DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.12.08
Nb-Ti-Co氢分离合金优化设计和渗氢性能:Ⅱ. 渗氢性能和机理
闵若男1,闫二虎1,黄浩然1,朱坤军2,赵光伟3,李新中2,徐 芬1,孙立贤1
(1. 桂林电子科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,桂林 541004;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001;
3. 三峡大学 机械与动力学院,宜昌 443002)
摘 要:系统研究Nb-Ti-Co三元合金系富Nb角相区渗氢成分区域内27种合金(膜)在523~673 K下的渗氢性能,并与Nb-Ti-Ni合金和纯Pd进行比较;而后分析区域内代表性合金(18#, 17#, 25#, 24#和33#)的持久性能、氢溶解和氢扩散特性,并结合“电阻模型”详细探讨Nb-Ti-Co合金(膜)的渗氢和抗氢脆机理。结果表明:在原有渗氢成分区域内排除六种氢脆合金后,重构渗氢区域,即区域III',该区域内18#合金(Nb65Ti20Co15)在673 K下具有最大的渗氢系数,为4.12×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2),其余合金按照渗氢系数高低(取前三)的排列顺序依次为17#、25#和24#,三者渗氢系数分别为3.99×10-8、3.72×10-8和3.58×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2);区域内33#、24#和18#合金的氢溶解和氢扩散系数依次增加,18#合金的氢溶解和氢扩散系数为15.6 mol/(m3·Pa0.5)和26.4×10-10 m2/s,分别是33#合金的1.16和1.35倍;区域III′内合金渗氢系数的增加(Ф18#>Ф24#>Ф33#)归结于同时增大的氢溶解和扩散系数,但后者起主要作用,18#合金的氢扩散激活能较低,氢原子容易跃迁,因此,该合金具有相对较高的氢扩散系数。
关键词:Nb-Ti-Co合金;氢渗透;氢溶解;氢扩散
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-12-2457-10 中图分类号:TG139 文献标志码:A
与传统Pd基合金(Pd-Ag和Pd-Cu)相比,新型Nb基双相渗氢合金由于具有相对较高的渗氢性能而备受关注。目前,双相渗氢合金主要分为两大类,一类是“固溶体/共晶型”渗氢合金,如 Nb-TiNi[1-6], Nb-TiCo[7-10]、Nb-HfNi[11-13]和Nb-HfCo[14]等,上述合金显微组织内部均包含初生固溶体Nb相和共晶相,在渗氢过程中,前者起渗氢作用而后者起抗氢脆作用;另外一类为“固溶体/固溶体型”渗氢合金,如V-(Ni, Cr, Fe, …)[15-16],Nb-(W, Re, Mo, …)[17-19]和V-Ni-Al[20]等,这些合金显微组织内部包含两种固溶体相,一种固溶体相起渗氢作用,另外一种固溶体相内部固溶大量斥氢元素,主要起抗氢脆作用。对于上述两类双相合金膜,氢渗透通过合金膜的渗氢流量J用Fick定律和Sievert定律均可表述为
 (1)
(1)
式中:K和D分别代表渗氢合金膜的氢溶解和氢扩散系数,二者乘积代表氢渗透系数Ф;pu和pd分别代表合金膜上表面和膜下表面的氢气分压;d为合金膜厚度。
由式(1)可知,增大合金膜氢渗透流量的方法主要有两个:1) 为择优选取渗氢系数Ф较大的合金(膜),并且氢扩散系数D应无限大,相反,氢溶解系数K应无限小,因为具有较高氢溶解系数的合金膜在渗氢过程中吸收大量的氢,容易发生氢脆,持久性能大幅度降低[14, 16];2) 为减小合金膜的厚度,但是该方法具有一定的局限性,因为合金膜越薄,在后期的渗氢过程中越容易发生脆性断裂,尤其在高温环境下,因此减小合金膜厚度的同时还需要合金膜具有较好的强度和优异的塑性。基于第一种方法,各国学者陆续开展了新型Nb基渗氢合金成分优化设计等系列研究,并相继开发出V-Ti-Ni[21],Ta-Ti-Ni[22]及Nb-Ti-Ni(Co)[23]等合金体系。在众多氢分离合金中,Nb-Ti-Co系合金被认为是最具有取代钯及其合金潜力的氢分离金属膜材料[8-9]。一方面,氢在Nb中比在V和Ta中的溶解度及扩散系数大,渗透性高[16, 24];另一方面,其共晶体中韧性金属间化合物TiCo的力学性能要优于化合物TiNi和HfCo的,故可以显著提高合金的抗氢脆性能[3, 8]。据日本LUO等[7]报道,Nb68Ti17Co15合金(膜)在673 K下的的渗氢性能为4.91×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa0.5),约为相同条件下纯Pd渗氢性能的3倍。鉴于第二种方法,即获取厚度更薄的合金膜,各国学者在传统电弧炉炼熔工艺[3, 7]的基础上,相继研发出了合金膜的特种制备工艺方法,如轧制工艺[10]、熔体旋淬工艺[25]以及后期的退火工艺[10, 25]。上述工艺制取的合金膜厚度一般为0.05~0.3 mm,远小于传统电弧炉炼熔工艺制备的合金膜厚度(约0.65 mm),膜厚度参数的减小可以大幅度提升合金膜的渗氢流量,进而提升合金膜的渗氢效率。目前,有大量关于特种工艺制备渗氢膜的研究,在此不一一列出,值得关注的是2016年哈工大李新中等[10]利用轧制工艺法制备Nb-Ti-Co渗氢膜的研究,发现该工艺制备的Nb40Ti30Co30渗氢膜(约0.13 mm)的渗氢流量为21 mL/(cm2·min),约为相同实验条件下传统铸态渗氢膜(约0.7 mm)渗氢流量的8.5倍,且抗氢脆性能进一步增加。虽然各国学者对Nb-Ti-Co双相渗氢合金进行了大量研究并取得了相对较好的成果,但是渗氢流量和持久性能仍然是该体系合金膜当前面临的巨大挑战。据美国DOE制定的渗氢合金(膜)标准[24]来看(使用温度为250~500 ℃,100 kPa下渗氢流量达到150 mL/(cm2·min),且持久性大于5年),关于Nb-Ti-Co双相渗氢合金的研究还有很长的路要走,尤其是对渗氢合金膜成分优化、渗氢/持久性能和渗氢/抗氢脆机理等根本性问题的理解和把握。
