文章编号:1004-0609(2009)10-1829-06
B对无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金环境氢脆的影响
洪 波,程晓英,陈宏源,马 杰
(上海大学 材料研究所,上海200072)
摘 要:
为了阐明金属间化合物中H2所致脆性的机理及B在抑制这类氢脆的作用,研究了B对无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金氢脆的影响及其预渗氢后断口沿晶深度的影响。结果表明:B能同时降低H在无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数,而且不管是否添加B,H在无序态Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数始终大于H在有序态Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数。因此,不能简单地从B影响Ni3Fe合金中H扩散来解释B能明显抑制有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中的环境氢脆。
关键词:
中图分类号:TG172; TG146.1 文献标识码: A
Effect of B doping on environmental embrittlement of disordered and ordered Ni3Fe alloys
HONG Bo, CHENG Xiao-ying, CHEN Hong-yuan, MA Jie
(Institute of Materials Science, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China)
Abstract: In order to understand the mechanism of H2-induced environmental embrittlement and boron effect on inhibitting this kind of embrittlement in intermetallics, the effects of boron doping on the sensitivity to environmental embrittlement of disordered and ordered Ni3Fe alloys and on its intergranular depth after hydrogen charging were investigated. The results show that boron can similarly reduce hydrogen diffusion along grain boundary in both disordered and ordered Ni3Fe alloys. The hydrogen diffusion coefficient in disordered Ni3Fe alloy is always larger than that in ordered Ni3Fe alloy with or without boron. This suggests that the effect of boron on suppressing H2-induced environmental embrittlement in ordered Ni3Fe alloys can not be simply attributed to the fact that boron retards hydrogen diffusion along grain boundaries.
Key words: Ni3Fe alloy; boron; environmental embrittlement; disordered state; ordered state
