挖掘机激光高程定位方法
谢习华,何清华,周 亮
(中南大学 机电工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:
摘 要:为实现挖掘机的三维空间定位,在安装工作装置各关节角度传感器的基础上,又安装平台回转角度检测装置和平台倾角传感器,并在斗杆上安装激光接收仪用于检测地面激光发射器发射的水平激光相对于接收仪零位的高度。建立挖掘机的运动学模型,推导车体相对于大地的坐标变换矩阵,即完成三维空间的车体定位,并得到常用而简单的车体高程定位公式。然后,推导该定位车体位姿下铲斗坐标系相对于大地的坐标变换矩阵,导出挖掘深度定位公式,实现了挖掘机挖掘轨迹的三维空间定位,为实现挖掘机的三维空间轨迹精确控制与挖掘深度控制打下了基础。
关键词:
中图分类号:TP24 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2007)05-0928-04
Laser height-finding of robotic excavator
XIE Xi-hua, HE Qing-hua, ZHOU Liang
(School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: In order to get the carriage position of excavator in three-dimensional space, in addition to of joints angle sensors,the obliquity sensor and the swing angle sensor of the platform were mounted, and a laser receiver was mounted on the boom to measure the relative height of the boom to the laser bean from the ground sender. The carriage positioning model of robotic excavator and the coordinate transformation matrix of carriage positioning were formulated, and the height of the body relative to the ground was gotten. The carriage positioning was finished, the coordinate transformation matrix of the bucket relative to the ground and the digging depth were obtained and it is easy to make the three-dimensional trace control of the hydraulic excavator bucket easy.
Key words: excavator; robot; laser height; positioning
目前,机电一体化、自动化已成为工程机械的发展方向之一。对于劳动强度大,劳动条件差以及安全得不到保障的工程建设,迫切需要用机器人来代替人工作业[1-2]。液压挖掘机作为功能最典型、结构最复杂、用途最广泛的工程机械之一,其自动化的研究(尤其是局部自动化)已逐渐成为各国关注的焦点。此外,实现挖掘自动化也是提高生产能力和挖掘机工作效率的需要。目前,一些研究者在智能控制、遥控、任务规划、自动挖掘装载等方面进行了研究[3-14]。但这方面的研究多数集中在对挖掘机的工作装置进行控制上,很少涉及回转与行走控制,对铲斗的位姿检测和轨迹跟踪也大多只是局限于铲斗相对于挖掘机动臂根部的位姿和轨迹[15-17]。中南大学与湖南山河智能股份有限公司研发的机电一体化挖掘机采用CANBus总线技术,具有激光高程定位、图形导引与状态监测、用于水下和夜间等不可见工作情况的盲操作、节能控制、自动挖掘(水平挖掘、坡度挖掘)、挖掘深度控制、租赁管理等功能,将挖掘机的自动化研究推向实用化。无论是图形导引还是自动挖掘或深度控制,都必须先有一个确定的参考坐标系,即进行车体定位,然后,才能实现对铲斗运动的精确跟踪与控制。本研究采用的工作装置,在动臂、斗杆、铲斗上安装有角度传感器,回转机构安装有回转角度传感器,回转平台上安装有双轴倾角传感器。其车体定位过程为:地面激光发射器发射水平激光,操作手操纵工作装置使地面发射的激光能被斗杆上的激光接收器所检测,然后采集各传感器的参数,可求出车体坐标相对地面坐标的坐标变换关系,得到车体相对地面坐标的高度与倾角。
1 坐标系的建立及转换矩阵推导
1.1 车体坐标系
以车体底盘中心点为原点,沿车体轴线向前为X轴,沿车体平面向左为Y轴,向上为Z轴,见图1中坐标系OvXvYvZv。
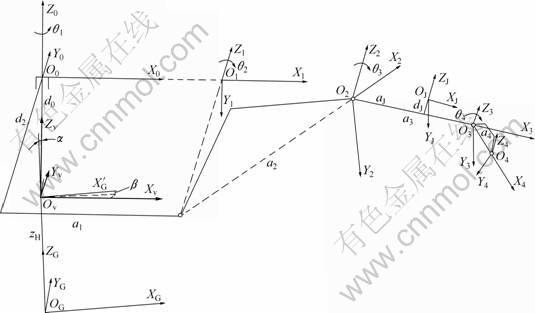
图1 车体坐标系示意图
