Role of ore mineralogy in optimizing conditions for bioleaching low-grade complex sulphide ores
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2008年第5期
论文作者:P. A. OLUBAMBI S. NDLOVU J. H. POTGIETER J. O. BORODE
文章页码:1234 - 1246
Key words:sulphide ore; ore mineralogy; mesophiles; bioleaching; processing parameters
Abstract: The role that ore mineralogy plays in understanding and optimizing the conditions favouring the bioleaching of complex sulphide ore containing high amounts of siderite was studied using mixed cultures of mesophilic bacteria, with emphasis on zinc, lead and copper recoveries. The influencing parameters investigated include particle size, stirring speed, volume of inoculum, pulp density, and pH. The results show that the mixed mesophilic cultures can extract about two and a half times the amount of zinc than copper over an equivalent period of time. The highest zinc and copper recoveries of 89.2% and 36.4% respectively are obtained at particle size of 75 μm, stirring speed of 150 r/min, pulp density of 10% (w/v), 12% (v/v) inoculum concentration, and a pH of 1.6. Variations in elemental composition within different particle sizes resulting from the mineralogy of the ore account for the bioleaching behaviour at varying particle sizes. The dissolution at varying pulp density, volume of inoculum, solution pH and the low solution potential observed are also influenced by ore mineralogy.

P. A. OLUBAMBI1, 2, S. NDLOVU1, J. H. POTGIETER1, J. O. BORODE2
1. School of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering, University of the Witwatersrand,
Johannesburg, South Africa;
2. Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Federal University of Technology,
Akure, Nigeria
Received 25 February 2008; accepted 2 July 2008
Abstract: The role that ore mineralogy plays in understanding and optimizing the conditions favouring the bioleaching of complex sulphide ore containing high amounts of siderite was studied using mixed cultures of mesophilic bacteria, with emphasis on zinc, lead and copper recoveries. The influencing parameters investigated include particle size, stirring speed, volume of inoculum, pulp density, and pH. The results show that the mixed mesophilic cultures can extract about two and a half times the amount of zinc than copper over an equivalent period of time. The highest zinc and copper recoveries of 89.2% and 36.4% respectively are obtained at particle size of 75 ?m, stirring speed of 150 r/min, pulp density of 10% (w/v), 12% (v/v) inoculum concentration, and a pH of 1.6. Variations in elemental composition within different particle sizes resulting from the mineralogy of the ore account for the bioleaching behaviour at varying particle sizes. The dissolution at varying pulp density, volume of inoculum, solution pH and the low solution potential observed are also influenced by ore mineralogy.
Key words: sulphide ore; ore mineralogy; mesophiles; bioleaching; processing parameters
1 Introduction
Microbially assisted recovery of base metals from low grade complex sulphide ores has become a significant research interest since the 20th century, due to the high depletion rate of the world’s deposits of high grade less complex ores. Recovering the constituent metals of these ores has in most cases been reported to be very difficult[1-2]. This could be attributed to the complexities in the mineralogical associations of these ores and the close similarities in the mineralogical characteristics of the constituting minerals which make them unsuitable for the conventional hydrometallurgical method of processing. The low solubility of these ores in many leaching reagents, low quantity of metal to be recovered from the ores, and the large amount of ores to be processed, limit the conventional hydrometallurgical methods of processing of them. Pre-treatment processes including roasting, pressure oxidation and chemical oxidation are often employed prior to solubilisation. These methods have been used over a long period for physically releasing the desired metals and making them amenable to leaching reagents through their conversion to water-soluble sulphates or oxides. They are however observed to be very complex, expensive[3-4] and mostly environmentally unsuitable[5] due to the large volume of reagents.
The biohydrometallurgical process has been reported to be an effective alternative for processing these ores and recovering the valuable metals[6-8], as it has proved to be cheaper, environmentally benign and less complex[9]. Despite the encouraging incentives of bioleaching as an alternative to chemical leaching, there are still a number of challenges to overcome. The heterogeneities and the complexities in the mineralogy of low grade complex sulphide ores, coupled with their general low solubility place a limitation during biohydrometallurgical processing. The slow kinetics of the reactions and high residence time during bioleaching, especially with mesophiles, also hinder the industrial application of biohydrometallurgical processing and limit its economic viability[1]. Moreover, bioleaching with mesophilic microorganisms has been observed to have limited applications, as these microorganisms show very slow metal leaching rates towards some minerals, e.g. chalcopyrite.
