梁侧向屈曲临界荷载分析
文 颖,曾庆元
(中南大学 土木建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410075)
摘 要:
摘 要:揭示梁侧倾分析中弯扭平衡方程的力学意义是梁截面内弯矩等于外弯矩及内扭矩等于外扭矩;提出采用梁截面力矩矢量分析法解决各种荷载类型和不同支承条件下侧向屈曲梁截面弯扭力矩的计算问题;采用伽辽金(Galerkin)法求解梁侧向屈曲平衡方程。研究结果表明:采用力矩矢量分析法可以方便地建立梁侧倾弯扭平衡方程;临界荷载计算值与传统的无穷级数解非常接近,且数值上稍低于无穷级数解,这说明采用伽辽金法进行梁抵抗侧向屈曲设计是偏于安全的。
关键词:
中图分类号:O317.2 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2008)02-0405-05
Analysis of critical load for lateral buckling of beam
WEN Ying, ZENG Qing-yuan
(School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: The physical meaning of lateral flexural-torsional equilibrium equations was simple that the external bending moments and twisting forces should balance the internal resisting moments at any cross-section of beam respectively. Therefore, the vector analysis approach was presented to determine the flexural-torsional moments of lateral buckling beams more efficiently under various load types and support conditions. In addition, the lateral buckling loads were obtained by solving the differential equation using Galerkin’s method. The results show that the equations of equilibrium for beam can be formulated directly using the method of couple vector analysis. An illustrative example suggests that the calculated critical load is very close to but lower than the magnitude obtained in an infinite series way. It can be concluded that it is safe to apply the Galerkin’s method to lateral buckling design of beams.
Key words: beam; vector analysis approach; lateral buckling; critical load
梁侧向屈曲临界荷载的分析是结构稳定性分析中的一个难题[1-15]:一是其侧向屈曲弯扭平衡方程的建立比较复杂;二是此种方程为变系数微分方程,难于精确求解。S. P. Timoshenko等[16]虽然详细地阐述了此种方程的建立过程,但物理概念不够明确。具体表现在有2个关键点未加说明:a. 根据坐标变换矩阵得到梁流动坐标系ξ,η和ζ下的外力矩Mξ,Mη和Mζ,为何还要考虑外力矩的正方向;b. 根据什么理念,列出梁侧向屈曲弯扭平衡方程。S. P. Timoshenko等[16-17]还采用无穷级数法求解梁弯扭变系数微分方程,应用于复杂梁结构的侧倾分析相当复杂;基于有限元分析的加权残值法也较复杂[1-2]。
针对上述问题,本文作者采用右手转轴螺旋前进方向表示力矩矩矢;提出梁截面力矩矢量分析法,确定流动坐标系下屈曲梁截面的外力矩Mξ,Mη和Mζ;明确梁曲率弯矩方程及梁的约束扭转方程的力学概念分别为梁截面内力矩等于梁截面外力矩和梁截面内扭矩等于梁截面外扭矩,以简便建立屈曲梁弯扭微分方程。采用伽辽金(Galerkin)变分法求解导出的弯扭微分方程,得出与无穷级数解非常接近且偏小的结果,这说明采用本文的方法进行梁的抗侧向屈曲设计是偏于安全的。
1 建立梁弯扭平衡方程的梁截面力矩矢量分析法
设图1(a)所示简支“工”字梁在竖向荷载P作用下处于竖直平面内弯曲平衡状态,由于外界干扰,侧向屈曲成图1(a)~(c)所示的弯扭平衡状态;图中平面曲线代表侧向屈曲梁的形心轴线在各坐标平面内的投影,x,y和z为固定的正交坐标系,ξ,η和ζ为沿侧向屈曲梁形心轴线流动的正交坐标系。假定沿x和y轴正向的梁形心轴的位移u和v为正,绕z轴顺时针的转角位移![]() 为正。在侧向屈曲梁左半跨截取梁微段隔离体,连同作用于其上的流动坐标系下的梁截面外力矩Mξ,Mη和Mζ分别如图1(d)~(f)所示;由图1(a)和1(b)可知,在ηζ和ξζ平面内的弯曲变形分别指向η轴和ξ轴的正方向;按照力矩右手螺旋法则及所取隔离体的弯扭变形,作用在ηζ平面隔离体左端的截面弯矩Mξ绕ξ轴旋转,其矩矢方向(图1中用双箭头表示,以下同)与ξ轴的正向相反,如图1(d)所示;作用在ζξ平面隔离体左端的截面弯矩Mη绕η轴旋转,其矩矢方向与η轴的正向相同,如图1(e)所示。
为正。在侧向屈曲梁左半跨截取梁微段隔离体,连同作用于其上的流动坐标系下的梁截面外力矩Mξ,Mη和Mζ分别如图1(d)~(f)所示;由图1(a)和1(b)可知,在ηζ和ξζ平面内的弯曲变形分别指向η轴和ξ轴的正方向;按照力矩右手螺旋法则及所取隔离体的弯扭变形,作用在ηζ平面隔离体左端的截面弯矩Mξ绕ξ轴旋转,其矩矢方向(图1中用双箭头表示,以下同)与ξ轴的正向相反,如图1(d)所示;作用在ζξ平面隔离体左端的截面弯矩Mη绕η轴旋转,其矩矢方向与η轴的正向相同,如图1(e)所示。
为了计算梁微段的外力矩Mξ,Mη和Mζ,从图1(a)所示的简支梁左端向![]() 轴正向透视梁,梁侧向屈曲前横截面位形、侧向屈曲后梁横截面位形、固定坐标系(x,y,z)、流动坐标系(ξ,η,ζ)、作用于梁
轴正向透视梁,梁侧向屈曲前横截面位形、侧向屈曲后梁横截面位形、固定坐标系(x,y,z)、流动坐标系(ξ,η,ζ)、作用于梁![]() 截面固定坐标系下的外力矩Mx及ζ截面的弯矩Mξ和Mη、梁z截面的扭转角位移
截面固定坐标系下的外力矩Mx及ζ截面的弯矩Mξ和Mη、梁z截面的扭转角位移![]() ,如图1(g)所示。
,如图1(g)所示。