鉴于此,本文作者在前文[26]构建的“Nb-Ti-Co渗氢成分区域”基础之上,系统研究了该区域内27种合金在523~673 K下的渗氢性能,并与Nb-Ti-Ni合金和纯Pd的渗氢结果进行了比较;而后分析了区域内代表性合金(18#, 17#, 25#, 24#和33#)的氢溶解行为和氢扩散特性,并结合“电阻模型”和“氢溶解模型”详细探讨了Nb-Ti-Co合金(膜)的渗氢和抗氢脆机理,为该系合金膜的大规模工业化生产实践以及Nb基氢分离合金的优化设计提供理论依据和技术支撑。
1 实验
1.1 氢渗透实验
氢渗透实验之前,首先利用磁控溅射工艺在抛光处理后的膜表面施镀一层均匀致密的钯膜,钯膜厚度约为150 nm,用于氢的催化和提高合金膜的高温抗氧化能力,镀膜后的样品在真空中保存。渗氢前,利用无氧铜密封圈将片状样品密封并用螺栓紧实,而后将其置于开启式电阻炉中,渗透实验装置示意图如1所示。首先利用分子泵将样品室内抽真空至8×10-3 Pa,开启电阻炉加热至523 K并保温30 min,以确保氢渗透样品均匀受热。向渗氢膜前侧的“进气口端”通入一定压力(0.2~0.5 MPa)的高纯氢气(纯度99.999%)进行氢渗透实验,而后靠膜两侧的氢气压力(或浓度)差迫使氢气扩散渗透到膜后侧的“出气口端”(氢气压力始终维持在0.1 MPa),最后用高精度气体流量计测量记录“出气口端”的渗氢流量。在523 K下测量完毕后,调节电阻炉温度至573 K、623 K和673 K,再次测量渗透通过样品的渗氢流量,最后将测量的渗氢流量带入式(1)并经过线性拟合得出各实验条件下的氢渗透系数Ф。
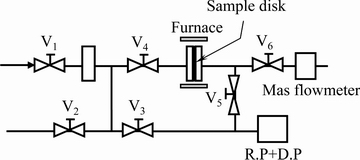
图1 氢渗透实验装置示意图 (V1~V6: 世伟洛克阀门)
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of hydrogen permeation measuring apparatus used in this work (V1-V6: Swagelok valves)
1.2 吸/放氢(PCT)实验
样品的吸/放氢实验在全自动气体吸附测量仪(PCT-Pro2000)上进行。在测试之前,需要将样品置于行星球磨机内进行研磨,转速和球磨时间分别为800 r/min和18 h,而后将其放入过滤筛中(200目)筛分,得到<75 μm的粉末状样品,真空保存备用。称取1 g样品,用多孔泡沫镍网包覆后放置于气体吸附测量仪的样品室内,与管道连接直至密封良好。将样品池加热至573 K抽真空30 min,而后冷却到室温并通入3 MPa的高纯氢气(纯度:99.999%),使其与样品充分反应。上述过程反复进行3次,以确保样品充分活化。将样品加热至523 K,而后向样品室内持续通入高纯氢气,在第一次通氢气之前需设定好吸氢饱和条件,用于程序自行判断样品内部吸氢是否达到饱和。实验压力范围为0~1 MPa,温度范围为523~673 K。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 渗氢性能
对渗氢区域内27种合金进行了不同温度(523~ 673 K)和压力(0.2~0.5 MPa)下的渗氢性能测试,图2给出了合金33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)在上述条件下的氢渗透系数/流量随时间变化曲线。由图2中可看出,在一定的膜前/后端压力下(pu和pd分别为0.5和0.1MPa),合金膜的渗氢系数Ф随着温度T的逐渐升高而增加,如图2(a)所示,在每一种测量温度下,合金膜的渗氢性能均表现出了良好的稳定性。另外,图2(a)左上角插图还列出了氢渗透系数Ф与温度T的Arrhenius关系曲线,为了对比,图2(a)中还列出了纯Pd的氢渗透系数,可看出,氢渗透系数Ф与温度T符合Arrhenius关系式,Ф=Ф0·exp[-EФ/(RT)]。当温度低于573 K时,合金的氢渗透系数低于纯Pd的,反之高于纯Pd的。图2(b)给出了该合金在673 K下的氢渗透流量随膜前端压力变化曲线,右下角插图所示为J·d与压力p0.5关系曲线,可以看出,随着压力的逐渐增加,合金膜的氢渗透流量逐渐变大,J·d与压力p0.5两者之间线性拟合系数因子 为0.992,说明二者具有良好的线性关系并且在523~673 K温度范围内氢渗透流量遵循式(1),且氢渗透穿过合金膜过程由“体扩散过程”控制,而非“膜表面反应”控制,与文献[27]研究结果相一致。
为0.992,说明二者具有良好的线性关系并且在523~673 K温度范围内氢渗透流量遵循式(1),且氢渗透穿过合金膜过程由“体扩散过程”控制,而非“膜表面反应”控制,与文献[27]研究结果相一致。
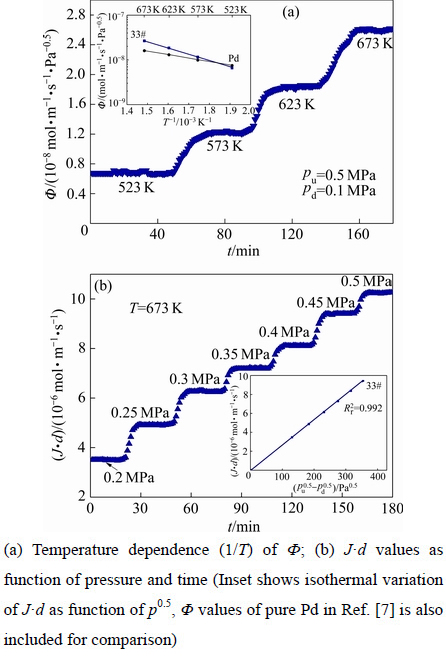
图2 33#合金(Nb30Ti35Co35)氢渗透系数/流量随时间变化曲线(为了便于比较,引入文献[7]中Pd的渗氢性能)
Fig. 2 Ф of alloy 33# membrane as function of time
