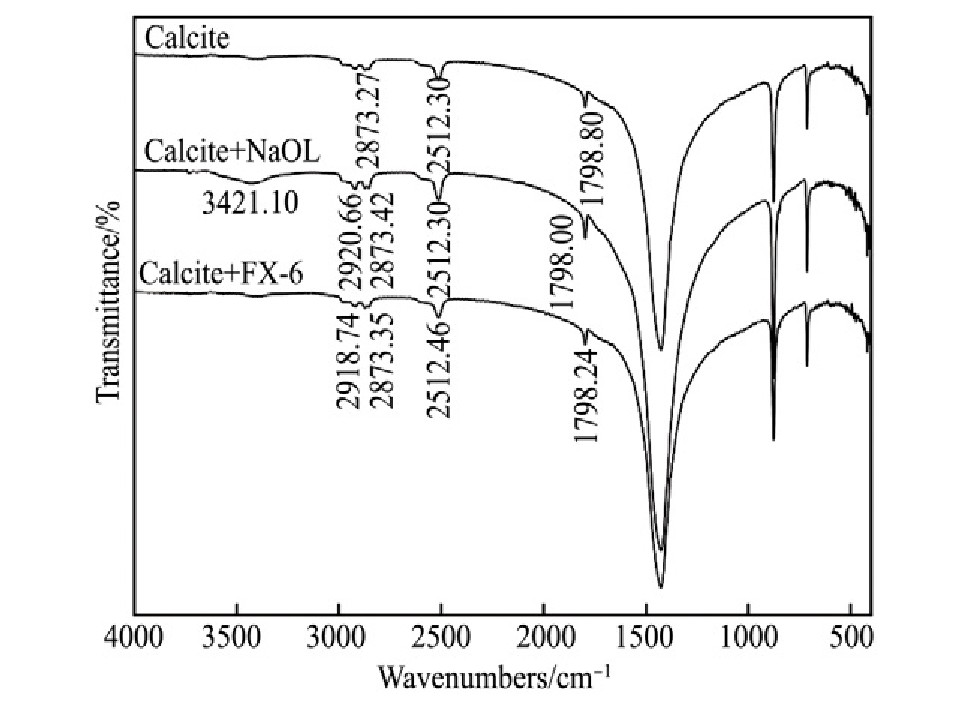
Na OL与FX-6的红外光谱见图8。3种含钙矿物和Na OL与FX-6作用前后的红外光谱见图9~11。
由图8可知,Na OL在2931.27和2856.06 cm-1处分别出现甲基和亚甲基中的C-H键对称伸缩振动吸收峰;在1562.06 cm-1处出现COO-的不对称伸缩振动吸收峰,在1457.62和1428.99 cm-1处出现COO-的对称伸缩振动吸收峰,在1704.77 cm-1处出现C=O键的伸缩振动吸收峰;在3428.82 cm-1处出现O-H键的缔合伸缩振动吸收峰,在723.18和698.10 cm-1出现O-H键的面外弯曲振动吸收峰。FX-6在2920.71和2850.32 cm-1处分别出现甲基和亚甲基中的C-H键不对称伸缩振动和对称伸缩振动吸收峰;在1559.67 cm-1处出现COO-的不对称伸缩振动吸收峰,在1422.27 cm-1处出现COO-的对称伸缩振动吸收峰;在3370.53和922.79cm-1出现O-H键的缔合伸缩振动吸收峰和面外弯曲振动吸收峰,表明FX-6含有官能团羧酸基和羟基。
图8 捕收剂红外光谱图
Fig.8 Infrared spectra of collector
图9 捕收剂作用前后白钨矿红外光谱图
Fig.9 Infrared spectra of scheelite treated before and after ac-tion by collector
图1 0 捕收剂作用前后萤石红外光谱图
Fig.10 Infrared spectra of fluorite treated before and after ac-tion by collector
图1 1 捕收剂作用前后方解石红外光谱图
Fig.11 Infrared spectra of calcite treated before and after ac-tion by collector