Studies on increasing bioleaching rate have thus been focused on the isolation and adaptation of thermophiles as they show considerably increased leaching rates due to high temperatures, higher metal tolerance capacity and their metabolic characteristics [10-12]. However, the use of thermophilic bacteria involves raising the temperature of the bioleaching system to 48 ℃ for moderate thermophiles and 68 ℃ or higher for extreme thermophiles. Raising operating temperature especially in tanks could thus result in high energy consumption and would require high temperature corrosion resistant equipment. In order to prevent such problems, efforts are being made to investigate accelerating parameters favouring mesophilic leaching. Apart from the conditions of physical parameters on mesophiles which have been widely studied[13-21], the use of mixed cultures of mesophiles has been observed to be an effective accelerating parameter. The use of mixed cultures has been observed to show better bioleaching capacities than the pure cultures[22-29], and their bioleaching capacities depend on the type of organisms used.
In spite of the knowledge of the better bioleaching capacities of mixed cultures over pure cultures, it is however observed that the effect of ore mineralogy, which is a major contributing factor during mesophilic leaching, has not been adequately taken into consideration. Relevant mineralogical information about the constituent mineral in an ore helps in understanding underlying mineralogical basis for interpreting microbial dissolution process. This is because mineralogical differences within an ore affect ore’s responses and behaviour in different bioleaching media due to the differences in the microbe-mineral interactions of individual’s mineral and different organisms. This might result in variations in the electrochemical galvanic interactions, because mineralogical differences and association between the phases of an ore affect galvanic interactions. The knowledge of mineralogical behaviour of the constituent minerals within the ore would therefore be very useful to aid the understanding of the microbial dissolution process, thereby revealing vital information about a process to allow process optimization and thus guiding decisions on processing parameters.
The purpose of this study is to investigate the role that ore mineralogy plays in understanding and optimizing the conditions favouring the bioleaching of low-grade complex sulphide ore containing high siderite using mixed mesophilic cultures of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, with reference to zinc and copper recoveries. Bioleaching conditions/processing parameters studied includes particle size, stirring speed, bio-dissolution time, volume of inoculum, pulp density and process pH.
2 Experimental
2.1 Ore
A complex sulphide ore obtained from Ishiagu, Nigeria was used for this study. The ore was stage crushed in the laboratory in a jaw crusher and a cone crusher. Size analysis of the ground product was carried out using the sieve analysis method in a laboratory test sieve. After sieving, 2 g each of homogenized particles of sizes of <53, 53, 75 and 106 ?m were mixed together, further ground to powder and subjected to elemental analysis to give the composition of the bulk ore totally. Identification of mineral distribution within the sizes and quantitative analysis of the mineralogical composition were carried out by X-ray diffractometry. Quantitative analysis of the elemental distribution within each particle size was determined by X-ray fluorescence and optical emission spectrometry using the inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer(ICP-OES). The mineralogical and elemental composition of the ore as previously reported by OLUBAMBI et al[30] is shown in Table 1.
2.2 Micro-organisms and bioleaching
The mixed culture bacteria used for the experiments were obtained from the Council for Minerals Technology (MINTEK), South Africa. The cells contained approximately 40% Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, 30% Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and 30% Leptospirillum ferrooxidans. The cultures were routinely sub-cultured in an incubator shaker at 32-35 ℃ and a pH of 2.0 in 9 K medium consisting of 3.0 g (NH4)2SO4, 0.5 g K2HPO4, 0.5 g MgSO4?7H2O, 0.1 g KCl, 0.01 g Ca(NO3)2, and 44.2 g FeSO4?7H2O used as energy source dissolved in 1 000 mL distilled water. After the cell has reached an exponential growth stage, culture was filtered through a Whatman filter No.1 to remove the precipitate and centrifuged at 6000 r/min for 30 min using a Sorval Centrifuge, Model RC 5C PLUS. The centrifuged cells were washed in sulphuric acid at pH 2.0. Washing and centrifugation were repeated until the cells were free from precipitates.
Bioleaching experiments were carried out using mixed cultures of an initial population of 1.5×106 cells/mL in 1 000 mL glass reactor. The glass reactor had four holes for temperature measurement, pH measurement, aeration and sampling. The reactor was placed in a thermostatically controlled heated water-bath and agitated from above using mechanical stirrer. The mechanical stirrers had four twisted blades. The suspension was maintained at 32-35 ℃ and air sparged with simultaneous adjustment of desired solution pH with diluted sulphuric acid.
Since solid feed to a bioleaching/biooxidation process does not have uniform distribution of particle size and uniform particle shape in practical applications[2], bioleaching tests were carried out at particles sizes of <53, 53, 75 and 106 ?m at pH value of 2.0 and a stirring speed of 150 r/min to determine optimal particle size range where the dissolution will be the highest. The pulp density was kept at 10% (w/v), while the volume of inoculum was 6% (v/v). The optimal stirring speed was determined by varying the speed of agitation of bioleaching using 6% (v/v) inoculum at four different stirring speeds on particle size where the highest dissolution was obtained. Initial bioleaching was conducted at no mechanical agitation, but occasional hand shaking with periodical air stirring. Further bioleaching were conducted at varying speeds of 100, 150 and 200 r/min.
