铝土矿浮选泡沫消泡研究
冯其明, 穆 枭, 张国范, 卢毅屏, 欧乐明, 邵延海, 陈 云
(中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院, 湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:
土矿浮选精矿泡沫为研究对象, 分析铝土矿浮选泡沫的稳定原因。 采用物理方法和化学方法, 进行三相泡沫的消泡研究。 结果表明: 油酸钠可以显著降低水溶液体系的表面张力, 同时微细疏水矿粒在气泡表面的吸附降低了气泡表面的排液速率, 并增强了气泡的机械强度, 导致铝土矿浮选泡沫稳定; 另外, 转速对机械搅拌消泡有较大的影响, 消泡效果随转速的提高而增强; 磷酸三丁酯、 Foamban-ms-575和BD3037对两相泡沫体系具有很好的消泡作用, 但在三相泡沫体系中由于在泡沫表面铺展速率的限制, 消泡效果并不明显; 利用机械搅拌和添加消泡剂, 可以在较低的转速下, 大大改善消泡效果。
关键词: 铝土矿; 浮选; 三相泡沫; 消泡剂
中图分类号:TD926 文献标识码:A 文章编号: 1672-7207(2005)06-0955-05
Investigation on antifoaming of flotation bauxite
FENG Qi-ming, MU Xiao, ZHANG Guo-fan, LU Yi-ping,
OU Le-ming, SHAO Yan-hai, CHEN Yun
(School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The flotation concentrates of bauxite were used to study the stability of three-phase foams. The physical method and chemical process were used to defoam the foam of flotation concentrate.The results show that the surface tension of aqueous solution can be decreased by sodium oleate. At the same time, the adsorption of fine hydrophobic particles on the surface of bubble retards film drainage, strengthens mechanical strength of bubble, leads to the stability of foams. The rotate speed shows significant influence on the antifoaming of stirring. The antifoaming effect improves with the increase of the rotate speed. In two-phase foam system, the antifoaming effect of tri-butyl-phosphate(TBP), and Foamban-ms-575 and BD3037 is good, but they have no influence on three-phase foam, because their spreading velocity is limited. Under the conditions of low rotate speed, the antifoaming effect is improved with mechanical agitation and the defoaming agent.
Key words: bauxite; flotation; three-phase foam; defoaming agent
矿物资源加工与回收利用过程中, 泡沫浮选分离法是普遍采用的分离手段, 其中有色金属矿物资源中80%以上的分离过程是以泡沫浮选法实现的。
然而, 有用矿物浮选和分离产生大量的泡沫, 是一种固-液-气三相泡沫, 具有一定的稳定性, 在较长时间内难以破裂。 特别是有用矿物与脉石共生紧密, 浮选精矿中小于10 μm的含量高, 三相泡沫稳定性极强, 严重影响浮选精矿的后期处理过程[1]。 主要表现有:
a. 用泥浆泵输送矿浆时往往会产生气室现象, 使离心泵送料困难, 如铝土矿浮选精矿中小于10 μm含量高达20%~30%, 精矿泵的输送能力就降低50%以上。
b. 三相泡沫降低了矿浆的密度。 为了改善精矿泡沫的流动性, 便于输送, 必须加入大量的水, 不仅增加能源消耗和浮选厂选矿成本, 而且增加浮选用水量和水的循环量, 浪费水资源。 在北方缺水的铝土矿主产区, 这种影响更加突出。
c. 在浓密池浓缩阶段, 泡沫往往会带走大量浮选精矿, 金属回收率降低, 造成很大的经济损失。
d. 泡沫上吸附了大量矿物浮选药剂, 当泡沫随同废水被排出浮选厂时, 泡沫漂浮在废水上面, 废水难以处理, 从而造成环境污染。
为此, 作者针对铝土矿浮选泡沫, 进行泡沫的形成与消泡研究, 为有效控制铝土矿选矿过程中泡沫的稳定与消除进行探讨。
1 实 验
实验矿样取自河南省中部地区, 为分布在河南中部几个矿区的矿样混合样。 实验中用到的测试方法主要有:
a. 两相泡沫消泡测定方法。 用气流法测定溶液的泡沫性能, 将氮气瓶里的氮气通过气体流量计(MC型)与测试容器用乳胶管连通。 容器为高49 cm、 内径4.5 cm、 外径5.5 cm的透明有机玻璃管, 圆管侧壁有刻度以便读取泡沫高度。 在起泡管中加入100 mL溶液, 溶液中加入消泡剂, 通入气速为300 mL/min的氮气, 测定30 s时泡沫的高度(h)[2], 其示意图如图1所示。
b. 三相泡沫消泡测定方法。 捕收剂为油酸钠, 调整剂为六偏磷酸钠, 矿浆pH值为9.6, pH值调整剂为碳酸钠。 采用挂槽浮选机, 所得精选泡沫产品作消泡使用。 具体做法是: 将泡沫刮入烧杯中, 添加消泡剂在搅拌机上以固定的速度搅拌, 以泡沫半衰期(t1/2)即泡沫体积衰减一半的时间, 作为泡沫的寿命。
c. 表面张力的测定。 用滴体积法测定溶液的表面张力。

图 1 气流法原理示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of gas pulsation method
2 影响泡沫稳定性的因素
泡沫是一个相当复杂的热力学体系, 影响泡沫稳定性的因素很多, 人们对泡沫稳定性因素进行了研究[3-13]。 泡沫的稳定性主要决定于排液快慢和液膜强度[14]。 下面对铝土矿浮选精矿三相泡沫稳定原因进行探讨。
2.1 表面张力的影响
铝土矿浮选中使用的油酸钠, 具有捕收剂和起泡剂的双重作用, 从图2可以看出, 20 ℃时, 水的表面张力为7.24×10-2 N/m, 而质量分数为0.01%的油酸钠溶液的表面张力仅为3.38×10-2 N/m。
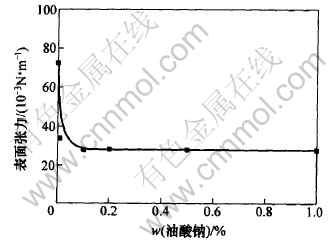
图 2 20 ℃时油酸钠水溶液的表面张力
Fig. 2 Surface tension of sodium oleate aqueous solution at 20 ℃
溶液表面张力的降低, 降低了泡沫体系的表面自由能, 根据Laplace公式, 有:
![]()
式中:Δp为曲率不同的液面两边的压力差, 方向指向曲率中心; γ为液体的表面张力; R1和R2为曲面的曲率半径。 表面张力低, 压差就小, 因而排液速度慢, 其泡沫稳定[15]。 另一方面, 泡沫形成时, 泡沫的液膜具有一定的弹性, 当泡沫的液膜受到冲击时, 在局部变薄处表面积增大, 吸附的表面活性剂分子密度减小, 表面张力升高, 这引起附近处表面活性分子力图向变薄处迁移, 使变薄处的表面吸附分子恢复到原来密度, 表面张力降低到原来水平, 在迁移过程中, 表面活性分子携带临近的液体一起迁移, 使变薄的液膜又恢复到原来的厚度。
2.2 微细疏水矿粒的影响
对纯油酸钠溶液测定结果表明, 在浮选条件下, 溶液起泡性较强, 但泡沫寿命仅为300 s左右, 而浮选泡沫体积衰减一半却需8 h。 这表明, 泡沫矿化后, 大大改变了泡沫的性质, 增大了泡沫的稳定性。
对于铝土矿而言, 有用矿物与脉石矿物共生紧密, 入选粒度很细, 浮选精矿中小于10 μm的含量高, 有用矿物在被矿化以后, 表面力比本身的重力有更突出的影响。 疏水的矿粒降低体系的表面张力, 阻碍排液过程。 由于疏水化程度不同, 形状不同。 开始在气泡表面呈较松散较混乱的排列, 但在泡沫输送及液膜自身排液过程中, 较大的矿粒由于自身的重力滑落至低层, 微细颗粒随泡沫界面面积的减小而靠拢、 重组, 形成一种相当坚固的界面膜结构。 对于浮选精矿的这种特殊的情况, 可能形成了一种类似“砖墙”结构。 由于气泡表面是弯曲的, 不规则形状的矿粒必然是大的一端朝向液面, 小的一端朝向气相, 在界面层中形成紧密的楔形定向排列(见图3), 这样能最大限度地降低气液的接触面积, 使体系能量达到最小。 在这种结构中, 矿粒与矿粒隙间的表面活性分子, 由于靠近, 其碳氢键开始产生疏水性缔合。 疏水缔合能比范德华引力要大的多。 试验中发现, 浮选泡沫放置较长时间后, 泡沫界面膜由于排液及液体蒸发已经干燥, 而其膜却完好无损。
