文章编号:1004-0609(2012)06-1680-17
稀土元素对无铅钎料组织和性能的影响
张 亮1, 2,韩继光1,何成文1,郭永环1,薛松柏3,皋利利3,叶 焕3
(1. 江苏师范大学 机电工程学院,徐州 221116;
2. 江苏科技大学 先进焊接技术省级重点实验室,镇江 212003;
3. 南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院,南京210016)
摘 要:
稀土元素以其独特的优势被称为金属材料的维他命,稀土元素的添加可以在不同程度上提高无铅钎料的性能。结合国内外在含稀土元素无铅钎料研究领域的最新研究成果,综合评论稀土元素对无铅钎料组织和性能的影响,阐述含稀土元素的无铅焊点可靠性研究现状,为该钎料的实际应用提供数据支撑,分析过量稀土元素对无铅钎料表面锡须的影响,探讨锡须的生长机制及潜在的问题,最后综合评述含稀土无铅钎料在研究过程中存在的问题以及相应的解决措施,为含稀土元素无铅钎料的研究和应用提供理论依据。
关键词:
中图分类号:TG454 文献标志码:A
Effect of rare earth on microstructures and properties of lead-free solders
ZHANG Liang1, 2, HAN Ji-guang1, HE Cheng-wen1, GUO Yong-huan1, XUE Song-bai3, GAO Li-li3, YE Huan3
(1. School of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, Xuzhou Normal University, Xuzhou 221116, China;
2. Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding Technology, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang 212003, China;
3. College of Materials Science and Technology, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China)
Abstract: The rare earth (RE) elements due to its particular function were called the vitamin of metals, RE can greatly enhance the properties of lead-free solders in different degrees. Based on the development of lead-free solders bearing RE at home and abroad, the effect of RE on the properties and microstructures of lead-free solders was reviewed systematically. The recent progress of soldered joints reliability was expatiated, which can provide data support for the application of these lead-free solders bearing RE. Through analyzing the tin whiskers of lead-free solders bearing excessive RE, the growth mechanism and possible issues were discussed. The problems and difficulty in the process of the applications of lead-free solders bearing RE were analyzed synchronously, some suggestions were put forward which maybe solve the issues mentioned above, which may provide theory guide for the investigation of lead-free solders bearing RE.
Key words: rare earth; lead-free solders; reliability; whiskers
随着电子工业的发展,传统SnPb钎料由于Pb的毒性被国家社会广泛关注,特别是2003年欧盟公布所谓的WEEE和RoHS指令后,无铅钎料代替传统SnPb钎料的研究迅速发展[1-3]。在诸多的无铅钎料中,SnAgCu[4-5]、SnCu[6-7]、SnAg[8-9]和SnZn[10-11] 4种无铅被认为是替代SnPb钎料的良好替代品。然而该系列无铅钎料仍然具有各自的缺点,如钎料内部存在脆性金属间化合物块(Cu6Sn5/Ag3Sn)、抗氧化能力差,抗蠕变能力差以及服役期间焊点的抗疲劳性能较低 等[12-14]。为了进一步提高钎料的性能及改善钎料的组织,诸多研究人员采用微合金化方法研究新型无铅钎料。
稀土元素被称为金属元素的维他命,即为添加一定量的稀土元素可以提高金属材料的性能以及改善组织。鉴于稀土元素这一特性,诸多研究者选择稀土作为钎料微合金化元素,早在20世纪90年代初,有研究者[15-16]在SnPb钎料中添加稀土元素来改善其性能和提高可靠性。这也为无铅钎料的研发提供一个思路,因此,后来者在前人的研究基础上选择在SnAgCu等几种无铅钎料中添加不同的稀土元素[17-18],稀土元素的添加提高了无铅钎料的某一或者综合性能,几种无铅钎料的缺陷也因为稀土元素的添加得到不同程度的解决,但是也给无铅钎料的应用和推广带来了新的问题:锡须[19]。因此,含稀土元素的无铅钎料有待于进一步的研究和探讨。
本文作者针对含稀土元素的无铅钎料,综合评论稀土元素对无铅钎料组织和性能的影响,阐述稀土元素的影响机制。对含稀土元素的无铅焊点可靠性进行综合分析,同时探讨过量稀土元素对无铅钎料表面锡须生长的影响,进而探讨含稀土元素无铅钎料的发展趋势及面临的挑战。为了含稀土元素的无铅钎料的研究和应用提供理论指导。
1 稀土元素对无铅钎料组织的影响
1.1 内部组织
研究稀土元素对金属材料的最早成果多关于钢材及其应用,稀土在钎焊材料改性中的应用,许多思路受稀土元素在钢中应用研究的启迪。稀土元素的添加会使原先两元、三元合金变为三元和四元合金,无疑这也会给新型合金组织的特性研究带来新的问题。同时材料组织决定性能以及相应的加工工艺[20],因此有必要首先研究稀土元素对无铅钎料内部组织的影响。
Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料基体中主要由β-Sn、Ag3Sn和Cu6Sn5组成,研究者[21]发现基体组织中存在大块的Cu6Sn5相,该相可以作为β-Sn的异相形核点,将混合稀土元素(Ce/La)添加到SnAgCu钎料后,基体组织随着稀土含量的增加得到不同程度的细化,针状双相共晶组织逐渐消失,变为细小的颗粒,致使很难区分双相共晶和三相共晶组织。同时,混合稀土含量为0.1%以后,基体组织开始出现稀土相[22]。对SnAgCu-RE焊点表面分析,焊点表面较为光滑、平整,同时金属间化合物尺寸较小,稀土元素含量过量时金属间化合物增多[23]。另外,在Sn0.7Cu0.05Ni中添加混合稀土,可以显著细化钎料基体的组织,抑制Cu6Sn5相的长大,但是研究者并未在钎料基体中发现稀土相[24]。部分稀土元素容易吸附在金属间化合物晶粒的边界,降低金属间化合物在不同晶体方向的生长速度,因此可以降低金属间化合物的表面张力,根据表面吸附理论,稀土元素的添加可以细化金属间化合物尺寸[25]。
微量稀土元素Ce会对Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu焊点内部组织产生明显的细化作用[26],和稀土元素Ce在其他材料中具有类似的作用[27]。所不同的是,稀土Ce可以减小β-Sn的树枝晶尺寸[28],减小Cu6Sn5和Ag3Sn颗粒的尺寸[29]。稀土元素的添加会在钎料基体中形成CeSn3相,有研究者表明Ce具有亲Sn效应,降低Sn的活度,减小Sn与其他元素结合的驱动力,这也是Ce使金属间化合物减小及组织细化的主要原因[30]。元素Y添加到Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料可以显著细化钎料组织,同时SnAgCu钎料内部大块金属间化合物的尺寸得到明显的减小,均匀地分布在Sn基体中[31]。另外,SHI等[32]研究稀土元素Er的添加对Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu组织中Ag3Sn、Cu6Sn5和共晶组织的细化作用,发现三相的尺寸均得到明显的减小。同时GAO等[33-34]研究发现Pr/Nd对Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料组织的细化作用和Ce、La等稀土元素相似。
在Sn3.5Ag钎料中添加稀土元素Lu,组织中出现LuSn3稀土相,稀土元素的添加可以促进钎料和半导体材料之间的化学反应[35-36]。在SnAg钎料中加入稀土元素La,β-Sn的晶粒尺寸和Ag3Sn颗粒得到明显的减小,增加钎料基体中共晶区域的体积分数,提高钎料在热失效过程的组织稳定性[37]。而稀土元素Ce的添加在一定程度上改善Sn1.0Ag钎料的基体组织,随着稀土Ce的添加,Sn1.0Ag钎料的组织得到明显细化,稀土元素Ce的添加最大量达到0.5%[38]。同时,CHEN等[39]和胡玉华等[40]试图在Sn-9Zn钎料中添加稀土元素Ce,进而改善钎料基体组织,细化钎料中的富Zn相,由于Sn-Ce形成的自由能明显低于Zn-Ce化合物的,因此,在慢冷过程中易于形成Sn-Ce化合物,同时在稀土Ce的添加过量时,钎料基体组织中出现明显的Sn-Ce化合物。稀土元素Ce添加到Sn0.7Cu0.5Ni钎料中也发现类似的规律[41]。
1.2 界面组织
在钎焊过程中,熔化的钎料与基板发生反应,在界面处形成金属间化合物层。金属间化合物的形成一方面表明钎焊质量可靠,即钎料通过与基板反应形成较薄的金属间化合物层有利于获得良好的冶金结合;另一方面,若金属间化合物层太厚,则会降低焊点的可靠性[42-44]。含稀土无铅钎料的界面反应以及稀土元素对界面影响机制成为诸多研究者追捧的热点。
混合稀土(Ce/La)的添加对Sn3.5Ag0.7Cu/Cu界面生长速度有显著的抑制作用,170 ℃时效过程中,稀土元素的抑制作用较为明显[45]。在Sn2.5Ag0.7Cu钎 料中添加0.1%的混合稀土,可以有效地阻止钎焊过程中Cu6Sn5金属间化合物的生长,由于稀土元素的亲Sn性,易与Sn反应降低Sn-Cu反应的机会[46]。稀土元素Er的添加可以降低Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu/Cu界面层的厚度,而且界面层的形态也发生明显的变化[47]。Y元素的添加可以减小Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu/Cu界面层金属间化合物的厚度[31],具有和稀土元素Er相类似的效果。稀土元素La对Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu焊点界面组织也有明显的影响,钎焊后界面形成的Cu6Sn5化合物层的厚度和平均颗粒直径均随钎料合金中La 含量的增加而减 小[48]。界面Cu6Sn5和Cu3Sn的总厚度随时效时间的增加而增厚,在相同的时效条件下,随La 含量的增加而减小。IMC 在时效过程中生长动力学的时间系数n 随着La 含量的增加逐渐增大。在Sn3.9Ag0.7Cu钎料中添加稀土La,界面层金属间化合物的厚度减小60%[49]。稀土元素Ce也可以降低Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu/Cu界面厚度[50],同时在服役期间,界面层出现明显的分层现象,出现Cu6Sn5和Cu3Sn两层金属间化合物,两层化合物厚度均因稀土元素Ce的添加而得到减小[51]。稀土元素Pr/Nd的添加可以减小SnAgCu/Cu界面层的厚度,但是添加过量时,界面层的厚度反而有所增加,同时在界面附近出现大块的稀土相[33-34]。