图3给出了Nb-Ti-Co渗氢成分区域27种合金在673K下的渗氢系数(合金成分上方的蓝色数字)和5种代表性合金(18#, 17#, 25#, 24#和33#)氢渗透系数Ф与温度T的Arrhenius关系曲线图。由图3可看出,6种合金(11#, 12#, 19#, 26#, 32#和38#)由于在渗氢过程中发生氢脆导致其渗氢系数无法测量(合金成分上方标注**),其余合金均具有一定的渗氢性能。上述结果表明,在Nb-Ti-Co相图的α-Nb固溶体相区内还存在这样一类型合金,其凝固过程中也会形成初生α-Nb相和共晶(α-Nb和TiCo)相组织,但由于含有过多的初生α-Nb相(表面体积分数大于60%)使其在渗氢过程中发生严重的氢脆而无法应用在氢分离过程中。因此,排除上述6种合金成分后,本文将渗氢区域进一步缩减,如图3(a)中区域Ⅲ′所示(为了与前文的渗氢成分区域相区分,在字母右上角加注符号')。在区域Ⅲ′内,18#合金(Nb65Ti20Co15)在673 K下具有最大的渗氢系数,为4.12×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2),约为相同条件下纯Pd渗氢性能的2.5倍,其余合金中按照渗氢系数由高到低(取前三)的排列顺序依次为:17#(Nb60Ti20Co20)、25# (Nb60Ti25Co15)和24#(Nb55Ti25Co20),三者的渗氢系数分别为3.99×10-8,3.72×10-8和3.58×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2)。另外,虽然17#(Nb60Ti20Co20)合金和25#(Nb60Ti25Co15)合金具有相同的Nb含量,但是前者的渗氢系数(3.99×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2))高于后者的(3.72×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2)),暗示出Nb-Ti-Co合金原始成分中除了Nb含量,Ti/Co比值也会影响合金的渗氢性能,Nb含量越低,Ti/Co比值越高,渗氢系数越小,也就是说Nb-Ti-Co合金渗氢性能至少受Nb含量和Ti/Co比值双重因素的影响,这也是LUO等[7]和HASHI等[8]研究结果出现矛盾的主要原因。图3(b)给出了上述4种合金(18#、17#、25#和24#)氢渗透系数与温度的Arrhenius关系曲线,为了与纯Pd对比,曲线中还列出了其氢渗透系数。从图3(b)中可看出,每一种合金的氢渗透系数Ф随着温度T的逐渐升高而增加。合金的氢渗透性能随着Nb含量的增加而增加。此外,当温度高于573 K时,4种合金的氢渗透性能均高于纯Pd且在氢渗透过程中不发生脆断,而在523 K时,合金膜的氢渗透性与Pd相当。值得注意的是虽然18#合金(Nb65Ti20Co15)在673 K下具有最大的渗氢系数,但其在523 K下的氢渗透过程中发生脆性断裂,导致渗氢实验失败,暗示出18#合金的抗氢脆性能要低于其他合金的,如17#、25#和24#合金。为了综合分析上述4种合金(18#、17#、25#和24#)的抗氢脆性能,本文紧接着还对其进行了长时间的渗氢实验,即持久性能测试。
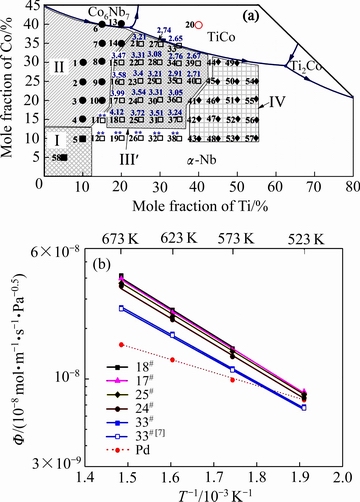
图3 Nb-Ti-Co相图渗氢区域内(Ⅲ′)合金在673 K下的氢渗透性能(合金成分上方的蓝色数字)和5种合金(18#, 17#, 25#, 24#和33#)渗透系数Ф与温度T的Arrhenius关系曲线(为了便于比较,引入文献[7]中Pd和Nb30Ti35Co35的渗氢性能)
Fig. 3 Hydrogen permeability at 673K in region Ⅲ′ (a) and temperature dependence of hydrogen permeability Φ for representative alloys (18#, 17#, 25#, 24# and 33#) in form of Arrhenius plot (b) (Φ values of pure Pd and Nb30Ti35Co35 in Ref. [7] are also included for comparison)
2.2 持久性能
合金膜的持久性能是表征膜综合性能的重要因素之一。综合性能优异的合金膜不仅具有较高的氢渗透系数,还应具有优异的持久性能,从而完成长时间渗氢实验。图4给出了Nb-Ti-Co渗氢区域内(III')5种合金(18#, 17#, 25#, 24#和33#)氢渗透流量随时间变化曲线,插图为渗氢后合金膜的表面形貌,合金膜边缘为无氧铜密封垫片。从图4可看出,4种合金膜的渗氢流量从渗氢开始急剧上升,经过约10 min后,达到最大值Jmax,而后保持该值持续渗氢。另外,上述合金的氢渗透流量Jmax从大到小依次为J18# (3.98 mL/min), J17# (3.72 mL/min), J25# (3.61 mL/min), J24# (3.47 mL/min)和J33# (2.57 mL/min),这是由于上述合金的氢渗透系数从大到小依次为:Ф18#, Ф17#, Ф25#, Ф24#和Ф33# (见图3),并且合金膜的膜厚和前后压力差相同,与式(1)相互吻合。虽然18#, 17#和25#合金的渗氢流量相对较高,但是上述合金在经历一段稳态渗氢后(18#:约5 h;17#:约7 h;25#:约8 h)均发生了脆性断裂,相反,24#和33#合金膜均能够连续渗氢达40 h且膜表面完好,如图4插图所示。此外,18#, 17#和25#合金的有效渗氢时间分别为5 h、7 h和8 h,且合金膜脆性断裂程度依次减弱(见图4插图),而24#和33#合金的有效渗氢时间高达40 h,并且合金膜的外观保持完整,暗示出上述合金的抗氢脆能力逐渐增强的顺序为18#、17#、25#、24#,与图3(b)中结果相互吻合。