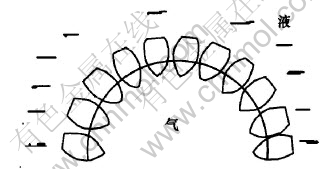
图 3 气液界面矿粒楔形定向排列
Fig. 3 Mineral particle of wedge type range directionally air-liquid interface
3 消泡研究
3.1 两相泡沫的消泡
在油酸钠体系, 用不同类型的消泡剂对两相泡沫进行消泡实验, 结果如图4所示。
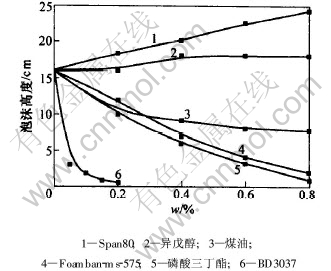
图 4 油酸钠水溶液的起泡性与消泡剂质量分数的关系
Fig. 4 Relationship between foamability of sodium oleate aqueous solution and mass fraction of antifoaming agent
由图4可知, Span80和醇类消泡剂异戊醇对油酸钠水溶液产生的泡沫没有消泡作用, 而且随着其用量增加, 油酸钠水溶液的起泡效果变好。 煤油对油酸钠水溶液的消泡效果也不太明显。 磷酸三丁酯、 Foamban-ms-575和BD3037随着用量增加, 消泡效果明显增强。 其中BD3037的消泡效果最好, 当其质量分数为0.2%时, 油酸钠水溶液已基本上不再产生泡沫。 因此, 对三相泡沫的消泡, 选择磷酸三丁酯、 Foamban-ms和BD3037为消泡剂。
3.2 三相泡沫的消泡
对于三相泡沫的消泡, 首先采用机械搅拌的方法进行消泡研究, 结果见表1。
表 1 搅拌实验结果
Table 1 Results of agitating experiment

从表1可以看出, 铝土矿浮选精矿三相泡沫十分稳定, 在静置自然消泡条件下, 泡沫半衰期t1/2达486 min。 随着搅拌转速的增加, 泡沫半衰期t1/2显著减小, 但转速过高, 工业上不能应用。
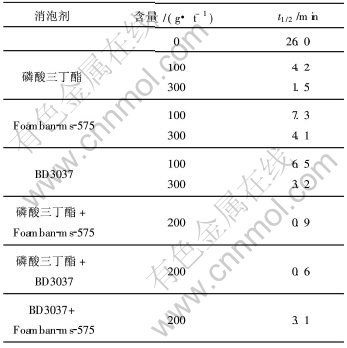
从表2可以看出, 单独使用消泡剂消除泡沫, 效果并不明显。 其原因是消泡剂不能通过自身的吸附, 在泡沫表面铺展开来。 在用量为600 g/t下, 消泡效果最好的磷酸三丁酯仍需要381 min。
表 2 消泡剂消泡实验结果
Table 2 Experimental results of antifoaming of defoaming agent

由表1和表2可见, 单独使用机械搅拌进行消泡, 能量消耗较大, 而且工业上不能应用。 单独使用消泡剂, 消泡效果不明显。 利用机械搅拌和消泡剂混合进行消泡实验, 结果见表3。
由表3可以看出, 当搅拌速度为250 r/min时, 加入消泡剂, 消泡效果明显。 尤其以磷酸三丁酯最好, 且随着其用量增加, 消泡效果增强。
从表3还可以看出, 磷酸三丁酯和Foamban-ms-575、 BD3037组合用药效果十分明显, 泡沫半衰期明显减小, 而且用量也减小, 比单独使用消泡剂效果更好。
表 3 用搅拌和消泡剂消泡实验结果
Table 3 Experimental results of antifoaming with agitating and defoaming agent
4 结 论
a. 影响铝土矿浮选泡沫过稳定的主要因素是由于表面活性物质和矿化的微细疏水矿粒的双重作用。 疏水的矿粒降低体系的表面张力, 阻碍排液过程。 表面活性物质和矿化的微细疏水矿粒的相互作用形成了具有一定弹性的类似“砖墙”结构的牢固的界面膜。
b. 转速是机械搅拌消泡的重要影响因素, 消泡效果随转速的提高而增强。 当转速为1000 r/min时, 泡沫寿命仅为12 s。 但单独使用消泡剂, 消泡效果不明显。
c. 利用机械搅拌和添加消泡剂相组合的消泡方法, 大大强化了消泡过程, 加快了消泡速度, 是有效的消泡方法, 在转速较低时, 添加磷酸三丁酯为300 g/t, 能使泡沫半衰期由8 h减小到1.5 min。
d. 在机械搅拌的情况下, 消泡剂的联合使用, 消泡效果最好, 而且用药量较小。
参考文献:
[1]吴连城. 钾盐浮选精矿消泡剂的研究[J]. 化工矿山技术, 1992, 21(3): 36-37.