The determination of optimal pulp density for bioleaching was carried out by varying pulp densities at the optimal particle size and stirring speed and 6% (v/v) inoculum. The dissolution was initially done at 10% (w/v) pulp density to establish optimal particle size and stirring speed. Further bioleaching was carried out at pulp densities of 5%, 15% and 20% (w/v). The optimal volume of innoculum was determined by carrying out bioleaching experiments at varying volumes of inoculum of 12%, 18% and 24% (v/v) on optimal pulp density of 10% (w/v). The pH was kept at 2.0, while the stirring speed and particle size were respectively maintained at the optimal parameters of 150 r/min and 75 ?m. A control experiment without the addition of cells was always carried out under the same conditions.
The solution potential of the system was measured every two days, while zinc, copper and lead dissolved in the solution were analyzed periodically similar to TORRES et al[31] by atomic absorption spectro- photometry(AAS). The morphologies of the particles were observed by SEM analysis before and after microbial attack, while the mineral phases of the bioleached residues were identified by XRD. Except otherwise stated, all measurements were carried out in triplicate for each sample to ensure the reliability of the process. The experimental results were obtained by the analysis of variance (ANOVA) using Stata software. In all the experiments, very good reproducibility was achieved, as there were very little variations among the triplicates. The results are however presented as arithmetic mean values. Reliability tests conducted data on the data using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient show that the results displayed high levels of reliability as zinc, copper and lead had alpha values of 0.92, 0.95 and 0.84 respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Ore Mineralogy
The elemental composition of the bulk ore and their distributions within the particle sizes of <53, 53, 75 and 106 ?m as previously reported by OLUBAMBI et al[30] are listed in Table 1. As particle size decreased, the amounts of lead, iron, sulphur and silica increased while zinc and copper concentrations decreased. XRD analysis of the bulk ore revealed that the ore contained 42% siderite, 35% sphalerite, 11% galena, 8% quartz, with traces of chalcopyrite and pyrite. The sphalerite mineral in the ore occurred as ferrous sphalerite, with variations in the ratios of zinc to iron at different particle sizes within the sphalerite phase (Table 2). Finer particles had lower percentages of iron, while coarser sphalerite grains contained more solid solution iron.
Table 1 Mineralogical composition of ore and distribution of elements within particle sizes (%)
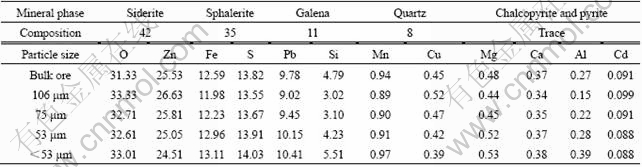
Table 2 Variations of Zn and Fe in sphalerite within particle sizes\
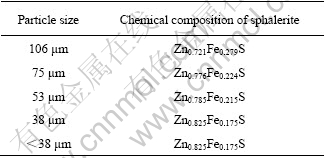
3.2 Optimizing bioleaching parameters
3.2.1 Effects of particle size
The various amounts of zinc, lead and copper recovered as presented in Figs.1-3 revealed that dissolutions increased initially as particles decreased down to 75 ?m, but later reduced as particle sizes decreased further to <53 ?m. The dissolutions of zinc and copper followed a similar trend of increments with time, with higher amounts of zinc dissolved than copper. Lead on the hand displayed a different dissolution pattern as dissolution initially increased up until the 12th day of bioleaching after which there was a general decrease.
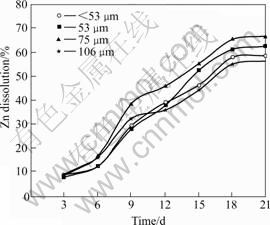
Fig.1 Effects of particle size on zinc dissolution (Stirring speed 150 r/min, pH 2.0, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
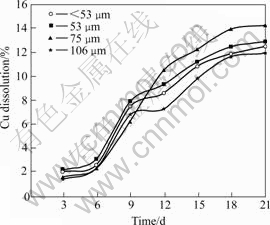
Fig.2 Effects of particle size on copper dissolution (Stirring speed 150 r/min, pH 2.0, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
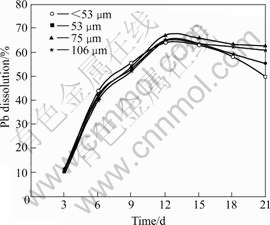
Fig.3 Effects of particle size on lead dissolution (Stirring speed 150 r/min, pH 2.0, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
3.2.1.1 Physical influence of particle size
The recovery rates of zinc, lead and copper at varying particle size could be explained from the view point of the surface area of the mineral that is available for microbial attack. According to HOSSAIN et al[20], the size of particles determines the surface area which also affects the bioleaching. By decreasing the particle size, the surface area per unit mass of the mineral is increased and, therefore, improved mass transfer and enhanced bioleaching rates are achieved[17]. Lower dissolution at particle sizes of 106 ?m can be attributed to the negative influence of larger particle sizes combined with agitation. Lower surface area of the larger particle size fraction of 106 ?m could result in a decrease in the number of active microbial attachment sites and a decrease in cell viability[13]. At larger particle sizes, less metal content is exposed to the reacting solution, thereby reducing the contact between the bacterial cells and metal content of the ore. Moreover, it can be believed that increase in heterogeneity at larger particle size fraction might lead to a non-uniform distribution of sulphur needed for microbial growth within the mineral sites.