综合比较上述合金(18#, 17#, 25#, 24#和33#)的渗氢系数(见图3)和持久性能(见图4),不难发现,18#,17#和25#合金膜的渗氢系数较高,在渗氢过程中的渗氢流量相对较大,但经历一段稳态渗氢后均发生了脆性断裂,导致渗氢失败;33#合金虽能维持较长时间的渗氢,但由于其渗氢流量较低(2.6 mL/min),无法满足美国DOE制定的渗氢合金(膜)标准;24#合金(Nb55Ti25Co20)很好的平衡了渗氢性能和持久性能,该合金在673 K下的渗氢系数为3.58×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2),渗氢流量为3.52 mL/min,且能持续渗氢高达40 h。
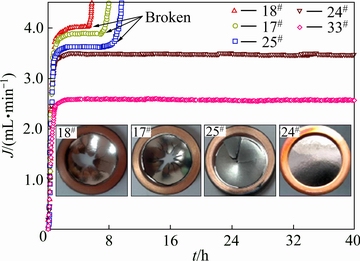
图4 渗氢区域内(III')5种合金(18#, 17#, 25#, 24#和33#)氢渗透流量J随着时间t变化曲线(插图为渗氢后合金膜的表面形貌)
Fig. 4 Curve of hydrogen permeation flux with change of time for representative alloys (18#, 17#, 25#, 24# and 33#) (Inset shows samples sandwiched between two copper seal gaskets after hydrogen permeation test)
2.3 吸氢性能
一般来讲,氢气由“膜上端”渗透到“膜下端”共经历6个过程[28-29]:1) 膜上端对氢分子进行吸附;2) 氢分子分裂为氢原子;3) 氢原子在“膜上端”表面溶解;4) 溶解的氢原子进行扩散穿过合金薄膜;5) 渗透到“膜下端”的氢原子结合为氢分子;6) 氢分子从“膜下端”脱离(解吸附过程)。在合金膜渗氢过程中,只有被Pd催化分解成为原子状态的氢,才能扩散透过合金膜,其他气体分子不能分解渗透通过,这也是为什么要在Nb-Ti-Co表面施镀Pd膜的主要原因。上述6个过程中,第3)和第4)个过程分别对应金属膜的氢溶解系数K和扩散系数D,二者乘积代表了渗氢系数Ф,即Ф = D·K。为了获取较高的渗氢系数,理论上讲氢溶解系数和扩散系数均应取最大值,但实际渗氢过程中,氢溶解系数较大的合金膜内会吸收溶解大量的氢,造成严重的晶格畸变,极容易发生脆性断裂,因此,合金膜的氢溶解和扩散特征值得重点关注。图5给出了Nb-Ti-Co渗氢区域内(III')典型合金(33#, 24#和18#)的氢溶解曲线,为了综合比较各合金的氢溶解系数,图5(b),(d),(f),(h)还给出了上述合金氢浓度和压力的Sieverts曲线。可以看出,当压力小于0.1 MPa时,合金的吸氢速率较快,说明氢快速溶解到合金中;当压力处于0.1~0.4 MPa,吸氢速率相对变缓,压力p0.5和氢浓度c之间呈现近线性关系,但并不符合Sievert’s公式c=K·p0.5;当压力大于0.4 MPa后,合金的吸氢速率更低,这与合金内部无序氢固溶体向有序氢化物转变有关[24],与AOKI等[30]关于Nb-Ti-Ni合金吸氢行为的研究结果相一致。另外,对每一种合金来讲,伴随着温度的逐渐增加,合金的吸氢量随之降低,如:33#合金在523 K、573 K、623 K和673 K下(氢压为0.4 MPa)的吸氢量分别为0.55%、0.49%、0.44%和0.37%(质量分数),这主要是由于过渡族元素Nb与H发生溶解反应时属于放热反应,所以伴随着温度的逐渐升高吸氢量反而减小,与LI等[19]的研究结果相吻合。虽然在0.1~0.4 MPa范围内合金的氢浓度c和p0.5之间不符合Sievert’s公式,但经线性拟合发现上述参数满足如下关系式,
c=K·p0.5+а (2)
式中:а为一无量纲常数,根据式(2)便可计算出各合金的氢溶解系数K,利用关系式Ф=D·K便可反算出氢扩散系数D,如表1所列。从表1可看出,相同温度下33#,24#,18#号的Ф值依次增大,并且33#、24#和18#合金相同温度下的氢溶解系数也依次增加,18#合金673 K时氢溶解系数为15.6 mol/(m3·Pa0.5),是33#合金的1.16倍;相类似,上述合金氢扩散系数也依次变大,18#合金673K时的氢扩散系数为26.4×10-10 m2/s,是33#合金的1.35倍。上述结果表明,合金渗氢系数的增加(Ф18#>Ф24#>Ф33#)归结于氢溶解和扩散系数的同时增大,但是氢扩散系数起主导作用。
2.4 渗氢/抗氢脆机理
一般来讲,氢在Nb金属及其固溶体中的氢扩散系数可以表述为[19]
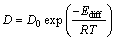 (3)
(3)
式中:D0为扩散前置因子;Ediff为扩散激活能;T为温度;R为理想气体常数。图6给出了18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)、24#(Nb55Ti25Co20)和33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)合金氢扩散因子D*与温度T的Arrhenius曲线,其中,D*=1000·R·ln(D/D0)。各拟合直线的斜率代表了合金的氢扩散激活能。经过线性拟合,得出18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)、24#(Nb55Ti25Co20)和33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)合金的氢扩散激活能分别为17.1、18.3和20.6 kJ/mol。