DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35987
基于未确知测度理论的矿山边坡稳定性评价方法
王 杰1, 2, 3, 胡 斌1, 3,李 京1, 3,常 剑2,崔阿能1, 3,崔 凯1, 3
(1. 武汉科技大学 资源与环境工程学院,武汉 430081;
2. 中钢集团马鞍山矿山研究总院股份有限公司,马鞍山 243000;
3. 冶金矿产资源高效利用与造块湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430081)
摘 要:
应用未确知测度理论,建立了露天矿山边坡稳定性评价模型。根据影响露天矿山边坡稳定性的成因,建立了露天矿山边坡稳定性评价体系。通过调查,选取了10项指标作为未确知测度函数评判指标。然后,构建单指标未确知测度函数,运用熵权法确定评价指标权重,采用距离判别法作为属性识别准则。利用建立的评价模型对某深凹露天矿北部边坡的稳定性进行了评价。结果表明:评价结果与实际情况一致,说明了该评价方法的有效性,为矿山提供了一种简便、低成本的露天矿山边坡稳定性评价新方法。同时,该方法为改善边坡稳定性优先采取措施,提供了科学依据。
关键词:
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-05-1388-07 中图分类号:X936 文献标志码:A
引文格式:王 杰, 胡 斌,李 京, 等. 基于未确知测度理论的矿山边坡稳定性评价方法[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(5): 1388-1394. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35987
WANG Jie, HU Bin, LI Jing, et al. Slope stability evaluation and application of open-pit mine based on uncertainty measurement theory[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(5): 1388-1394. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35987
我国是矿业大国,但长久以来,露天矿山边坡失稳事故多发。根据2018年中华人民共和国应急管理部发布的《2017年全国非煤矿山生产安全事故统计分析报告》,从2013年至2017年,我国发生的边坡垮塌事故,不论是死亡人数还是事故起数,一直高居第二,仅次于冒顶坍塌[1]。这警示我们,在不断向露天矿山索取矿产资源的同时,要密切关注矿山边坡失稳引起的灾害。矿山边坡稳定性研究多借鉴其他行业边坡研究成果。在边坡研究中,郑颖人等[2-3]引入有限元强度折减法进行边坡稳定分析,开创了计算岩质边坡滑动面与稳定安全系数的先例。陈祖煜等[4]对岩体抗剪强度参数进行了修正对边坡稳定进行分析。李典庆等[5]提出了基于随机有限元法的边坡可靠度分析方法。CAO等[6]对不同条件下三维边坡失稳规律展开了研究。这些研究为边坡稳定性评价提供了途径,但是影响边坡稳定因素众多,而矿山边坡受爆破、开挖等影响,影响因素更复杂且不确定性更明显。同时,传统的边坡稳定性分析方法,不论是极限平衡法还是数值分析法,前期均需做大量的工程地质勘察,工程量大,费用高,存在一定的缺陷[7-8]。
中国工程院院士王光远教授[9]提出了未确知性概念,刘开第等[10]建立了未确知测度数学理论。未确知测度数学方法专门用于解决由于受客观条件限制,造成客观信息不全,而无法确定事物的真实状态的问题。未确知测度理论已被应用于很多领 域[11-13]。露天矿山边坡稳定性属于典型的未确知性问题。
本文引入未确知测度理论,建立了露天矿山边坡稳定性分析模型,通过熵权法确定各影响因素的权重[14-15]。熵权法是一种客观赋权方法,可大大降低人为因素对指标权重的影响,让分析结果更为合理。同时,采用距离判别法作为属性识别准则[16-17],以避免采用置信度准则,人为选择置信度可能产生结果的非唯一性。本文提供了一种简便的、成本低的边坡稳定性评价方法,以某深凹露天矿北部边坡为例,对其稳定性进行了分析。
1 未确知测度理论