未添加稀土元素的情况下,混合稀土(Ce/La)对Sn9Zn/Au/Ni/Cu界面附近出现大块的AuSn4和Au-Zn两种化合物[52];而在添加0.5%稀土后,界面没有出现以上两种大块的化合物,取而代之的是一层分离的Au-Zn层,随着时效时间的增加,这一层化合物的厚度也会随之增加,但研究者并未给出稀土元素添加前后该变化的直接原因。Sn9Zn-xCe/Cu界面组织为Cu5Zn8相,没有发现Cu-Sn化合物,同时随着稀土Ce的添加界面层的厚度明显增加,当稀土元素Ce添加量为0.5%时,界面层的厚度是未添加稀土元素界面厚度的5倍,主要是由于稀土元素的亲Sn性,促进Zn元素向界面处扩散[39]。XIAO等[53]和HU等[54]选择在Sn9Zn钎料中添加稀土元素Pr/Nd,发现界面的生长可以在适当添加稀土Pr/Nd的基础上得到抑制,研究结果和添加稀土元素Ce[39]似乎完全相反,鉴于此,含稀土的Sn9Zn钎料的界面组织演化规律有待于进一步研究。稀土元素La的添加会对Sn3.5Ag焊点界面产生明显的影响,图1所示为焊后及150 ℃时效时界面组织图[55]。由图1可以看出,焊后SnAg/Cu界面Cu6Sn5相呈现明显扇贝状,添加稀土元素La后,界面层厚度明显减小,同时也变得较为平滑。发现在钎料中析出LaSn3相,该相在钎料凝固过程中充当异相形核的作用[56]。同时,经在150 ℃时效625 h时,界面层厚度明显增加,SnAg/Cu界面层厚度为5 μm,SnAgLa/Cu界面层厚度为3 μm,进一步说明稀土La可以抑制界面层的生长。
无铅钎料界面反应因为稀土元素的添加而发生明显的变化,这无疑也在一定程度说明了稀土元素在界面反应过程中起到重要作用。诸多研究者采用扩散动力学的相关理论解释稀土对界面层生长的影响。金属间化合物的形成动力由其组元成分的活性决定的,对于Cu6Sn5金属间化合物来说,其吉布斯自由能ΔG由焊点中Sn元素的活性决定[13, 57]:
![]() (1)
(1)
式中:R为摩尔气体常数;T为绝对温度;![]() 为Sn的活度。
为Sn的活度。
Cu6Sn5主要是依靠Cu原子穿越金属间化合物 层,扩散至金属间化合物/钎料界面,与Sn反应得 到[58]。Cu6Sn5的吉布斯自由能ΔG,主要是由Cu6Sn5/钎料界面处Sn的活度决定,因此,降低Sn的活度是抑制界面金属间化合物的有效手段。基于诸多研究 者[59-60]采用热力学的研究结果,发现稀土元素具有亲Sn性,在Cu-Sn界面层降低Sn的活度,减少Cu与Sn的反应机会,在一定层次上抑制Cu6Sn5的生长。
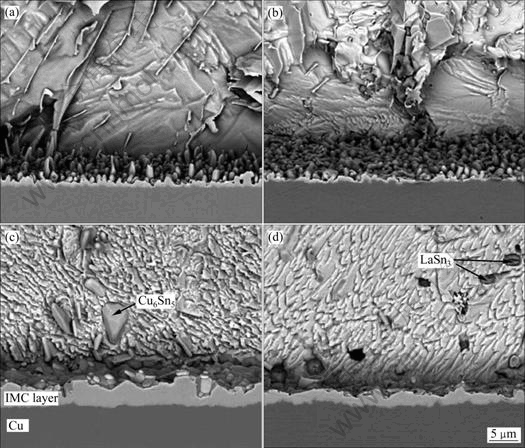
图1 SnAgxLa/Cu界面组织[55]
Fig. 1 Interface microstructures of SnAgxLa/Cu[55]: (a) Sn3.5Ag (as soldered); (b) Sn3.5Ag0.5La (as soldered); (c) Sn3.5Ag (150 ℃ for 625 h); (d) Sn3.5Ag0.5La (150 ℃ for 625 h)
2 稀土元素对无铅钎料性能的影响
无铅钎料组织的变化直接决定性能的变化,由于稀土元素的添加,钎料基体组织的细化和界面层结构/厚度的变化直接决定稀土元素的添加可以改善钎料的性能,例如润湿性、力学性能和蠕变性能等。同时,也有诸多研究者[21-22, 31, 61-62]分析稀土元素的添加对无铅钎料熔化特性的影响,发现稀土元素的添加对钎料的熔化温度几乎没有影响。因此,在该部分主要分析稀土元素对无铅钎料润湿性、力学性能和蠕变性能的影响。
2.1 润湿性
钎料润湿性是指一种液态钎料在母材表面铺展的能力[63-64]。对于钎料来说,能否与基板形成良好的浸润是完成钎焊的关键, 为了保证钎焊牢固,钎料必须很好地润湿基板材料。和传统的SnPb钎料相比,无铅钎料存在一个较大的缺陷:润湿性差。影响钎料润湿性的主要因素[65]有钎料和母材的成分、温度、金属表面氧化物、助焊剂、母材表面的状态、表面活性物质等而稀土元素的添加在一定程度上可以大幅度上提高无铅钎料的润湿铺展性能。目前,针对无铅钎料润湿性测试主要有4个对比参数:润湿时间、润湿力、润湿角和铺展面积。
在Sn3.5Ag0.7Cu钎料中添加0.1%混合稀土(Ce和La),钎料/钎剂表面张力得到明显的降低从而促进钎料的润湿力,添加过量的稀土会致使钎料的润湿性恶化,这主要是由于在钎焊过程中钎料表面黏性增 加[45]。在Sn3.5Ag0.7Cu钎料中添加0.1%混合稀土,钎料的润湿力得到显著的提高,同时,润湿角明显小于Sn2.5Ag0.7Cu、Sn3.5Ag0.7Cu、Sn3.5Ag0.7Cu0.25RE无铅钎料的[66]。稀土元素Ce添加到Sn3.0Ag2.8Cu钎料可以显著提高其铺展面积,最优添加量为0.1%[67]。对于Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu粉体颗粒的润湿性测试,发现稀土元素Ce可以显著提高钎料的润湿性,最佳添加量为0.03%[68]。在N2气氛保护下也发现稀土元素Ce类似的作用[69]。有研究者选择在Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu中添加0.05%Ce,发现稀土元素对钎料的润湿性起到明显的恶化作用[70],研究结果和已有的文献恰恰相反,这可能是稀土元素的添加工艺导致的,目前,在合金中添加稀土元素有直接添加和中间合金添加两种方式,不管是那种方式必须注意钎料在冶炼过程的保护,防止氧化。Sn3.8Ag0.7CuxY随着稀土元素Y量的变化润湿性有明显的促进作用。Y最优添加量为0.15%[31]。超过该添加量后润湿性会明显下降,主要是由于稀土元素为活性元素,稀土元素容易在钎料/钎剂界面累积,进而降低界面自由能,但是过量的稀土容易出现氧化,增加钎料表面的表面张力,降低钎料的润湿性。
SnAgRE钎料的润湿性和混合稀土添加量之间存在明显的非线性关系, 当稀土元素添加量为0.5%时,润湿角达到最小(32°±2°), 当稀土添加量超过1.0%,润湿角明显增加。进一步说明在SnAg钎料中添加混合稀土元素的最佳添加量为0.5%[71]。另外, 有研究者发现,Sn3.5Ag中添加0.25%RE可以显著提高钎料的润湿力,润湿力较为接近传统的SnPb钎料的,润湿时间为0.6s[72]。单独稀土元素Ce对Sn1.0Ag润湿性也有相类似的影响,稀土Ce的最佳含量为0.3%[38]。稀土元素Ce的添加对Sn7Ag10Sb和Sn3.1Ag8.0Bi2.1- Cu1.7In的润湿性影响的最佳含量也为0.3%,发现适量的稀土元素不仅可以增大钎料的铺展面积,且可以获得较为光亮的焊点表面形貌[73]。
混合稀土元素(Ce/La)可以显著改善Sn0.7Cu钎料的润湿性,研究者把稀土元素控制在0.5%[74]。Sn0.5Cu0.05Ni钎料的润湿性较差,添加稀土元素Ce以后,钎料的润湿性明显提高,在铜基板上在相同的温度下可使润湿时间缩短10%~45%[13]。在N2保护气氛下,润湿时间缩短20%~50%[75]。N2气保护可以减少氧化渣的形成[76],减少氧化渣对钎料润湿的阻止。有研究者选择稀土元素Ce添加到Sn0.7Cu3Bi钎料,发现稀土元素的最佳添加量为0.03%~0.05%,钎料的润湿性有一定的提高[77]。
混合稀土可以显著提高Sn9Zn钎料的润湿性[78],同时配合适当的钎剂效果更佳[79]。因此,有研究者[80-81]提出选择适宜的钎剂可以弥补无铅钎料润湿性较差的缺陷。在Sn9Zn添加Ce元素,添加范围为0.05%~ 0.07%时,润湿性最佳,主要是稀土元素Ce是表面活性元素,可降低液态钎料的表面张力、改善润湿性;同时Ce化学性质活泼,极容易氧化,因此添加量较大时,表面富集的Ce大部分以氧化物的形式存在,从而恶化钎料润湿性[14]。Sn9ZnCe钎料的润湿性也因为钎剂选择的不同,润湿力和润湿时间均有很大的差别,但却具有相同的最佳添加量[82]。同时,有研究 者[83]选择改变钎剂的浓度,SnZn-xLa的润湿性也随之增加,La最佳添加量为0.3%。稀土元素Nd和La可以显著降低Sn8Zn3Bi钎料的表面张力,Nd的效果要高于La的[84],稀土元素Nd对Sn8Zn3Bi的润湿性具有明显的促进作用,当Nd的添加量为0.1%时,钎料的最大铺展面积为39.6 mm2,较为接近传统的SnPb钎料的铺展润湿性(最大铺展面积为42.2 mm2)[85]。有研究者[86]开发含稀土元素La的Sn8.9Zn2.7Bi1.0Ga- 0.5Cu0.2La无铅钎料,其润湿角为25.1°,发现La和合金元素Ga的含量对SnZnBi系无铅钎料的润湿性能有较大影响。
2.2 力学性能
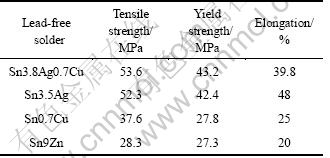
在集成电路中,焊点在服役期间即承担电子器件与基板之间的电气连接,也承担着一定的机械支撑作用[87]。因此,在实际的使用中,无铅钎料必须具备较高的力学性能才能保证焊点的机械支撑作用。目前,针对无铅钎料的力学性能测试主要集中在拉伸、剪切和压缩3种试验,试验样品有钎料或者焊点两种形式,同时在尺寸上也有大尺寸件和模拟焊点的小尺寸件。因此,相同试验材料因为不同的试验者、不同的试验设备以及不同的试验样品尺寸等原因也会得到不同的试验数据。在无铅钎料力学性能测试中,大尺寸钎料拉伸是应用较为广泛的一种试验方法,表1所列为4种常用无铅钎料拉伸试验数据[88-89]。
表1 材料拉伸试验数据[88-89]
Table 1 Tensile testing data of lead-free solders[88-89]
混合稀土(Ce/La)使Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu 钎料的抗拉强度的提高有限, 略低于SnPb 钎料, 伸长率有较大增加, 最高可达30%。随着稀土含量的增加, 又逐渐降低, 当稀土元素的添加量超过0. 25 % 时, 即低于SnAgCu 水平,主要是稀土相的出现恶化了钎料的性能[90]。有研究者[91]对比研究SnAgCu和SnAgCu0.1RE焊点的剪切强度,发现SnAgCu0.1RE焊点的剪切强度明显小于SnAgCu的,但是在时效过程中发现,稀土可以降低SnAgCu焊点的剪切性能劣化程度。稀土元素Er的添加可以提高Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料的剪切强 度[32],当添加量为0.1%时,钎料的剪切强度提高近18%。当Er的添加量超过0.5%时,钎料的剪切强度明显下降,但是数值仍然高于SnAgCu钎料的。稀土元素Y对Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu焊点剪切强度和拉伸强度均有明显影响,当Y的添加量为0.15%时,焊点的力学性能达到最大值[31]。研究者认为这主要和稀土元素易氧化有关,过量的氧化物会恶化焊点的性能。稀土元素Ce对QFP器件Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu焊点的拉伸力有明显的促进作用,Ce的最佳添加量为0.03%[68]。相对SnAgCu焊点,SnAgCu0.03Ce焊点的拉伸力(QFP100)和剪切力分别提高12.06%和10.31%[13]。添加0.05%稀土Nd可以显著提高Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料拉伸力,拉伸力幅值增加近19.4%[34]。