由图9~11可知,与捕收剂作用后,3种矿物表面均出现C-H键不对称伸缩振动吸收峰和C-H键对称伸缩振动吸收峰,说明Na OL和FX-6在3种矿物表面吸附。白钨矿与Na OL作用后,在3441.35cm-1处出现O-H键伸缩振动吸收峰,与Na OL相比偏移12.53 cm-1,说明Na OL在白钨矿表面发生化学吸附;白钨矿与FX-6作用后,在3397.96和1540.85 cm-1两处分别出现O-H键伸缩振动吸收峰、COO-中C-O不对称伸缩振动吸收峰,与FX-6相比分别偏移27.43,18.82 cm-1,同样出现化学吸附。萤石与Na OL作用后,在1631.59 cm-1处出现了COO-中的C=O的伸缩振动吸收峰,与Na OL相比偏移73.16 cm-1,同时萤石在3420.06 cm-1处的特征峰偏移16.27 cm-1,可能是Na OL与萤石产生氢键作用,说明Na OL在萤石表面发生化学吸附;萤石与FX-6作用后,未出现FX-6的特征官能团吸收峰,在萤石表面发生物理吸附。方解石与Na OL作用后,在3421.10 cm-1处出现O-H键伸缩振动吸收峰,说明Na OL在其表面发生化学吸附;方解石与FX-6作用之后,未出现FX-6特征官能团吸收峰,发生物理吸附。解释了单矿物和人工混合矿浮选试验中,FX-6对白钨矿具有良好的捕收能力和选择性。
2.2.2 捕收剂在单矿物表面的吸附量测定
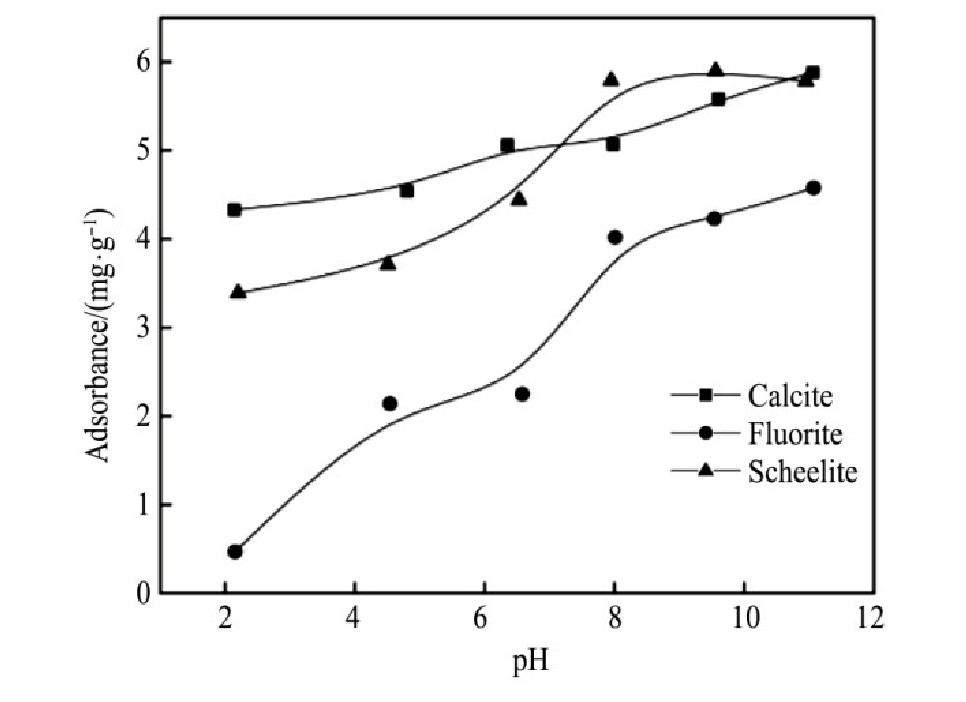
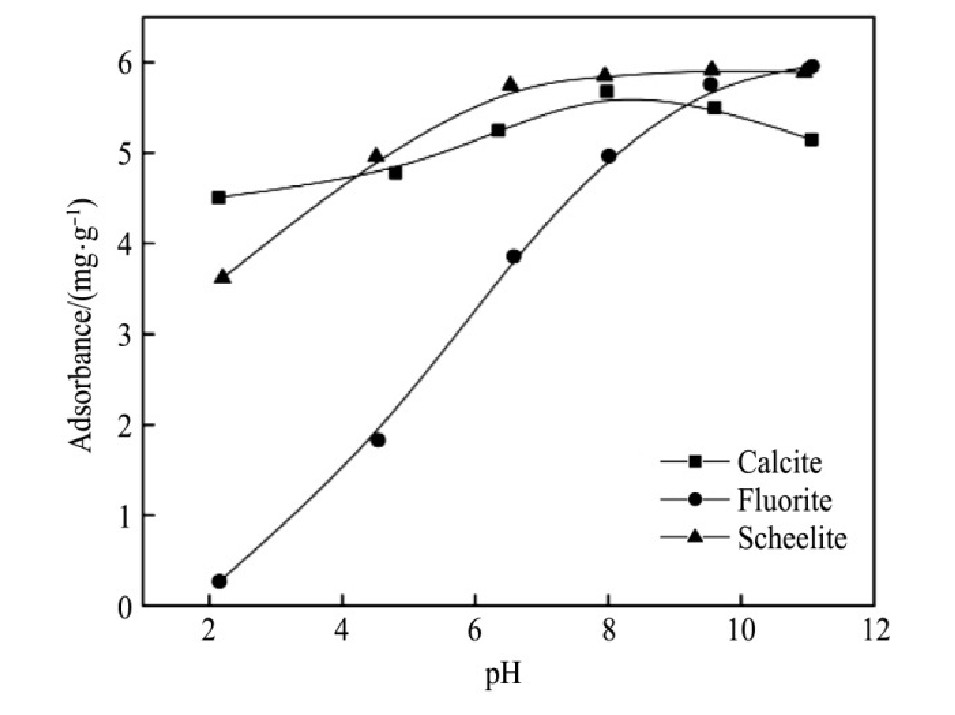
测定两种捕收剂在不同矿浆p H值条件下的吸附量,考查其作用效果。矿浆中捕收剂的初始浓度为150mg·L-1,根据作用前后药剂浓度差异得到其吸附量,结果如图12~13所示。