Fig.1 Sketch map of coordinates of the carriage
1.2 关节坐标系
各关节坐标系按Denavit-Hartenberg方法[18]建立,如图1所示,分别为O0X0Y0Z0,O1X1Y1Z1,O2X2Y2Z2,O3X3Y3Z3,O4X4Y4Z4。
斗杆(杆件3)上安装有激光接收器,激光接收器的坐标系为OJXJYJZJ。
根据Denavit-Hartenberg方法,第n个关节坐标系相对于第n-1个关节坐标系的坐标变换矩阵为:
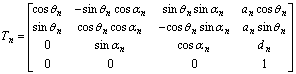 。 (1)
。 (1)
式中:![]() 为两关节轴的公垂线长度,即连杆长度;
为两关节轴的公垂线长度,即连杆长度;![]() 为连杆之间的距离;
为连杆之间的距离;![]() 为连杆扭转角;
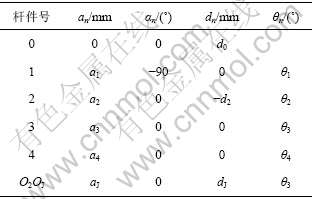
为连杆扭转角;![]() 为连杆夹角;n=1,2,3,4。各杆件的参数如表1所示。
为连杆夹角;n=1,2,3,4。各杆件的参数如表1所示。
表1 各杆件参数表
Table 1 Parameters of links
各关节间的变换矩阵分别为:
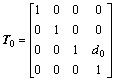 ;
;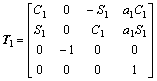 ;
;
 ;
;
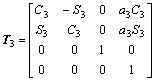 ;
;
 ;
;
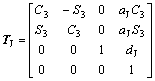 。
。
式中:TJ为坐标系OJXJYJZJ相对于坐标系O2X2Y2Z2的坐标变换矩阵;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() 。
。
2 车体定位
设车体前后俯角为b,左右侧倾角为a,车体相对于大地的坐标高为zH,则车体坐标系相对于地面坐标系的变换矩阵为:
![]()
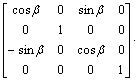
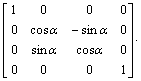
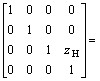 。 (2)
。 (2)
进行车体定位时,使回转平台处于中位,即![]() 。此时,安装在平台上的倾角传感器可以检测到平台的左右倾角和前后俯仰角,平台的左右倾角即车体底盘的左右倾角a,平台的前后俯仰角即车体底盘的前后俯仰角b(如图1所示),平台坐标系相对大地坐标系的变换矩阵为:
。此时,安装在平台上的倾角传感器可以检测到平台的左右倾角和前后俯仰角,平台的左右倾角即车体底盘的左右倾角a,平台的前后俯仰角即车体底盘的前后俯仰角b(如图1所示),平台坐标系相对大地坐标系的变换矩阵为:
![]()
 (3)
(3)
其中:A=![]() ;B=
;B=![]() 。
。
进行激光高程定位时,地面激光发生器发射水平激光,操作工作装置使地面发射的水平激光能被斗杆上的激光接收器所检测,已知激光相对于大地的坐标高为hj,设激光接收器检测到的激光相对高度为xJ=h,则激光接收点相对大地坐标系的坐标为:
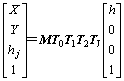 。 (4)
。 (4)
由此得:
![]()
![]() 。
。
其中:a1, a2, aJ , d0, d2, dJ为已知参数,于是,求解得到车体相对于大地的坐标高为:
![]()
这样,便完成车体的高程定位,再将a,b和zH代入式(2)即得到车体定位变换矩阵M。
3 铲斗挖掘深度定位
对车体进行定位得到变换矩阵M后,在任意工作位姿,采集动臂、斗杆、铲斗上的角度传感器值(q2~q4),回转机构的回转角度传感器值(q1),即可得到铲斗坐标系相对大地的坐标变换矩阵:
![]()
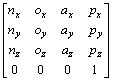 。 (6)
。 (6)
铲斗齿尖相对大地坐标系的坐标为(px, py, pz),
![]() 。 (7)
。 (7)
这就是铲斗齿尖的相对大地坐标系的高度,负值![]() 即为挖掘深度。
即为挖掘深度。
4 结 论
a. 在工作装置各杆件安装角度传感器,通过安装平台倾角传感器、回转角度检测装置以及在斗杆上安装激光高度检测仪,实现了车体三维空间定位功能。
b. 根据Denavit-Hartenberg方法建立了挖掘机各关节运动学坐标,并推导出车体坐标相对地面坐标的坐标变换矩阵,从而完成车体定位,然后,推导了挖掘作业中的车体高程定位公式。
c. 获得车体定位坐标变换矩阵后,推导了铲斗坐标系相对大地的坐标变换矩阵,实现了包括回转在内的挖掘机工作装置三维空间挖掘轨迹定位,并导出了挖掘深度定位公式。
d. 三维空间的车体定位有助于实现水平面、斜坡面挖掘以及三维空间轨迹的精确控制。
参考文献:
[1] 张海涛, 何清华, 陈欠根. 遥控挖掘机器人轨迹跟踪的电液比例控制系统[J]. 液压与气动, 2004(7): 11-13.
