大规模采场三维探测及回采指标可视化计算
罗周全1,刘晓明1,张木毅2,姚 曙2,曹胜祥2,罗泽华2
(1. 中南大学 资源与安全工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 凡口铅锌矿,广东 韶关,512325)
摘 要:
摘 要:针对我国金属矿山大规模采场回采指标难以准确获取的现状,综合运用空区激光探测系统(CMS)和大型矿床三维软件Surpac等数字化工具,结合凡口铅锌矿N3-4采场实际,研究一种新颖的大规模采场回采指标可视化计算方法。采用CMS探测三维采场空区,以空区实测数据为基础运用Surpac构建采空区三维可视化模型,获取采场空区的三维形态和实际边界;运用采场设计资料,建立采场回采设计模型及矿岩边界模型,通过模型间的布尔运算,计算出采场存留矿量、回采总体积、采下废石量、采下充填体量、采下纯矿石量、回采总量及回采贫化率等,从而有效地实现了大规模采场回采指标的可视化计算。研究结果表明:采用该方法计算获得的采场回采指标可靠,可用于矿山实际生产管理和回采质量评估。
关键词:
中图分类号:TD853.391 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)06-1732-05
Stope 3D monitoring and its mining index visible calculation
LUO Zhou-quan1, LIU Xiao-ming1, ZHANG Mu-yi2, YAO Shu2, CAO Sheng-xiang2, LUO Ze-hua2
(1.School of Resources and Safety Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Fankou Lead-Zinc Mine, Shaoguan 512325, China)
Abstract: Aimed at the difficulty in gaining large-scale stope mining index accurately in domestic metal mines, and with the cavity monitoring system (CMS), mining 3D software Surpac, and the actual situation of stope N3-4 of Fankou Lead-Zinc Mine, a new visible calculation method of mining index for large stope was developed. Firstly, the stope vacancy was monitored using CMS, taking cavity measured data as foundation, cavity three-dimensional model of the stope opening was created using Surpac software and gain the stope three-dimensional configuration and the actual boundary accurately. Then, the stope designed model and ore-rock interface digital terrain model (DTM) were established according to the stope design material. Finally, using ore-rock interface DTM to cut cavity model or through Boolean calculation among the models, ore remains, mining total volume, mullock, backfilling, pure ore and dilution rate of stope N3-4 were calculated accurately, thus the large-scale stope mining index visible calculation was realized effectively. The practice indicates that the stope mining indexes obtained by this method are reliable and can be used in actual production management and mining quality appraisal.
Key words: cavity monitoring system; three-dimensional model; mining index; visible