It would have been expected that a greater surface area exposed to bacterial attack at smaller particle sizes of 53 ?m and <53 ?m would result in increased metal dissolution. It was however observed that decreasing particle size below 75 ?m did not improve bioleaching rates, but resulted in lower recoveries. Lower recovery at finer particle size fractions might be attributed to possible cell damage and deactivation[2], which could be caused by finer particles arising from probable oxygen deficiency due to limiting air flow rate. A similar situation was observed by NEMATI et al[17], where particle size less than 25 ?m did not improve the rate of bioleaching, but apparently damaged the structure of the cells and resulted in a dramatic decrease in concentration of the cells. It was also concluded that a reduction of particle size below a critical level could increase the extent of the particle-particle collision and impose severe attrition which might disrupt the structure of the cells. MAKITA[32] attributed the decrease in dissolution at lower particle size to possible higher complexity of minerals at lower particle sizes that could enhance specific interactions. These interactions are affected by the particles of smaller sizes where the greater surface area leaves each particle exposed to a greater amount of different mineral species, which increase the complexity of the medium thus affecting directly the dissolution. Since larger particles and finer particles both have impeding effects on microbial-mineral activities, the dissolution results confirmed a particle size of 75 ?m as the optimum size supporting, and accelerating biodissolution. It can therefore be concluded that particle size fraction of 75 ?m satisfies both surface area effects and conduciveness for microbial growth, which leads to improved mass transfer and enhanced bioleaching rates.
3.2.1.2 Mineralogical influence of particle size
Apart from the physical effects of particle size on bioleaching, the understanding of the optimal recoveries obtained at particle size fraction of 75 ?m could be reasoned from the mineralogical knowledge of the ore as mineralogical differences within varying particle sizes could affect their responses and behaviour during bioleaching. Investigation reported by OLUBAMBI et al [33] on the influence of ore mineralogy on the bioleaching behaviour of the low grade complex sulphide ores used in this study, showed that zinc and copper recoveries were influenced by mineralogical variations and phase distribution within different particle size fractions. It was reported that mineralogical difference including higher amounts of acid consuming siderite, galena, and quartz at lower particle sizes negatively affected the major bioleaching influencing factors: process pH, iron mobility and oxidation, and precipitate formation, which in turn reduced the possibility for zinc and copper to dissolve.
The distribution of elements within the particle size fractions as reported by OLUBAMBI et al[30] suggested that higher amounts of zinc and copper contained in the particle size fractions of 75 and 106 ?m could have resulted in higher amounts of zinc and copper available for dissolution than at lower particle sizes. The highest dissolutions at particle sizes of 75 ?m can thus be concluded to be attributed to the lower amounts of acid consuming siderite and galena, coupled with higher amount of Fe in the sphalerite matrix within the particle sizes of 75 ?m. Higher amount of Fe within sphalerite would thereby promote the oxidation of ferrous ions for ferric ions required for accelerating zinc and copper dissolution at particle sizes of 75 ?m. According to SHI et al[34], higher iron existing in the crystal lattice of sphalerite solid solution would be released to liquid phase and then oxidized into Fe3+ ions by bacterial strains to accelerate the dissolution of sphalerite during the bioleaching process.
In contrast to copper and zinc dissolution, higher amounts of lead were found in lower particle sizes of 53 and <53 ?m (Table 1). Decrease in lead dissolution at these lower sizes could result from possible increase in the formation of anglesite which promotes passivation of leaching surfaces. The dissolution trend displayed by lead could be reasoned from the solubility of galena and its concurrent passivation. The initial increase in dissolution in the first 12 d of bioleaching could be attributed to its high solubility. Decrease in dissolution observed beyond the 12th day of bioleaching could be reasoned from the view point of lead precipitating to form insoluble anglesite precipitate, which could have increased passivation of the leaching surfaces. This might lead to limit of the transfer of both the reactants and the bioleaching products, thereby resulting in a decrease in further oxidation and subsequently reducing the amounts of lead and other metals dissolved.