混合稀土(Ce/La)添加到Sn3.5Ag钎料,可以提高钎料的力学性能,0.5%的混合稀土可以显著提高钎料的最大抗拉强度,稀土添加量为1.0%时,拉伸断裂表面出现明显的稀土相,恶化钎料的性能[70]。对BGA器件Sn3.5Ag和Sn3.5Ag0.5RE焊点进行剪切测试,发现Sn3.5Ag0.5RE焊点的剪切强度明显高于Sn3.5Ag的,说明稀土元素的添加可以显著提高焊点的强 度[92]。Sn3.5Ag添加稀土元素La可以提高其焊点的强度,稀土元素La为1.0%时,焊点强度得到明显的提高[93]。在AgCuTi三元合金中也发现类似稀土元素La提高其力学性能的现象[94]。在Sn3.5Ag、Sn0.7Cu和Sn9Zn无铅钎料添加混合稀土(Ce/La),其拉伸试验的数据如图2所示(在应变率为0.005 s-1的条件下测试)。可以看出,混合稀土的添加可以显著提高3种无铅钎料的抗拉强度[95]。0.25%RE可以使 Sn3.5Ag焊点的最大抗拉强度提高20%,0.5%RE可以使Sn3.5Ag焊点的最大抗拉强度提高27%[96]。稀土元素Ce的添加可以显著提高Sn0.5Cu0.05Ni的性能,提高幅值范围为12.27%~25.78%[13]。而Ce对Sn9Zn的力学性能也有一定的促进作用,Ce的最佳添加量为0.08%,同时拉伸力提高27.6%[82]。也有研究者选择研究Sn9Zn-xLa/Cu (x=0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5)焊点的剪切强度,发现稀土元素La的添加降低SnZn焊点的剪切强度,有研究者[83]认为,La元素加入SnZn中,La首先与活性较强的Zn结合形成Zn5La相,当La的含量超过0.3%时,合金中还出现游离态的La,Zn5La的形成降低界面Cu5Zn8形成的机会,同时游离态的La也会氧化,从而降低焊点的剪切强度,然而却并没有给出具体的Zn5La和游离La的组织图,同时研究者[10, 14, 18-19, 22, 49, 52, 82]已经证实了稀土元素亲Sn性,并且Sn-稀土相的吉布斯自由能比Zn-稀土低很 多,从而也说明了稀土元素优先与Sn反应,同时研究者[10, 14, 18-19, 22, 49, 52, 82]也给出了具体的稀土相组织,从在一定意义上也否定了Sn9Zn-xLa中Zn5La和游离La的存在。微量的稀土Nd可以显著提高Sn8Zn3Bi力学性能,添加过量时力学性能会明显下降,同时稀土添加量在0.10~0.15范围时,伸长率提高近30%[85]。
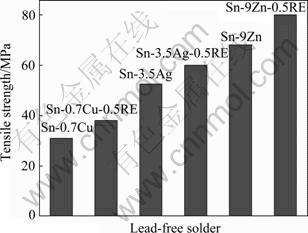
图2 常应变速率下含稀土无铅钎料的抗拉强度[95]
Fig.2 Tensile strength of three lead-free solders with rare earths (at constant strain rate of 0.005 s-1)[95]
2.3 蠕变特性
蠕变是指材料在高温和低于材料宏观屈服极限的应力下发生的缓慢的塑性变形。对于SnAgCu、SnZn、SnCu、SnAg等无铅钎料,由于钎料熔点较低,室温下,工作温度已经明显超过熔点的0.5倍[97],因此该系列无铅钎料在服役期间的蠕变行为应是高温蠕变。
Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料中添加混合稀土(Ce/La),焊点的蠕变断裂寿命会得到明显的提高,在室温下,稀土元素含量为0.1%时,焊点蠕变寿命达到最高,达到SnAgCu的7倍以上,稀土元素的添加量超过1.0%,蠕变寿命明显下降,且低于SnAgCu焊点[62]。同时,研究者[98]构建SnAgCu/SnAgCuRE两种焊点的稳态蠕变本构方程,本构方程如方程(2)~(5)所示。研究结果表明,在低应力和高应力下,SnAgCuRE焊点的应力指数及激活能都比相应的SnAgCu焊点的高。而有研究者[99]发现,含稀土元素的SnAgCu无铅钎料蠕变行为主要受Ag3Sn颗粒控制,而较高的应变速率主要归因于稀土相的存在。
SnAgCu的蠕变特性如下:
1) 低应力下,
![]() (2)
(2)
2) 高应力下,
![]() (3)
(3)
SnAgCuRE的蠕变特性如下:
1) 低应力下,
![]() (4)
(4)
2) 高应力下,
![]() (5)
(5)
式中:![]() 为应变速率;G为剪切变量;T为绝对温度;
为应变速率;G为剪切变量;T为绝对温度;![]() 为剪切力;R为摩尔气体常数。
为剪切力;R为摩尔气体常数。
在Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料中添加Er可以显著提高其蠕变断裂寿命,添加0.1%Er的可以使钎料的蠕变断裂寿命提高至7.1倍,Er的添加量超过0.25%时,蠕变寿命明显下降,Er的最适宜添加量为0.05%~0.25%[32]。稀土元素Ce的添加可以显著提高Sn3.0Ag2.8Cu焊点的蠕变性能,最佳添加量为0.1%Ce,蠕变寿命提高近9倍[66]。微量稀土可以细化组织,降低晶体边界应变,预防空洞形核[96, 100],因此蠕变断裂寿命明显提高。当稀土元素Ce添加量超过0.1%,由于大块稀土相(硬脆相)的形成,焊点的蠕变断裂寿命明显下降。在Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu钎料中添加微量稀土元素Ce可以将焊点的断裂蠕变寿命提高到SnAgCu的7.5倍[29]。通过拉伸蠕变试验研究SnAgCu和SnAgCuCe两种无铅钎料的蠕变行为,ZHANG等[101]构建两种钎料的Dorn和Garofalo-Arrhenius稳态蠕变模型,两种本构方程如式(6)~(7),发现SnAgCuCe的蠕变激活能明显高于SnAgCu的,主要是因为稀土元素Ce细化钎料基体中的金属间化合物颗粒,同时SnAgCuCe钎料的抗蠕变能力远高于SnAgCu钎料的。
Dorn 模型:
![]() (6)
(6)
式中:A为材料系数;Q为激活能。
Garofalo-Arrhenius模型:
![]() (7)
(7)
式中:![]() 为蠕变剪切应变速率;C为材料系数;
为蠕变剪切应变速率;C为材料系数;![]() 为应力级数。
为应力级数。
混合稀土元素(Ce/La)添加到Sn3.5Ag钎料,对其蠕变性能也有明显影响[72]。Sn3.5Ag在不同温度下(393、348和303 K)的应力因子分别为9.9、11.3、12.3,而Sn3.5Ag0.25RE钎料对应的应力因子为9.05、12.04和12.08,析出强化合金表现出高应力因子[102-103],Sn3.5Ag和Sn3.5Ag0.25RE两种钎料的在试验温度的范围内的蠕变行为也证实为析出强化机制[72]。材料的蠕变速率和析出强化合金组织的关系可以表示为式(8)[104],蠕变速率和![]() 成正比,而稀土元素添加到SnAg钎料中,金属间化合物颗粒的尺寸和间距得到明显的减小,因此混合稀土提高材料的蠕变抗力。有研究者[105]选择单一稀土La为添加元素,发现稀土元素La可以使Sn3.5Ag钎料的蠕变抗力提高近15%。
成正比,而稀土元素添加到SnAg钎料中,金属间化合物颗粒的尺寸和间距得到明显的减小,因此混合稀土提高材料的蠕变抗力。有研究者[105]选择单一稀土La为添加元素,发现稀土元素La可以使Sn3.5Ag钎料的蠕变抗力提高近15%。
![]() (8)
(8)
式中:ρ为位错密度;b为伯氏矢量;Λ为钉扎位错线上障碍物之间的间距;Δt为越过障碍物的时间;![]() 为滑移面上的颗粒面积。
为滑移面上的颗粒面积。
Sn0.7Cu0.5RE(Ce/La)钎料的蠕变抗力明显高于Sn0.7Cu钎料的,混合稀土可以明显提高Sn0.7Cu钎料的蠕变寿命[72]。混合稀土对Sn9Zn钎料的蠕变性能的影响也具有类似的规律。稀土元素可以减小钎料基体金属间化合物尺寸,减弱焊点的蠕变疲劳损伤和微裂纹延伸[106],同时稀土元素可以降低晶粒边界能和界面能,阻止晶粒边界滑移和位错移动[107],故而,稀土元素可以提高钎料的抗蠕变性能。通过压痕蠕变测试研究Sn9Zn-xRE(x=0.1%、0.25%、0.5%)蠕变行为,发现Sn9Zn0.25RE的蠕变速率最低,即具有最高的蠕变抗力,抗蠕变性能较高主要归因于析出的稀土相作为钎料基体中的强化相,当稀土含量超过0.25%时,蠕变抗力较低主要归因于Sn-Zn-RE金属间化合物的形成导致钎料基体中富Zn相的体积分数降低[108]。稀土元素对SnBi钎料的抗蠕变性能的促进作用和Sn9Zn0.25RE钎料类似[109]。
3 含稀土元素无铅焊点可靠性
无铅钎料的润湿性能优良、力学性能较好以及较高的抗蠕变性能,仅仅只能说明无铅钎料在焊接前后具有优良的性能,但是和实际应用仍有一段距离。主要是因为焊点的服役期间仍有许多意想不到情况出现,例如,因为电子器件、焊点和电路板整体结构之间材料线膨胀系数的差异,由于电子产品长期的开-关,整个结构中会出现交变的温度场,周期的运行就会在焊点中导致热应力的存在,在长时间作用下使焊点发生疲劳破坏,进而使电子产品失效[110-111]。因此,有必要在含稀土无铅钎料在实际应用和推广之间进行焊点的可靠性研究。目前主要采取试验和数值模拟两种方法针对无铅焊点可靠性主要集中在热循环、时效、跌落和弯曲等方面进行研究。但是针对含稀土无铅焊点可靠性的研究相对较少。
在150 ℃对Sn2.5Ag0.7Cu和Sn2.5Ag0.7Cu0.1RE两种焊点进行时效研究,两种焊点的界面层金属间化合物Cu6Sn5的厚度随着时间的增加呈现抛物线递增,SnAgCuRE焊点的界面层生长速度明显小于SnAgCu焊点的,同时在SnAgCu焊点的界面和SnAgCuRE焊点的内部萌生一定的微裂纹[46]。有研究者[45]针对Sn3.5Ag0.7Cu和Sn3.5Ag0.7Cu0.25RE在170 ℃进行分析,在时效100 h后界面分为Cu6Sn5和Cu3Sn两层。同时在Cu3Sn发现大量Kirkendall空洞存在,这主要是由于Sn和Cu在时效过程中不同的扩散属性造成。在时效过程中SnAgCuRE焊点的界面层生长速度明显低于SnAgCu焊点。另外,金属间化合物厚度(X)和时效时间(t)的关系如式(9)所示 [112]。时间常数n的选择可以通过试验结果进行计算,有研究者[113]认为当界面生长受扩散机制控制时,n的值取0.5。根据动力学理论,温度相关的扩散系数[114]如式(10)所示。目前针对含稀土元素无铅钎料在服役期间的界面扩散的扩散系数的计算鲜见报道。
![]() (9)
(9)
![]() (10)
(10)
式中:Xt为t时刻界面的厚度;X0为焊后界面层的厚度;k为扩散系数;t为服役时间;n为时间指数;A为扩散常数。