对于采用深孔或中深孔大规模爆破采场开采的金属矿山,如何准确、有效地获取采场回采后的实际采矿总量、采下纯矿石量、采下废石量、存留矿石量以及回采贫化率、损失率等回采指标,对改进回采工艺和评价开采质量具有重要现实意义[1-4]。以前由于安全原因,测量人员难以进入采场空区进行实际测量,对于上述回采指标往往只能根据采矿设计,并结合经验进行简单估算,其结果往往与实际情况相差较大。为此,本文作者以凡口铅锌矿N3-4采场为实际研究对象,研究了一种新颖的大规模采场回采指标可视化计算方法。其基本技术思路是:运用空区激光精密探测系统(Cavity monitoring system,CMS)对采场空区进行三维探测,以空区实测数据为基础,运用三维矿业软件Surpac建立采空区的三维可视化模型,准确获取采场空区的三维形态和实际边界;运用采场设计资料,建立采场回采设计模型及矿岩边界模型;运用形成的矿岩边界模型对所建立的模型进行剖切或通过模型间的布尔运算,计算获取采场回采的总体积、采下废石量、采下充填体量、采下纯矿石量、回采总量及回采贫化率和损失率,从而有效地实现大规模采场回采指标的可视化计算,为矿山进一步改进采场大爆破回采工艺,提高开采质量提供可靠依据。
1 采场空区激光探测
1.1 采场概况
凡口铅锌矿N3-4采场为间柱采场,采场南北两帮分别为N3号和N4号采场的充填体,采场西头为F102断层,从断层往东至y=718控制线以内为采场长度范围。回采高度从-280 m二分段到-240 m中段平面,采场宽为8 m。底部到-280 m分段平面为充填体,顶部-240 m中段平面到-240 m一分段为充填体。采场内矿体形态简单,矿石的主要组成为块状致密状黄铁铅锌矿,松散黄铁铅锌矿在断层的破碎带中存在。块状黄铁铅锌矿平均密度为4.11 t/m3,围岩平均密度为2.74 t/m3,矿岩松散系数为1.4~1.6。矿凿岩性等级为Ⅴ~Ⅵ级,爆破性等级为Ⅳ~Ⅶ级。矿石为高硫矿石,易发热和结块。矿石中,Pb,Zn和S品位分别为6.04%, 10.70%和29.39%。
1.2 空区激光探测
空区激光探测系统是一种基于激光的空区三维探测系统,因其能准确测定井下采空区及其他洞室空间的三维形态而被广泛应用于国外金属地下矿山[5-8]。探测成果可直接用于计算空区体积,确定矿柱实际边界,指导空区充填、矿柱爆破设计、回采贫损控制以及空区稳定性分析等相关采矿管理和过程控制。CMS的基本构成包括激光扫描头、控制箱、手持式控制器、支撑杆架及数据处理软件[5]。CMS探测及其后处理基本流程如图1所示。
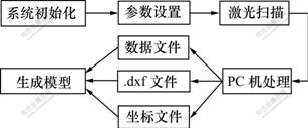
图1 CMS探测及后处理工作流程
Fig.1 Workflows of CMS and post-processing
2 采空区三维模型生成
CMS探测空区所获得的原始数据需采用CMS预处理软件CMSPosProcess进行处理,以形成“.dxf”格式的原始数据文件,该文件可被第3方软件Surpac和Gocad等接受,用以生成空区三维实体模型。
对空区原始探测数据进行处理后,运用Surpac生成采空区三维实体模型,具体方法如下:
a. 利用Surpac数据导入接口将“.dxf”格式文件转换成实体模型的“.DTM”格式文件;
b. 验证实体模型;
c. 若实体模型验证有错误,则转入步骤d,否则转入步骤e;
d. 重新进行原始探测数据的转换及处理,返回步骤e;
e. 利用Surpac的实体模型编辑工具对空区模型进行必要的编辑(通常采用实体模型布尔运算的方法对空区旁的巷道部分进行切割处理);
f. 再次验证修改后的实体模型,若错误则返回步骤e,再次编辑模型,反之,完成采空区三维模型构建[9-16]。图2所示为用大型矿山三维软件Surpac生成的凡口铅锌矿N3-4采场空区三维模型。

图2 N3-4采场空区三维模型
Fig.2 Three-dimensional cavity model of N3-4 stope
3 采场回采指标计算
3.1 存留矿石量计算
一般地,采用大爆破回采的采场,由于矿石性质、块度、底部结构参数以及出矿进路坍塌等因素的影响,回采完毕后,采场内部往往还有部分矿石无法完全回收。无法回收的采场存留矿石是造成采场回采损失的主要原因。然而,凡口矿N3-4采场采用进路式出矿硐室,可视遥控铲运机出矿,出矿硐室底板是平整而坚实的胶结面,因此,采下的矿石可以完全回收,只是在采场空区探测时,采场底部有部分暂时没有出完的存留矿石。为计算这部分矿石量,以采场空区探测模型为基础,提取探测采空区模型的底部边界线和采场底部设计边界线,运用Surpac建立存留矿量三维模型,将其与采空区三维模型复合,如图3所示。运用存留矿量三维模型计算其体积,进而计算出存留矿石量,其结果见表1。
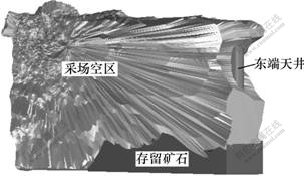
图3 N3-4采场存留矿量与探测空区三维模型复合
Fig.3 Cavity and ore remains compositing model of stope N3-4
表1 N3-4采场存留矿量计算结果
Table 1 Ore remains calculation results of stope N3-4

3.2 回采总体积计算
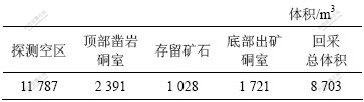
为计算回采总体积,先根据实测数据构建采场底部出矿硐室三维模型,其结果如图4所示。根据矿山要求,为准确计算回采总体积,需要扣除原存在于采场东端用于切割的断面体积,相当于半径为1.05 m的圆形天井体积。为此,根据天井的实际位置建立天井三维模型(参见图3),并将采场空区探测模型与天井模型进行布尔运算,获得扣除天井后的采场空区三维模型。由于采场空区探测时采场内尚有部分暂时未出完的存留矿量,所以,计算时,需加上这部分体积。另外,探测空区的范围包括了采场顶部凿岩硐室计算回采总体积时,因此,这部分体积也要减去。最后计算获得的N3-4采场回采总体积见表2。

