文章编号:1004-0609(2013)10-2985-08
含砷污酸资源化回收铜和砷的新工艺
郑雅杰,张胜华,龚 昶
(中南大学 冶金与环境工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:
以含砷污酸为原料,通过中和除杂—沉砷—洗涤—浸出—蒸发结晶—溶解制取三氧化二砷,实现含砷污酸的资源化。结果表明:将污酸中和至pH为2,使污酸的酸度降低;在中和液中加入硫酸铜,控制Cu和As的摩尔比为1.5:1,调节体系pH为8沉淀As,得到亚砷酸铜,As的沉淀率达到97.81%;通过洗涤除杂提高亚砷酸铜中As和Cu的含量;采用10%硫酸溶液,在液固比为5:1条件下浸出亚砷酸铜,所得溶液蒸发结晶得到三氧化二砷与硫酸铜的混合物;用水溶解该混合物后过滤得到硫酸铜溶液及符合YS/T-99-1997As2O3-3号产品标准的三氧化二砷。
关键词:
中图分类号:X703 文献标志码:A
Novel technique for recovery of copper and arsenic from arsenic-containing waste acid
ZHENG Ya-jie, ZHANG Sheng-hua, GONG Chang
(School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: A novel technique for recovery of copper and arsenic from arsenic-containing waste acid discharged from copper smelter was proposed, and the process was composed of neutralization and purification—precipitation of arsenic—washing—leaching—evaporative crystallization—dissolution. Arsenic trioxide and cupric sulfate were obtained and resource of waste acid was accomplished. The results show that the acidity of the waste acid decreases and a certain amount of impurities is removed when the pH value of the system is neutralized to 2 by lime milk. Copper arsenite precipitates with arsenic precipitation efficiency of 97.81% when cupric sulfate is added into the neutralized solution. At the same time, the molar ratio of Cu and As is controlled at 1.5:1 and pH value of system is adjusted to 8 by sodium hydroxide. The contents of copper and arsenic in the precipitate of copper arsenite are increased by washing. 10% sulfuric acid was adopted to treat copper arsenite by leaching at liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, and then, a mixture of arsenic trioxide and cupric sulfate is obtained after the leachate is evaporated and crystallized. Finally, through dissolution and filtration of the solid mixture, cupric sulfate remains in the residual solution while arsenic trioxide meeting the product standard of YS/T-99-1997As2O3-3 is collected in the filter cake.
Key words: waste acid; leaching; recovery; arsenic trioxide; cupric sulfate