根据美国军用标准(MIL-STD-883)[115],军用电子器件可靠性测试的热循环范围为-55~125 ℃,图3所示为QFP器件Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu0.03Ce焊点经过3个温度循环的蠕变应变云图[116]。可以看出,焊点、焊跟和焊趾为蠕变应变集中的区域,焊跟部分的应变值最大, 该处是裂纹潜在的发源地,同时通过实验研究也证实了这一研究结果。进一步研究发现[117],SnAgCuCe焊点的蠕变变形明显小于SnAgCu焊点,SnAgCuCe焊点在热循环载荷作用下的疲劳寿命明显高于SnAgCu焊点的,增加幅值为12.66%,这主要归因于添加稀土元素后焊点内部颗粒的生长得到一定程度的抑制[51],SnAgCuCe焊点的裂纹路径和焊点内部金属间化合物Cu6Sn5颗粒粗化有明显的联系[118],由于颗粒和Sn之间线膨胀系数的失配,容易在两者的界面处形成裂纹,同时,随着热循环的增加,裂纹会沿着焊点内部进一步延伸至焊点界面,导致SnAgCuCe焊点的界面失 效[51]。有研究者对BGA器件Sn3Ag0.5Cu/Sn3Ag- 0.5Cu0.05Ce焊点通过施加循环应力进行机械疲劳试验,研究结果发现SnAgCuCe焊点的可靠性低于SnAgCu焊点[119]。同时,有研究者发现在0~125 ℃的循环过程中,QFP器件Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu0.03Ce焊点的拉伸力随着温度循环次数的增加明显下降[13]。
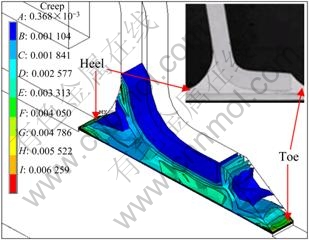
图3 SnAgCuCe焊点蠕变云图[117]
Fig.3 Creep nephogram of SnAgCuCe solder joints[117]
稀土元素Ce添加到Sn0.5Cu0.05Ni钎料,对应的焊点在热循环过程中性能和界面生长发生明显变化,经过2000周热循环后,QFP32器件SnCuNiCe焊点拉伸力相比,SnCuNi的焊点提高了21.16%,此时,界面层出现了Cu3Sn相,导致焊点力学性能下降,微量稀土元素Ce能有效抑制界面处以及钎料内部金属间化合物的粗化,从而缓解热循环对焊点力学性能的不利影响,使得SnCuNiCe的焊点可靠性优于SnCuNi焊点的[120]。混合稀土添加到SnAg钎料组织和性能有明显的影响,对应SnAg和 SnAgRE焊点的可靠性也有相关报道。LAW和WU[92]针对Au/Ni镀层BGA器件Sn3.5Ag和Sn3.5Ag0.5RE焊点在150 ℃时效1 000 h下的界面组织演化规律和焊点的剪切强度进行研究,时效过程中在两种焊点的内部和界面均发现大块状的(Au,Ni)Sn4相,同时界面层厚度均随着时间的增加明显增厚,在时效过程中,两种焊点的强度均具有较好的稳定性,SnAgRE焊点的强度明显高于SnAg焊点的。另外有研究者[121]证实,在Sn3.5Ag中添加微量的稀土元素La,对应焊点的疲劳寿命可以提高近5倍,对应稀土含量为0.1%时焊点具有最高的疲劳寿命。对于焊点的疲劳寿命计算目前主要有基于塑形应变、蠕变应变和应变能密度 [122-125]。但是,就目前文献的研究还缺乏相关含稀土无铅焊点的疲劳寿命预测方程的报道。
含稀土元素Ce的SnZn系焊点在150 ℃时效界面组织演化也有相关报道[14, 126]。由于界面处Cu原子的扩散速度远大于Zn原子的,在界面处形成Zn耗尽区域,进而导致Cu5Zn8层溶解、破碎,另外,原子间的相互扩散在界面处形成空洞,导致焊点力学性能的恶化,而采用Au/Ni/Cu基板时,由于Ni层可以作为Cu的扩散阻挡层,可显著提高含稀土元素Ce的SnZn系焊点的可靠性。针对含稀土的无铅焊点的可靠性研究成果目前还相对缺乏,为了进一步深化含稀土无铅焊点的可靠性,应该针对焊点的界面层生长、元素扩散、焊点应力—应变响应和焊点疲劳寿命进行研究。
4 过量稀土元素对钎料表面锡须的影响
稀土元素的添加在一定程度上可以提高钎料的力学性能、改善钎料的润湿性、细化钎料的基体组织。但是由于稀土极容易氧化[127],会导致在钎料表面出现锡须,因此,在电子器件服役期间,锡须的生长会引起电子器件相邻引脚的短路[128-129],直接导致电子器件的报废,无疑这也给含稀土元素的无铅钎料的推广带来了致命的打击。
但是在含稀土元素的无铅钎料中,发现锡须是在稀土元素添加过量的情况下出现的。CHUANG[130]发现在Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu中添加1.0%Ce,钎料表面会出现明显的锡须。DUDEK和CHAWLA[131-132]在Sn3.9- Ag0.6Cu钎料中添加2%的稀土元素La、Ce和Y,均发现在稀土相表面生长大量的锡须。郝虎等[133]在Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu的钎料添加过量的稀土元素Ce(1%),由于钎料内部稀土相暴露于空气中,稀土相将发生氧化而产生体积膨胀,钎料基体对体积膨胀的抑制作用将使稀土相内部产生巨大的压应力从而加速锡须的生长,图4所示为稀土相表面的锡须。同时,在含稀土元素Er的SnAgCu钎料中也发现了类似含Ce钎料中的锡须[134],主要是稀土相与氧发生反应:CeSn3+O2→ 3Sn+CeO2,4ErSn3+ 3O2→12Sn+2Er2O3,在该过程中,氧原子向稀土相晶格内部的扩散将导致其体积膨胀,而周围钎料基体对体积膨胀的抑制作用将使其内部产生巨大的压应力,此压应力将为锡须的生长提供驱动力,同时,稀土相氧化过程中释放出来的Sn原子将为锡须的生长提供生长源[135]。
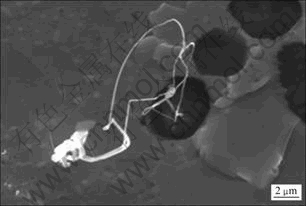
图4 稀土相表面的锡须[133]
Fig.4 Tin whiskers on Sn-RE phases[133]
CHUANG和LIN[136]对比SnAgCuCe和SnZnCe钎料组织,发现SnZnCe钎料中并未发现锡须,因此,通过进一步的研究发现在Sn3Ag0.5Cu0.5Ce钎料中添加0.2%Zn元素可以抑制锡须的生长[137]。同时,他 们[138]对Sn9Zn添加稀土元素Ce和La(含量均为0.5%)的钎料进行研究,发现SnZnLa钎料的组织中生长出明显的锡须,而SnZnCe仍然没有出现锡须。YE 等[139]采取在Sn9Zn0.5Ga钎料中添加过量的稀土元素Pr(0.7%),发现在钎料中出现大量针状锡须生长在稀土相表面,并且短期内得到快速的生长。可以看出,Zn对锡须的抑制作用也仅仅局限于国立台湾大学的实验研究中,Zn的抑制作用可以认为是有限的,仅仅使用单一的实验条件(稀土含量为0.5%)和稀土元素(Ce),具体的抑制作用有待于进一步的研究和证实。LIU等[140]研究发现在Sn0.7Cu钎料中添加稀土元素Nd(0.1%~5%),即使是在稀土元素含量为0.1%时,也会出现类似的锡须。
通过对文献[134]分析发现,稀土元素在添加过量时会出现锡须现象,综合目前的研究报道发现稀土添加量最少也在0.1%(Nd)时出现锡须,大部分的研究者还是将稀土元素的含量控制在0.5%以上来研究锡须生长。为了对推广含稀土无铅钎料的进一步应用,首当其冲的是解决含锡须无铅钎料锡须问题,在解决该问题的过程中必须考虑到以下三方面:首先,含微量稀土元素的无铅钎料表面锡须的存在与否的问题;其次,含稀土无铅焊点在服役期间的锡须存在与否的问题;再次,含稀土无铅焊点表面锡须的预防问题。只有在无铅钎料解决以上3个方面的内容,无铅钎料才能够在电子工业中获得广泛的应用和推广。
5 含稀土无铅钎料研究中所存在的问题
随着电子工业的发展,无铅钎料的研究日新月异,近年来国内国际报道了大量的无铅钎料专利,在这其中含稀土元素的无铅钎料占据重要的一席。尽管在测试分析过程中发现含稀土元素的无铅钎料具有润湿性好、力学性能优良等系列优点,但是含稀土元素的无铅钎料距离实际应用和推广仍有很长的路要走。困扰该系列钎料的问题主要有3个,分别列举如下:
1) 稀土资源:稀土是稀有金属,稀土在世界的分布因地而异,中国是稀土大国,但是随着国家资源储备计划的实施和推进,财政部和国家税务总局下发通知,决定自2011年4月1日起,将稀土矿原矿资源税税额标准统一上调10倍[141]。无疑这在一定层次上也影响了稀土的进一步使用,增加了相关成本。为了应对这一问题,可以采取以下措施解决这一问题:首先是对需添加痕量稀土元素的情况,在对无铅钎料成本影响不大的前提下可坚持添加稀土元素,而对需添加大量稀土元素的情况,可以选择研究开发新型无铅钎料,使新型无铅钎料的性能和含稀土的无铅钎料相近。
2) 锡须问题:锡须的出现一直和引线框架有着直接的联系[142]。对于含稀土元素的无铅钎料来说,锡须算是其研究过程中的一个意外,研究者的初衷是希望添加稀土元素提高钎料的性能,锡须的突然出现,无疑也为业界带来了新的问题,直接阻碍了含稀土无铅钎料的进一步推广和应用。为了突破这一问题,CHUANG和CHI[143]采取在Sn3Ag0.5Cu0.5Ce中添加Ge元素,由于Ge的存在,钎料中CeSn3的氧化得到缓和,致使没有足够压应力供锡须的生长。另外,尽量控制稀土元素的添加量在一个痕量范围,如在SnAgCu钎料中添加0.03%Ce,SnAgCuCe焊点内部发现了小颗粒的CeSn3相,但并没有锡须生长[51]。从而也说明锡须的生长和稀土添加量有着必然的关系。
3) 失效问题:根据美国空军电子工业部门的统 计[144-145],电子元器件失效的原因55%是由于温度的变化引起的,20%是由于振动引起的,19%是因为潮气的原因,另外6%是灰尘的原因造成的。焊点是整个电子器件中最薄弱的环节[146],温度、振动、潮气和灰尘对焊点可靠性影响有必要进行深入的研究和探讨。由于稀土元素的加入,无铅焊点在4种环境下的可靠性是提高还是恶化仍然需要进行研究,目前稀土元素的影响机制研究主要在稀土元素的亲Sn性[147]、稀土元素的吸附现象[148]、晶界富集[149]等,同时,研究者又发现,含稀土的焊点由于稀土相的析出可以阻止焊点疲劳裂纹的扩展[150],也有研究者发现稀土相的析出对裂纹路径几乎没有影响[51]。因此,含稀土无铅焊点在服役期间的失效问题是无铅钎料研究中的一个重要课题。
6 结论
综合评述国内外在含稀土元素无铅钎料的研究现状,总结稀土元素对无铅钎料组织和性能的影响,发现适量稀土元素的添加在一定程度上可以细化钎料基体组织、减小金属间化合物颗粒尺寸和降低界面厚度。稀土元素的添加可以提高无铅钎料某一性能或者综合性能,但是也有部分相悖的观点出现,这主要和稀土的添加方式、钎料冶炼工艺及试验设备等条件有关。目前,针对含稀土无铅焊点可靠性的研究成果包括服役期间界面层生长和裂纹路径,缺乏关于焊点在不同环境条件下可靠性的深入探讨和研究。另外,含稀土无铅钎料锡须问题制约着含稀土无铅钎料的应用和推广。综合分析含稀土无铅钎料研究中存在问题,并给出潜在可能的解决措施,为含稀土无铅钎料的进一步研究提供基础支撑。
REFERENCES
[1] 尹立孟, 张新平. 电迁移致无铅钎料微互连焊点的脆性蠕变断裂行为[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(2): 253-257.
YIN Li-meng, ZHANG Xin-ping. Electromigration induced brittle creep fracture behavior of lead-free solder micro-interconnections[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(2): 253-257.
[2] ZENG K, TU K N. Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2002, 38(2): 55-105.
[3] ZOU C D, GAO Y L, YANG B, ZHAI Q J. Melting and solidification properties of nanoparticles of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu lead-free solder alloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2010, 61(4): 474-480.