33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)合金氢扩散激活能最大,说明氢原子从合金中的从一个平衡位置跃迁到另一个平衡位置所克服能垒较高,不容易实现跃迁过程,相反,18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)的氢扩散激活能较低,氢原子容易跃迁,这也是18#合金具有较高氢扩散系数的原因。另外,结合上述三种合金的显微组织发现,可以利用“电阻模型”来分析Nb-Ti-Co合金(膜)的氢扩散机理,如图6插图所示。图6中的Nb和TiCo相分别代表了合金组织中的两相。其中,Nb相为渗氢相,TiCo相为基体相,也为支撑相,Nb相四周的虚线代表相边界。R1、R2和R3分别代表了氢于TiCo相、Nb相以及相边界的氢扩散障碍,三者中,R2的值要远远小于R1和R3,也就说H于渗氢Nb相中的扩散相对较为容易。结合前文合金的显微组织,可发现33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)合金微组织中的共晶组织形态为α-Nb和TiCo棒状共晶,两相共晶的形态示意图如图6右上角插图所示,对于最上层的TiCo相,其等效电阻值为R1,相应地,第二层的α-Nb和TiCo棒状共晶等效电阻值为“2R1+3R2+4R3”,二者并联后的电阻值记为RA。18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)合金微组织由初生α-Nb相和(α-Nb+TiCo)棒状共晶构成,示意图见图6左下角插图,长条状Nb相代表初生α-Nb相,对照示意图,第一层和第二层等效电阻值分别为R1和R2,两层中间的虚线代表相边界,其等效电阻值为R3,三者并联后的电阻值记为RB。由于R2的值要远远小于R1和R3,所以RA远远高于RB,也就是说,18#合金中氢的扩散障碍值要低于33#合金,氢在33#合金中扩散相对较为困难,所以33#合金膜的氢扩散系数相对较低,而18#合金膜的氢扩散系数相对较高。
表1 33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)、24#(Nb55Ti25Co20)和18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)合金在523~673 K下的氢渗透系数(Ф),氢溶解系数(K),氢扩散系数(D)和渗氢流量(J)
Table 1 Hydrogen permeability (Ф), hydrogen solubility coefficient (K), hydrogen diffusion coefficient (D) and hydrogen permeation flux (J) for 33#(Nb30Ti35Co35), 24#(Nb55Ti25Co20) and 18#(Nb65Ti20Co15) alloys at 523-673 K
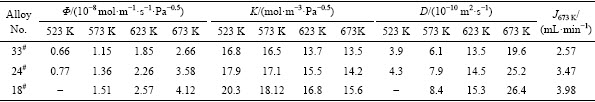

图5 33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)、24#(Nb55Ti25Co20)和18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)合金在523~673 K的PCT曲线和氢浓度-压力Sieverts曲线
Fig. 5 PCT (pressure-composition-temperature) curves for 33#(Nb30Ti35Co35), 24#(Nb55Ti25Co20) and 18#(Nb65Ti20Co15) alloys at 523-673 K ((a), (c), (e), (g)) and Sieverts’ plot, i.e., p0.5 vs. hydrogen composition c ((b), (d), (f), (h))
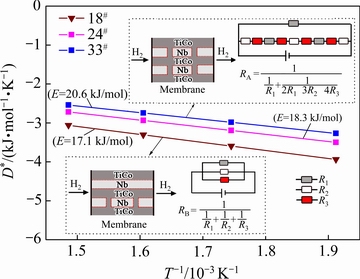
图6 18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)、24#(Nb55Ti25Co20)和33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)合金的氢扩散因子D*与温度T的Arrhenius曲线(插图为以电阻模型来分析上述合金中的氢扩散机理示意图)
Fig. 6 Temperature dependence of average D* in form of an Arrhenius plot for 33#(Nb30Ti35Co35), 24#(Nb55Ti25Co20) and 18#(Nb65Ti20Co15) alloys (Inset shows schematic illustration of an electrical analogy to analyze hydrogen diffusion in dense membrane)
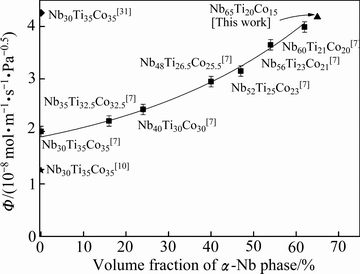
图7 Nb-Ti-Co 氢分离合金初生Nb相体积分数和渗氢性能Ф673 K之间的关系曲线
Fig. 7 Ф673 K values plotted against volume fraction of primary α-Nb phase in Nb-Ti-Co alloys