图4 N3-4采场底部出矿硐室三维模型
Fig.4 Three-dimensional model of ore output laneway at bottom of stope N3-4
表2 N3-4采场回采总体积计算结果
Table 2 Mining total volume calculation result of stope N3-4
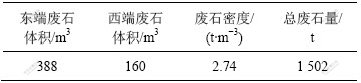
3.3 采下废石量计算
图5所示为N3-4采场空区、底部硐室及东、西两端矿岩分界面模型复合图。可以看出,在采场的东、西两端均存在采下废石现象。计算采下废石量的具体步骤如下:
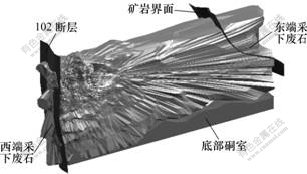
图5 N3-4采场空区、底部洞室及东西端矿岩分界面复合模型
Fig.5 Composite model of cavity, bottom ore output laneway and ore-rock interface of stope N3-4
a. 提取采场爆破设计剖面中的采场矿体东西两端边界线,其中西端以断层F102为分界面;
b. 将边界线导入大型矿床三维软件Surpac,进行坐标三维转换,使其与矿山实际坐标相符;
c. 分别按东、西两端生成矿岩边界面DTM;
d. 分别将东、西边界面与探测空区模型复合,并进行布尔运算,形成独立的采场东、西两端采下废石三维模型;
e. 根据生成的采下废石三维模型计算采下废石量,其结果见表3。
表3 N3-4采场采下废石量计算结果
Table 3 Mullock quality calculation results of stope N3-4
3.4 采下充填体量计算
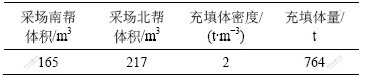
N3-4为间柱采场,其两侧矿房均已采完并进行充填,因此,在回采过程中,难免使两帮的充填体崩落。为获取实际回采过程中采场两帮崩落充填体量,应用实测的N3-4间柱采场空区三维模型,结合矿山提供的采场两侧矿房回采时实测的各个分层边界图,建立N3-4采场两帮边界面的三维模型,再将两帮回采边界面模型与采场空区三维模型复合,进行布尔运算,对模型进行剖切,获得采场两帮采下充填体三维模型,运用该模型可分别计算采场两帮采下充填体量。图6所示为N3-4采场南、北两帮采下充填体三维模型。N3-4采场采下充填体量的计算结果见表4。
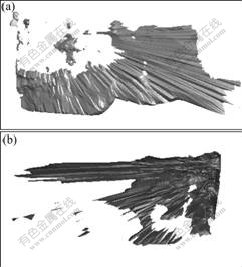
(a) 南帮; (b) 北帮
图6 N3-4采场南、北两帮采下充填体三维模型
Fig.6 Backfilling three-dimensional model of south and north side of stope N3-4
表4 N3-4采场两帮采下充填体量计算结果
Table 4 Backfill quality calculation results of stope N3-4
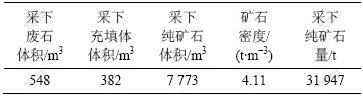
3.5 采下纯矿石量计算
回采过程中的采下纯矿石量为回采总量减去采下废石量和采下充填体量,结合上面计算结果获得N3-4采场回采过程中采下的纯矿石量,见表5。
表5 N3-4采场采下纯矿石量计算结果
Table 5 Pure ore quality calculation results of stope N3-4
3.6 贫化损失计算
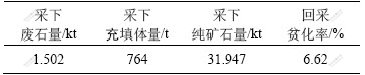
采场贫化主要是地质条件和采矿技术等原因,使采下的矿石中混有废石,从而引起矿石品位降低[4]。回采贫化率是指回采过程中采下的废石量占采下矿石量即回采总量(包括混入的废石量)的百分比。矿石损失则是指由于多方面原因造成的矿石丢弃或不能完全采出的量,通常包括采下损失和未采下损失。对于N3-4采场,回采总量为回采过程中采下的纯矿石量、采下废石量与充填体量的总和。尽管N3-4采场空区探测时,采场内仍有部分存留矿石,但这部分矿石将来可以完全回收,因此,认为该采场没有采下损失。此外,根据探测获得的采场空区三维模型分析和现场观察,N3-4采场也不存在未采下损失现象。N3-4采场回采贫化率应为回采过程中采下废石量与采下充填体量之和再除以回采总量。N3-4采场回采总量及贫化率的计算结果见表6。
表6 N3-4采场回采贫化率计算结果
Table 6 Dilution rate calculation results of stope N3-4
4 结 论
a. 针对我国金属矿山大规模采场回采指标难以准确获取的现状,综合运用空区激光精密探测系统CMS和大型矿床三维软件Surpac等数字化工具,结合凡口铅锌矿实际,研究了一种新颖的大规模采场回采指标可视化计算方法。
b. 采用该大规模采场回采指标可视化计算方法不仅可以精确构建采场空区可视化程度高、可编辑性强的三维模型,准确地获取采场空区的三维形态和实际边界,而且可有效地进行采场回采的回采总体积、采下废石量、采下充填体量、采下纯矿石量、回采总量及回采贫化率等回采指标的可视化计算。
c. 该大规模采场回采指标可视化计算方法实用、可靠,从而为矿山准确掌握开采质量、改善回采工艺开辟了一条新的有效途径。
参考文献:
[1] 罗周全, 鹿 浩, 刘晓明, 等. 基于空区探测的采场超欠挖量计算及顶板安全分析[J]. 金属矿山, 2007(12): 36-38.