[4] GAO Li-li, XUE Song-bai, ZHANG Liang, SHENG Zhong, JI Feng, DAI Wei, YU Sheng-lin, ZENG Guang. Effect of alloying elements on properties and microstructures of SnAgCu solders[J]. Microelectronic Engineering, 2010, 87(11): 2025-2034.
[5] 王丽凤, 孙凤莲, 吕 烨, 申旭伟. Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-xNi无铅焊料及焊点的性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2009, 30(1): 9-12.
WANG Li-feng, SUN Feng-lian, L? Ye, SHEN Xu-wei. Properties of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-xNi lead-free solders and soldering joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2009, 30(1): 9-12.
[6] CHEN W M, YANG S C, TSAI M H, KAO C R. Uncovering the driving force for massive spalling in the Sn-Cu/Ni system[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63(1): 47-49.
[7] LI Xian-fen, ZHANG Fei, ZU Fang-qiu, L? Xue, ZHAO Zhen-xing, YANG Dong-dong. Effect of liquid-liquid structure transition on solidification and wettability of Sn-0.7Cu solder[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 505(2): 472-475.
[8] SHEN J, LIU Y C, WANG D J, GAO H X. Nano ZrO2 particulate-reinforced lead-free solder composite[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Processing, 2006, 22(4): 529-532.
[9] 李仕明, 余 春, 陆 皓. 锗元素对Sn-3.5Ag合金/铜界面反应的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2009, 33(9): 21-24.
LI Shi-ming, YU Chun, LU Hao. Effect of Ge on interfacial reaction Sn-3.5Ag alloy/Cu interface[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 33(9): 21-24.
[10] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, SHENG Z, YE H, XIAO Z X, ZENG G, CHEN Y, YU S L. Development of Sn-Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(1): 1-15.
[11] 周 健, 王常亮, 薛 烽. Sn-Zn钎料Cu接头的界面反应及力学性能[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 39(3): 615-622.
ZHOU Jian, WANG Chang-liang, XUE Feng. Interfacial reaction and joint strength of Sn-Zn solder/Cu[J]. Journal of Southeast University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 39(3): 615-622.
[12] LI B, SHI Y W, LEI Y P, GUO F, XIA Z D, ZONG B. Effect of rare earth element addition on the microstructure of Sn-Ag-Cu solder joint[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2005, 34(3): 217-224.
[13] 王俭辛. 稀土Ce对Sn-Ag-Cu和Sn-Cu-Ni钎料性能及焊点可靠性影响的研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2009.
WANG Jian-xin. Study on effects of Ce on properties of Sn-Ag-Cu & Sn-Cu-Ni solders and reliability of soldered joints[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009.
[14] 王 慧. 微合金化对Sn-9Zn无铅钎料性能影响及相关机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010.
WANG Hui. Study on solderability and wetting mechanisms of micro-alloyed Sn-9Zn lead-free solder[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010.
[15] 朱 颖, 方洪渊, 钱乙余, 丁克俭, 薛利忠. Sn-Pb-Ce-La钎料合金的显微组织分析[J]. 稀土, 1994, 15(1): 57-59.
ZHU Ying, FANG Hong-yuan, QIAN Yi-yu, DING Ke-jian, XUE Li-zhong. Microstructures of Sn-Pb-Ce-La solders[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 1994, 15(1): 57-59.
[16] 邱小明, 李世权, 万传庚, 赵旭日. 稀土对锡铅钎料润湿性和接头强度的影响[J]. 吉林工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 1994, 24(76): 73-77.
QIU Xiao-ming, LI Shi-quan, WAN Chuan-geng, ZHAO Xu-ri. The influence of rare earth on the wettability, flowability and joint strength of Sn-Pb solders[J]. Journal of Jilin University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 1994, 24(76): 73-77.
[17] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, ZENG G, SHENG Z, CHEN Y, YU S L. Effects of rare earths on properties and microstructures of lead-free solder alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Material in Electronics, 2009, 20(8): 685-694.
[18] WU C M L, YU D Q, LAW C M L, WANG L. Properties of lead-free solder alloys with rare earth element additions[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2004, 44(1): 1-44.
[19] CHUANG T H, YEN S F. Abnormal growth of tin whiskers in a Sn3Ag0.5Cu0.5Ce solder ball array package[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2006, 35(8): 1621-1627.
[20] 韩宗杰. 电子组装元器件半导体激光无铅软钎焊技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2009.
HAN Zong-jie. Diode laser soldering to electronic mounting components/devices[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009.
[21] CHEN Z G, SHI Y W, XIA Z D, YAN Y F. Study on the microstructure of a novel lead-free solder alloy SnAgCu-RE and its soldered joints[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2002, 31(10): 1122-1128.
[22] CHEN Z G, SHI Y W, XIA Z D, YAN Y F. Properties of lead-free solder SnAgCu containing minute amounts of rare earth[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2008, 32(4): 235-243.
[23] 李 擘, 史耀武, 夏志东, 雷永平, 郭 福. 添加微量稀土元素的SnAgCu无铅钎料的研究[J]. 电子工艺技术, 2004, 25(5): 193-198.
LI Bo, SHI Yao-wu, XIA Zhi-dong, LEI Yong-ping, GUO Fu. Research on the SnAgCu lead-free solder with minute amount rare earth elements[J]. Electronics Process Technology, 2004, 25(5): 193-198.
