文章编号:1004-0609(2007)07-1172-05
M型钡铁氧体纳米粉体的溶胶-凝胶制备与结晶特性
孙 昌1, 2,孙康宁1
(1. 山东大学 材料液态结构及其遗传性教育部重点实验室,济南 260061;
2. 山东交通学院 土木工程系,济南 250023)
摘 要:
以化学计量比的硝酸钡、硝酸铁和柠檬酸为原料采用溶胶-凝胶工艺制备M型钡铁氧体纳米粉体,通过XRD、TEM等测试手段表征粉体的结晶特性及微观结构,并研究反应机理以及烧结温度、保温时间对晶粒尺寸的影响,结果表明:粉体的平均晶粒尺寸为40~70 nm,烧结温度显著影响结晶过程、晶粒尺寸及其分布;烧结温度为800 ℃,保温时间为0.5 h的条件下形成的粉体颗粒呈棒状,棒的长度约为150~200 nm,直径约为30~50 nm。
关键词:
中图分类号:O 614.23 文献标识码:A
Preparation and crystalline properties of M-type barium ferrite nanopowder by sol-gel process
SUN Chang1, 2, SUN Kang-ning1, 2
(1. Key Laboratory of Liquid Structure and Heredity of Materials, Ministry of Education,
Shandong University, Ji’nan 250061, China;
2. Department of Civil Engineering, Shandong Jiaotong University, Ji’nan 250023, China)
Abstract: M-type barium ferrite (BaFe12O19) nanopowders were synthesized by a sol-gel process. The crystalline properties and morphologies of the powders were characterized by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The reaction mechanism and the effects of calcinations temperature and calcinations time on grain size were studied. The results show that M-type barium ferrite powders with the average grain size range of 40-70 nm can be prepared at 800 ℃ and the calcinations temperature has obvious influence on crystalline process, the particle size and its distribution. The as-prepared samples obtained after heat-treatment at 800 ℃ for 0.5 h exhibit that the rod-like particles have a length of about 150-200 nm and a diameter of about 30-50 nm.
Key words: M-type barium ferrite; sol-gel process; crystalline property; calcination
M型钡铁氧体(BaFe12O19)具有独特的物理化学性质,是一种重要的硬磁材料,被广泛应用于高密度磁记录媒介、永磁体、彩色显示和微波吸收剂等领域[1-5]。M型钡铁氧体呈高饱和磁化强度(Ms =70 Am2/kg,室温)和强单轴各向异性[6-7];六角晶系铁氧体还具有片状结构,片状结构是吸波剂最佳的结构。为获得具有最佳性能的M型钡铁氧体,多种制备工艺被用于制备M型钡铁氧体粉体,例如化学共沉淀法、高温固态反应、水热法和溶胶-凝胶法等[2, 8-14]。溶胶-凝胶工艺具有分子水平均质混合、较低的热处理温度、宜于制备纳米颗粒和薄膜等内在优势,因此,溶胶-凝胶工艺常被用于生产玻璃、玻璃-陶瓷和陶瓷粉体。在制备钡铁氧体粉体的研究中,王艳丽等[15]采用柠檬酸为前驱体,得到晶粒度为30~80 nm, 其比饱和磁化强度Ms=60.61 Am2/kg, 矫顽力Hc=382.7 kA/m 的M型钡铁氧体。张晏清等[16]采用柠檬酸盐溶胶凝胶法,在加热速率为60 ℃/h升温至850 ℃的条件下,产物的主要物相为六角磁铅石型钡铁氧体BaFe12O19,颗粒尺寸为50 nm,并研究了钡铁氧体的粒径对吸波性能的影响。甘治平等[17]采用一种化学自组装方法以聚(苯乙烯-共-丙烯酸)乳胶粒子为模板, 利用酸醇相互作用, 将在聚乙二醇水溶液中得到的钡铁氧体前驱物包覆在模板粒子上,形成聚(苯乙烯-共-丙烯酸)/钡铁氧体前驱物核壳纳米复合粒子,复合粒子经750 ℃的热处理,可获得主晶相为BaFe12O19的钡铁氧体亚微空心球。黄应 等[18]应用溶胶-凝胶技术制备纳米钡铁氧体,其比饱和磁化强度Ms=70.12 A·m 2/kg,矫顽力Hc=31.26×103 A/m。卓长平等[19]采用溶胶-凝胶法制备掺杂钡离子的纳米六角晶型铁氧体,利用乙醇分散的稀浓度试样能在原子力显微镜下很好地观察到颗粒的粒径,其平均粒径约为52.68 nm。