ZHANG Hai-tao, HE Qing-hua, CHEN Qian-gen. The electrohydraulic proportional control system for robotic excavator[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2004(7): 11-13.
[2] Muramatsu T, Kenji C. A concept of control system for construction robot[C]//Proceedings IEEE/RSJ International Workshop on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Tsukuba, 1989.
[3] Ha Q, Santos M, Nguyen Q, et al. Robotic excavation in construction automation[J]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2002(3): 20-28.
[4] Seward D, Bradley D, Mann J, et al. Controlling an intelligent excavator for autonomous digging in difficult ground[C]// Proceedings Ninth International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction. Tokyo, 1992.
[5] Singh S, Simmons R. Task planning for robotic excavation[C]// Proceedings IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Raleigh, 1992.
[6] Bradley D A, Seward D W. The development, control and operation of an autonomous robotic excavator[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 1998, 21: 73-75.
[7] Stentz A, Bares J, Singh S, et al. A robotic excavator for autonomous truck loading[C]//Proceedings International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Victoria, 1998.
[8] Cannon H. Extended earthmoving with an autonomous excavator[D]. Pittsburgh: Carnegie Mellon University, 1999.
[9] Ha Q P, Nguyen Q H, Rye D C, et al. Impedance control of a hydraulically-actuated robotic excavator[J]. Automat Construction, 2000, 9(5): 421-435.
[10] Nguyen H Q. Robust low level control of robotic excavation[D]. Sydney: Australian Centre for Field Robotics, University of Sydney, 2000.
[11] Terwelp C R. Remote control of hydraulic equipment for unexploded ordnance remediation[D]. Blacksburg: Department of Mechanical, Science and Engineering, Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 2003.
[12] 何清华, 张大庆, 郝 鹏, 等. 液压挖掘机工作装置模型及控制的试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 37(3): 542-546.
HE Qing-hua, ZHANG Da-qing, HAO Peng, et al. Model and experimental research on control of hydraulic excavator’s manipulator[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(3): 542-546.
[13] HE Qing-hua, ZHANG Da-qing, HAO Peng, et al. Modeling and control of hydraulic excavator’s arm[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(4): 422-427.
[14] 李兰生, 边仁国, 邹占江. 液压挖掘机工作装置运动学分析及轨迹规划[J]. 矿山机械, 1998(2): 23-25.
LI Lan-sheng, BIAN Ren-guo, ZOU Zhan-jiang. Kinematics analysis and trace scheme of the working device in a hydraulic excavator[J]. Mining & Processing Equipment, 1998(2): 23-25.
[15] 张大庆, 何清华, 郝 鹏, 等. 液压挖掘机铲斗的轨迹跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2005, 35(5): 490-494.
ZHANG Da-qing, HE Qing-hua, HAO Peng, et al. Trajectory tracking control of hydraulic excavator bucket[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Engineering and Technology Edition, 2005, 35(5): 490-494.
[16] 陈欠根, 吴晓健, 赵 娟. 液压挖掘机工作装置姿态检测[J]. 工矿自动化, 2005(5): 14-16.
CHEN Qian-gen, WU Xiao-jian, ZHAO Juan. The gesture measuring of working unit of hydraulic excavator[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2005(5): 14-16.
[17] 张海涛, 何清华, 张新海, 等. 机器人液压挖掘机运动系统的建模与控制[J]. 机器人, 2005, 27(2): 113-117.
ZHANG Hai-tao, HE Qing-hua, ZHANG Xin-hai, et al. Modeling and control of the motion system of a hydraulic robotic excavator[J]. Robot, 2005, 27(2): 113-117.
[18] Paul R P. Robot manipulators: Mathematics, programming, and control[M]. Massachusetts: MIT Press, 1981.
收稿日期:2006-12-10;修回日期:2007-01-25
基金项目:国家“863”计划资助项目(2003AA430200)
作者简介:谢习华(1969-),男,湖南涟源人,博士研究生,讲师,从事机器人控制技术、计算机控制系统、企业信息化等研究
通信作者:谢习华,男,博士研究生,讲师;电话:0731-4020687;E-mail: xxh_zh@mail.csu.edu.cn