A major contributing factor to optimal dissolutions at 75 ?m can be attributed to cracks and faults within the particles during crushing and grinding. The SEM/BSI micrographs of particle sizes reported by OLUBAMBI et al[30] revealed the presence of more cracks in larger particle sizes of 106 and 75 ?m, with finer sizes having less. These cracks would thus aid dissolution by promoting crevices dissolution, as they might contribute additional and preferential electrochemical sites for dissolution.
In order to determine if the differences in dissolution at varying particle sizes were statistically significant, a separate one-way analysis of variance was done on the data, at 95% confidence. For zinc dissolution, analysis showed that there was no significant difference between the means of the particles sizes at day 3. However, for the remaining leaching period, that is, days 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 21, the dissolutions obtained at particle size fraction of 75 ?m were significantly more than those of the other particle size fractions. For copper and lead, significant differences were found between the dissolutions obtained at particle size fraction of 75 ?m and the other particle size fractions. These data clearly indicated the potential significance of particle size on bioleaching behaviours of these metals.
3.2.2 Process agitation and mixing
The amounts of zinc, copper and lead bioleached at varying stirring speed during the bioleaching of particle size 75 ?m (optimal size) are respectively shown in Figs.4-6. The dissolution rates increased as stirring speed increased until 150 r/min, beyond which the dissolution rates were reduced at 200 r/min. The highest zinc and copper dissolutions of 67% and 14.2% respectively were obtained on the 21st day and 67.2% lead dissolution was obtained on the 12th day of leaching at a stirring speed of 150 r/min, while the least recoveries were obtained with no mechanical stirring. The sharp reduction in the amounts of zinc and copper recovered, and the slight reduction in lead dissolution, after the 6th day of bioleaching at stirring speed of 200 r/min, might be a result of probable bacteria shear that could result from friction and attrition at this speed. It could be believed that dissolution after the 6th day was therefore predominantly chemically controlled[21] as the amounts of bacterium that might be present in the media to oxidize sulphur would be reduced. This was evident in the considerable increase in its solution pH (Fig.7) when compared with other stirring speed. Therefore, dissolution after day 6 was observed to be lower and linearly increased for copper and zinc until day 20, and slightly increased for lead until the 18th day of bioleaching when dissolution was higher than dissolution at no mechanical stirring.
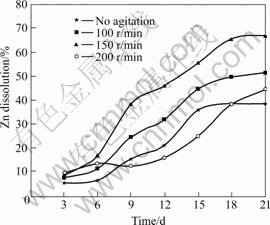
Fig.4 Effects of agitation on zinc recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
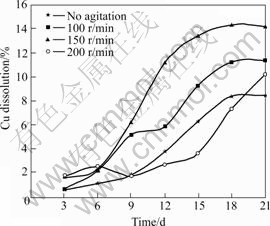
Fig.5 Effects of agitation on copper recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
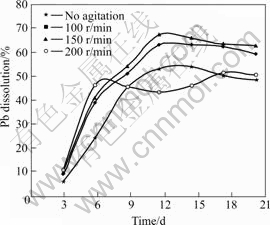
Fig.6 Effects of agitation on lead recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
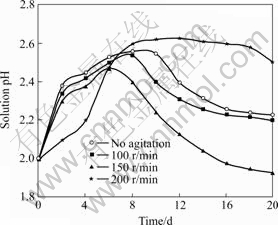
Fig.7 Effects of agitation on solution pH (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
The increase in the rates of dissolution up to 150 r/min observed in this study could be attributed to the fact that stirring aids mass flow of reactants and products. According to DEVECI[2], adequate mixing during bioleaching aids sufficient transfer of oxygen, carbon dioxide and heat to or from the growth medium to suspended solids, thereby maintaining suitable growth conditions for the bacteria. Therefore, as the stirring speed increased, the transportation of nutrients and gases to both the attached and suspended cells increased. Likewise, at increased stirring rate, the transportation of metabolic products from the cell back to the liquid and the solubilized species from the mineral’s surface to the liquid could increase. These could result in an increase in microbial activity which promoted acidity that led to a reduction in solution pH at stirring speed of 150 r/min when compared with other stirring.
At an increased stirring rate of 200 r/min, it could be assumed that the probability of cells to disintegrate increased, and therefore resulting in cell deactivation at prolonged stirring. According to DEVECI at al[18], cell deactivation during mixing can be attributed predominantly to the collisions between the particles. The resultant effects could include inhibition of cell growth, reduction in the synthesis of product, and overall change in cell morphology. This situation would therefore lead to disruption of bacterial cells, the inhibition of the attachment of bacteria to sulphide minerals and the detachment of the cells from the mineral surface[35]. When this situation arises, there could be reduction in cell productivity and possible death, which might thus reduce the oxidation of ferrous to ferric ions, which could lead to the observed increase in its solution pH.