据估计,我国有色冶炼系统每年有1万t以上的砷进入烟气,烟气净化时部分砷进入污酸,其含量一般达到2~6 g/L[1-3]。有色冶炼污酸具有酸度高,重金属离子种类多,砷浓度高等特点,已成为我国砷的主要污染源之一[4]。目前,国内外处理含砷废水的主要方法有中和沉淀法、絮凝沉淀法、铁氧体法、硫化物沉淀法等[5-9],这些方法适用于处理高浓度含砷废水,但生成的污泥易造成二次污染[10]。因此,污酸的高效治理与资源化利用已受到了人们的高度关注。金属砷剧毒[11],可与细胞中含巯基的酶结合,抑制细胞氧化过程,还能麻痹血管运动中枢,使毛细血管麻痹、扩张及通透性增高[12]。另外,砷具有致癌作用及潜伏期较长的远期效应[13-14]。砷在人体内有明显的积蓄性,人体摄入较低量砷化物,经过1~2年、甚至十年或几十年后,可能会出现砷中毒病症,已被美国疾病控制中心和国际防癌研究机构确定为第一类致癌物[15]。但是,有证据表明As亦是动物体必需的一种微量元素,可能对人体新陈代谢有益,尽管需求量很低[16]。铜冶炼污酸中的砷和铜含量高,是十分重要的资源。As2O3 (砒霜)为砷最普遍存在形式的化合物,是提取砷元素的原料,在医药、防腐、制革、制乳白色玻璃、军工等方面亦有广泛用途[17-18]。因此,含砷污酸的清洁化处理及资源化回收具有重要的环境及经济效益。作者研究了砷铜混合有色冶炼废水处理技术[19],该技术被2012年国家先进污染防治示范技术名录收录[20],但是该方法存在一些缺点,如二氧化硫还原亚砷酸铜时间长、所得红盐需要进一步氧化酸浸制备硫酸铜等。
本研究将含砷污酸中的砷经过沉淀转化制备成三氧化二砷[21],克服二氧化硫还原亚砷酸铜制备三氧化二砷的缺点,并且得到高于YS/T-99-1997As2O3-3号产品标准的三氧化二砷,实现污酸的治理及铜砷资源的再利用。
1 实验
1.1 实验步骤及工艺流程
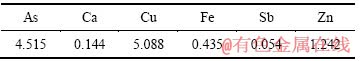
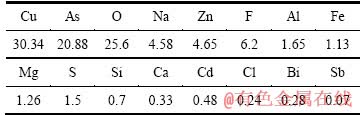
取某铜冶炼厂烟气洗涤废水,经扩散渗析回收硫酸后所得含砷污酸为研究对象,其中H+浓度为1.256 mol/L,成分如表1所列。
表1 含砷污酸主要成分
Table 1 Main chemical compositions of waste acid solution (g/L)
取一定量的氧化钙,加水打浆得到氢氧化钙乳液;取一定体积的含砷污酸,滴加氢氧化钙乳液调节pH值,过滤;所得滤液按一定Cu和As的摩尔比加入硫酸铜,采用氢氧化钙调节pH值沉淀As,得到亚砷酸铜,用水洗涤;将亚砷酸铜用硫酸溶解,之后通入二氧化硫还原得到亚砷酸和硫酸铜混合溶液;加热蒸发、冷却结晶,过滤得到含有三氧化二砷和硫酸铜的混合物;用水溶解三氧化二砷和硫酸铜混合物,过滤、洗涤、干燥得到三氧化二砷;过滤后得到的滤液含As及硫酸铜,其可返回利用于沉As步骤,使As得到回收,Cu得到循环利用。其工艺流程如图1所示。
1.2 分析与检测
溶液化学成分采用美国热电元素公司的Intrepid Ⅱ XSP型电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP)分析;固体物质成分采用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)分析;固体物相采用日本理学D/max-TTR Ⅲ型X射线衍射仪分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 中和除杂
取500 mL含砷污酸于1 L烧杯中,用D1JC-60W搅拌器搅拌,逐渐滴加氢氧化钙乳液,中和至所需pH值,pH值对溶液中砷及其他主要离子去除率的影响如图2所示。
污酸中加入氢氧化钙时发生中和反应,体系pH升高。随着氧化钙用量的增加,体系pH值逐渐升高,当氧化钙中和后溶液pH值从1升高到6时,氧化钙用量从10.69 g逐渐增加到20.42 g。由图2可知,As及其他金属离子去除率随着pH值的升高而增加。pH值从1升高到6时,As的去除率由1.02%增加到49.73%,Cu的去除率从0.08%增加到44.45%。
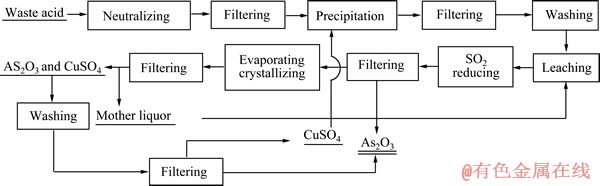
图1 含砷污酸回收砷制备三氧化二砷工艺流程图
Fig. 1 Flow chart of recovery and preparation of arsenic trioxide from arsenic-containing waste acid
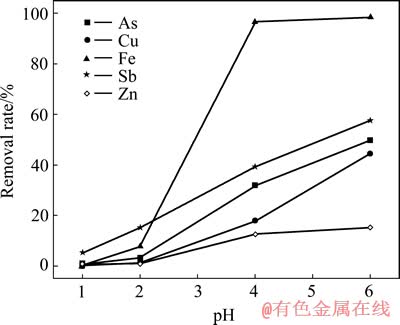
图2 pH值对砷及其他金属离子去除率的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of pH on removal rate of arsenic and other metal ions
加入氢氧化钙乳液时,污酸中Fe3+、Sb3+、Zn2+将生成氢氧化物沉淀,Fe3+、Sb3+、Zn2+去除率随pH值升高而增加。随着pH值的升高,污酸中Cu2+和AsO2-发生反应生成绿色亚砷酸铜沉淀,pH值升高得越多,其损失越大。为了减少溶液中砷和铜的损失,适宜的pH值为2,此时,As、Cu、Fe、Sb和Zn的去除率分别为3.24%、1.30%、7.95%、15.20%和0.97%。