最后,本文研究了Nb-Ti-Co系氢分离合金成分、相构成、制备工艺和渗氢性能之间的关系,并与国内外学者[7, 10, 31]的研究结果进行了对比,如图7所示。从中可看出:1) 合金的渗氢性能取决于合金的原始成分,例如,国外LUO等[7]的研究结果表明,合金的渗氢性能伴随着合金中的Nb含量和显微组织内部初生Nb相的体积分数增加而增加,Nb60Ti21Co20合金组织内初生Nb相的体积分数为62%,在673 K下的渗氢性能为3.99×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa0.5 ),约为相同实验条件下Nb30Ti35Co35合金的1.5倍。另外,本文研究结果(见图3)表明,17#合金(Nb60Ti20Co20)673 K下的渗氢性能(3.99×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa0.5))高于25#合金(Nb60Ti25Co15)的,说明除了合金中的原始Nb含量,Ti和Co含量也会影响合金的渗氢性能,相类似,原始Nb含量相同的23#合金(Nb50Ti25Co25)、30#合金(Nb50Ti30Co20)和15#合金(Nb50Ti20Co30)也表现出了相同的规律,Ti/Co比率高(或低)于1均会提升合金的渗氢性能,但是过高(或过低)的Ti/Co比率使合金接近区域Ⅳ和Ⅱ,伴随着Co6Nb7相和Ti2Co相的析出[26],不利于合金的渗氢过程。2) 相对于合金的原始成分,制备工艺对合金渗氢性能影响更大。例如:定向凝固后Nb30Ti35Co35合金[31]的组织由原来的铸态非规则共晶转为规则共晶,相应的,渗氢性能由原来的2.62×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa0.5)提高到4.26×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa0.5);然而,当对其进行轧制和退火处理后[10],合金的组织由原来的铸态非规则共晶转变为颗粒状双相共晶,渗氢性能降低至原铸态合金的0.5倍。3) 18#合金(Nb65Ti20Co15,图7中实心三角)在673 K下具有最大的渗氢系数,为4.12×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2),约为相同条件下纯Pd渗氢性能的2.5倍,该合金目前为Nb-Ti-Co系氢分离合金中的最大值,该合金显微组织仅由初生α-Nb相和共晶(α-Nb+TiCo)相构成,较高的初生α-Nb相体积分数 (68%)保证了该合金具有较高的渗氢性能,若能够采用其他的制备工艺,如定向凝固,制备出由初生α-Nb相连续贯穿膜上下两端的渗氢合金,进一步降低其内部的氢扩散激活能(见图6),促使更多的氢原子发生跃迁,合金的渗氢性能将会大幅度提升,接下来,本文作者将会开展相关工作。
3 结论
1) Nb-Ti-Co相图α-Nb固溶体相区内11#,12#,19#,26#,32#和33# 6种合金凝固过程中也会形成初生α-Nb相和共晶(α-Nb和TiCo)相组织,但由于含有过多的初生α-Nb相(表面体积分数大于60%)使其在渗氢过程中发生严重的氢脆,无法应用在氢分离过程中。在原有渗氢成分区域内去除上述6种氢脆合金后,重构渗氢区域,即区域Ⅲ′。区域内18#合金(Nb65Ti20Co15)在673 K下具有最大的渗氢系数,为4.12×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2),约为相同条件下纯Pd渗氢性能的2.5倍。其余合金中按照渗氢系数由高到低的排列顺序依次为17#(Nb60Ti20Co20)、25#(Nb60Ti25Co15)和24#(Nb55Ti25Co20),三者的渗氢系数分别为3.99×10-8、3.72×10-8和3.58×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2)。
2) 区域Ⅲ′内合金(0.1~0.4MPa)的氢浓度c和压力p0.5和之间符合关系式c=K·p0.5+α,33#、24#和18#合金在相同温度下的氢溶解和氢扩散系数依次增加,18#合金673 K时的氢溶解和氢扩散系数为15.6 mol/(m3·Pa0.5)和26.4×10-10 m2/s,分别是33#合金的1.16和1.35倍,区域III'内合金渗氢系数的增加(Ф33#>Ф24#>Ф18#)归结于氢溶解和扩散系数的同时增大,但氢扩散系数起主导作用。
3) 区域Ⅲ′内18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)、24#(Nb55Ti25Co20)和33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)合金的氢扩散激活能分别为17.1、18.3和20.6 kJ/mol。33#(Nb30Ti35Co35)合金氢扩散激活能最大,氢原子从合金中的从一个平衡位置跃迁到另一个平衡位置所克服能垒较高,不容易实现跃迁过程,相反,18#(Nb65Ti20Co15)的氢扩散激活能较低,氢原子容易跃迁。因此,18#合金具有相对较高的氢扩散系数。
REFERENCES
[1] MAGNONE E, JEON S, PARK J H. FLEURY E. Relationship between microstructure and hydrogen permeation properties in the multiphase Ni21Ti23Nb56 alloy membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 384: 136-141.