设研究对象X={X1, X2, …, Xm},它表示研究对象有m个评价因素。令指标对象F={F1, F2, …, Fn},它表示评价因素有n个评价指标。令研究空间U={C1, C2, …, Cp},它表示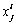 有p个等级C1, C2, …, Cp,而
有p个等级C1, C2, …, Cp,而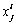 表示评价因素Xi关于评价指标Fj的测量值。记Ck为第k级评价等级,Ck>Ck+1(第k级比第k+1级安全程度高)。若{C1, C2, …, Cp}满足条件:C1>C2>…Cp,则可称其为评价空间U的一个有序分割集。令
表示评价因素Xi关于评价指标Fj的测量值。记Ck为第k级评价等级,Ck>Ck+1(第k级比第k+1级安全程度高)。若{C1, C2, …, Cp}满足条件:C1>C2>…Cp,则可称其为评价空间U的一个有序分割集。令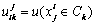 ,在u满足如下条件的情况下,可称其为未确知测度。u必须同时满足非负“有界性”(式(1))、“归一性”(式(2)),还有“可加性”(式(3))。
,在u满足如下条件的情况下,可称其为未确知测度。u必须同时满足非负“有界性”(式(1))、“归一性”(式(2)),还有“可加性”(式(3))。
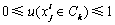 (1)
(1)
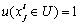 (2)
(2)
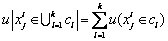 (3)
(3)
i=1, 2, …, m; j=1, 2, …, n; k=1, 2, …, p
1.1 构造单指标未确知测度
为解决不确定性问题,首先应根据未确知测度理论来构造单指标测度函数。构造单指标测度函数有许多方法,但直线型被认为是最简单,应用最广泛的方法。但不论用何种方法,都必须满足“有界性”、“归一性”,还有“可加性”。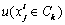 ( i=1, 2, …, m; j=1, 2, …, n; k=1, 2, …, p)为未确知测度,
( i=1, 2, …, m; j=1, 2, …, n; k=1, 2, …, p)为未确知测度,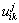 为评价因素Xi的测度值,则各指标测度值
为评价因素Xi的测度值,则各指标测度值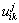 构成的单指标测度评价矩阵
构成的单指标测度评价矩阵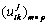 为:
为:
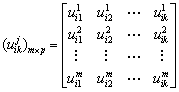 (4)
(4)
1.2 指标权重的确定
确定指标权重可采用熵权法、相关系数法等,熵权法由于其客观性,不受人为因素影响,而应用广泛。本文引入熵权法,客观确定指标权重,具体步骤如下:
1) 归一化指标值
由于各项指标的计量单位并不统一,因此在计算他们权重前,先要对单指标测度评价矩阵(式4)进行标准化处理,使其具有可比性。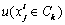 (i=1, 2, …, m; j=1, 2, …, n)为未确知测度。令Yij为标准化后指标值,则,
(i=1, 2, …, m; j=1, 2, …, n)为未确知测度。令Yij为标准化后指标值,则,
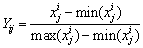 ,
, 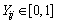 (5)
(5)
i=1, 2, …, m; j=1, 2, …, n
2) 计算指标值的比重pij
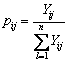 (6)
(6)
3) 计算第j项指标的熵值Ej
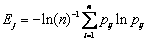 (7)
(7)
若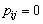 ,则定义
,则定义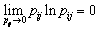 。