2.2 As的沉淀
2.2.1 Cu和As摩尔比对As、Cu沉淀率的影响
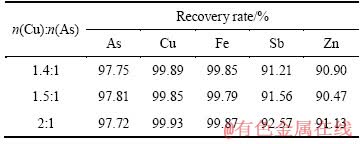
取中和液500 mL(pH=2,成分见表2),加入所需量的硫酸铜,用氢氧化钠调节体系pH值至8,搅拌反应1 h,考察Cu和As的摩尔比对As、Cu沉淀率的影响,其结果见表3。
由表3可知,Cu、As的摩尔比对As、Cu的沉淀率影响不大,当Cu、As的摩尔比从1.4:1增加到2:1时,As的沉淀率约为97.7%,而Cu和Fe沉淀率达到99.79%以上,Sb、Zn的沉淀率在90%以上。为了减少硫酸铜的用量,适宜的Cu、As的摩尔比取1.5:1。
表2 中和液的成分
Table 2 Main chemical compositions of neutralized solution (g/L)
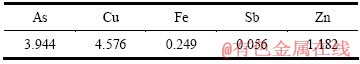
表3 Cu和As的摩尔比对As、Cu回收率的影响
Table 3 Effect of molar ratio of Cu to As on recovery rates of arsenic and copper
2.2.2 pH值对As、Cu沉淀率的影响
取中和液500 mL,按Cu和As的摩尔比为1.5:1加入所需量的硫酸铜,用NaOH调节溶液pH值,搅拌反应1 h,pH值对As、Cu及其他离子沉淀率的影响如图3所示。
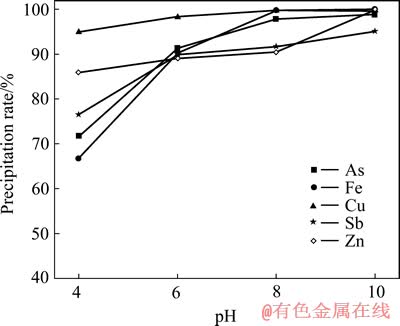
图3 pH值对As、Cu等离子沉淀率的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of pH on precipitation rates of arsenic, copper and other coexisting metal ions
由图3可知,As、Cu、Fe、Sb及Zn的沉淀率随pH值的升高而增加,当pH从4升高到10时,As的沉淀率从71.72%增加到98.96%,Cu的沉淀率从94.73%增加到99.99%;当pH值从8升高10时,As和Cu的沉淀率分别增加了1.15%和0.14%,沉淀率增加较少,故适宜pH为8,此时,As和Cu的沉淀率分别为97.81%和99.85%。
由于中和液中Cu2+、As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)的存在,加入硫酸铜调节pH值时发生如下反应[22]:
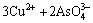 =Cu3(AsO4)2↓ (1)
=Cu3(AsO4)2↓ (1)
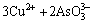 =Cu3(AsO3)2↓ (2)
=Cu3(AsO3)2↓ (2)
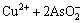 =Cu(AsO2)2↓ (3)
=Cu(AsO2)2↓ (3)
溶液中存在以下电离平衡[4, 23]:
Cu3(AsO4)2
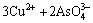 (4)
(4)
Cu3(AsO3)2 
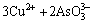 (5)
(5)
Cu(AsO2)2 
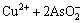 (6)
(6)
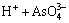
 H3AsO4 (7)
H3AsO4 (7)
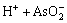
 HAsO2 (8)
HAsO2 (8)
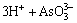
 H3AsO3 (9)
H3AsO3 (9)
砷酸、亚砷酸为弱酸,当pH升高时,H+浓度降低,电离平衡向左移动,因此,As和Cu的沉淀率随pH值的升高而增加。
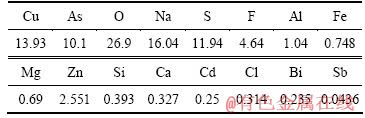
根据实验所得适宜条件,进行放大实验制备亚砷酸铜。取4 L一段中和液置于5 L的烧杯中,按Cu和As摩尔比为1.5:1加入所需量的硫酸铜,用氢氧化钠调节溶液pH为8,搅拌反应1 h,过滤,将渣烘干。用X荧光分析其中各元素含量如表4所示。
由表4可知,所得亚砷酸铜中As含量为10.1%,Cu含量为13.93%,Cu、As摩尔比为1.6:1。除Cu和As外,F、Zn、Na和S含量分别为4.64%、2.551%、16.04%和11.94%,溶液中的Cu和As绝大部分沉淀进入亚砷酸铜中。
表4 亚砷酸铜中各元素成分
Table 4 Main chemical compositions of copper arsenite (mass fraction, %)
2.3 亚砷酸铜洗涤除杂