3.2.3 Mineral pulp density and ore mineralogy
The results of the effects of pulp density determined by bioleaching at a stirring speed of 150 r/min, pH of 2.0 and 6% (v/v) inoculum addition are shown in Figs.8-10. The results showed a considerable decrease in dissolution when the mineral pulp density was increased, with the highest dissolutions of 83%, 16.5% and 69.7% respectively for zinc, copper and lead obtained at a pulp density of 5% (w/v). The reduction in dissolution with increasing pulp density could be attributed to the negative effect of high pulp density on bacterial growth [36-37]. This could lead to an increase in the friction between particles and attrition of bacterial cells, which might possibly affect interactions between the particle and bacteria, and cell damage. ACEVEDO et al[38] noted that higher pulp density could diminish the rate of bacterial growth and increase the rate of ferric reduction to ferrous than the ferrous oxidation. This could be attributed to the fact that pulp density can affect gas flow rate, and thereby reducing the availability of oxygen, which is an essential nutrient for bacterial growth. Bacterial oxidation of minerals (Eqns.(1) and (2)) and oxidation of ferrous iron to ferric iron (Eqn. (3)) requires oxygen, therefore, insufficient oxygen concentration could be a limiting factor for the bioleaching reaction.
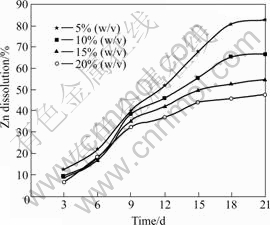
Fig.8 Effects of pulp density on zinc recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, stirring speed 150 r/min, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
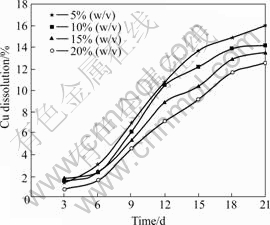
Fig.9 Effects of pulp density on copper recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, stirring speed 150 r/min, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
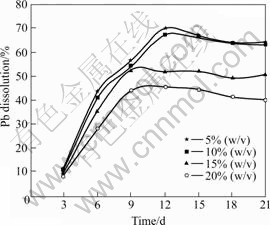
Fig.10 Effects of pulp density on lead recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, stirring speed 150 r/min, and 6% (v/v) volume of inoculum addition)
CuFeS2+O2+4H+→Cu2++Fe2++2S0+2H2O (1)
ZnS+2H++0.5O2→Zn2++S0+H2O (2)
In the presence of oxygen, ferrous ions are oxidized in the presence of bacteria to ferric ions which are highly oxidizing.
4Fe2++O2+4H+→4Fe3++2H2O (3)
A major inhibiting effect of increasing pulp density on bioleaching could be attributed to the increase in the galena contents at higher pulp density, which would promote the formation of anglesite precipitates. Anglesite could decrease microbial activities by hindering bacterial access to the mineral surface and build up a non-conducting product layer within the system, thereby lowering the galvanic interaction effect needed to promote further dissolution. Moreover, cells will attach themselves to anglesite instead of attaching to minerals surface, thus decreasing microbial/minerals attachment and reactivity.
3.2.4 Influence of volume of inoculum and mineralogy
The results of the study on the influence of pulp density clearly showed that higher pulp density resulted in lower metal recoveries at an inoculum volume of 6% (v/v). Should a bioleaching process be operated at 5% (w/v) pulp density which gave the highest recoveries, there is presupposition that running a biooxidation plant at 5% (w/v) pulp might not be industrially economical. Bioleaching experiments on particle size fraction of 75 ?m were therefore conducted on a higher mineral pulp density of 10% (w/v) at varying volumes of inoculum of 12%, 18% and 24% (v/v), and without bacteria addition. The solution was kept at pH 2.0 and stirred at 150 r/min.
The dissolution results presented in Figs.11-13 indicated that the mixed cultures played an important role in the dissolution of the metals, as the amounts of zinc, copper and lead dissolved were little in the sterilized control. This result proved in agreement with QIU et al[39] that the efficacy of bacterial leaching was better than the efficacy of chemical leaching. The amounts of metal extracted were observed to increase as a function of time, including the uninoculated controls. However, the rate of increase in metal dissolution was greatest in samples inoculated with 12% (v/v) of the cells. The initial highest recoveries at increased inoculated cell numbers of 24% (v/v) could be understood from the view point that bacteria catalyze ferrous oxidation (Eqn.(3)), oxidize and dissolve insoluble metal sulphide ore, thus releasing the entrapped metal particles. The increase in solubilization might also be catalysed through either or both the contact and non-contact mechanisms of microbial attack (Eqns.(4) to (7)).
be a result of probable bacteria shear that could result from friction and attrition at this speed. It could be believed that dissolution after the 6th day was therefore predominantly chemically controlled[21] as the amounts of bacterium that might be present in the media to oxidize sulphur would be reduced. This was evident in the considerable increase in its solution pH (Fig.7) when compared with other stirring speed. Therefore, dissolution after day 6 was observed to be lower and linearly increased for copper and zinc until day 20, and slightly increased for lead until the 18th day of bioleaching when dissolution was higher than dissolution at no mechanical stirring.