由结果可知,不同矿浆p H值条件下,Na OL在萤石表面的吸附量均低于在方解石和白钨矿表面的吸附量;Na OL在方解石和白钨矿表面的吸附量随矿浆p H值变化趋势较为接近,在矿浆p H=7~11的范围内,Na OL在白钨矿表面的吸附量高于其他两种矿物表面的吸附量。随着矿浆p H值上升,FX-6在萤石表面的吸附量有上升趋势;FX-6在方解石和白钨矿表面的吸附量较为接近,在矿浆p H=4~11时,FX-6在白钨矿表面的吸附量大于其它两种矿物表面的吸附量,此时FX-6在白钨矿表面有较强的作用。结合单矿物浮选试验可知,当捕收剂在矿物表面的吸附量较大时,其在矿物表面的作用较为强烈,此时对应矿物的回收率也相对较高;两种捕收剂在普遍的矿浆p H值条件下,在白钨矿和方解石表面的吸附量较为接近,在一定程度上说明了含有白钨矿与方解石的人工混合矿较难浮选分离;同时,在较宽的p H值范围内,FX-6都可以在白钨矿表面进行良好的吸附,有效地作用在白钨矿表面,解释了单矿物试验中FX-6在较宽的p H值范围内,对白钨矿具有较强的捕收能力。
图1 2 p H对Na OL在矿物表面吸附量的影响
Fig.12 Effect of p H on adsorbtion of Na OL on minerals sur-face
图1 3 p H对FX-6在矿物表面吸附量的影响
Fig.13 Effect of p H on adsorbtion of FX-6 on minerals surface
硅酸钠作抑制剂时,两种捕收剂对3种矿物的捕收效果均受到了不同程度的抑制,因此,考查硅酸钠用量对两种捕收剂在矿物表面吸附量的影响。矿浆中捕收剂的初始浓度仍为150 mg·L-1。测定结果见图14~15。
由结果可知,硅酸钠阻碍了Na OL和FX-6在矿物表面的吸附,随着硅酸钠用量的增大,阻碍作用增强。其中,硅酸钠对两种捕收剂在萤石表面吸附的阻碍作用最为强烈,随着硅酸钠用量的增大,吸附量急剧下降。硅酸钠对捕收剂在方解石表面抑制作用的影响要强于在白钨矿表面作用时的影响。进一步解释了人工混合矿分离浮选试验中,萤石得到了有效的抑制的原因,在硅酸钠浓度大于6×10-3mol·L-1时,捕收剂在萤石表面的吸附量已经下降到较低水平,继续增加用量,吸附量下降趋势不明显,而白钨矿和方解石表面的捕收剂吸附量仍缓慢下降。因此,加入硅酸钠后,捕收剂在3种矿物表面吸附量的差别增大,有益于三者的浮选分离。
