热处理对橄榄石型磷酸铁锂电化学性能的影响
张 宝,彭春丽
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:
摘 要: 以FeSO4?7H2O和NH4H2PO4为原料,H2O2为氧化剂,通过液相沉淀法制备前驱体FePO4,然后通过碳热还原法合成LiFePO4;研究降温速度对产物晶型结构、形貌以及电化学性能的影响。从LiFePO4的扫描照片可以看出,随着降温速度的变慢,样品的粒径逐渐增大。电化学性能研究表明:降温速度不宜过大或过小,最适宜的降温速度为2 ℃/min。该条件下合成的材料以0.1C倍率充放电时其首次放电容量为153 mA?h/g,以1C倍率充放电时其首次放电容量达136 mA?h/g,且循环性能好。
关键词:
中图分类号:TM912.9 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2007)06-1106-04
Effect of heat treatment on electrochemical performance of
olivine type lithium iron phospho
ZHANG Bao, PENG Chun-li
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: LiFePO4 was prepared by carbothermal reduction of FePO4, which was synthesized by aqueous precipitation from FeSO4?7H2O and NH4H2PO4 and hydrogen peroxide as the oxidizing agent. The effect of cooling rate on the structure, morphology and electrochemical performance was investigated. Scanning electron microscope images show that the particle size of LiFePO4 becomes bigger as cooling rate gets slower. The optimum performance of sample is synthesized at cooling rate of 2 ℃/min, with the discharge capacity of 153 mA?h/g at rate of 0.1C and 136 mA?h/g at rate of 1C and good cycling performance is obtained.
Key words: LiFePO4; aqueous precipitation; carbothermal reduction; cooling rate
1997年Padhi等[1]报道了LiFePO4具有充放电性能,其理论比容量为170 mA?h/g,放电平台为3.4 V,具有良好的循环性能[2]和热稳定性能[3],且无毒、价格便宜等特点使其有望成为新一代的锂离子电池正极材料。但这种材料也存在一些不足阻碍了它的实际应 用[4-6]:一是合成中Fe2+易氧化成Fe3+,不易得到单相的LiFePO4;二是LiFePO4导电性差,因而大电流放电性能差。现有的研究通过以下几方面来提高LiFePO4的性能[7-9]:a. 采用惰性气氛来保护Fe2+;b. 合成小粒径的LiFePO4提高锂离子的扩散能力;c. 加电导剂来提高电导率。此外,合成方法对材料的性能及实际应用有很大的影响,现有的方法主要有固相 法[10-12]、溶胶-凝胶法[13-14]和碳热还原法[15]。碳热还原法被认为比较有前途的一种方法,因为合成的材料电化学性能好且实验易于扩大化。
本文作者采用碳热还原法合成LiFePO4,即以FeSO4?7H2O和NH4H2PO4为原料采用液相沉淀法制备FePO4前驱体,然后将前驱体、Li2CO3及乙炔黑混合均匀并在560 ℃煅烧12 h,主要研究降温速度对LiFePO4材料结构和性能的影响。
1 实 验
1.1 LiFePO4的制备
称取等物质的量的FeSO4?7H2O和NH4H2PO4,分别用去离子水溶解配成溶液。然后,将2种溶液混合加入反应器中,搅拌反应30 min后加入H2O2,立即有大量的FePO4白色沉淀产生。反应完全后进行离心分离与洗涤,然后烘干。将烘干后的磷酸铁、碳酸锂及乙炔黑按化学计量比(乙炔黑过量10%)混合均匀,然后在Ar气的保护下于560 ℃煅烧12 h,然后分别以随炉冷却(平均降温速度为3~4 ℃/min),降温速度为2 ℃/min,降温速度为1 ℃/min得到3组样品,记为样品a,b和c,以上材料的降温范围控制在560~ 250 ℃。
1.2 仪 器
采用 CS800红外碳硫检测仪(Eltar公司, 德国)对合成材料中碳的含量进行分析;采用美国SDT Q600型热分析,氩气保护,升温速度为10 ℃/min,对前驱体进行热分析;采用X射线衍射仪(XRD) (Rint-2000,Rigaku)和扫描电镜仪(SEM)(JEOL,JSM-5600LV)分别表征样品的晶体结构和表面形貌。
1.3 电池组装和测试
将原料按m(LiFePO4)?m(乙炔黑)?m(PVDF)=8?1?1混合均匀后涂片,经过120 ℃真空干燥10 h压片后得正极。以金属锂片作负极,1 mol/L LiPF6/(碳酸二甲酯(EC)+碳酸乙烯酯(DMC) (体积比1?1))为电解液,在手套箱里组装成CR2025型扣式电池。采用新威测试仪测试电池的充放电性能,在电压为2.3~4.1 V时进行充放电试验。
2 结果与讨论
图1所示为前驱体磷酸铁的热重-差热分析(TG-DTA)曲线。可见,在150 ℃左右出现明显的吸热峰,同时伴随着质量的损失,此峰应为前驱体失去结晶水的过程;而在580 ℃和710 ℃左右出现2个放热峰而又没有质量的损失,这可能分别对应着磷酸铁从无定型转变为α晶型,及从α晶型转变为β晶型的2个过程[5]。从TG曲线可以看出,在20~500 ℃之间,前驱体质量损失率为19%,采用重铬酸钾滴定前驱体铁的含量,测得其含量为29.88%,这些数据与文献[13]中报道的磷酸铁具有2个结晶水相吻合。图2所示为前驱体FePO4的扫描电镜照片。从图2可以看出,合成的前驱体颗粒呈类球状,分布非常均匀,平均粒径为0.1 μm左右,且比表面积大。