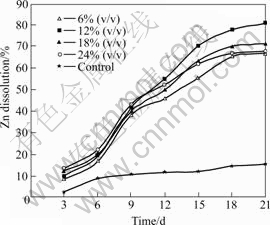
Fig.11 Effect of inoculum addition on zinc dissolution (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, stirring speed 150 r/min, and 10% (w/v) pulp density)
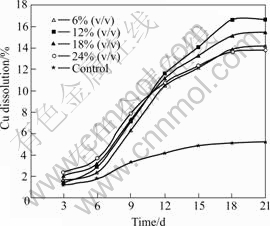
Fig.12 Effect of inoculum addition on copper dissolution (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, stirring speed 150 r/min, and 10% (w/v) pulp density)
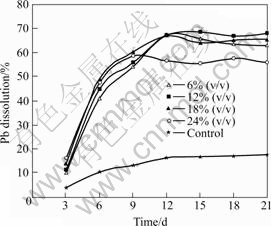
Fig.13 Effect of inoculum addition on lead dissolution (Particle size 75 ?m, pH 2.0, stirring speed 150 r/min, and 10% (w/v) pulp density)
Contact mechanism:

Non-contact mechanism:
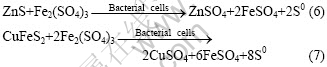
The soluble sulphates of zinc and copper produced in Eqns.(6) and (7) become very easy to dissolve, while the elemental sulphur produced is oxidized by attached cells to yield sulphuric acid (Eqn.(8)), which increases the dissolution power of the medium.
![]()
3.2.5 Effects of process pH and mineralogy
3.2.5.1 Effects of pH on zinc, copper, and lead dissolu- tions
The results presented in Figs.14-16 showed that the bioleaching potentials of mixed cultures of mesophiles were favorably influenced by decreasing pH from 2.0 to 1.6. These results showed the consistency with studies reported by BHATTI et al[40] and DEVECI et al[19]. It was observed that decreasing the pH down to 1.6 had more positive effects on copper recovery than on zinc and lead recovery, as copper dissolution showed wider recovery differences between the various pH values. The favorable influence of decreasing pH on zinc, lead and copper recoveries could be attributed to the fact that the pH of the bioleaching medium significantly influences the growth and activity of acidophilic microorganisms. This was indicated by the change in the solution redox potential shown in Fig.17.
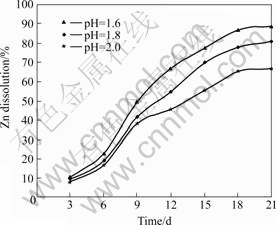
Fig.14 Effects of pH change on zinc recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, stirring speed 150 r/min, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 12% (v/v) cell addition)
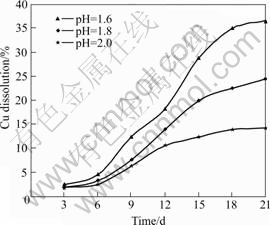
Fig.15 Effects of pH change on copper recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, stirring speed 150 r/min, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 12% (v/v) cell addition)
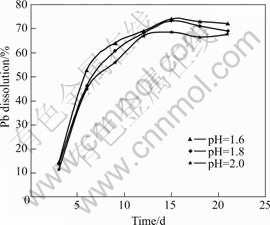
Fig.16 Effects of pH on lead recovery (Particle size 75 ?m, stirring speed 150 r/min, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 12% (v/v) cell addition)
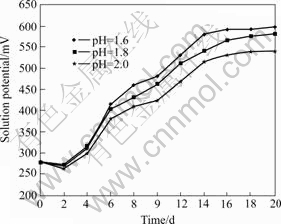
Fig.17 Change in solution potential at varying process pH (Particle size 75 ?m, stirring speed 150 r/min, 10% (w/v) pulp density, and 12% (v/v) cell addition)
The increase in the growth and mesophilic activity and interaction with minerals at low pH could be probably due to the fact that bacterial growth is usually higher at a very low pH values. It should be understood that H+ is a very essential nutrient for the bacterial growth[21], because during the oxidation of ferrous ions to ferric ions, bacteria takes up H+ ions from its external environment[41]. According to HOSSAIN et al[20], the bacterial interaction with metals at lower pH probablyresults from the effective competition by H+ ions for negatively-charged sites at the cell surface. Since ferrous oxidation (Eqn.(3)) involves H+ consumption, it is obvious that the generation of ferric ions requires more H+ which in turns depends basically on the pH and the ferrous iron concentration, and on the ferrous iron conversion achieved. Since lower pH corresponds to higher H+, bacteria/mineral interaction therefore increases and the tendency for the contact mechanism (Eqns.(5) and (6)) becomes higher. Similarly, lower pH promotes the conversion of Fe2+ to Fe3+, thereby consequently favouring the non-contact mechanism.