[2] ISHIKAWA K, SEKI Y, KITA K, MATSUDA M, NISHIDA M, AOKI K. Hydrogen permeation in rapidly quenched amorphous and crystallized Nb20Ti40Ni40 alloy ribbons[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36: 1784-1792.
[3] HASHI K, ISHIKAWA K, MASTSUDA T, AOKI K. Hydrogen permeation characteristics of multi-phase Ni-Ti-Nb alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 368: 215-220.
[4] 刘 菲, 王仲民, 黄贺伟, 邓健秋, 周怀营. Nb-Ti-Ni体系合金的结构及其氢渗透性能[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43: 82-88.
LIU Fei, WANG Zhong-min, HUANG He-wei, DENG Jian-qiu, ZHOU Huai-ying. Phase structure and hydrogen diffusion properties of Nb-Ti-Ni alloys[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43: 82-88.
[5] YAN E H, LI X Z, LIU D M, SU Y Q, GUO J J, FU H Z. A skull-aided technique for directional solidification of Nb-41Ni-40Ti hydrogen permeablealloy[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2014, 391: 78-84.
[6] LUO W, ISHIKAWA K, AOKI K. High hydrogen permeability in the Nb-rich Nb-Ti-Ni alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 407: 115-117.
[7] LUO W M, ISHIKAWA K, AOKI K. Highly hydrogen permeable Nb-Ti-Co hypereutectic alloys containing much primary bcc-(Nb, Ti) phase[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37: 12793-12797.
[8] HASHI K, ISHIKAWA K, MATSUDA T, AOKI K. Microstructure and hydrogen permeability in Nb-Ti-Co multiphase alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 425: 284-290.
[9] 闫二虎, 李新中, 唐 平, 苏彦庆, 郭景杰, 傅恒志. Nb-Ti-Co氢分离合金近共晶点处的显微组织及其渗氢性能[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50: 71-78.
YAN Er-hu, LI Xin-zhong, TANG Ping, SU Yan-qing, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Microstructure and hydrogen permeation characteristic of near eutectic Nb-Ti-Co hydrogen separation alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50: 71-78.
[10] LI X Z, LIU D M, LIANG X, CHEN R R, RETTENMAYR M, SU Y Q, GUO J J, FU H Z. Hydrogen transport behavior of as-cast, cold rolled and annealed Nb40Ti30Co30 alloy membranes[J]. Journal Membran Science, 2016, 514: 294-304.
[11] SHI F, SONG X P. Effect of Hf/Ni ratio on microstructure and hydrogen permeation of Nb-Hf-Ni ternary alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: L134-L136.
[12] LI X Z, LIU DM, CHEN R R, YAN E H, LIANG X, RETTENMAYE M, SU Y Q, GUO J J, FU H Z. Changes in microstructure, ductility and hydrogen permeability of Nb-(Ti, Hf) Ni alloy membranes by the substitution of Ti by Hf[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 484: 47-56.
[13] SHI F. Microstructure and hydrogen permeability of Nb40Hf30Ni30 ternary alloy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35: 10556-10559.
[14] YAN E H, SUN L X, XU F, XU D M, QIU S J, XIANG C L, ZHANG H Z, SUN Y X. Changes in microstructure, solidification path and hydrogen permeability of Nb-Hf-Co alloy by adjusting Hf/Co ratio[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41: 1391-1400.
[15] DOLAN M D, SONG G, LIANG D, KELLAM M, CHANDRA D, LAMB J H. Hydrogen transport through V85Ni10M5 alloy membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 373: 14-19.
[16] DOLAN M D, SONG G, MCLENNAN K G, KELLAM M, LIANG D. The effect of Ti on the microstructure, hydrogen absorption and diffusivity of V-Ni alloy membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 415/416: 320-327.
[17] KIM K H, PARK H C, LEE J, CHO E, SANG M L. Vanadium alloy membranes for high hydrogen permeability and suppressed hydrogen embrittlement[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 68: 905-908.
[18] TSUCHIMOTO K, YUKAWA H, NAMBU T, MATSUMOTO Y, MURATA Y. Design of Nb-W-Mo alloy membrane for hydrogen separation and purification[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 580: S391-S396.
[19] LI X Z, LIANG X, LIU D M, CHEN R R, HUANG F F, WANG R, RETTENNARY M, SU Y Q, GUO J J, FU H Z. Design of (Nb, Mo)40Ti30Ni30 alloy membranes for combined enhancement of hydrogen permeability and embrittlement resistance[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 209-219.
[20] OZAKI T, ZHANG Y, KOMAKI M, NISHIMURA C. Hydrogen permeation characteristics of V-Ni-Al alloys[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2003, 28: 1229-1235.
[21] ADAMS T M, MICKALONIS J. Hydrogen permeability of multiphase V-Ti-Ni metallic membranes[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61: 817-820.
[22] HASHIA K, ISHIKAWA K, MATSUDA T, AOKI K. Hydrogen permeation characteristics of (V, Ta)-Ti-Ni alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 404: 273-278.
[23] LI X Z, YAN E H, RETTENNARY M, LIU D M, SU Y Q, GUO J J. Hydrogen permeation behavior of Nb30Ti35Ni35-xCox (x= 0…35) alloys containing high fractions of eutectic[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39: 9366-9374.
[24] DOLAN M D, DAVE N C, ILYUSHECHKIN A Y, MORPETH L D, MCLENNAN K G. Composition and operation of hydrogen-selective amorphous alloy membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2006, 285: 30-55.