1979年AOKI和IZUMI[1]首次发现B可以显著提高Ni3Al合金的室温塑性。随后大量研究[2-6]认为,B在Ni3Al中主要是抑制环境氢脆,其机理为:B偏聚在Ni3Al晶界,占据晶界上的有效位置,导致H原子无位可占,影响了H原子沿晶界的扩散,从而抑制了合金的环境氢脆。TAKASUGI等[7]研究了B在与Ni3Al有类似结构的Ni3Si合金中的作用,认为加入B抑制环境氢脆是由于B和H竞争占位的结果,与B在Ni3Al中的作用相同。而同样是在L12型结构的Co3Ti合金中加B,其中的B并没有抑制环境氢脆,这是因为B在Co3Ti的晶界上不偏聚或仅有极微弱的偏聚[8]。Ni3Fe合金易于得到完全无序的面心结构和有序状态的L12型结构,在H2环境中,无序态Ni3Fe合金不存在H2诱发的环境氢脆,与之具有相同化学成分的有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2环境中严重脆化,万晓景等[9-13]认为这和金属间化合物表面对H2的催化裂解能力有关,但B在Ni3Fe合金中的作用还不是非常清楚。添加0.03%B(质量分数)能够有效地抑制有序态Ni3Fe合金的环境氢脆,推测是B偏聚在有序态Ni3Fe-0.03%B 晶界的结果[14]。为此,本文作者研究不同B含量对无序态、有序态Ni3Fe合金环境氢脆的影响以及B对无序态、有序态Ni3Fe合金中H的扩散系数的影响,以期从氢扩散入手,阐明Ni3Fe合金中B的作用。
1 实验
实验所用材料成分如下:Ni-24%Fe(摩尔分数),Ni-24%Fe-0.01%B(质量分数),Ni-24%Fe-0.03%B(质量分数),Ni-24%Fe-0.07%B(质量分数)。用纯度高于99.9%的Ni、Fe和Fe-19.75%B(摩尔分数)合金,经真空电弧炉熔炼,铸成直径为44 mm的铸锭,铸锭在真空炉中经过(1 000 ℃, 35 h)的均匀化退火后,在1 050 ℃温度下热轧成厚度为2 mm的板材,经去应力退火后再把板材冷轧至1 mm左右。用线切割沿轧制方向切标距尺寸为10 mm×2 mm×0.9 mm的拉伸试样。拉伸试样经(800 ℃, 2 h)处理后,空冷得到无序态试样。再取其中一部分试样封入真空石英管中,经(470 ℃, 200 h)有序化处理后随炉冷却得到有序态试样。所有试样用砂纸打磨以除去氧化膜。拉伸实验在带有环境室的MTS-810电-液压伺服材料实验机上进行,形变速率为2×10-3s-1。当在H2中拉伸时,首先将环境室抽成2.0×10-2Pa的真空,再充入高纯H2,如此重复两次,试验中H2压力为101 kPa。用S-570扫描电镜观察拉伸试样的断口形貌。
预充氢是在不同温度的0.5 mol/L H2SO4+0.05 mg/L NaAsO4溶液中电解渗氢5 h,渗氢电流密度为45 mA/cm2 ,充氢后将试样迅速用丙酮及酒精清洗,干燥后投入液氮中冷冻,目的是防止H的再扩散。预充氢的试样均在空气中以2.0×10-2s-1速率拉伸。利用扫描电镜上的标尺测量沿晶断口深度,随机测定两侧沿晶断口深度10个点然后取平均值作为沿晶断口深度。由公式DA=d2/6τ计算氢的表观氢扩散系数DA,其中d为沿晶断口深度,cm;τ为渗氢时间,s。
2 实验结果
图1所示为无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2和真空中的应力—应变曲线。由图1(a)可知,在H2中,不
加B的无序态Ni3Fe合金没有出现塑性损失(对比图1(a)中曲线1与曲线2),在无序态Ni3Fe中加入0.01%B和0.03%B,无序态Ni3Fe合金的抗拉强度略有提高,伸长率也略有提高(对比图1(a)中曲线1与曲线3和4)。不加B的有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中拉伸的伸长率和抗拉强度严重损失(对比图1(b)中曲线1与曲线2),在有序态Ni3Fe合金中加入0.01%B,其在H2中拉伸的伸长率明显提高(对比图1(b)中曲线3与曲线2),当加入0.03%B后,在H2中拉伸的伸长率和抗拉强度有更进一步提高(对比图1(b)中曲线4与曲线2)。无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金中B含量达到0.07%时,其在H2中抗拉强度有一定下降,而伸长率下降并不明显(见图1(a)中曲线5和图1(b)中曲线5)。这表明无论无序态Ni3Fe合金中是否含B,均不存在环境氢脆;而有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中存在严重的环境氢脆,随着有序态Ni3Fe合金中B含量的增加,氢脆程度急剧下降,加入0.03%B,已经完全消除了环境氢脆,加入0.07%B,虽然抗拉强度有所下降,但是伸长率并没有明显下降。