(a) 梁正立面图; (b) 梁俯视内力示意图; (c) 梁俯视变形图; (d) ζ-η平面梁微段示意图;
(e) ζ-ξ平面梁微段示意图; (f) 梁微段扭转示意图; (g) 梁截面变形图
图1 梁侧向屈曲分析整体变形图
Fig.1 Deflected profiles of beam for lateral buckling analysis
简支梁左端反力P/2对梁z截面的作用弯矩Mx=Pz/2,作用在yz平面,其矩矢与x轴的正向相反,如图1(b)所示。图1(g)中,Mξ和Mη分别为Mx在ξ和η轴的分量。于是,下面计算梁微段左端的外扭矩Mζ。该扭矩由2部分组成:
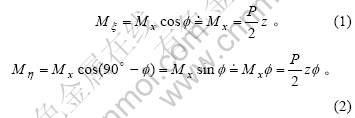
一部分是外力矩Mx在ζ轴的分量Mζ1,由图1(b)可知,Mx产生的作用于梁微段左端的扭矩Mζ1为:

式(3)中的负号表示此分量矩矢与ζ轴的正向相反。观察发现Mζ1的矩矢方向与图1(f)所示的Mζ1的正方向一致,故去掉式(3)中的负号,即有Mζ1=Pzdu/(2dz)。
另一部分扭矩是由梁的竖向荷载P及梁左端支座反力P/2产生的作用于梁微段左端的外扭矩Mζ2。由图1(c)和1(g)可知,梁侧倾后荷载P的作用点沿x轴移动的距离为![]() ,这样引起梁左、右支座反力矩为
,这样引起梁左、右支座反力矩为![]() ,其转向如图1(c)所示,此处um为梁跨中截面形心沿x轴的位移,a为梁高的一半,
,其转向如图1(c)所示,此处um为梁跨中截面形心沿x轴的位移,a为梁高的一半,![]() 为梁跨中截面的扭转角位移。梁侧倾后,左支座反力P/2对z截面的扭矩为Pu/2,其转向与图1(f)所示梁微段左端外扭矩方向相反。于是有
为梁跨中截面的扭转角位移。梁侧倾后,左支座反力P/2对z截面的扭矩为Pu/2,其转向与图1(f)所示梁微段左端外扭矩方向相反。于是有

则由式(3)和(4)可得到作用于图1(f)梁微段左端的外扭矩为:
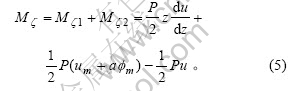
按图1(d)和1(e)侧向屈曲梁微段![]() 截面的内弯矩分别为
截面的内弯矩分别为![]() 和
和![]() [18-19]。由薄壁结构扭转理论[17, 20]可知,侧向屈曲梁微段z截面的内扭矩为
[18-19]。由薄壁结构扭转理论[17, 20]可知,侧向屈曲梁微段z截面的内扭矩为![]() ,其中,GJk和EJω分别为梁截面自由扭转刚度和约束扭转刚度。由侧向屈曲梁
,其中,GJk和EJω分别为梁截面自由扭转刚度和约束扭转刚度。由侧向屈曲梁![]() 截面内力矩等于外力矩及式(1)~(5),得出梁侧向屈曲弯扭微分方程组为:
截面内力矩等于外力矩及式(1)~(5),得出梁侧向屈曲弯扭微分方程组为:

式(6)~(8)与文献[16]中的公式(6-26)~(6-28)有差异,一是因为本文坐标系的布置与文献[16]的坐标系的布置不同;二是本文计算梁左半跨截面内外力矩的平衡,而文献[16]是计算梁右半跨截面内外力矩的平衡;三是本文假定荷载作用在梁的上翼缘,文献[16]的荷载则作用在梁截面的形心。虽然方程不同,但反映梁的工作性质相同。根据梁侧向屈曲失稳临界力的计算过程,发现文献[16]中6.4节的算例实际上是本文的一个特例。
2 伽辽金(Galerkin)变分法求解梁的侧向屈曲方程
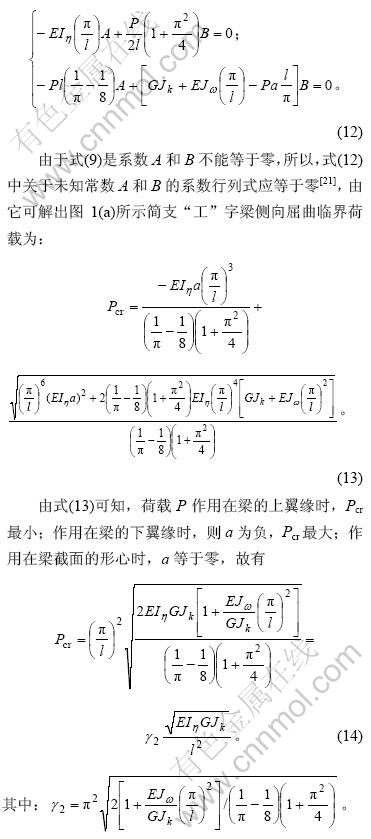
式(6)实际上是梁的竖平面内弯曲平衡方程。当梁竖向弯曲刚度远大于其侧向弯曲刚度时,求解梁侧向屈曲临界力时可以忽略梁面内弯曲变位的影响[1, 16]。本文假定梁竖向变位很小,故不需计算式(6)。梁的侧向屈曲临界力由式(7)和(8)确定。式(7)和(8)为变系数常微分方程,假定满足梁的几何和力学边界条件的梁屈曲近似位移函数为:

将式(9)代入式(7)和(8),并不能使方程右端等于零,即梁内外力矩不平衡。现将式(7)和(8)分别记为![]() ,
,![]() 。若降低要求,则令侧向屈曲梁内外力矩对虚位移
。若降低要求,则令侧向屈曲梁内外力矩对虚位移![]() 及
及![]() 所作虚功的总和分别等于零,即
所作虚功的总和分别等于零,即

这2个方程就是求解梁侧向屈曲问题的伽辽金(Galerkin)变分式。因为方程![]() ,
,![]() 只在梁左半跨有效,而梁受力对称于跨中,故式(10)和(11)在半跨内积分并乘以系数2。将式(7)~(9)分别代入式(10)和(11),积分整理后得到齐次线性方程组为:
只在梁左半跨有效,而梁受力对称于跨中,故式(10)和(11)在半跨内积分并乘以系数2。将式(7)~(9)分别代入式(10)和(11),积分整理后得到齐次线性方程组为:
按照γ2的计算式算出集中荷载P作用于梁的形心时的γ2如表1所示。
由以上计算结果表明,采用伽辽金变分法的计算结果与文献[16]中用无穷级数求解的结果很接近,略小于无穷级数解,这说明采用伽辽金变分法分析梁侧倾临界荷载是偏于安全的;本文计算过程简单,但求解精度与位移函数的选取有关,因此,可将该思想与有限元法结合起来,得到复杂梁结构的侧倾荷载的高度近似解。
表1 集中荷载作用于简支“工”字梁中点截面形心的因子γ2
Table 1 Factor γ2 for simply supported I beams with concentrated force at centroid of middle cross-section