亚砷酸铜中含有杂质,进行洗涤去除可溶性杂质。取50 g亚砷酸铜,加入pH值为2的硫酸溶液,搅拌0.5 h。当液固比分别为2:1、3:1、4:1和6:1时,Na的去除率分别为30.21%、35.56%、40.95%和41.63%,Na去除率随液固比增加而增加,其适宜的液固比为4:1。
取 50 g亚砷酸铜,按液固比为4:1加入200 mL硫酸溶液,搅拌洗涤0.5 h。pH值分别为1、2、3、4和7时,As溶解率为8.89%、0.74%、0.48%、0.45%和0.43%,Na去除率分别为41.78%、40.95%、35.69%、34.81%和34.58%。酸性越强,亚砷酸铜溶解损失越大,适宜洗涤除杂pH值为2。
按实验所得适宜条件,取500 g亚砷酸铜进行洗涤除杂放大实验,所得洗涤后的亚砷酸铜烘干,用X荧光分析其中各元素的含量,结果如表5所列。
表5 洗涤后亚砷酸铜中各元素成分
Table 5 Main chemical compositions of copper arsenite after washing (mass fraction, %)
比较表4和5可知,洗涤过程中,亚砷酸钠溶解在水中除去,洗涤之后,亚砷酸铜中的Na、S含量降低,Na含量由16.04%降至4.58%,S含量由11.94%降至1.5%;Cu含量从13.93%提高到30.34%,As含量从10.1%提高到20.88%。
2.4 亚砷酸铜浸出
2.4.1 液固比对As、Cu浸出率的影响
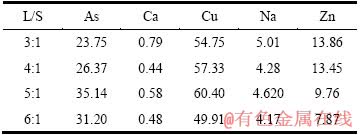
取50 g亚砷酸铜加入10%的硫酸溶液中,搅拌反应0.5 h,Cu和As及其他物质浸出率与液固比的关系如图4所示,浸出液成分如表6所列。
由图4可知,随液固比的增加,As的浸出率逐渐增加,液固比为5:1时达到平衡,此时,As的浸出率为79.91%,Cu的浸出率为89.62%。根据表6可知,液固比为5:1时,浸出液中As和Cu的含量达到35.14 g/L和60.40 g/L。
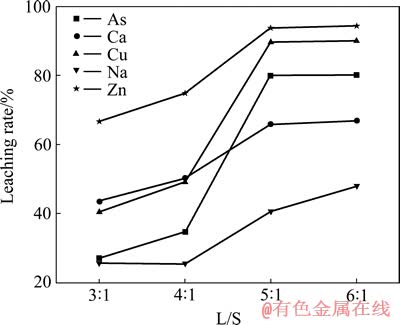
图4 液固比对亚砷酸铜浸出率影响
Fig. 4 Effect of L/S on leaching rate of copper arsenite
表6 不同液固比条件下浸出液成分
Table 6 Leaching liquid ingredients obtained at different L/S (g/L)
2.4.2 硫酸浓度对As、Cu浸出率的影响
取50 g亚砷酸铜,液固比5:1条件下进行浸出,硫酸浓度对As、Cu及其他金属浸出率影响如图5所示。由图5可知,随硫酸浓度的升高,亚砷酸铜中各元素的浸出率逐渐升高。当硫酸浓度为15%时,As和Cu的浸出率分别为98.39%和99.14%。此时,浸出液中As的浓度为40.38 g/L,Cu的浓度为62.36 g/L。
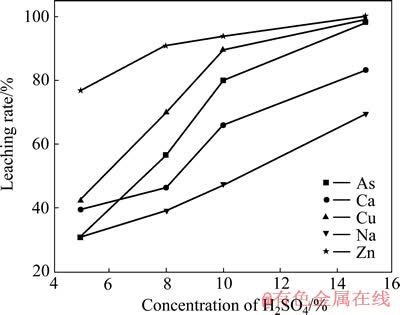
图5 硫酸浓度对亚砷酸铜浸出率影响
Fig. 5 Effect of concentration of H2SO4 on leaching rate of copper arsenite
亚砷酸铜和砷酸铜可溶于硫酸,溶解后生成砷酸、亚砷酸和硫酸铜,其反应式如下:
Cu3(AsO3)2+3H2SO4=3CuSO4+2H3AsO3 (10)
Cu(AsO2)2+H2SO4=CuSO4+2HAsO2 (11)
Cu3(AsO4)2+3H2SO4=3CuSO4+2H3AsO4 (12)
亚砷酸铜浸出过程中,随着硫酸量的增加,As和Cu的浸出率升高。因此,适宜的浸出液固比为5:1时,硫酸浓度为15%。
2.5 三氧化二砷制备
2.5.1 亚砷酸铜溶液还原提取三氧化二砷
硫酸浸出亚砷酸铜所得混合溶液成分如表7所列。混合溶液总砷为26.66 g/L, 进一步分析可知As(Ⅲ)为18.492 g/L,As(Ⅴ)为8.168 g/L。在混合溶液中通入SO2还原,至As(Ⅴ)全部转化为As(Ⅲ)后,溶液中析出灰白色沉淀,其成分如表8所列,XRD分析结果如图6所示,过滤后滤液成分如表9所列。
表7 蒸发结晶料液成分
Table 7 Main chemical compositions of evaporated and crystallized liquid (g/L)
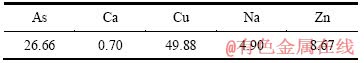
表8 灰白色沉淀物的主要成分
Table 8 Main chemical compositions of grey precipitating solid (mass fraction, %)
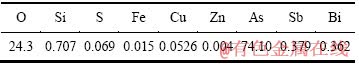
表9 滤液成分
Table 9 Main chemical compositions of filtrate (g/L)
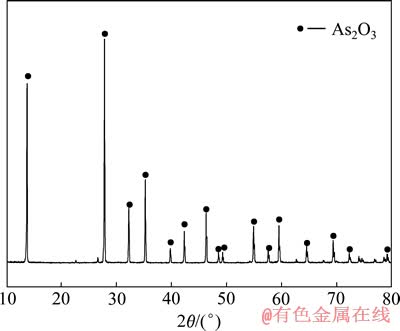
图6 还原后所得滤渣XRD谱
Fig. 6 XRD pattern of filter residue after reduction