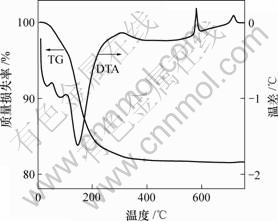
图1 FePO4的TG-DTA曲线
Fig.1 TG and DTA curves for precipitated FePO4

图2 FePO4的扫描电镜照片
Fig.2 SEM image of FePO4
图3所示为不同冷却速度所得到LiFePO4的XRD谱。从图3可以看出,各样品均为单一的LiFePO4纯相,衍射图谱上没有出现碳峰;随着冷却速度的减小,样品的衍射峰逐渐变尖锐,半峰宽变窄,这说明样品的晶粒随着冷却速度的减小而有所长大。图4所示为不同冷却速度所得到LiFePO4的SEM照片。从图4可以看出,随着降温速度的减小,所得到LiFePO4的颗粒逐渐变大。降温速度为1 ℃/min时,颗粒的粒径大于0.6 μm;降温速度为2 ℃/min时,颗粒的粒径约为0.5 μm;而降温速度升至3~4 ℃/min时,颗粒的粒径约为0.3 μm。
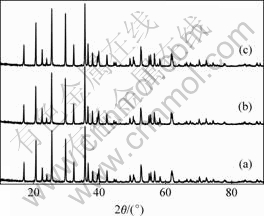
降温速度/(℃?min-1): (a) 3~4; (b) 2; (c) 1
图3 不同降温速度下得到LiFePO4的XRD谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of LiFePO4 prepared at different cooling rates
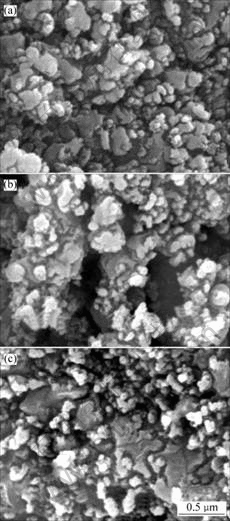
降温速度/(℃?min-1): (a) 3~4; (b) 2; (c) 1
图4 不同降温速度下得到LiFePO4的SEM照片
Fig.4 SEM images of LiFePO4 prepared at different cooling rates
图5所示为不同冷却速度得到的LiFePO4在0.1C倍率下的充放电曲线。由图5可以看出,各样品的充放电曲线都非常平稳,充电平台在3.47 V左右,样品a和b的放电平台在3.41 V左右,样品c的放电平台略有降低。此外,冷却速度的快慢对小电流放电比容量没有太大的影响。降温速度为3~4,2和1 ℃/min的样品,其放电容量分别为151,153和150 mA?h/g。
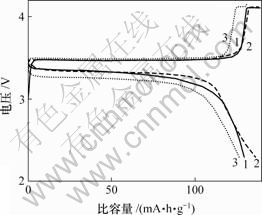
图6所示为于不同降温速度下得到的LiFePO4在1C倍率下的充放电曲线。可以看出,样品a,b和c的放电容量分别为129,136和126 mA?h/g,同时,样品c的放电平台比其他样品的放电平台明显偏低,大
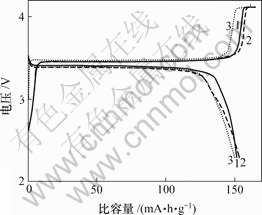
降温速度/(℃?min-1): 1—3~4; 2—2; 3—1
图5 不同降温速度下得到的LiFePO4在0.1C倍率下的首次充放电曲线
Fig.5 The first charge-discharge curves of LiFePO4 synthesized at different cooling rates recorded at rate of 0.1C
降温速度/(℃?min-1): 1—3~4; 2—2; 3—1
图6 不同降温速度下得到的LiFePO4在1C倍率下的首次充放电曲线
Fig.6 The first charge-discharge curves of LiFePO4 synthesized at different cooling rates recorded at rate of 1C
约相差0.1 V。这说明降温速度为2 ℃/min比较理想,若降温速度过快,虽然得到的磷酸铁锂颗粒比较细小,但材料可能存在很多缺陷,因而放电比容量不是最理想的;而若降温速度过慢,虽然磷酸铁锂结晶比较完善,但由于颗粒较大,其放电比容量低,且极化大。
图7 所示为不同降温速度下合成的LiFePO4以1C倍率放电时的循环性能图。可以看出,样品a,b和c都具有良好的循环性能。大电流放电条件下循环30次,其放电容量基本不变。结果表明,降温速度为2 ℃/min的样品其电化学性能比较理想。以0.1C倍率放电时,其容量达153 mA?h/g;以1C倍率放电时,其容量达到136 mA?h/g,且循环性能良好。
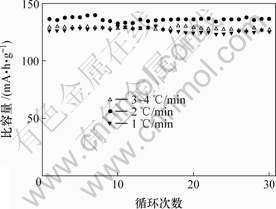
图7 不同降温速度下得到的LiFePO4循环性能图
Fig.7 Electrochemical cycling performance of LiFePO4 synthesized at different cooling rates
3 结 论
a. 通过碳热还原法,采用不同的热处理方式合成了LiFePO4。随着降温速度的变慢,样品的粒径逐渐变大。
b. 降温速度为2 ℃/min时,得到样品颗粒的平均粒径约为0.5 μm,且分布比较均匀,以0.1C倍率充放电时其首次放电容量为153 mA?h/g,以1C倍率充放电时其首次放电容量达136 mA?h/g,且循环性能 良好。
参考文献:
[1] Padhi A K, Nanjundaswamy K S, Goodenough J B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1997, 144(4): 1188-1194.
[2] Anna S A, Beata K, Lennart H, et al. Lithium extraction/insertion in LiFePO4: An X-ray diffraction and mossbauer spectroscopy study[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2000, 133(1/2): 41-52.