[24] 易江龙, 张宇鹏, 许 磊, 刘凤美, 杨凯珍. 混合稀土对Sn-0.70Cu-0.05Ni钎料组织与性能的影响[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2011, 30(2): 25-28.
YI Jiang-long, ZHANG Yu-peng, XU Lei, LIU Feng-mei, YANG Kai-zhen. Effect of adding mixed RE on microstructure and properties of Sn-0.70Cu-0.05Ni solder alloy[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2011, 30(2): 25-28.
[25] XIA Z D, CHEN Z G, SHI Y W, MU N, SUN N. Effect of rare earth element additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of tin-silver-bismuth solder[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2002, 31(2): 564-567.
[26] 薛松柏, 刘 琳, 代永峰, 姚立华. 微量稀土元素铈对Sn-Ag-Cu无铅钎料物理性能和焊点抗拉强度的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2005, 26(10): 23-26.
XUE Song-bai, LIU Lin, DAI Yong-feng, YAO Li-hua. Effects of rare-earth element Ce on physical properties and mechanical properties of SnAgCu lead-free solder[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2005, 26(10): 23-26.
[27] 赖忠民. Ga/In与稀土Ce对Ag30CuZnSn钎料显微组织及钎焊接头性能影响的研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2011.
LAI Zhong-min. Effects of Ga/In and rare earth Ce on microstructures and properties of brazed joint of Ag30CuZn filler metal[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2011.
[28] DUDEK M A, SIDHU R S, CHAWLA N, RENAVIKAR M. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of novel rare earth-containing Pb-free solders[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2006, 35(12): 2088-2097.
[29] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, CHEN Y, YU S L, SHENG Z, ZENG G. Microstructure and creep properties of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solders bearing minor amounts of the rare earth cerium[J]. Soldering & Surface Mount Technology, 2010, 22(2): 30-34.
[30] 张 亮, 薛松柏, 曾 广, 皋利利, 陈 燕, 盛 重, 禹胜林. 铈对SnAgCu钎料的显微组织和性能的影响[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2009, 27(2): 246-250.
ZHANG Liang, XUE Song-bai, ZENG Guang, GAO Li-li, CHEN Yan, SHENG Zhong, YU Sheng-lin. Effects of cerium on microstructure and properties of SnAgCu solders[J]. Journal of Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2009, 27(2): 246-250.
[31] HAO H, TIAN J, SHI Y W, LEI Y P, XIA Z D. Properties of Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu solder alloy with trace rare earth element Y additions[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007, 36(7): 766-774.
[32] SHI Y W, TIAN J, HAO H, XIA Z D, LEI Y P, GUO F. Effects of small amount addition of rare earth Er on microstructure and property of SnAgCu solder[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 453(1/2): 180-184.
[33] GAO L L, XUE S B, ZHANG L, XIAO Z X, DAI W, JI F, YE H, ZENG G. Effect of praseodymium on the microstructure and properties of Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu solder[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(9): 910-916.
[34] GAO L L, XUE S B, ZHANG L, SHENG Z, ZENG G, JI F. Effects of trace earth Nd addition on microstructure and properties of SnAgCu solder[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(7): 643-648.
[35] RAMIREZ A G, MAVOORI H, JIN S. Bonding nature of rare-earth-containing lead-free solders[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 80(3): 398-400.
[36] MAVOORI H, RAMIREZ A G, JIN S. Universal solders for direct and powerful bonding on semiconductors, diamond and optical materials[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 78(19): 2976-2978.
[37] PEI M, QU J M. Effect of lanthanum doping on the microstructure of tin-silver solder alloys[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2008, 37(3): 331-338.
[38] NOH B I, CHOI J H, YOON J W, JUNG S B. Effects of cerium content on wettability, microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-Ag-Ce solder alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 499(2): 154-159.
[39] CHEN W X, XUE S B, WANG H, HU Y H, WANG J X. Effects of rare earth Ce on properties of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(7): 719-725.
[40] 胡玉华, 薛松柏, 陈文学, 王 慧. Sn-9Zn-xCe钎料显微组织及钎焊性能的分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(6): 77-80.
HU Yu-hua, XUE Song-bai, CHEN Wen-xue, WANG Hui. Microstructure and solderability of Sn-9Zn-xCe lead-free solder[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(6): 77-80.
[41] 卢 斌, 王娟辉, 栗 慧, 朱华伟, 焦羡贺. 微量铈对Sn-0.7Cu-0.5Ni焊料合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2007, 25(2): 217-223.
LU Bin, WANG Juan-hui, LI Hui, ZHU Hua-wei, JIAO Xian-he. Effect of cerium on microstructure and properties of Sn-0.7Cu-0.5Ni lead-free solder alloy[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2007, 25(2): 217-223.
[42] ZENG G, XUE S B, ZHANG L, GAO L L, DAI W, LUO J D. A review on the interfacial intermetallic compounds between Sn-Ag-Cu based solders and substrates[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(5): 421-440.
[43] YOON J W, LEE Y H, KIM D G, KANG H B, SUH S J, YANG C W, LEE C B, JUNG J M, YOO C S, JUNG S B. Intermetallic compounds layer growth at the interface between Sn-Cu-Ni solder and Cu substrate[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 381(1/2): 151-157.
[44] 卢 斌, 王娟辉, 栗 慧, 焦羡贺. 添加0.10%Ce对Sn-0.7Cu-0.5Ni焊料与Cu基板间界面IMC的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(3): 390-395.
LU Bin, WANG Juan-hui, LI Hui, ZHU Hua-wei, JIAO Xian-he. Effect of 0.10% Ce on intermetallic compounds at Sn-0.7Cu-0.5Ni/Cu interface[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(3): 390-395.
[45] LAW C M T, WU C M L, YU D Q, WANG L, LAI J K L. Microstructure, solderability and growth of intermetallic compounds of Sn-Ag-Cu-RE lead-free solder alloys[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2006, 35(1): 89-93.
[46] 王要利, 张柯柯, 刘 帅, 赵国标. 微连接用Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE)钎料焊点界面Cu6Sn5的长大行为[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(1): 117-121.
WANG Yao-li, ZHANG Ke-ke, LIU Shuai, ZHAO Guo-biao. Growth behavior of Cu6Sn5 at the interface of Sn-2.5Ag-0.7Cu(0.1RE) solder joints for micro-joining[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(1): 117-121.
[47] HAO H, SHI Y W, XIA Z D, LI Y P, GUO F. Microstructure evolution of SnAgCuEr lead-free solders under high temperature aging[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2008, 37(1): 2-8.
[48] 周迎春, 潘清林, 李文斌, 梁文杰, 何运斌, 李运春, 路聪阁. La对Sn-Ag-Cu无铅钎料与铜钎焊接头金属间化合物的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(9): 1651-1657.
ZHOU Ying-chun, PAN Qing-lin, LEI Wen-bin, LIANG Wen-jie, HE Yun-bin, LI Yun-chun, LU Cong-ge. Effect of La on intermetallic compounds of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free alloy soldered with copper[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(9): 1651-1657.
[49] DUDEK M A, SIDHU R S, CHAWLA N. Novel rare-earth-containing lead-free solders with enhanced ductility[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2006, 58(6): 57-62.
[50] ZENG G, XUE S B, ZHANG L, SHENG Z, GAO L L. Reliability evaluation of SnAgCu/SnAgCuCe solder joints based on finite element simulation and experiments[J]. Soldering & Surface Mount Technology, 2010, 22(4): 57-64.
[51] 张 亮. SnAgCu系无铅焊点可靠性及相关理论研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2011.
ZHANG Liang. Study on reliability of SnAgCu based lead-free soldered joint and related theory[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011.
[52] LAW C M L, WU C M L, YU D Q, LI M, CHI D Z. Interfacial microstructure and strength of lead-free Sn-Zn-RE BGA solder bumps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Advanced Packaging, 2005, 28(2): 252-257.
[53] XIAO Z X, XUE S B, HU Y H, YE H, GAO L L, WANG H. Properties and microstructure of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder alloy bearing Pr[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2011, 22(6): 659-665.
[54] HU Y H, XUE S B, WANG H, YE H, XIAO Z X, GAO L L. Effects of rare earth element Nd on the solderability and microstructure of Sn-Zn lead-free solder[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2011, 22(5): 481-487.
[55] LEE H T, CHEN Y F. Influence of lanthanum additions on the microstructure and microhardness of Sn-3.5Ag solder[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2009, 38(10): 2148-2157.
[56] DUDEK M A, CHAWLA N. Three-dimensional (3D) microstructure visualization of LaSn3 intermetallics in a novel Sn-rich rare-earth-containing solder[J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(9): 1364-1368.
[57] MA X, QIAN Y Y, YOSHIDA F. Effect of la on the Cu-Sn intermetallic compound (IMC) growth and solder joint reliability[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 334(1/2): 224-227.
[58] LEE T Y, CHOI W, TU K N, JANG J W, KUO S M, LIN J K, FREAR D R, ZENG K, KIVILAHTI J K. Morphology, kinetics and thermodynamics of solid-state aging of eutectic SnPb and Pb-free solders[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(2): 291-301.
[59] 陈 燕. 稀土铈对锡银铜无铅钎料组织性能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 机械科学研究总院, 2006.
CHEN Yan. Effects of cerium on property and microstructure for SnAgCu lead free solder[D]. Harbin: China Academy of Machinery Science & Technology, 2006.
[60] MA X, YOSHIDA F. Interaction relation in 60Sn-Pb-0.05La ternary solder alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 56(4): 441-445.
[61] 于大全. 电子封装互连无铅钎料及其界面问题研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2004.
YU Da-quan. Development of lead free solder and its interfacial issues in electronics packaging[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2004.
[62] 陈志刚. SnAgCuRE钎焊蠕变行为的研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2003.
CHEN Zhi-gang. Study on the creep behavior of SnAgCuRE solder joints[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2003.
[63] 孙凤莲, 胡文刚, 王丽凤, 马 鑫. Bi对Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu无铅钎料熔点及润湿性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2008, 29(10): 5-8.
SUN Feng-lian, HU Wen-gang, WANG Li-feng, MA Xin. Influence of Bi on the melting point and wettability of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu lead-free solder[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2008, 29(10): 5-8.
[64] 卢 斌, 栗 慧, 王娟辉, 朱华伟, 焦羡贺. 稀土Er对Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu无铅焊料合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(4): 518-524.
LU Bin, LI Hui, WANG Juan-hui, ZHU Hua-wei, JIAO Xian-he. Effect of Er on microstructure and properties of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu lead-free solder alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(4): 518-524.