LUO Zhou-quan, LU Hao, LIU Xiao-ming, et al. The volume calculation of stope over-excavation and under-excavation and upper openings safety analysis based on CMS survey[J]. Metal Mine, 2007(12): 36-38.
[2] 郭忠平. 放顶煤开采顶煤贫化率优化研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2000, 25(2): 137-140.
GUO Zhong-ping. Study of optimization on the dilution ratio of roof coal in sublevel caving mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2000, 25(2): 137-140.
[3] 刘晓明, 罗周全, 张 保, 等. CMS空区探测的环境影响及误差分析与纠正[J]. 矿冶工程, 2008, 28(4): 1-5.
LIU Xiao-ming, LUO Zhou-quan, ZHANG Bao, et al. Error analysis and amend of model under environmental impact for cavity monitoring system[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2008, 28(4): 1-5.
[4] 罗周全, 张 保, 刘晓明, 等. 基于CMS精密探测的采场贫化损失计算方法[J]. 金属矿山, 2007(10): 84-88.
LUO Zhou-quan, ZHANG Bao, LIU Xiao-ming, et al. Calculation method for mining loss and dilution based on CMS precision survey[J]. Metal Mine, 2007(10): 84-88.
[5] Optech System Corporation. Cavity monitoring system wireless user manual[M]. Toronto: Optech System Corporation, 2004.
[6] Jarosz A, Shepherd L. Application of cavity monitoring system for control of dilution and ore loss in open stopes[C]// Proceedings of 11th International Congress of ISM. Cracow, Poland, 2000: 155-164.
[7] Daniel F H, Nicolas V. Automatic three-dimensional underground mine mapping[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2006, 25(1): 7-18.
[8] Huber D, Vandapel N. Automatic 3D underground mine mapping[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2005, 25(1): 7-17.
[9] 刘晓明, 罗周全, 孙利娟, 等. 三维GIS空间数据集成和可视化技术研究[J]. 科技导报, 2008, 26(10): 65-68.
LIU Xiao-ming, LUO Zhou-quan, SUN Li-juan, et al. Integration of 3D GIS spatial data and its visualization[J]. Science and Technology Review, 2008, 26(10): 65-68.
[10] LUO Zhou-quan, LIU Xiao-ming, SU Jia-hong, et al. Deposit 3D modeling and application[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(2): 225-229.
[11] 周智勇, 陈建宏, 杨立兵. 大型矿山地矿工程三维可视化模型的构建[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(3): 423-428.
ZHOU Zhi-yong, CHEN Jian-hong, YANG Li-bing. 3D visualization modeling on geological and mining engineering in a large-sized mine[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2008, 39(3): 423-428.
[12] Lemon A M, Jones N L. Building solid models from boreholes and user-defined cross-sections[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2003, 29(3): 547-555.
[13] John G H, Hani S M. Numerical modelling of ore dilution in blasthole stoping[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2007, 44(5): 692-703.
[14] LIU Yu-zhou, LI Xiao-hong. Safety analysis of stability of surface gas drainage boreholes above goaf areas[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2007, 13(2): 149-153.
[15] GONG Jian-ya, CHENG Peng-gen, WANG Dong-yang. Three dimensional modeling and application in geological exploration engineering[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2004, 30(4): 391-404.
[16] FANG Yuan-min, DENG Jin-can, MI Hong-yan. Construction and visualization of 3D vacant place model[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2005, 15(S1): 61-64.
收稿日期:2008-11-08;修回日期:2009-03-02
基金项目:国家“十一五”科技支撑计划项目(2007BAK22B04-12;2006BAB02B05-01-02-01);中南大学研究生学位论文创新基金资助项目(1960-71131100008)
通信作者:罗周全(1966-),男,湖南邵阳人,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事矿床深井开采与安全预警数字化理论与技术研究;电话:13808421339;E-mail: lzq505@hotmail.com