3 结 论
a. 从梁侧倾失稳分析的物理概念出发,明确了侧向屈曲梁弯扭平衡方程的力学意义是梁截面外力矩等于其内力矩,力学概念明确,使初学者更易理解。
b. 采用梁截面力矩矢量分析法分析任意梁截面的力矩大小和方向,将各截面力矩矩矢显示在侧向屈曲梁形心轴上,使各截面外力矩与侧向屈曲梁截面位移u,v和![]() 及坐标系的几何关系十分明确,从而可以简便地算出在各种荷载类型和不同支承条件下侧向屈曲梁在流动坐标系下的截面外力矩Mξ,Mη和Mζ,为梁侧向屈曲弯扭平衡方程的建立提供保障。
及坐标系的几何关系十分明确,从而可以简便地算出在各种荷载类型和不同支承条件下侧向屈曲梁在流动坐标系下的截面外力矩Mξ,Mη和Mζ,为梁侧向屈曲弯扭平衡方程的建立提供保障。
c. 用伽辽金(Galerkin)变分法求解梁侧向屈曲弯扭平衡方程,与现有的计算方法相比具有物理概念明确,计算简便等优点,结果准确且略偏小于无穷级数解,这说明采用伽辽金(Galerkin)变分法进行梁侧倾设计是偏于安全的。
参考文献:
[1] WANG Quan-feng. A simple solution for lateral buckling of thin-walled symmetric members[J]. Communications in Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2003, 19(1): 49-58.
[2] WANG Quan-feng. Stability of shear-wall building using method of weighted residuals[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1991, 117(3): 700-706.
[3] PI Yong-lin, Bradford M A. Effects of approximations in analysis of beams of open thin-walled cross-section—Part I: Flexural- torsional stability[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2001, 51(3): 757-772.
[4] PI Yong-lin, Trahair N S. Energy equation for beam lateral buckling[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1992, 118(6): 1462-1479.
[5] PI Yong-lin, Trahair N S. Prebuckling detections and lateral buckling I: Theory[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1992, 118(11): 2949-2966.
[6] De J H. An approach to more complicated lateral-buckling problems[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 1990, 16(3): 231-246.
[7] Bradford M A, Cuk P E. Lateral buckling of tapered monosymmetric I-beams[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1988, 114(5): 966-977.
[8] Al-Bermani F G A, Kitipornchai S. Nonlinear analysis of thin-walled structures using least element/member[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1990, 116(1): 215-234.
[9] 署恒木. 集中力偶下工字型简支梁的侧向屈曲临界荷载[J]. 青岛大学学报, 1999, 14(4): 48-51.
SHU Heng-mu. Lateral buckling critical load of I-shape pin-ended beam under a couple applied at one end of beam[J]. Journal of Qingdao University, 1999, 14(4): 48-51.
[10] 署恒木, 罗文莉, 何 云. 狭长矩形简支梁一端受力偶作用时的侧向屈曲临界载荷[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2001, 25(6): 65-67.
SHU Heng-mu, LUO Wen-li, HE Yun. Lateral buckling of pin-ended beam with a couple applied at one end of pin-ended[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2001, 25(6): 65-67.
[11] Sapkas A, Kollar L P. Lateral-torsional buckling of composite beams[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2002, 39(11): 2939-2963.
[12] Kim N, Shin D K, Kim M Y. Exact lateral buckling analysis for thin-walled composite beam under end moment[J]. Engineering Structures, 2007, 29(8): 1739-1751.
[13] Park J S, Stallings J M, Kang Y J. Lateral-torsional buckling of prismatic beam with continuous top-flange bracing[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2004, 60(2): 147-160.
[14] Thevendran V, Shanmugam N E. Lateral buckling of doubly symmetric beams containing openings[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1991, 117(7): 1427-1441.
[15] Bradford M A, Hancock G J. Elastic interaction of local and lateral buckling in beams[J]. Journal of Thin-Walled Structures, 1984, 2(1): 1-25.
[16] Timoshenko S P, Gere J M. Theory of elastic stability[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1961.
[17] Murray N W. Introduction to the theory of thin-walled structures[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1984.
[18] 文 颖, 戴公连, 曾庆元. 关于规定曲率弯矩方程正负号的问题[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2006, 3(5): 93-96.
WEN Ying, DAI Gong-lian, ZENG Qing-yuan. The problem of designating the sign of bending moment in the curvature-bending moment equation[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2006, 3(5): 93-96.
[19] Trahair N S. Flexural-torsional buckling of structures[M]. London: E & FN Spon, 1993.
[20] Vlasov V Z. Thin-walled elastic beams[M]. Israel: Israel Program for Scientific Translations, 1961.
[21] Crandall S. Engineering analysis[M].New York: McGraw Hill Book Company, 1956.
收稿日期:2007-05-28;修回日期:2007-07-30
基金项目:教育部高等学校博士点科研基金资助项目(20010533004)
通信作者:文 颖(1981-),男,湖南长沙人,博士研究生,从事桥梁结构分析;电话:0731-2656645;E-mail: zhwen@mail.csu.edu.cn