由表8可知,还原渣中三氧化二砷含量达到了98.9%,符合YS/T-99-1997AS2O3-2号产品标准。由图6可知,还原产物为三氧化二砷。由表9可知,滤液中含As、Cu,可返回沉淀处理。
2.5.2 蒸发结晶提取三氧化二砷
每次取含不同硫酸浓度上述滤液200 mL,在搅拌状态下蒸发至50 mL,冷却结晶,过滤,取滤液检测其中成分,所得结果如表10所列。
表10 蒸发结晶滤液成分
Table 10 Main chemical compositions of evaporated and crystallized filtrate
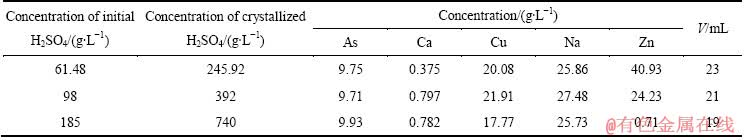
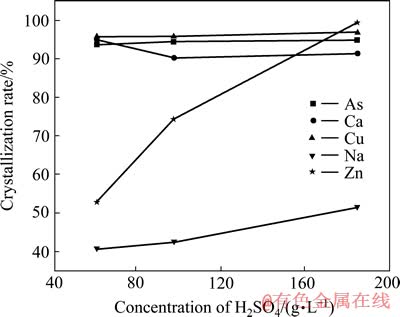
图7 硫酸浓度对As结晶产率的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of concentration of H2SO4 on crystallization rate of arsenic
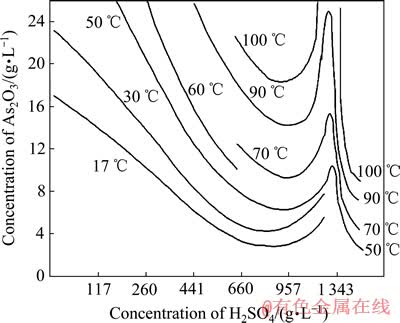
图8 不同温度下As2O3在硫酸溶液中溶解度曲线[24]
Fig. 8 Solubility curves of As2O3 in sulfuric acid solution at various temperatures[24]
考察不同硫酸浓度对结晶率的影响,其结果如图7所示,图8所示为不同温度和硫酸浓度下三氧化二砷的溶解度曲线[24]。
由图7可知,当初始溶液硫酸浓度为61.48、98、185 g/L时,蒸发结晶后As的结晶产率分别为93.77%、94.33%、94.77%。从图8中可以看出,三氧化二砷在硫酸溶液中的溶解度随硫酸变化比较复杂,随着硫酸浓度的增加,三氧化二砷溶解度在800 g/L左右时达到一个极低值。也就是说,当硫酸浓度低于800 g/L时,同一温度下,三氧化二砷的溶解度随硫酸浓度的增加而降低,实验结果与图8所示结果一致。但是,当硫酸浓度从61.48 g/L增加到185 g/L时,Zn、Na的结晶产率分别从52.76%、40.75%升高到99.33%、51.31%,Cu的结晶产率略有上升。因此,在蒸发结晶提取三氧化二砷时,适宜的初始硫酸浓度选择为61.48 g/L,此时,Cu的结晶产率为95.75%。
当硫酸浓度为61.48 g/L时,蒸发结晶产物主要成分如表11所列。过滤后滤液中的硫酸浓度为245.92 g/L,其可返回利用硫酸浸出亚砷酸铜。
表11 蒸发结晶产物主要成分含量
Table 11 Main chemical compositions of evaporated and crystallized product (mass fraction, %)
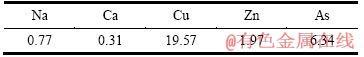
由表11可知,结晶产物成分为Cu、As和Zn。在硫酸溶液中蒸发结晶,可以推断结晶产物为硫酸铜、三氧化二砷和硫酸锌。溶液中的As(Ⅲ)主要以H3AsO3的形态存在,其析出反应式[25]如下:
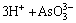
 As(OH)3
As(OH)3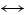 As3++3OH- (13)
As3++3OH- (13)
HAsO2+H2O H3AsO3 (14)
H3AsO3 (14)
2H3AsO3  As2O3↓ +3H2O (15)
As2O3↓ +3H2O (15)
由于三氧化二砷中含有大量杂质,需用水洗涤去除其可溶性物质,液固比对三氧化二砷洗涤效果的影响如表12所列,液固比4:1所得的产物XRD结果如图9所示。
从表12可知,As和杂质溶解率随液固比增加而增加,当液固比为4:1时,As、Cu、Ca和Zn溶解率分别达到16.19%、99.99%、97.99%和99.98%。为了去除三氧化二砷中杂质,适宜的液固比为4:1。洗涤三氧化二砷后的溶液为硫酸铜溶液,将返回一段中和液沉淀砷,使之得到循环利用。由图9可知,产物为三氧化二砷。采用化学方法分析,液固比4:1所得产品中三氧化二砷含量为96.84%,达到了YS/T-99-1997 As2O3含量为95%的As2O3-3号产品标准。
表12 液固比对各元素溶解率的影响
Table 12 Effect of L/S on dissolution rate of water soluble impurities
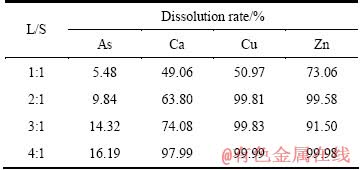
图9 As2O3的XRD谱
Fig. 9 XRD pattern of As2O3
3 结论
1) 以含砷污酸为原料,通过中和除杂—沉砷—洗涤除杂—硫酸浸出—蒸发结晶—溶解制备得到符合YS/T-99-1997As2O3-3号产品标准的三氧化二砷,实现污酸的资源化,工艺可行,且操作简便。