图1 4 硅酸钠用量对Na OL在矿物表面吸附量的影响
Fig.14 Effect of dosage of sodium silicate on adsorbtion of Na OL on minerals surface
图1 5 硅酸钠用量对FX-6在矿物表面吸附量的影响
Fig.15 Effect of dosage of sodium silicate on adsorbtion of FX-6 on minerals surface
2.3实际矿石试验研究
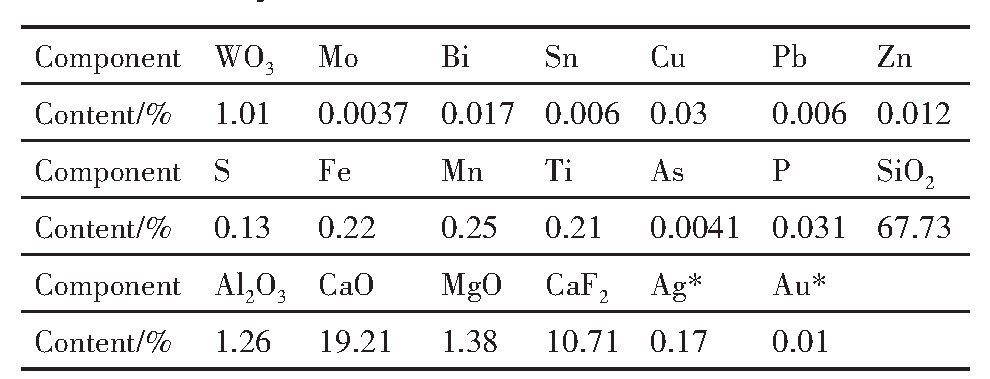
试验样品取自江西修水香炉山钨矿白钨矿浮选原矿。本试验以Na OL和FX-6作为对比,考察FX-6对香炉山钨矿中白钨的回收效果。浮选原矿多元素分析结果见表3,钨物相化学分析结果见表4。
由原矿多元素分析及钨物相分析结果可知,此次试样的WO3含量为1.01%,其中有回收利用价值的白钨矿中WO3含量为0.987%,占WO3总含量的97.72%,其余WO3赋存于少量的黑钨和钨华中,基本无回收利用价值。根据香炉山钨矿现场白钨浮选流程,采用常温粗选加加温精选流程,浮选原矿经过一粗、三扫、二精的常温粗选作业获得白钨粗精矿,然后白钨粗精矿经过一粗、三扫、四精的加温精选作业最终获得白钨精矿,所有中矿顺序返回。p H调整剂为碳酸钠,抑制剂为水玻璃,选取捕收剂用量为550 g·t-1,进行闭路试验。Na OL作捕收剂时,常温粗选闭路流程得到WO3回收率93.04%,WO3含量5.36%的粗精矿;FX-6作捕收剂时,常温粗选闭路流程得到WO3回收率93.45%,WO3含量5.54%的粗精矿。将粗精矿分别浓缩至60%的浓度,加温搅拌。当温度升至65℃时,加入氢氧化钠100 g·t-1,继续加热,当温度升至85℃时,加入水玻璃9000 g·t-1,温度升至90℃后,保温并搅拌35 min后进行浮选,最终闭路试验结果见表5。