[65] 陈 铮, 周 飞. 材料连接原理[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2001: 65-99.
CHEN Zhong, ZHOU Fei. The principle of material bonding[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2001: 65-99.
[66] YU D Q, ZHAO J, WANG L. Improvement on the microstructure stability, mechanical and wetting properties of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder with the addition of rare earth elements[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 376(1/2): 170-175.
[67] ZHAO X Y, ZHAO M Q, CUI X Q, TONG M X. Effect of cerium on microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-Ag-Cu system lead-free solder alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(4): 805-810.
[68] XUE S B, YU S L, WANG X Y, LIU L, HU Y F, YAO L H. Effects of rare earth element Ce on solderabilities of micron-powdered Sn-Ag-Cu solder[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2005, 15(6): 1285-1289.
[69] WANG J X, XUE S B, HAN Z J, YU S L, CHEN Y, SHI Y W, WANG H. Effects of rare earth Ce on microstructures, solderability of Sn-Ag-Cu and Sn-Cu-Ni solder as well as mechanical properties of soldered joints[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 467(1/2): 219-226.
[70] 董文兴, 史耀武, 雷永平, 夏志东, 郭 福. Ni/P/Ce元素对SnAgCu无铅钎料性能和组织的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(10): 1759-1763.
DONG Wen-xing, SHI Yao-wu, LEI Yong-ping, XIA Zhi-dong, GUO Fu. Effects of Ni/P/Ce elements on the properties and microstructure of SnAgCu lead-free solders[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(10): 1759-1763.
[71] WANG L, YU D Q, ZHAO J H, HUANG M L. Improvement of wettability and tensile property in Sn-Ag-RE lead-free solder alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 56(6): 1039-1042.
[72] WU C M L, YU D Q, LAW C M T, WANG L. Improvements of microstructure, wettability, tensile and creep strength of eutectic Sn-Ag alloy by doping with rare-earth elements[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(12): 3146-3154.
[73] 袁宜耀. 稀土Ce对Sn基无铅焊料的组织、性能及界面影响[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2008.
YUAN Yi-yao. Effects of the rare earth Ce on the microstructures, properties and interface of Sn based lead free solders[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2008.
[74] LAW C M T. Reliability and interfacial reaction of lead-free solder alloys doped with rare earth elements[D]. Hongkong: City University of Hongkong, 2004.
[75] 王俭辛, 薛松柏, 黄 翔, 韩宗杰, 禹胜林. 气氛保护对Sn-Cu-Ni-Ce无铅钎料润湿性的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2007, 28(1): 49-52.
WANG Jian-xin, XUE Song-bai, HUANG Xiang, HAN Zong-jie, YU Sheng-lin. Effect of N2 protection on wettability of Sn-Cu-Ni-Ce lead-free solder[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2007, 28(1): 49-52.
[76] 史益平. 微量稀土Ce对Sn-Cu-Ni钎料焊点可靠性影响的研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2008.
SHI Yi-ping. Research on effects of minute amount of rare -earth element Ce on reliability of the joints soldered with Sn-Cu-Ni solder[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008.
[77] 李建新. 新型Sn-Cu系无银无铅焊料的研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2009.
LI Jian-xin. The research of Sn-Cu system without Ag lead-free solder[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2009.
[78] WU C M L, LAW C M T, YU D Q,WANG L. The wettability and microstructure of Sn-Zn-RE alloys[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2003, 32(2): 63-69.
[79] WU C M L, YU D Q, LAW C M T,WANG L. The properties of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder alloys doped with trace rare earth elements[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2002, 31(9): 921-927.
[80] 张启运. 无铅钎焊的困惑、出路和前景[J]. 焊接, 2007(2): 6-10.
ZHANG Qi-yun. A puzzle in lead free soldering, its outlet and application prospect[J]. Welding & Joining, 2007(2): 6-10.
[81] 薛松柏, 张 亮, 皋利利, 禹胜林, 朱 宏. 微量稀土元素对无铅钎料性能影响的研究现状和发展趋势[J]. 焊接, 2009(3): 24-33.
XUE Song-bai, ZHANG Liang, GAO Li-li, YU Sheng-lin, ZHU Hong. Current situation and prospect on effects of micro alloying elements on properties of lead-free solders[J]. Welding & Joining, 2009(3): 24-33.
[82] 陈文学. Ag、Ga、Al及Ce对Sn-9Zn无铅钎料性能的影响[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010.
CHEN Wen-xue. Effects of Ag, Ga, Al and Ce on the properties of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010.
[83] 王 炜. 无铅焊料Sn-Zn-xLa的制备和研究[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2008.
WANG Wei. Sn-Zn-xLa lead-free solders[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2008.
[84] ZHOU J, SUN Y S, XUE F. Effect of Nd and La on surface tension and wettability of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solders[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2005, 15(5): 1161-1165.
[85] ZHOU J, HUANG D, FANG Y L, XUE F. Investigation on properties of Sn-8Zn-3Bi lead-free solder by Nd addition[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 480(2): 903-907.
[86] 张建纲, 黄继华, 戴志锋, 张 华, 赵兴科. 含稀土Sn-Zn-Bi系无铅钎料润湿性能的研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2006, 24(5): 586-591.
ZHANG Jian-gang, HUANG Ji-hua, DAI Zhi-feng, ZHANG Hua, ZHAO Xing-ke. Wettability of Sn-Zn based lead-free solder with rare earths[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2006, 24(5): 586-591.
[87] ZHANG L, XUE SONGBAI, HAN Z J, WANG J X, GAO L L, SHENG Z. Mechanical properties of fine pitch devices soldered joints based on creep model[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 21(6): 82-85.
[88] 黄明亮. 电子封装无铅钎料的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2001.
HUANG Ming-liang. Development of lead-free solder alloys in electronics packaging[D]. Dalian, Dalian University of Technology, 2001.
[89] DALY A A W, HAMMAD A E. Effects of small addition of Ag and/or Cu on the microstructure and properties of Sn-9Zn lead-free solders[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(20): 5212-5219.
[90] 陈志刚, 史耀武, 夏志东. 微量混合稀土对SnAgCu钎料合金性能的影响[J]. 电子工艺技术, 2003, 24(2): 53-58.
CHEN Zhi-gang, SHI Yao-wu, XIA Zhi-dong. Effect of mixed rare earth on the properties of SnAgCu lead-free solder alloy[J]. Electronics Process Technology, 2003, 24(2): 53-58.
[91] LI G D, SHI Y W, HAO H, XIA Z D, LEI Y P, GUO F, LI X Y. Effect of rare earth addition on shear strength of SnAgCu lead-free solder joints[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2009, 20(2): 186-192.
[92] LAW C M T, WU C M L. Microstructure evolution and shear strength of Sn-3.5Ag-RE lead-free BGA solder balls[C]// Proceeding of the Sixth IEEE CPMT Conference on High Density Microsystem Design and Packaging and Component Failure Analysis, Shanghai: IEEE, 2004: 60-65.
[93] LEE H T, CHEN Y F, SCHWEDT A, MAYER J. Effect of La addition on adhesive strength and fracture behavior of Sn-3.5Ag solder joints[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(10/11): 3630-3638.
[94] 杨长勇, 徐九华, 丁文峰, 傅玉灿. 稀土La改性Ag-Cu-Ti钎料的显微组织和力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(1): 67-70, 74.
YANG Chang-yong, XU Jiu-hua, DING Wen-feng, FU Yu-can. Microstructure and mechanical property of Ag-Cu-Ti fillers added with rare earth lanthanum[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(1): 67-70, 74.
[95] WU C M L, WONG Y W. Rare-earth additions to lead-free electronic solders[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2007, 18(1/3): 77-91.
[96] WU C M L, YU D Q, LAW C M T, WANG L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of new lead-free Sn-Cu-RE solder alloys[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2002, 31(9): 928-932.
[97] TAI F, GUO F, HAN M T, XIA Z D, LEI Y P, SHI Y W. Creep and thermomechanical fatigue properties of in situ Cu6Sn5 reinforced lead-free composite solder[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(15): 3335-3342.
[98] CHEN Z G, SHI Y W, XIA Z D. Constitutive relations on creep for SnAgCuRE lead-free solder joints[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2004, 33(9): 964-971.
[99] DUDEK M A, CHAWLA N. Effect of rare-earth (La, Ce, and Y) additions on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of Sn-3.9Ag-0.7Cu solder alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2010, 41(3): 610-620.
[100] 冯武锋, 王春青, 李明雨. 电子元件焊接中的钎料合金研制及设计方法[J]. 电子工艺技术, 2000, 21(2): 47-52, 59.
FENG Wu-feng, WANG Chun-qing, LI Ming-yu. Development and design methods of solder alloys applied in joining electronic components[J]. Electronics Process Technology, 2000, 21(2): 47-52, 59.
[101] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, ZENG G, CHEN Y, YU S L, SHENG Z. Creep behavior of SnAgCu solders with rare earth Ce doping[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(3): 412-417.
[102] McCABE R J, FINE M E. The creep properties of precipitation-strengthened tin-based alloys[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2000, 52(6): 33-35.
[103] IGOSHEV V I, KLEIMAN J I, SHANGGUAN D, LOCK C, WONG S, WISEMAN M. Microstructure changes in Sn-3.5Ag solder alloy during creep[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 1998, 27(12): 1367-1371.
[104] OLIVER W C, NIX W D. High temperature deformation of oxide dispersion strengthened Al and Al-Mg solid solutions[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1982, 30(7): 1335-1347.
[105] PEI M. Effects of lanthanum doping on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of a SnAg alloy[D]. Georgia: Georgia Institute of Technology, 2007.
[106] XIAO W M, SHI Y W, XU G C, REN R, GUO F, XIA Z D,LEI Y P. Effect of rare earth on mechanical creep-fatigue property of SnAgCu solder joint[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 472(1/2): 198-202.
[107] HE H W, XU G C, GUO F. Effect of small amount of rare earth addition on electromigration in eutectic SnBi solder reaction couple[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(8): 2089-2096.
[108] MAHMUDI R, GERANMAYEH A R, ZAHIRI B, MARVASTI M H. Effect of rare earth element additions on the impression creep of Sn-9Zn solder alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(1): 58-64.
[109] MAHMUDI R, GERANMAYEH A R, SALEHI M, PIRAYESH H. Impression creep of the rare-earth doped Sn-2%Bi lead-free solder alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(3): 262-269.
[110] 张 亮, 薛松柏, 卢方焱, 韩宗杰, 禹胜林, 赖忠民. 基于蠕变模型细间距器件焊点疲劳寿命预测[J]. 机械工程学报, 2009, 45(9): 279-284.