2) 含砷污酸中Cu和As的资源化回收适宜工艺条件:含砷污酸Ca(OH)2中和除杂的适宜pH值为2,As、Cu、Fe、Sb和Pb的去除率分别为3.24%、1.30%、7.95%、15.20%和0.97%;As的沉淀条件为Cu和As的摩尔比为1.5:1,pH值为8,此时,As沉淀率为97.81%,Cu沉淀率为99.85%;亚砷酸铜洗涤除杂,适宜的硫酸溶液pH为2,液固比4:1,在此条件下洗涤亚砷酸铜30 min,Na含量由16.04%降至4.58%,S含量由11.94%降至1.5%,As含量由10.1%升高到20.88%,Cu含量由13.93%升高到30.34%,较大程度地提高了亚砷酸铜的纯度;硫酸浸出亚砷酸铜的浸出条件为15%硫酸溶液,液固比为5:1,As和Cu的浸出率分别可达98.39%和99.14%;浸出液蒸发结晶制备三氧化二砷,蒸发前后溶液体积比为4:1,适宜的溶液硫酸浓度为61.48 g/L,As的回收率为93.77%;用水洗涤硫酸铜和三氧化二砷的混合物提取三氧化二砷,适宜液固比为4:1,得到的三氧化二砷纯度为96.84%。
3) 使用此工艺回收污酸中的Cu和As制备三氧化二砷,As的总收率达到94.23%,Cu的总收率达到98.55%,得到的三氧化二砷高于YS/T-99-1997标准中As2O3-3标准,硫酸铜得到循环利用。
REFERENCES
[1] 庄明龙, 柴立元, 闵小波, 于 霞. 含砷废水处理研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2004, 24(7): 13-17.
ZHUANG Ming-long, CHAI Li-yuan, MIN Xiao-bo, YU Xia. Progress of the research on the treatment of As-containing wastewater[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2004, 24(7): 13-17.
[2] 郑雅杰, 刘万宇, 白 猛, 张传福. 采用硫化渣制备三氧化二砷工艺[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(6): 1157-1163.
ZHENG Ya-jie, LIU Wan-yu, BAI Meng, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Preparation of arsenic trioxide from arsenic sulfide slag[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2008, 39(6): 1157-1163.
[3] 王 勇, 曹龙文, 罗 园, 郑雅杰. 硫酸装置含砷废水处理及三氧化二砷制备[J]. 硫酸工业, 2010(4): 21-25.
WANG Yong, CAO Nong-wen, LUO Yuan, ZHENG Ya-jie. Treatment of arsenic-containing wastewater from sulphuric acid plants and preparation of As2O3[J]. Sulphuric Acid Industry, 2010(4): 21-25.
[4] 王 勇, 赵攀峰, 郑雅杰. 含砷废酸制备亚砷酸铜及其在铜电解液净化中的应用[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(6): 1115-1120.
WANG Yong, ZHAO Pan-feng, ZHENG Ya-jie. Preparation of copper arsenite from waste acid containing arsenic and its application in copper electrolyte purification[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(6): 1115-1120.
[5] MOHAN D, PITTMAN Jr C U. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents: A critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 142(1/2): 1-53.
[6] WANG H J, GONG W X, LIU R P, LIU H J, QU J H. Treatment of high arsenic content wastewater by a combined physical-chemical process[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2011, 379(1/3): 116-120.