本文作者利用溶胶-凝胶工艺,使用化学计量比的硝酸钡、硝酸铁和柠檬酸为原料,采用不同的烧结制度制备不同晶粒尺寸的M型钡铁氧体纳米粉体。使用X射线衍射仪(XRD,RIGAKUD/Max-A)和透射电镜(TEM,HITACHI-2500)表征粉体的结晶性质与微观结构。在探索制备和表征M型钡铁氧体材料上具有一定的指导意义。
1 实验
实验所用的试剂主要有:Ba(NO3)2·6H2O,分析纯,天津市天河化学试剂厂;Fe(NO3)3·9H2O,分析纯,天津市福晨化学试剂厂;柠檬酸(C6H8O7·H2O),分析纯,江苏南京中山集团公司化工厂;NH3·H2O:浓度25%~28%,分析纯,青岛海滨化学试剂厂生产;蒸馏水:实验室自制。
主要仪器:FA2004N型电子天平,上海精密科学仪器有限公司;磁力搅拌器,WCJ-802型,江苏泰县姜埝无线电厂;水浴锅,余姚市东方电工仪器厂;DZF-6050型真空干燥箱,上海博迅实业有限公司医疗设备厂;煅烧设备:SX2-8-13箱式电阻炉,龙口市电炉制造厂。
利用溶胶-凝胶工艺制备M型钡铁氧体,反应中所需的金属阳离子来自Ba(NO3)2?6H2O 和Fe(NO3)3?9H2O。具体合成步骤如下:按一定化学计量配比称取硝酸钡和硝酸铁,n(硝酸钡)?n(硝酸铁)=1?12,分别溶于柠檬酸溶液中,柠檬酸与金属阳离子的摩尔比为1?1。几分钟后得到均一透明的混合溶液,向混合液中滴入一定量的氨水调整pH值为7。电磁搅拌2 h,室温下老化12 h,将混合溶液置于水浴锅中80 ℃水浴3 h形成溶胶,然后将其移入干燥箱中120 ℃ 干燥1~2 d直至形成干凝胶。干凝胶置于烧结炉中,210 ℃ 保温3 h去除凝胶中的有机成分。分别在600、800、900、1 100和1 300 ℃下进行煅烧。随炉冷却后将样品取出并研磨,过44 μm筛后备用。
利用X射线衍射仪(XRD, RIGAKUD/Max-A)对合成的粉体进行相分析,工作电压60 kV,工作电流40 mA,扫描方式:10?~70?范围,步距0.02?,Cu靶Ka辐射(λ=0.154 05 nm)。通过透射电镜(TEM, HITACHI- 2500)观察合成粉体的微观形貌。
2 结果与讨论
图1所示为在不同烧结温度下制备的钡铁氧体粉体的XRD谱。从图 1可以看出,600 ℃时粉体的主晶相是γ-Fe2O3 ,并含有少量的BaCO3 和a-Fe2O3。在烧结温度为800 ℃时,钡铁氧体粉体中没有发现γ-Fe2O3、a-Fe2O3 和 BaCO3 相,反应形成单一的 M型钡铁氧体。由于晶体结构的复杂性,一般很难直接形成单一的M型钡铁氧体,反应过程中常会有Fe2O3 、BaCO3 和BaFe2O4 中间相出现。M型钡铁氧体在800 ℃ 开始形成,并没有发现在陶瓷工艺合成中常见的BaFe2O4 和钡的其他铁氧化合物。中间相γ-Fe2O3 和BaCO3的出现有利于钡铁氧体相的形成,因为γ-Fe2O3 为立方尖晶石结构,其化学分子表达式为Fe(Fe5/3□1/3)O4 ,□代表阳离子空位,其结构同钡铁氧体分子表达式中的Fe6O82+ 相似,所以γ-Fe2O3与BaCO3 反应更容易在较低烧结温度下形成单一的钡铁氧体相。而a-Fe2O3 由于在结构上没有这种相似,要完全转变成单一的钡铁氧体相需要较高的烧结温 度[20]。根据上述分析,溶胶-凝胶法制备纳米钡铁氧体粉体可能机理为
C6H8O7+ 2NH3·H2O—C6H6O7(NH) 2+2H2O
C6H6O7(NH) 2+Ba2+—BaC6H6O7(NH) 2+ 2H+
C6H6O7(NH) 2+2Fe3+—Fe2(C6H6O7(NH) 2) 3+ 6H+
干凝胶—Fe2O3+CaCO3
Fe2O3+CaCO3—BaFe12O19+CO2↑
图2所示为在烧结温度为800 ℃ 时不同保温时间下制备的钡铁氧体粉体的XRD谱。由图可以看出XRD谱中除了衍射峰的强度有变化外,其余没有发生变化。因此,通过保温时间对钡铁氧体的形成的影响,利用溶胶-凝胶工艺在相对较短的保温时间下可以得到钡铁氧体,而利用固态反应法在相同的条件下却需要更长的保温时间。
图3所示为烧结温度分别为800、1100和1 300 ℃保温5 h条件下制备的粉体的XRD谱。尖锐、单一的
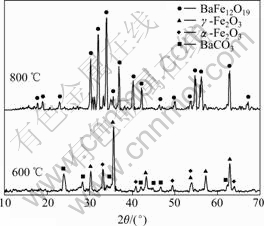
图1 保温0.5 h 不同烧结温度下制备的钡铁氧体粉体的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of barium ferrite at different temperatures for 0.5 h