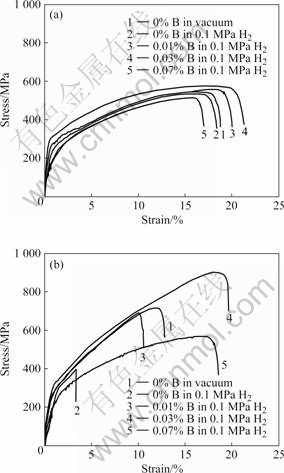
图1 Ni3Fe合金在真空和H2中的应力—应变曲线
Fig.1 Stress—strain curves for Ni3Fe alloy with different B content tested in vacuum and H2: (a) Disordered; (b) Ordered
图2所示为无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中拉伸断口形貌。在H2中,无序态Ni3Fe合金的断口为韧性穿晶断口(见图2(a)),同样表明无序态Ni3Fe合金不存在由H2诱发的环境氢脆;有序态Ni3Fe、Ni3Fe-0.01%B以及Ni3Fe-0.03%B合金断口形貌由脆性沿晶断口(见图2(b))→穿晶和沿晶的混合断口(见图2(c))→韧性穿晶断口(见图2(d)),这与性能具有很好的一致性。
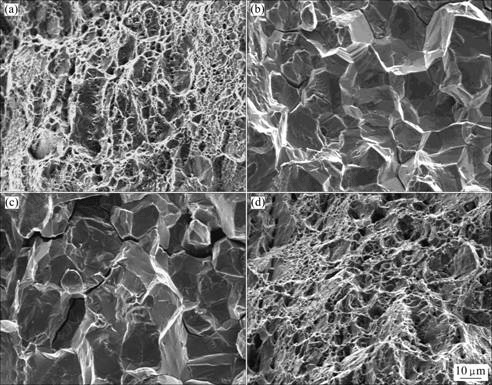
图2 无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中的拉伸断口SEM像
Fig.2 SEM fractographs of disordered and ordered Ni3Fe alloys tested in H2: (a) Disordered Ni3Fe; (b) Ordered Ni3Fe; (c) Ordered Ni3Fe-0.01%B; (d) Ordered Ni3Fe-0.03%B
图3和4所示分别为在不同温度下充氢5 h后无序态和有序态Ni3Fe-0.03%B合金拉伸断口形貌,与无序态和有序态Ni3Fe、无序态和有序态Ni3Fe-0.01%B合金拉伸的断口形貌类似,其断口总是表层为沿晶,而中心为穿晶,其间存在一个较明显的界限,表面的沿晶深度随渗氢温度增加而增加。
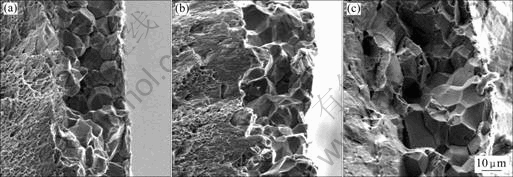
图3 无序态Ni3Fe-0.03%B合金充氢5 h后的拉伸断口SEM像
Fig.3 SEM fractographs of disordered Ni3Fe-0.03%B alloy pre-charged H2 for 5 h at different temperatures: (a) 15 ℃; (b) 30 ℃; (c) 45 ℃
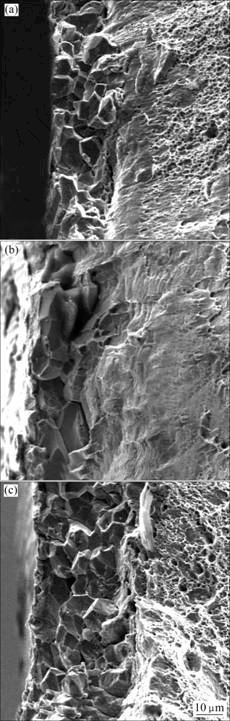
图4 有序态Ni3Fe-0.03%B合金充氢5 h后的拉伸断口 SEM像
Fig.4 SEM fractographs of ordered Ni3Fe-0.03%B alloy pre-charged H2 for 5 h at different temperatures: (a) 15 ℃; (b) 30 ℃; (c) 45 ℃
根据测得的沿晶断口深度d,由公式DA=d2/6τ求出H的表观扩散系数,其扩散系数与渗氢温度的关系曲线如图5所示,两者关系符合Arrhenius方程:
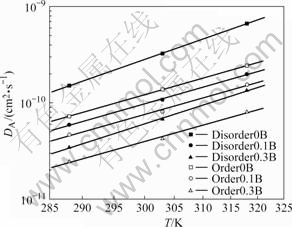
图5 无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金表观氢扩散系数与温度的关系
Fig.5 Apparent hydrogen diffusivity vs temperature for disordered and ordered Ni3Fe alloys

在相同渗氢温度下,H在无序态Ni3Fe合金中的扩散系数大于在有序态中的扩散系数,加B能同时减小无序态与有序态中H的表观扩散系数;但有序度及B对H的扩散激活能影响不大。
3 讨论
B在相同结构的Ni3Al 和Co3Ti合金中具有不同的作用[15-18]。万晓景等[15-17]用电化学预渗氢的方法研究了Ni-21%Al-0.1%B、Ni-23%Al-0.012%B、Ni-24%Al- 0.04%B和Ni-24%Al-0.1%B合金中H的扩散系数,发现在相同条件下,含有0.012%B的Ni3Al合金中H的扩散系数分别是含有0.04%B或0.1%B的Ni3Al合金中H的扩散系数的20倍及40倍,他们认为B抑制Ni3Al合金环境脆性的机理是B原子在晶界处的聚集,降低了H原子沿晶界的扩散系数,从而抑制了Ni3Al合金的环境氢脆。但是,B并不影响Co3Ti合金的环境氢脆,即使在Co3Ti合金中加入0.1%B甚至0.2%B也不能抑制Co3Ti合金的环境氢脆。有无加B的Co3Ti合金断口,在真空中均为穿晶韧窝断口,在空气中均为穿晶与沿晶的混合断口。他们认为B不能抑制Co3Ti合金环境氢脆的机理是B原子不在晶界处聚集,因而不能有效降低H原子沿晶界的扩散系数,抑制Co3Ti合金中的环境氢脆[8, 18]。