。
4) 计算各指标的权重值wj
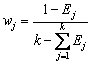 (j=1, 2, …, k) (8)
(j=1, 2, …, k) (8)
1.3 多指标未确知测度
令向量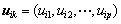 为Xi多指标综合测度评价向量,则uik必然满足:
为Xi多指标综合测度评价向量,则uik必然满足:
0≤uik≤1, 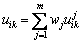 (k=1, 2, …, p) (9)
(k=1, 2, …, p) (9)
1.4 距离判别评价
采用距离判别法作为属性识别准则,令欧式距离dk为多指标综合测度uik到分类等级Ck的距离,其计算式如下:
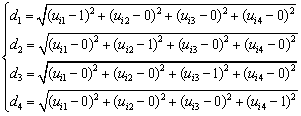 (10)
(10)
则,对象的分类等级为:
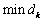 (1≤k≤4) (11)
(1≤k≤4) (11)
2 露天矿山边坡稳定性评价指标体系建立
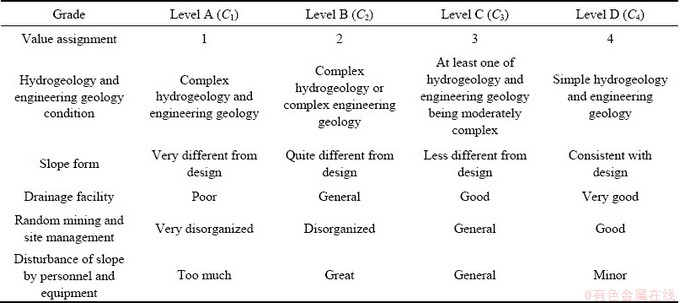
影响矿山边坡稳定性的因素很多,通过查阅相关资料、对相关露天矿山边坡失稳现场调查并结合相关技术规范[18-20],采用Delphi法确定了4大类影响条件:①地质条件、②工程条件、③气象条件、④人为条件。在4大类的基础上进一步细化,确定了10项评价指标,详见表1。①地质条件细化为:边坡高度、总边坡角、水文工程地质条件、边坡形态;②工程条件细化为:排水设施、爆破质点振动速度;③气象条件细化为:最大地震烈度、日最大降雨量;④人为条件细化为:乱采乱挖及现场管理、人员及设备对边坡的扰动(相对边坡范围)。
细类评价指标共分为5个定性指标和5个定量指标。定性指标通过表2,实现定性指标转换为定量指标。最终定量指标见表1。传统边坡稳定性评价结论只有稳定和不稳定,缺乏对边坡稳定程度的评价。本文为进一步细化边坡稳定性程度评价,将每个细类评价指标分为4个评价等级,A级、B级、C级和D级,分别与{C1, C2, C3, C4}对应,分别表示露天矿山边坡稳定性极差、较差、一般和较好。
根据单指标测度函数定义和表1,选择应用最广泛的直线型测度函数,构建露天矿山边坡稳定性评价指标体系的各指标测度函数,如式(12)所示。令ai为对象属性观测值区间上的点,在点ai左测属性值处于i状态,当属性值从ai增加到ai+1过程中,属性i状态程度逐渐减弱。ai+1时,i状态程度减为0,同时,观测值从ai增加至ai+1时,属性观测值i+1状态程度由0增加至1。
表1 露天矿山边坡稳定性评判标准表
Table 1 Standard table for slope stability analysis in open pit mines
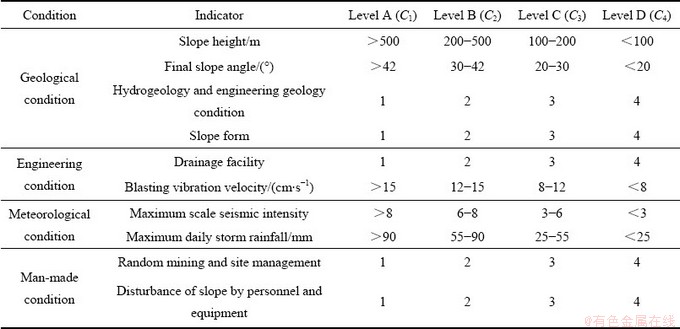
表2 露天矿山边坡稳定性评判定性指标分级标准
Table 2 Classification standard for qualitative index of slope stability analysis in open pit mines
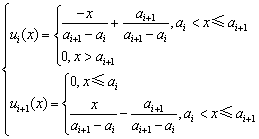 (12)
(12)
5个定量评价指标的单指标测度函数如图1~5所示。5个定性指标的单指标测度函数相同,如图6所示。
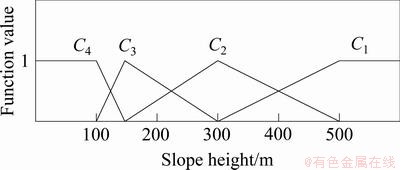
图1 边坡高度测度函数
Fig. 1 Uncertainty measurement function of slope height
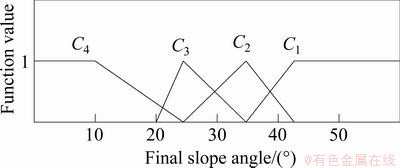
图2 总边坡角测度函数
Fig. 2 Uncertainty measurement function of total slope angle
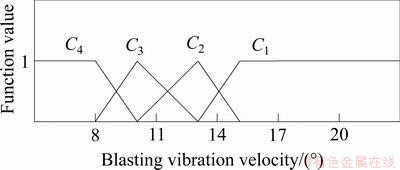
图3 爆破质点振动速度测度函数
Fig. 3 Uncertainty measurement function of blasting particle vibration velocity
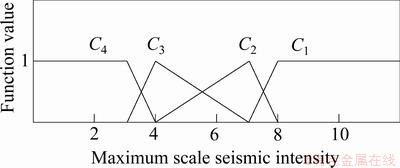