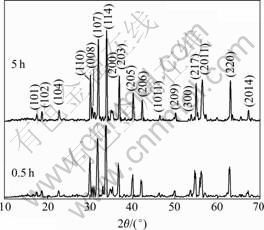
图2 烧结温度为800 ℃时不同保温时间下制备的钡铁氧体粉体的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of barium ferrite calcined at 800 ℃ for different holding time

图3 保温5 h不同烧结温度下制备的钡铁氧体的粉体的XRD谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of barium ferrite at different temperatures for 5 h
衍射峰说明试样的均质性较好,结晶度很高。从XRD谱分析可知,合成的粉体是具有六角型结构的单一相的钡铁氧体。利用XRD数据,根据公式

图4所示为当保温时间为5 h时钡铁氧体晶格常数随烧结温度的变化。由图可以看出,随着温度的升高a轴的值逐渐减少, 1 100 ℃后a轴的值大约为一恒值。而c轴的值随着温度的升高逐渐升高,1 100 ℃后c轴的值大约为一恒值。这说明在800 ℃时形成较少数量的均一结构和

图4 保温5 h不同烧结温度下制备的钡铁氧体粉体的晶格常数变化曲线
Fig.4 Lattice parameters of barium ferrite at different temperatures for 5 h
部分晶化的结构,当温度高于1 100 ℃时形成较完善的晶化结构,与图 3得出的分析结果相一致。
钡铁氧体粉体的平均晶粒尺寸可以根据Scherrer公式计算得到:

式中 λ为入射X射线波长(λ=0.154 05 nm),θ为布拉格衍射角,βi为X射线衍射峰的半高宽。计算采用(114)衍射峰的半高宽。图 5所示为钡铁氧体粉体的平均晶粒尺寸与烧结温度的关系曲线。由图可以清楚地看到,实验制备的粉体平均晶粒尺寸为40~70 nm,随着烧结温度的升高平均晶粒尺寸逐渐增加。
图6所示为烧结温度为800 ℃、保温时间为0.5 h时制备的钡铁氧体粉体的透射电镜照片。由图可以看

图5 钡铁氧体纳米粉体平均晶粒尺寸随烧结温度变化的曲线
Fig.5 Mean grain size of barium ferrite as function of calcination temperature
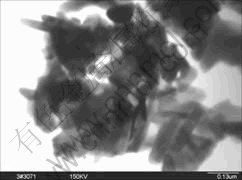
图6 烧结温度800 ℃时保温0.5 h 制备的钡铁氧体粉体的TEM像
Fig.6 TEM micrograph of barium ferrite calcined at 800 ℃ for 0.5 h
到,在该条件下形成的粉体颗粒大部分呈棒状,棒长约150~200 nm,直径约为30~50 nm。由于颗粒间的相互磁性作用,大部分可以聚集成群,一些纳米棒因此不能被观察到。M型钡铁氧体属于六角晶系,结晶时沿c轴方向生长,粒子在c轴方向上堆砌排列从而呈现棒状形态,这点与TEM像反映的情况相一致。
3 结论
1) 制备的M型钡铁氧体平均晶粒尺寸为40~70 nm,烧结温度在800 ℃以上。
2) 烧结温度为800 ℃、保温时间为0.5 h的条件下制备的粉体颗粒呈现棒状,棒长约150~200 nm,直径约30~50 nm。
3) 通过改变烧结温度可以控制晶体的生长,制备适合不同实际应用、不同晶粒尺寸的磁性纳米粉体。
REFERENCES
[1] Pullar R C, Bhattacharya A K. Crystallisation of hexagonal M- ferrites from a stoichiometric sol-gel precursor, without formation of the α-BaFe2O4 intermediate phase[J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 57(3): 537-542.
[2] Mali A, Ataie A. Structural characterization of nano-crystalline BaFe12O19 powders synthesized by sol-gel combustion route[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 53(9): 1065-1070.
[3] Zhang H J, Wu M Z, Yao X, Zhang L Y. Complex permittivity, permeability, and microwave absorption of barium ferrite by citrate sol-gel process[J]. Rare Metals, 2003, 22(2): 125-130.