WU Lian-cheng. Investigation of antifoaming agent on flotation concentrate of hoevellite[J]. Technology of Chemical Industry and Mine, 1992, 21(3): 36-37.
[2]徐振洪, 朱建华. 浮选起泡剂泡沫稳定性的评价方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 1999, 50(3): 399-403.
XU Zhen-hong, Zhu Jian-hua. Assessment method of foam stability about frothing agent[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 1999, 50(3): 399-403.
[3]Phianmongkhol A. A multi point conductivity measurement system for characterization of protein foams[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointer Faces, 1999, 12(3): 247-259.
[4]Cohen-Addad S, di Meglio J M. Stabilization of aqueous foam by hydrosoluble polymers 2. Role of polymer/surfactant interaction[J]. Langmuir, 1994, 10(3): 773-778.
[5]Lionti-Addad S, di Meglio J M. Stabilization of aqueous foam by hydrosoluble polymers 1. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyethylene oxide system[J]. Langmuir, 1992, 8(1): 324-327.
[6]Khristov K, Krugljakov P, Exerowa D. Influence of the pressure in the plateau-Gibbs borders on the drainage and foam stability[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 1979, 257(5): 506-511.
[7]Bals A. The influence of the pore size, the foaming temperature and the viscosity of the continuous phase on the properties of foam produced by membrane foaming[J]. Journal of Membrance Science, 2003, 220(1-2): 5-11.
[8]Khristov K, Exerowa D, Krugljakov P. Influence of the type of foam films and the type of surfactant on foam stabilization[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 1983, 261(3): 265-270.
[9]Kao R L, Wasan D T, Nikolov A D, et al. Mechanisms of oil removal from a solid surface in the presence of anionic micellar solutions [J]. Colloids and Surfaces, 1989, 34(4): 389-398.
[10]Ronteltap A D, Damste B R, de Gee M, et al. Role of surface viscosity in gas diffusion in aqueous foam.Ⅰ: Theoretical[J]. Colloids and Surfaces, 1990, 47(1): 269-283.
[11]Krotov V V, Nekrasov A G, Rusanov A I. A new method for studying foaminess[J]. Kolloidnyi Zhurnal, 2002, 64(6): 793-795.
[12]Pugh R J. Foaming, foam films, antifoaming and defoaming[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 1996, 64: 67-142.
[13]Hudales J B M, Stein H N. Influence of solid partical on foam and film drainage[J]. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 1990, 140(2): 307-313.
[14]赵晓东. 泡沫稳定性综述[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 1992, 9(1): 7-14.
ZHAO Xiao-dong. Roundup of foam stability[J]. Drilling Fluid and Completion Fluid, 1992, 9(1): 7-14.
[15]赵国玺. 表面活性剂作用原理[M]. 北京: 轻工业出版社, 2003.
ZHAO Guo-xi. Action Principle of Surfactant[M]. Beijing: Light Industry Press, 2003.
收稿日期:2005-02-20
基金项目: 国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2005CB623700)
作者简介: 冯其明(1962-), 男, 湖北天门人, 教授, 从事矿物加工、 矿物材料和再生材料等研究
论文联系人: 穆 枭(1978-), 男, 硕士; 电话: 0731-8830227(O); E-mail: muxiao2003@126.com
摘要: 以河南混合铝土矿浮选精矿泡沫为研究对象, 分析铝土矿浮选泡沫的稳定原因。 采用物理方法和化学方法, 进行三相泡沫的消泡研究。 结果表明: 油酸钠可以显著降低水溶液体系的表面张力, 同时微细疏水矿粒在气泡表面的吸附降低了气泡表面的排液速率, 并增强了气泡的机械强度, 导致铝土矿浮选泡沫稳定; 另外, 转速对机械搅拌消泡有较大的影响, 消泡效果随转速的提高而增强; 磷酸三丁酯、 Foamban-ms-575和BD3037对两相泡沫体系具有很好的消泡作用, 但在三相泡沫体系中由于在泡沫表面铺展速率的限制, 消泡效果并不明显; 利用机械搅拌和添加消泡剂, 可以在较低的转速下, 大大改善消泡效果。