[7] 蒋国民, 王云燕, 柴立元, 舒余德, 王庆伟, 陈润华. 高铁酸钾处理含砷废水[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009, 9(6): 1109-1114.
JIANG Guo-min, WANG Yun-yan, CHAI Li-yuan, SHU Yu-de, WANG Qing-wei, CHEN Run-hua. Treatment of arsenic- containing wastewater by potassium ferrate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(6): 1109-1114.
[8] ZHOU Wen-ke, PENG Ying-lin, ZHENG Ya-jie, MA Yu-tian, CUI Tao. Reduction and deposition of arsenic in copper electrolyte[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(12): 2772-2777.
[9] 刘锐平, 李 星, 夏圣骥, 武荣成, 李圭白. 高锰酸钾强化三氯化铁共沉降法去除亚砷酸盐的效能与机理[J]. 环境工程, 2005, 26(1): 72-75.
LIU Rui-ping, LI Xing, XIA Sheng-ji, WU Rong-cheng, LI Gui-bai. Effectiveness and mechanism of permanganate enhancing arsenite co-precipitation with ferric chloride[J]. Environmental Science, 2005, 26(1): 72-75.
[10] 易求实, 杜冬云, 鲍霞杰, 曹龙文, 李敦顺. 高效硫化回收技术处理高砷净化污酸的研究[J]. 硫酸工业, 2009(6): 6-10.
YI Qiu-shi, DU Dong-yun, BAO Xia-jie, CAO Long-wen, LI Dun-shun. Study on treatment of high-arsenic waste acid from cleaning section using high-efficiency sulphuration recovery technology[J]. Sulphuric Acid Industry, 2009(6): 6-10.
[11] 张学洪, 朱义年, 刘辉利. 砷的环境化学作用过程研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 1-2.
ZHANG Xue-hong, ZHU Yi-nian, LIU Hui-li. Role in the process of study of the environmental chemistry of arsenic[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 1-2.
[12] HEI T K, FILPIC M. Role of oxidative damage in the genotoxicity of arsenic[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2004, 37(5): 574-581.
[13] 李 远, 刘起展. 砷化物所致细胞恶性转化的信号通路研究进展[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2011, 45(7): 657-660.
LI Yuan, LIU Qi-zhan. Arsenide induced malignant transformation of signaling pathway of research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2011, 45(7): 657-660.
[14] 凌 敏, 刘起展. 砷所致表观遗传改变与致癌作用的研究进展[J]. 中国地方病学杂质, 2012, 31(1): 107-110.
LING Min, LIU Qi-zhan. Arsenic due to epigenetic changes and carcinogenesis studies progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 2012, 31(1): 107-110.
[15] SHARMA V K, SOHN M. Aquatic arsenic: Toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation[J]. Environment International, 2009, 35(4): 743-759.
[16] 闵世俊, 曾 英, 韩 璐. 含砷工业废水处理现状与进展[J]. 广东微量元素科学, 2008, 15(8): 1-7.
MIN Shi-jun, ZENG Ying, HAN Lu. Present situation and progress of technology for treating As-containing industrial wastewater[J]. Trace Elements Science, 2008, 15(8): 1-7.
[17] LAKSHMIPATHIRAJ P, PRABHAKAR S, RAJU G B. Studies on the electrochemical decontamination of wastewater containing arsenic[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 73(2): 114-121.
[18] 郑雅杰, 罗 园, 王 勇. 采用含砷废水沉淀还原法制备三氧化二砷[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 40(1): 48-54.
ZHENG Ya-jie, LUO Yuan, WANG Yong. Arsenic trioxide made by precipitation-reduction method from As-containing wastewater[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2009, 40(1): 48-54.
[19] 郑雅杰, 罗 园, 王 勇. 利用含砷废水制备三氧化二砷的方法: 中国, 200710035704.2[P]. 2008-02-20.
ZHENG Ya-jie, LUO Yuan, WANG Yong. The method of arsenic trioxide of preparation from As-containing wastewater: CN 200710035704.2[P]. 2008-02-20.
[20] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 关于发布《2012年国家先进污染防治示范技术名录》和《2012年国家鼓励发展的环境保护技术目录》的公告[EB/OL]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/ hbb/bgg/201207/t20120711_233344.htm. 2012-07-05.
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Announcement on the release of 2012 national advanced pollution prevention demonstration technology List and 2012 state encourages the development of environmental protection technology directory [EB/OL]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/ bgg/201207/t20120711_233344.htm. 2012-07-05.
[21] 郑雅杰, 张胜华, 龚 昶. 含砷废水沉淀转化为三氧化二砷的一种方法: 中国, 201210198735.0[P]. 2012-06-10.