图4 最大地震烈度测度函数
Fig. 4 Uncertainty measurement function of maximum seismic intensity
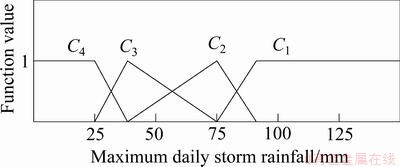
图5 日最大降雨量测度函数
Fig. 5 Uncertainty measurement function of daily maximum rainfall
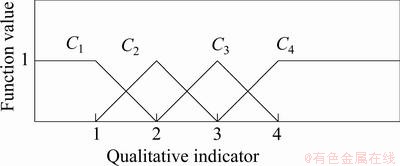
图6 定性指标未确知测度函数
Fig. 6 Uncertainty measurement function of qualitative indexes
3 案例分析
本次案例分析针对某深凹露天矿矿体下盘采场北部边坡。目前,矿体下盘采场北部边坡高度达336 m,总边坡角达27°。采用公路开拓汽车运输,陡帮组合台阶剥离岩土、缓帮采矿的采矿工艺。矿区雨季为每年6~10月,日最大降雨量43 mm。矿山水文地质条件、工程地质条件均属于中等类型。矿山除个别台阶清扫平台宽度不足,存在超采情况外,总体上按照设计进行施工。矿山为深凹露天矿,矿体位于当地最低侵蚀基准面以上。目前,在矿区露天采坑外围设有截洪沟。露天坑封闭圈内雨水汇入露天坑。在现有露天坑底以下50 m设有排水平硐,采场各平台积水通过泄水孔至排水平硐自流。由于采用地质钻孔作为泄水孔,个别钻孔小时疏水能力受限(地质钻孔在采场施工过程中,存在破坏堵塞)。矿区属“极震区(Ⅷ度区)范围”,具有强烈新构造活动的深大断裂带从矿区西侧通过。数据收集时,由于矿山新近调整施工队伍,存在施工队不听指挥的情况。
表3 采场北部边坡现状调查表
Table 3 Investigation of current situation of northern slope of stope
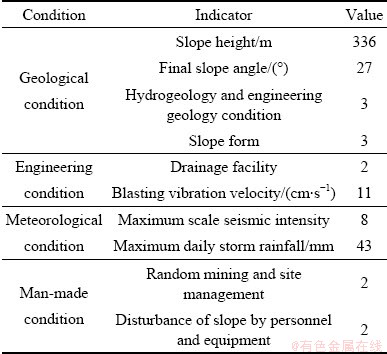
采场采用公路开拓-汽车运输方案。运输道路按45 t级载重自卸汽车、双车道Ⅱ级矿山道路设置。为降低总体边坡角、减少挂帮矿体损失,矿(废)石运输道路主要沿北部最终边坡折返设置。同时,由于采用陡帮组合台阶剥离岩土、缓帮采矿的采矿工艺,挖掘机及汽车等设备需要频繁的移动,对边坡扰动较大。
单指标评价矩阵如下:
 (13)
(13)
评价指标权重为:
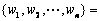
{0.07648, 0.07406, 0.11589, 0.11589, 0.11589,
0.06268, 0.111589, 0.09144, 0.11589, 0.11589}
综合测度向量为{0.12966, 0.59502, 0.27532, 0.00000}。然后求得未确知测度欧式距离d1、d2、d3、d4分别为1.0897、0.5066、0.9466、1.2028。由于d2<d3<d1<d4,最后根据最小未确知测度欧式距离判别法得出,露天采场北部现状边坡稳定性等级为B级,边坡稳定性较差。稳定性分析数据搜集于2019年10月底,11月中旬北部边坡发生了较大规模的滑坡,验证了方法的实用性和可靠性。根据评价指标权重及单指标在评价矩阵中所处的等级,可得为了改善边坡的稳定性等级,目前矿山需要优先改善的指标为:排水设施、乱采乱挖及现场管理、边坡活动人员及设备工作数。
4 结论
1) 露天矿山边坡稳定性受诸多不确定性因素影响,建立了未确知测度理论的露天矿山边坡稳定性评价模型,为降低人为因素对指标权重的影响,运用熵权法确定评价指标的权重。为避免人为选择置信度,结果非唯一性的情况,采用距离判别法作为边坡稳定性等级评判准则。
2) 运用评价模型对某深凹露天矿北部边坡进行了稳定性评价,评价结论与矿山实际情况一致;为露天矿山边坡稳定性评判提供了一种简便、低成本的新方法。同时,该方法还能为改善边坡稳定性优先采取措施,提供科学依据。
3) 评价指标的选取及分级很大程度上影响着评价结论,但这方面尚无统一标准,未来需要进一步研究。影响露天矿山边坡稳定性的因素众多,为进一步提高模型的适用性和准确性,还需深入调查更多矿山的边坡稳定性影响因素,完善评价指标体系,使这种理论方法更科学、更合理。
REFERENCES
[1] 中华人民共和国应急管理部. 2017年全国非煤矿山生产安全事故统计分析报告[R]. 北京, 2018: 1-24.