Ni3Fe、Ni3Al 和Co3Ti合金中,B所起到的作用各不相同。Ni3Fe合金中的B能有效抑制有序态Ni3Fe合金中H2诱发的环境氢脆,但在降低H在无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数方面,其作用并没有像Ni3Al 合金中的B的作用那么明显。另外,完全无序态的Ni3Fe合金中H的扩散系数大于有序态Ni3Fe合金中H的扩散系数,但完全无序态的Ni3Fe合金并不存在由H2诱发的环境氢脆。这似乎说明,H的表观扩散系数大小并没有与H2诱发的环境氢脆直接相关。所以,B降低H在 Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数并不是B抑制合金环境氢脆的主要原因,不能简单地从B影响H的扩散来解释B抑制有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中的环境氢脆。
在采用三维原子探针研究时,本文作者没有发现B原子在无序态或有序态Ni3Fe合金中晶界的偏聚。透射电镜的研究表明:Ni3Fe-0.03%B合金和Ni3Fe-0.07%B合金中析出的硼化物并不都分布在晶界上[19],说明Ni3Fe合金中的B并不像Ni3Al 合金中的B那样强烈偏聚于晶界,所以,Ni3Fe合金中的B也不能像Ni3Al 合金中的B那样大大降低H沿晶界的表观扩散系数。然而,Ni3Fe合金中的B却能像Ni3Al 合金中的B那样有效抑制有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中的环境氢脆,这是值得思考和进一步研究的。
4 结论
1) 无序态Ni3Fe合金不存在由氢气诱发的环境脆性,在无序态Ni3Fe合金中加入0.01%B和0.03%B,合金的抗拉强度和伸长率都略有提高;有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中却表现出强烈的环境氢脆,在有序态Ni3Fe合金中加入0.03%B,能有效消除环境氢脆。
2) B能同时降低H在无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数,而且H在无序态Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数大于H在有序态Ni3Fe合金中的表观扩散系数,所以不能简单地从B影响H的扩散来解释B抑制有序态Ni3Fe合金在H2中的环境氢脆。
REFERENCES
[1] AOKI A, IZUMI O. Improvement in room temperature ductility of the L12 type intermetallic Ni3Al by boron addition[J]. Nippon Kinzoku Grakkaishi, 1979, 43: 1190-1196.
[2] LIU C T, WHITE C L, HORTON J A. Effect of boron on grain-boundaries in Ni3Al[J]. Acta Metall, 1985, 33: 213-219.
[3] TAUB A I, BRIANT C L, HUANG S C, CHANG K M, JACKSON M R. Ductility in boron-doped, nickel-base L12 alloys processed by rapid solidification[J]. Scripta Metall, 1986, 20(1): 129-134.
[4] CHOUDHURY A, WHITE C L, BROOKS C R. The effect of thermal history on intergranular boron segregation and fracture morphology of substoichiometric Ni3Al[J]. Scripta Metall, 1986, 20(7): 1061-1066.