表3 原矿多元素分析结果 下载原图
Table 3 Analysis results of multi-elements of ore
The unit of*is g·t-1
表4 钨物相分析结果 下载原图
Table 4 Tungsten phase analysis results

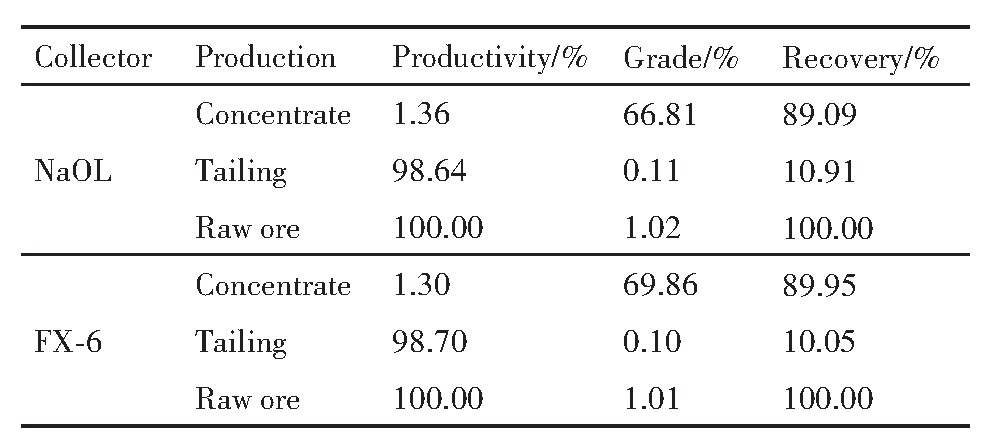
由表5可知,Na OL作捕收剂时,最终白钨精矿WO3含量为66.81%,WO3回收率为89.09%;FX-6作捕收剂时,最终白钨精矿WO3含量为69.86%,回收率为89.95%。相对于Na OL作捕收剂时,使用FX-6取得的最终精矿WO3含量高3.05%,WO3回收率高0.86%。
表5 闭路试验结果 下载原图
Table 5 Close flow test results
3结论
本论文通过对FX-6浮选性能和作用机制的研究,得到以下主要结论:
1.单矿物浮选试验和人工混合矿分离浮选结果显示,在较宽的p H值范围内,FX-6捕收剂对白钨矿的捕收能力要大于萤石和方解石;FX-6对3种含钙矿物的捕收能力较为接近,在硅酸钠作抑制剂的浮选体系下,可以实现白钨矿与萤石的高效分离,当混合矿中含有方解石时,分离效果较差。相对于常规的白钨捕收剂Na OL,FX-6的捕收能力和选择性都要更强。
2.红外光谱检测结果显示FX-6在白钨矿表面产生化学吸附。同时,由药剂吸附量测定可知,FX-6在较广泛的矿浆p H范围内都能够有效地吸附在白钨矿表面其进行捕收,加入硅酸钠扩大了捕收剂在矿物表面吸附量的差距,有助于3种矿物之间的分离。
3.采用FX-6作捕收剂,对江西香炉山白钨矿的浮选试验研究结果表明:闭路试验使用FX-6作捕收剂时,取得了最终白钨精矿WO3含量为69.86%,回收率为89.95%的较优指标。
参考文献