Ministry of Emergency Management of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical analysis report of production safety accidents in China’s non-coal mines 2017[R]. Beijing, 2018: 1-24.
[2] 郑颖人, 赵尚毅, 张鲁渝. 用有限元强度折减法进行边坡稳定分析[J]. 中国工程科学, 2002, 4(10): 57-61.
ZHENG Ying-ren, ZHAO Shang-yi, ZHANG Lu-yu. Analysis of slope stability by finite element strength reduction method[J]. Engineering Science, 2002, 4(10): 57-61.
[3] 赵尚毅, 郑颖人, 时卫民, 等. 用有限元强度折减法求边坡稳定安全系数[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2002, 24(3): 343-346.
ZHAO Shang-yi, ZHENG Ying, SHI Wei-min, et al. Analysis on safety factor of slope by strength reduction FEM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2002, 24(3): 343-346.
[4] 陈祖煜, 徐 昱, 孙 平. 考虑岩体抗剪强度各向异性特征的边坡稳定分析方法[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(6): 759-767.
CHEN Zu-yu, XU Yu, SUN Ping. Rock slope stability analysis using anisotropic shear strength parameters[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2015, 51(6): 759-767.
[5] 李典庆, 肖 特, 曹子君, 等. 基于高效随机有限元法的边坡风险评估[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(7): 1994-2003.
LI Dian-qing, XIAO Te, CAO Zi-jun, et al. Slope risk assessment using efficient random finite element method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(7): 1994-2003.
[6] ZHANG K, CAO P, LIU Z Y. Simulation analysis on three-dimensional slope failure under different conditions[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(11): 2490-2502.
[7] 洪本根, 罗嗣海, 胡世丽, 等. 全覆式离子型稀土矿山临界注液范围的计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(7): 1509-1518.
HONG Ben-gen, LUO Si-hai, HU Shi-li, et al. Calculation of critical liquid injection range in full clad ion-absorbed rare earth mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(7): 1509-1518.
[8] 张永兴. 边坡工程学[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2008.
ZHANG Yong-xing. Civil engineering graduate[M]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2008.