ZHANG Liang, XUE Song-bai, LU Fang-yan, HAN Zong-jie, YU Sheng-lin, LAI Zhong-min. Fatigue life prediction for fine pitch device soldered joints based on creep model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(9): 279-284.
[111] KIM D H. Reliability study of SnPb and SnAg solder joints in PBGA packages[D]. Austin: The University of Texas, 2007.
[112] BI J L, HU A M, HU J, LUO T B, LI M, MAO D L. Effect of Cr additions on interfacial reaction between the Sn-Zn-Bi solder and Cu/electroplated Ni substrates[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2011, 51(3): 636-641.
[113] LIU N S, LIN K L. Evolution of interfacial morphology of Sn-8.5Zn-0.5Ag-0.1Al-xGa/Cu system during isothermal aging[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 456(1/2): 466-473.
[114] HE M, CHEN Z, QI G J. Solid state interfacial reaction of Sn-37Pb and Sn-3.5Ag solders with Ni-P under bump metallization[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(7): 2047-2056.
[115] HU Y F, XUE S B, WU Y X. FEM analysis of stress and strain and evaluation on reliability of soldered CBGA joints under thermal cycling[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2005, 15(S3): s317-s322.
[116] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, SHENG Z, YU S L, CHEN Y, DAI WEI, JI F, ZENG G. Reliability study of Sn-Ag-Cu-Ce soldered joints in quad flat packages[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2010, 50(12): 2071-2077.
[117] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, SHENG Z, ZENG G, CHEN Y, YU S L. Properties of SnAgCu/SnAgCuCe soldered joints for electronic packaging[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(6): 635-642.
[118] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, SHENG Z, DAI W, JI F, YE H, CHEN Y, YU S L. Effect of bulk Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compounds on properties of Sn-Ag-Cu-Ce solder joints[J]. Soldering & Surface Mount Technology, 2011, 23(1): 4-9.
[119] 郑智元. 锡银铜合金添加Ce无铅焊锡球格阵列封装之能态疲劳可靠度评估[D]. 台湾: 国立台湾大学, 2009.
ZHENG Zhi-yuan. Dynamic fatigue life evaluation of Ce doped Sn-Ag-Cu solder ball grid array packages[D]. Taiwan: National Taiwan University, 2009.
[120] 王俭辛, 赖忠民, 薛松柏. Sn-Cu-Ni(-Ce)焊点热循环可靠性[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(2): 36-40.
WANG Jian-xin, LAI Zhong-min, XUE Song-bai. Thermal cycling reliability of Sn-Cu-Ni(-Ce) joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(2): 36-40.
[121] PEI M, QU J M. Creep and fatigue behavior of SnAg solders with lanthanum doping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components and Packaging Technologies, 2008, 31(3): 712-718.
[122] LEE W W, NGUYEN L T, SELVADURAY G S. Solder joint fatigue models: Review and applicability to chip scale packages[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2000, 40(2): 231-224.
[123] ZAHN B A. Solder joint fatigue life model methodology for 63Sn37Pb and 95.5Sn4Ag0.5Cu materials[C]//Proceedings of 53rd Electronic Components and Technology Conference, New Orleans: IEEE, 2003: 93-94.
[124] SYED A. Accumulated creep strain and energy density based thermal fatigue life prediction models for SnAgCu solder joints[C]//Proceedings of 54th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vegas, NV: IEEE, 2004: 737-746.
[125] SCHUBERT A, DUDEK R, AUERSWALD E, GOLLHARDT A, MICHEL B, REICHL H. Fatigue life models for SnAgCu and SnPb solder joints evaluated by experiments and simulation[C]// Proceedings of 53rd Electronic Components and Technology Conference, New Orleans: IEEE, 2003: 603-610.
[126] WANG H. Investigations of Sn-9Zn-Ag-Ga-Al-Ce solder wetted on Cu, Au/Ni/Cu, and Sn-plated Cu substrates[J]. Welding Journal, 2010, 89(12): 249-255.
[127] 史晓亮, 杨凯华, 汤凤林, 邵刚勤. 稀土Ce的添加方式对WC-Co硬质合金性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2005, 36(2): 204-208.
SHI Xiao-liang, YANG Kai-hua, TANG Feng-lin, SHAO Gang-qin. Effect of adding method of rare earth Ce on property of WC-Co cemented carbide[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology: Natural Science, 2005, 36(2): 204-208.
[128] LIU S H, CHEN C, CHOU T. Tin whisker growth driven by electrical currents[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2004, 95(12): 7742-7747.
[129] HOWARD H P, CHENG J, VIANCO P T, LI J C M. Interface flow mechanism for tin whisker growth[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(5): 1957-1763.
[130] CHUANG T H. Rapid whisker growth on the surface of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu-1.0Ce solder joints[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 55(11): 983-986.
[131] DUDEK M A, CHAWLA N. Mechanisms for Sn whisker growth rare earth-containing Pb-free solders[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(15): 4588-4599.
[132] DUDEK M A, CHAWLA N. Nanoindentation of rare earth-Sn intermetallics in Pb-free solders[J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18(5): 1016-1020.
[133] 郝 虎, 李广东, 史耀武, 夏志东, 雷永平, 郭 福, 李晓延. 稀土Ce加速Sn晶须生长的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(5): 866-869.
HAO Hu, LI Guang-dong, SHI Yao-wu, XIA Zhi-dong, LEI Yong-ping, GUO Fu, LI Xiao-yan. Study of rapid growth of tin whisker accelerated by rare earth Ce[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(5): 866-869.
[134] 郝 虎, 史耀武, 夏志东, 雷永平, 郭 福, 李晓延. Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu-1.0Er无铅钎料中Sn晶须变截面生长现象[J]. 金属学报, 2009, 45(2): 199-203.
HAO Hu, SHI Yao-wu, XIA Zhi-dong, LEI Yong-ping, GUO Fu, LI Xiao-yan. Cross section changing growth phenomenon of Sn whiskers in Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu-1.0Er lead-free solder[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(2): 199-203.
[135] 郝 虎, 李广东, 史耀武, 雷永平. SnAgCuCe/Er无铅钎料表面锡晶须的形态及特性[J]. 焊接学报, 2009, 30(5): 25-28.
HAO Hu, LI Guang-dong, SHI Yao-wu, LEI Yong-ping. Morphologies and characteristics of tin whiskers on surface of SnAgCuCe/Er lead-free solder[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2009, 30(5): 25-28.
[136] CHUANG T H, LIN H J. Size effect of rare-earth intermetallics in Sn-9Zn-0.5Ce and Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu-0.5Ce solders on the growth of tin whiskers[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2008, 39(12): 2862-2866.
[137] LIN H J, CHUANG T H. Effects of Ce and Zn additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu solder joints[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 500(2): 167-174.
[138] LIN H J, CHUANG T H. Effects of Ce and La additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-9Zn solder joints[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2010, 39(2): 200-208.
[139] YE H, XUE S B, ZHANG L, XIAO Z X, HU Y H, LAI Z M, ZHU H. Sn whisker growth in Sn-9Zn-0.5Ga-0.7Pr lead-free solder[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(5): 52-55.
[140] LIU M, XIAN A P. Tin whisker growth on the surface of Sn-0.7Cu lead-free solder with a rare earth (Nd) addition[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2009, 38(11): 2353-2361.
[141] 王正明, 张许静. 稀土资源对“寡头”国出口市场势力的影响研究[J]. 经济经纬, 2012(2): 52-55.
WANG Zheng-ming, ZHANG Xu-jing. Research into the effect of rare earth resource tax on the export market power of “oligarch”country[J]. Economic Survey, 2012(2): 52-55.
[142] KIM K S, YU C H, YANG J M. Tin whisker formation of lead-free plated lead frames[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2006, 46(7): 1080-1086.
[143] CHUANG T H, CHI C C. Effect of adding Ge on rapid whisker growth of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu-0.5Ce alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 480(2): 974-980.
[144] GAO Q, ZHAO M, WANG H F. SMT solder joint’s semi-experimental fatigue model[J]. Mechanics Research Communications, 2005, 32(3): 351-358.
[145] 张 亮, 薛松柏, 禹胜林, 韩宗杰, 皋利利, 卢方焱, 盛 重. 有限元模拟在微连接焊点可靠性研究中的应用[J]. 电焊机, 2008, 38(9): 13-21, 72.
ZHANG Liang, XUE Song-bai, YU Sheng-lin, HAN Zong-jie, GAO Li-li, LU Fang-yan, SHENG Zhong. Application of FEM analysis in reliability of micro-soldered joints[J]. Electronic Welding Machine, 2008, 38(9): 13-21, 72.
[146] NADIMPALLI S P V, SPELT J K. Effect of geometry on the fracture behavior of lead-free solder joints[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2011, 78(6): 1169-1181.
[147] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, CHEN Y, YU S L, SHENG Z, ZENG G. Effects of trace amount addition of rare earth on properties and microstructure of Sn-Ag-Cu alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2009, 20(12): 1193-1199.
[148] 肖正香. 稀土Pr对Sn-9Zn无铅钎料组织与性能的影响[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2011.
XIAO Zheng-xiang. Effect of Pr on the microstructure and properties of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011.
[149] BUBAN J P, MATSUNAGA K, CHEN J, SHIBATA N, CHING W Y, IKUHARA Y. Grain boundary strengthening in alumina by rare earth impurities[J]. Science, 2006, 311(5758): 212-215.
[150] 朱 颖. 锡铅稀土钎料SMT焊点热循环失效机制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 1996.
ZHU Ying. Failure mechanism of SMT Sn-Pb-RE solder joint during thermal cycling[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 1996.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:江苏科技大学先进焊接技术省级重点实验室开放研究基金资助课题(JSAWS-11-03);江苏师范大学自然科学研究基金项目(11XLR16)
收稿日期:2011-05-31;修订日期:2012-01-17
通信作者:张 亮,讲师,博士;电话:0516-83500260;E-mail: zhangliang@jsnu.edu.cn
摘 要:稀土元素以其独特的优势被称为金属材料的维他命,稀土元素的添加可以在不同程度上提高无铅钎料的性能。结合国内外在含稀土元素无铅钎料研究领域的最新研究成果,综合评论稀土元素对无铅钎料组织和性能的影响,阐述含稀土元素的无铅焊点可靠性研究现状,为该钎料的实际应用提供数据支撑,分析过量稀土元素对无铅钎料表面锡须的影响,探讨锡须的生长机制及潜在的问题,最后综合评述含稀土无铅钎料在研究过程中存在的问题以及相应的解决措施,为含稀土元素无铅钎料的研究和应用提供理论依据。