[4] 曾爱香, 周琼花, 周 艺. 钡铁氧体超细粉末的制备[J]. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 3(2): 86-90.
ZENG Ai-xiang, ZHOU Qiong-hua, ZHOU Yi. Preparation of ultra fine BaFe12O19 powder[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2006, 3(2): 86-90.
[5] Mishra D, Anand S, Panda R K, Das R P. Studies on characterization, microstructures and magnetic properties of nano-size barium hexa-ferrite prepared through a hydrothermal precipitation–calcination route[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 86(1): 132-136.
[6] Kojima H. Fundamental properties of hexagonal ferrites with magnetoplumbite structure, ferromagnetic materials[M]. Netherlands: North-Holland, 1982: 305-391.
[7] Braun P B. The crystal structures of a new group of ferromagnetic compounds[J]. Philips Res Rep, 1957, 12: 491-548.
[8] Hong Y K, Jung H S. New barium ferrite particles: Spherical shape[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 85(8): 5549-5551.
[9] Kaneko Y, Iyi N, Kurashima K, Matsumoto T, Fujita T, Kitamura K. Hexagonal-structured polysiloxane material prepared by sol-gel reaction of aminoalkyltrialkoxysilane without using surfactants[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(18): 3417-3423.
[10] 刘先松, 都有为. M型永磁铁氧体的现状与进展[J]. 磁性材料及器件, 2001, 32(1): 27-32.
LIU Xian-song, DU You-wei. Present states and recent advances in M-type ferrites[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2004, 16(18): 3417-3423.
[11] 周克省, 王 达, 尹荔松, 孔德明, 黄可龙. La0.8Sr0.2- Mn1-yFeyO3微波电磁特性与损耗机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 6(5): 753-757.
ZHOU Ke-sheng, WANG Da, YIN Li-shong, KONG De-ming, HUANG Ke-long. Electromagnetic properties and loss mechanism of La0.8Sr0.2Mn1-yFeyO3 in microwave band[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 6(5): 753-757.
[12] Wang J, Wu Y, Zhu Y, Wang P Q. Formation of rod-shaped BaFe12O19 nanoparticles with well magnetic properties[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(7): 1522-1525.
[13] Qiu J, Gu M. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of barium ferrite synthesized using GSPC and HEBM[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 415(1/2): 209-212.
[14] SUN Chang, SUN Kang-ning. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of Ce-substituted lithium ferrite[J]. Solid State Communications, 2007, 141(5): 258-261.
[15] 王艳丽, 黄 英, 闫 梨, 黄 飞. 两种凝胶-溶胶前驱体制备钡铁氧体的研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2006, 29(3): 37-41.
WANG Yan-li, HUANG Ying, YAN Li, HUANG Fei. Barium ferrite prepared with two kinds of sol-gel precursor[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2006, 29(3): 37-41.
[16] 张晏清, 张 雄. 钡铁氧体的颗粒粒径与吸波性能研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(2): 225-228.
ZHANG Yan-qing, ZHANG Xiong. Effect of particle size on microwave absorption property of barium ferrite[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2006, 34(2): 225-228.
[17] 甘治平, 官建国. 化学自组装法制备钡铁氧体亚微空心球[J]. 物理化学学报, 2006, 22(2): 189-192.
GAN Zhi-ping, GUAN Jian-guo. Chemical self-assembly route to fabricate hollow barium ferrite submicrospheres[J]. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2006, 22(2): 189-192.
[18] 黄 英, 王琦洁, 王广东, 黄 飞, 熊 佳. 制备工艺对纳米钡铁氧体生成过程的影响[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2005, 23(2): 193-196.
HUANG Ying, WANG Qi-jie, WANG Guang-dong, HUANG Fei, XIONG Jia. A better preparation process on formation of BaFe12O19 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2005, 23(2): 193-196.
[19] 卓长平, 张 雄. 纳米级钡铁氧体的原子力显微镜分析及微波性能的研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 2005, 24(3): 14-17.
ZHUO Chang-ping, ZHANG Xiong. Atomic force microscopic analysis and microwave properties of nano-scale M-type barium hexaferrite[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2005, 24(3): 14-17.
[20] Zhong W, Ding W, Zhang N, Du Y, Yan Q, Hong J. Key step in synthesis of ultrafine BaFe12O19 by sol-gel technique[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 1997, 168(1/2): 196-202.
(编辑 李向群)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(30540061, 50672051)
收稿日期:2006-09-30;修订日期:2007-05-21
通讯作者:孙康宁,教授,博士;电话:0531-88392439; E-mail: sunkangning@sina.com