[9] 王光远. 论未确知性信息及其数学处理[J]. 哈尔滨建筑工程学院学报, 1990, 23(4): 52-58.
WANG Guang-yuan. Uncertainty information and its mathematical treatment[J]. Journal of Harbin Architecture and Engineering Institute, 1990, 23(4): 52-58.
[10] 刘开第, 吴和琴, 庞彦军. 不确定信息数学处理及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999.
LIU Kai-di, WU He-qin, PANG Yan-jun. Mathematics treatment and application of unascertained information[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999.
[11] 彭 康, 李夕兵, 王世鸣, 等. 基于未确知测度模型的尾矿库溃坝风险评价[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(4): 1447-1452.
PENG Kang, LI Xi-bing, WANG Shi-ming, et al. Optimization model of unascertained measurement for dam-break risk evaluation in tailings dams[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(4): 1447-1452.
[12] LI S C, WU J, XU Z H. Unascertained measure model of water and mud inrush risk evaluation in karst tunnels and its engineering application[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2017, 21(4): 1170-1182.
[13] DONG L J, SHU W W, LI X B. Quantitative evaluation and case studies of cleaner mining with multiple indexes considering uncertainty factors for phosphorus mines[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018: 319-334.
[14] 王胜寒, 郭 伟, 孙就忠. 基于AHP-熵权法的市政工程项目管理效果综合分析[J]. 山东交通学院学报, 2019, 27(4): 1-7.
WANG Sheng-han, GUO Wei, SUN Jiu-zhong. Comprehensive evaluation of municipal engineering project management effect based on AHP-Entropy weight method[J]. Journal of Shandong Jiaotong University, 2019, 27(4): 1-7.
[15] 章 清. 基于熵权法和可拓理论的西北油气管道坡面水毁危险性分析研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018: 36-37.
ZHANG Qing. Assessment of risk of flood damage at slope of oil and gas pipeline of northwest China based on combination of entropy method and extension theory[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2018: 36-37.
[16] 宫凤强, 李夕兵. 距离判别分析法在岩体质量等级分类中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(1): 190-194.
GONG Feng-qiang, LI Xi-bing. Application of distance discriminant analysis method to classification of engineering quality of rock masses[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 26(1): 190-194.
[17] 程爱平, 高永涛, 梁兴旺, 等. 基于未确知聚类法的底板采动破坏深度动态预测[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2014, 31(5): 739-744.
CHENG Ai-ping, GAO Yong-tao, LIANG Xing-wang, et al. Dynamic forecasting of mining-induced failure depth of floor based on unascertained clustering method[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2014, 31(5): 739-744.
[18] AQ/T 2063—2018. 金属非金属露天矿山高陡边坡安全监测技术规范[S].
AQ/T 2063—2018. Technical specification for safety monitoring of steep slope of metal and nonmetal open pit mine[S].
[19] GB 16423—2006. 金属非金属矿山安全规程[S].
GB 16423—2006. Safety regulations for metallic and non-metallic mines[S].
[20] GB 6722—2014. 爆破安全规程[S].
GB 6722—2014. Safety regulations for blasting[S].
Slope stability evaluation and application of open-pit mine based on uncertainty measurement theory
WANG Jie1, 2, 3, HU Bin1, 3, LI Jing1, 3, CHANG Jian2, CUI A-neng1, 3, CUI Kai1, 3
(1. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
2. Sinosteel Ma’anshan General Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd., Ma’anshan 243000, China;
3. Hubei Key Laboratory for Efficient Utilization and Agglomeration of Metallurgic Mineral Resources, Wuhan 430081, China;)
Abstract: The unascertained theory was applied to establish the evaluation model of slope stability in open-pit mines. According to the cause of influencing the slope stability of open-pit mines, an evaluation system of slope stability of open-pit mines was established, and 10 factors were selected as the evaluation indexes of unascertained measurement function. Then, the unascertained measurement functions of single index were constructed, and the entropy method was used to determine the weights of evaluation index. Distance discriminant was adopted as the criterion of attribute recognition. By using the established evaluation model, the stability of the northern slope of a mine was evaluated. The results show that the evaluation results are consistent with the actual situation, providing a new method for the mines to evaluate the stability of the open pit mine slope. Besides, the method provides a scientific basis for taking priority measures to improve the stability of slope.