[25] HARA S, HATAKEYAMA N, ITOH N, KIMURA H M, INOUE A. Hydrogen permeation through amorphous Zr36-xHfxNi64 alloy membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2003, 211: 149-156.
[26] 黄浩然, 闫二虎, 闵若男, 朱坤军, 赵光伟, 李新中, 徐 芬, 孙立贤. Nb-Ti-Co氢分离合金优化设计和渗氢性能研究 Ⅰ. 合金相图和渗氢成分区域构建[J]. 有色金属学报, 2018, 28(10): 2058-2069.
HUANG Hao-ran, YAN Er-hu, MIN Ruo-nan, ZHU Kun-jun, ZHAO Guang-wei, LI Xin-zhong, XU Fen, SUN Li-xian. Study on optimum design and hydrogen permeability of Nb-Ti-Co separation alloy Ⅰ. Construction of phase diagram and hydrogen permeable component region[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(10): 2058-2069.
[27] XIONG L Y, LIU S, RONG L J. Fabrication and characterization of Pd/Nb40Ti30Ni30/Pd/porous nickel support composite membrane for hydrogen separation and purification[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35: 1643-1649.
[28] YUKAWA H, ZHANG G X, WATANABE N, MORINAGA M, NAMBU T, MATSUMOTO Y. Analysis of hydrogen diffusion coefficient during hydrogen permeation through niobium and its alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 476: 102-106.
[29] ZHANG G X, YUKAWA H, WATANABE N, SAITO Y, FUKAYA H, MORINAGA M, NAMBU T, MATSUMOTO Y. Analysis of hydrogen diffusion coefficient during hydrogen permeation through pure niobium[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33: 4419-4423.
[30] WANG W, ISHIKAWA K, AOKI K. Microstructural change-induced lowering of hydrogen permeability in eutectic Nb-TiNi alloy[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 351: 65-68.
[31] LI X Z, LIANG X, LIU D M, CHEN R R, RETTENMAYR M, SU Y Q, GUO J J, FU H Z. Microstructure dependent hydrogen permeability in eutectic Nb30Ti35Co35[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41: 13086-13092.
[32] 罗林山, 周 健, 文小强, 刘雯雯, 管建红. Ti/Cr比对(VFe)50Ti26-xCr24+x(0≤x≤2.0)储氢合金吸放氢性能的影响[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2016, 7(1): 20-23.
LUO Lin-shan, ZHOU Jian, WEN Xiao-qiang, LIU Wen-wen, GUAN Jian-hong. Effect of Ti/Cr on hydrogen absorption/ desorption properties of (VFe)50Ti26-xCr24+x(0≤x≤2.0) hydrogen storage alloys[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2016, 7(1): 20-23.
Optimum design and hydrogen permeability of Nb-Ti-Co separation alloy: Ⅱ. Hydrogen permeability and mechanism
MIN Ruo-nan1, YAN Er-hu1, HUANG Hao-ran1, ZHU Kun-jun2, ZHAO Guang-wei2, LI Xin-zhong2, XU Fen1, SUN Li-xian1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin 541004, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
3. College of Mechanical and Power Engineering, Three Gorges University, Yichang 443002, China)
Abstract: The hydrogen permeability of 27 kinds of alloys in the hydrogen permeable component region of Nb-Ti-Co alloy system was studied in the region of 523-673 K, and compared with Nb-Ti-Ni and pure Pd. And then the durable performance, hydrogen dissolution and diffusion behaviors of typical alloys in the above component region were analyzed. The hydrogen permeable and anti-hydrogen brittleness mechanisms were also discussed by using the resistance model and the hydrogen dissolved model. The results show that after removing 6 hydrogen embrittlement alloys in original hydrogen permeable component region, an new component region was constructed, i.e., the region III'. 18# alloy in the region III′ possesses the highest hydrogen permeability with 4.12×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2) at 673 K. The hydrogen permeability of the remaining alloys is listed in the order as follows: 17# (3.99×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2)), 25# (3.72×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2)) and 24# (3.58×10-8 mol/(m·s·Pa1/2)). The hydrogen dissolution and diffusion coefficients of 33#, 24# and 18# alloys in the region III' increase in sequence. The hydrogen dissolution and diffusion coefficients of 18# alloy are 15.6 mol/(m3·Pa0.5) and 26.4×10-10 m2/s, which are 1.16 and 1.35 times larger than those of 33# alloy. The increase of hydrogen permeability in the region III'(Ф18#>Ф24#>Ф33#) can be attributed to the simultaneous increment of hydrogen dissolution and diffusion coefficient, but the later plays a key role. The hydrogen diffusion activation energy of 18# alloy is low and the hydrogen atoms are easy to jump. Therefore, this alloy has relatively high hydrogen diffusion coefficient.
Key words: Nb-Ti-Co alloy; hydrogen permeation; hydrogen dissolution; hydrogen diffusion
Foundation item: Projects(51761009, 51701048, 51371060, 51671062, 51201093) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017YJCX116) supported by the Innovation Project of Guet Graduate Education, China; Projects(2016GXNSFAA380166, 2015GXNSFBA139208) supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, China
Received date: 2017-09-05; Accepted date: 2018-03-16
Corresponding author: YAN Er-hu; Tel: +86-773-2216607; E-mail: yeh@guet.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51761009,51701048,51371060,51671062,51201093);桂林电子科技大学研究生教育创新计划项目(2017YJCX116);广西自然科学基金资助项目(2016GXNSFAA380166,2015GXNSFBA139208)
收稿日期:2017-09-05;修订日期:2018-03-16
通信作者:闫二虎,副研究员,博士;电话:0773-2216607;E-mail:yeh@guet.edu.cn