[3] Macneil D D, Lu Z, Chen Z, et al. A comparison of electrode/electrolyte reaction at elevated temperature for various Li-ion battery cathodes[J]. J Power Sources, 2002, 108: 8-14.
[4] Prosini P P, List M, Scaccia S, et al. Synthesis and characterization of amorphous hydrated FePO4 and its electrode performance in lithium batteries[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2002, 149: A297-A301.
[5] Prosini P P, List M, Zane D. Determination of the chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148(1/2): 45-51.
[6] Iucheu N, Chen Y, Okada S, et al. LiFePO4 storage at room and elevated temperature[J]. J Power Sources, 2003, 119/121: 749-754.
[7] Cho T, Chung H. Synthesis of olivine-type LiFePO4 by emulsion-drying method[J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 133: 272-276.
[8] Doeff M M, Hu Y, Mclaron F, et al. Effect of surface carbon structure on the lectrochemical performance of LiFePO4[J]. Electrochem and Solid State Lett, 2003, 6(10): A207-A209.
[9] Herstedt M, Stjerndahl M, Nyten A, et al. Surface chemistry of carbon-treated LiFePO4 particles for Li-ion battery cathodes studied by PES[J]. Electrochem and Solid State Lett, 2003, 6(9): A202-A206.
[10] Andersson A S, Thomas J O. The source of first-cycle capacity loss in LiFePO4[J]. J Power Sources, 2001, 97/98: 498-502.
[11] Yamada A, Chung S C, Hinokuma K. Optimized LiFePO4 for lithium battery cathodes[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2001, 148(3): A224-A229.
[12] Huang H, Cyin S, Nazar L F. Approaching theoretical capacity of LiFePO4 at room termperature at high rates[J]. Electrochem and Solid State Lett, 2001, 4(5): A170-A172.
[13] 张 宝, 彭春丽, 王志兴, 等. 加碳方式对磷酸铁锂动力学及电化学性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(5): 863-866.
ZHANG Bao, PENG Chun-li, WANG Zhi-xing, et al. Effect of adding carbon modes on kinetic and electrochemical performances of LiFePO4[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(5): 863-866.
[14] Hu H Q, Doeff M M, Kostecki R, et al. Electrochemical performance of sol-gel synthesized LiFePO4 in lithium batteries[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2004, 151(8): A1279-A1285.
[15] 张 宝, 李新海, 罗文斌, 等. LiFe(1-x)MgxPO4锂离子电池正极材料的电化学性能[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 37(6): 1094-1097.
ZHANG Bao, LI Xin-hai, LUO Wen-bin, et al. Electrochemical properties of LiFe(1-x)MgxPO4 for cathode materials of lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(6): 1094-1097.
收稿日期:2007-02-05;修回日期:2007-03-28
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50302016)
作者简介:张 宝(1971-),男,江苏盱眙人,博士后,从事材料及电化学领域的研究
通信作者:张 宝,男,博士后,电话:0731-8836357;E-mail: csuzb@vip.163.com