ZHENG Ya-jie, ZHANG Sheng-hua, GONG Chang. Method for arsenic trioxide of preparation by precipitation from As-containing wastewater: CN 201210198735.0[P]. 2012-06-10.
[22] 王 勇, 赵攀峰, 郑雅杰, 罗 园. 洗涤冶炼烟气产生的含砷酸性废水的利用及处理[J]. 矿冶工程, 2008, 28(3): 60-63.
WANG Yong, ZHAO Pan-feng, ZHENG Ya-jie, LUO Yuan. Recovery and treatment of arsenic-containing acidic wastewater from smelter washing smoke[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2008, 28(3): 60-63.
[23] 冯树屏. 砷的分析化学[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1986: 183-185.
FENG Shu-ping. Analytical chemistry of arsenic[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1986: 183-185.
[24] DALWASKI F. Removing arsenic from copper smelter gases[J]. Journal of the Minerals Metals and Materials Society, 1999, 51(9): 24-26.
[25] 曹忠良, 王珍云. 无机化学反应方程式手册[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 1982: 61-80.
CAO Zhong-liang, WANG Zhen-yun. Inorganic chemical reaction equation Manual[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1982: 61-80.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:广东省教育部产学研重大项目(2009B090200053)
收稿日期:2012-11-24;修订日期:2013-07-20
通信作者:郑雅杰,教授,博士;电话:0731-88836285;E-mail: 13974810738@163.com
摘 要:以含砷污酸为原料,通过中和除杂—沉砷—洗涤—浸出—蒸发结晶—溶解制取三氧化二砷,实现含砷污酸的资源化。结果表明:将污酸中和至pH为2,使污酸的酸度降低;在中和液中加入硫酸铜,控制Cu和As的摩尔比为1.5:1,调节体系pH为8沉淀As,得到亚砷酸铜,As的沉淀率达到97.81%;通过洗涤除杂提高亚砷酸铜中As和Cu的含量;采用10%硫酸溶液,在液固比为5:1条件下浸出亚砷酸铜,所得溶液蒸发结晶得到三氧化二砷与硫酸铜的混合物;用水溶解该混合物后过滤得到硫酸铜溶液及符合YS/T-99-1997As2O3-3号产品标准的三氧化二砷。
[1] 庄明龙, 柴立元, 闵小波, 于 霞. 含砷废水处理研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2004, 24(7): 13-17.
[2] 郑雅杰, 刘万宇, 白 猛, 张传福. 采用硫化渣制备三氧化二砷工艺[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(6): 1157-1163.
[3] 王 勇, 曹龙文, 罗 园, 郑雅杰. 硫酸装置含砷废水处理及三氧化二砷制备[J]. 硫酸工业, 2010(4): 21-25.
[4] 王 勇, 赵攀峰, 郑雅杰. 含砷废酸制备亚砷酸铜及其在铜电解液净化中的应用[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(6): 1115-1120.
[7] 蒋国民, 王云燕, 柴立元, 舒余德, 王庆伟, 陈润华. 高铁酸钾处理含砷废水[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009, 9(6): 1109-1114.
[9] 刘锐平, 李 星, 夏圣骥, 武荣成, 李圭白. 高锰酸钾强化三氯化铁共沉降法去除亚砷酸盐的效能与机理[J]. 环境工程, 2005, 26(1): 72-75.
[10] 易求实, 杜冬云, 鲍霞杰, 曹龙文, 李敦顺. 高效硫化回收技术处理高砷净化污酸的研究[J]. 硫酸工业, 2009(6): 6-10.
[11] 张学洪, 朱义年, 刘辉利. 砷的环境化学作用过程研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 1-2.
[13] 李 远, 刘起展. 砷化物所致细胞恶性转化的信号通路研究进展[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2011, 45(7): 657-660.
[14] 凌 敏, 刘起展. 砷所致表观遗传改变与致癌作用的研究进展[J]. 中国地方病学杂质, 2012, 31(1): 107-110.
[16] 闵世俊, 曾 英, 韩 璐. 含砷工业废水处理现状与进展[J]. 广东微量元素科学, 2008, 15(8): 1-7.
[18] 郑雅杰, 罗 园, 王 勇. 采用含砷废水沉淀还原法制备三氧化二砷[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 40(1): 48-54.
[19] 郑雅杰, 罗 园, 王 勇. 利用含砷废水制备三氧化二砷的方法: 中国, 200710035704.2[P]. 2008-02-20.
[21] 郑雅杰, 张胜华, 龚 昶. 含砷废水沉淀转化为三氧化二砷的一种方法: 中国, 201210198735.0[P]. 2012-06-10.
[22] 王 勇, 赵攀峰, 郑雅杰, 罗 园. 洗涤冶炼烟气产生的含砷酸性废水的利用及处理[J]. 矿冶工程, 2008, 28(3): 60-63.
[23] 冯树屏. 砷的分析化学[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1986: 183-185.