[5] LIU C T. Environmental embrittlement and grain-boundary fracture in Ni3Al[J]. Scripta Metall Mater, 1992, 27(1): 25-28.
[6] GEORGE E P, LIU C T, POPE D P. Environmental embrittlement: The major cause of room-temperature brittleness in polycrystalline Ni3Al[J]. Scripta Metall Mater, 1992, 27(3): 365-370.
[7] TAKASUGI H, SUENAGA H, IZUMI O. Environmental-effect on mechanical-properties of recrystallized L12-type Ni3(Si, Ti) intermetallics[J]. J Meter Sci, 1991, 26(5): 1179-1186.
[8] TAKASUGI T, HONO K, SUZUKI S. Environmental embrittlement and grain boundary segregation of boron in Ni3(Si,Ti) and Co3Ti alloys[J]. Scripta Metall Mater, 1993, 29(12): 1587-1591.
[9] 陈爱萍, 陈业新, 万晓景, 王建国, 程晓英. 有序度对Ni3Fe合金环境氢脆的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 2003, 17(1): 74-78.
CHEN Ai-ping, CHEN Ye-xin, WAN Xiao-jing, WANG Jian-guo, CHENG Xiao-ying. Effect of degree of order on the environmental embrittlement of Ni3Fe intermetallics[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2003, 17(1): 74-78.
[10] 陈业新, 陈爱萍, 万晓景, 闫世润. Ni3Fe 的有序化及合金环境脆性的作用[C]// 2004年中国材料研讨会论文摘要集, 2004: 758-763.
CHEN Ye-xin, CHEN Ai-ping, WAN XIAO-jing, YAN Shi-run. Effect of ordering on environmental embrittlement for Ni3Fe alloy[C]// Paper abstracts of the New Progress on Material Science and Engineering, 2004: 758-763.
[11] WAN Xiao-jing, CHEN Ye-xin, CHEN Ai-ping, YAN Shi-run. The influence of atomic order on H2-induced environmental embrittlement of Ni3Fe intermetallics[J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13(5): 454-459.
[12] ZHONG Xiao-yan, ZHU Jing, ZHANG Ai-hua. H2-induced environmental embrittlement in ordered and disordered Ni3Fe: An electronic structure approach[J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15(4): 495-499.
[13] WAN Xiao-jing, CHENG Xiao-ying, CHEN Ai-ping, CHEN Ye-xin. Effect of order/disorder transformation on the sensitivity to environmental embrittlement of intermetallics[J]. Journal of Shanghai University (English edition), 2007, 11(3): 197-204.
[14] SHI Dan-dan, CHEN Ye-xin, WAN Xiao-jing, LIU C T. The influence of boron-doping on the H2-induced environmental embrittlement of Ni3Fe intermetallics[J]. Journal of Shanghai University, 2007, 11(2): 102-105.
[15] WAN Xiao-jing, ZHU Jia-hong, JING Kai-liang. Hydrogen diffusivity in boron-doped polycrystalline Ni3Al[J]. Scripta Metall Mater, 1994, 31(6): 677-681.
[16] WAN Xiao-jing, ZHU Jia-hong, JING Kai-liang. Environmental embrittlement in Ni3Al+B[J]. Scripta Metall Mater, 1992, 26(3): 473-479.
[18] CHENG Xiao-ying, WAN Xiao-jing, CHEN Ye-xin. Environmental embrittlement and hydrogen diffusion in Co3Ti alloys[J]. Scripta Mater, 1997, 37(7): 1065-1069.
[19] 洪 波. 硼对无序态和有序态Ni3Fe合金在氢气气氛中氢脆的影响[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2008.
HONG Bo. Effect of boron on the H2-induced environmental embrittlement of disordered and ordered Ni3Fe alloys[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2008.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50671057)
收稿日期:2008-06-17;修订日期:2009-04-28
通讯作者:程晓英,副研究员,博士;电话:021-56336532;E-mail: chengxy@staff.shu.edu.cn