Key words: open pit mines; slope stability; uncertainty measurement; entropy method; distance discriminant
Foundation item: Projects(U1802243, 41672317) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017ACA184) supported by the Hubei Province Technical Innovation Special Project (Major Project), China; Project(2018TDX01) supported by the Major Science and Technology Projects of WUST Cultivate Innovation Teams, China
Received date: 2020-08-03; Accepted date: 2020-12-26
Corresponding author: HU Bin; Tel: +86-13971330172; E-mail: hbin74@wust.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(U1802243,41672317);湖北省技术创新专项(重大项目)(2017ACA184);武科大重大科技项目培育类创新团队项目(2018TDX01)
收稿日期:2020-08-03;修订日期:2020-12-26
通信作者:胡 斌,教授,博士;电话:13971330172;E-mail:hbin74@wust.edu.cn
摘 要:应用未确知测度理论,建立了露天矿山边坡稳定性评价模型。根据影响露天矿山边坡稳定性的成因,建立了露天矿山边坡稳定性评价体系。通过调查,选取了10项指标作为未确知测度函数评判指标。然后,构建单指标未确知测度函数,运用熵权法确定评价指标权重,采用距离判别法作为属性识别准则。利用建立的评价模型对某深凹露天矿北部边坡的稳定性进行了评价。结果表明:评价结果与实际情况一致,说明了该评价方法的有效性,为矿山提供了一种简便、低成本的露天矿山边坡稳定性评价新方法。同时,该方法为改善边坡稳定性优先采取措施,提供了科学依据。
[1] 中华人民共和国应急管理部. 2017年全国非煤矿山生产安全事故统计分析报告[R]. 北京, 2018: 1-24.
[2] 郑颖人, 赵尚毅, 张鲁渝. 用有限元强度折减法进行边坡稳定分析[J]. 中国工程科学, 2002, 4(10): 57-61.
[3] 赵尚毅, 郑颖人, 时卫民, 等. 用有限元强度折减法求边坡稳定安全系数[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2002, 24(3): 343-346.
[4] 陈祖煜, 徐 昱, 孙 平. 考虑岩体抗剪强度各向异性特征的边坡稳定分析方法[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(6): 759-767.
[5] 李典庆, 肖 特, 曹子君, 等. 基于高效随机有限元法的边坡风险评估[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(7): 1994-2003.
[7] 洪本根, 罗嗣海, 胡世丽, 等. 全覆式离子型稀土矿山临界注液范围的计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(7): 1509-1518.
[8] 张永兴. 边坡工程学[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2008.
ZHANG Yong-xing. Civil engineering graduate[M]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2008.
[9] 王光远. 论未确知性信息及其数学处理[J]. 哈尔滨建筑工程学院学报, 1990, 23(4): 52-58.
[10] 刘开第, 吴和琴, 庞彦军. 不确定信息数学处理及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999.
[11] 彭 康, 李夕兵, 王世鸣, 等. 基于未确知测度模型的尾矿库溃坝风险评价[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(4): 1447-1452.
[14] 王胜寒, 郭 伟, 孙就忠. 基于AHP-熵权法的市政工程项目管理效果综合分析[J]. 山东交通学院学报, 2019, 27(4): 1-7.
[15] 章 清. 基于熵权法和可拓理论的西北油气管道坡面水毁危险性分析研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018: 36-37.
[16] 宫凤强, 李夕兵. 距离判别分析法在岩体质量等级分类中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(1): 190-194.
[17] 程爱平, 高永涛, 梁兴旺, 等. 基于未确知聚类法的底板采动破坏深度动态预测[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2014, 31(5): 739-744.
[18] AQ/T 2063—2018. 金属非金属露天矿山高陡边坡安全监测技术规范[S].
[19] GB 16423—2006. 金属非金属矿山安全规程[S].
GB 16423—2006. Safety regulations for metallic and non-metallic mines[S].