At a higher pH, the rates of Eqns.(3)-(5) are slowed down, and instead of ferric ions being produced, ferric sulphate is likely precipitated. Since copper has a higher affinity for precipitation, instead of copper existing in ionic form in aqueous solution, it combines with the precipitated iron. This phenomenon could therefore lead to a reduction in the total amount of copper recovered at higher pH. A similar situation was reported by KEELING et al[42] where it was noted that at higher pH in a heap, the amount of soluble ferric ion was depleted through precipitation as a basic ferric sulphate and consequently resulted in a reduction in copper extraction. This might probably account for the high difference in copper recoveries at the varied pH values. Since a pH higher than 1.6 considerably promotes ferric iron precipitation as jarosite[43-44], it is believed that reduction in copper dissolution at higher pH would be due to the interaction between copper and jarosite, whereby copper is preferentially precipitated.
3.2.5.2 Effects of pH on solution potentials
The changes in solution potentials with pH presented in Fig.17 revealed that the highest solution potential was obtained at pH of 1.6. This could be an indication of the highest microbial growth at this pH range which results in the highest zinc, lead and copper dissolutions. Lower solution potential values obtained at higher pH values could be an indication that microbial activity was lower at these pH values, as the formation of jarosite precipitate at higher pH values could significantly immobilize bacterial strains[44]. At the initial stage of bioleaching, a decrease in the solution potential was observed. The decrease in the solution potential observed could also be attributed to higher amounts of ferrous ions in the system resulting from the fast dissolution of siderite. Since redox potential depends on the Fe3+/Fe2+ relationship, higher Fe2+ concentration within the system would affect the ferrous/ferric ratio in the system. The initial low solution potential could therefore be an indication that the ferrous ions were not oxidized at the initial stage of bioleaching. This could have also resulted from the initial decrease in the bacteria cells within the system resulting in a corresponding decrease in the oxidation of ferrous to ferric ions. The acid consumption of the galena and siderite contents of the ore might also increase the solution pH within the first two days, and possibly leading to an initial decrease in bacterial activities needed for the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+. Beyond the first two days of bioleaching, the increase in the solution potentials could be an indication that the dissolution reaction had entered an acid producing phase which could be accelerated by ferrous sphalerite, pyrite and chalcopyrite. This phase would therefore be favourable for microbial activities and the subsequent oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+, which concurrently increased the solution potential.
Fig.17 also revealed a generally low solution potential during the bioleaching process. This generally low solution potential could be due to the limited amounts of sulphur in the ore (i.e. 13.82%) as siderite took 42%. This could result in a decrease in food source for organisms and a probably corresponding decrease in microbial activities. The general low solution potential during the bioleaching process could also be attributed to the imbalance in the Fe3+/Fe2+ relationship that might be caused by the high contents of the acid consuming siderite and galena that could promote precipitation. The anglesite and iron silicates produced could decrease microbial activities, as the cells will attach themselves to the precipitates instead attach to minerals surface.
3.2.5.3 Effects of process pH on precipitate formation
The types of the various precipitates formed during bioleaching at the various pH values as determined by XRD and listed in Table 3 revealed more minerals phases in all the residues. It was observed that no trace of siderite (the major mineral in the ore) was found in any of the residues. Similarly, no ferrous was found within the sphalerite phases identified in the residues. Anglesite and elemental sulphur were the major precipitates in all the solutions exposed to various pH values. The peak intensities of pyrite, although minor constituents, were observed similar to the observations reported by BHATTI et al[40] and PACHOLEWSKA[45], slightly increase in the bioleached residues. Jarosite was the most abundant phase identified at pH of 2.0, but none was identified at pH 1.6 and 1.8. Instead of jarosite precipitation at pH 1.8, a very crystalline phase, KNaCuSi4O10 was identified. Anglesite and elemental sulphur were observed as the major phases at pH of 1.6. Pyrite phase, which occurred as a trace in the bulk ore before leaching, was observed to be high in all the residues.
Table 3 Phases analysis of bioleached residues by XRD
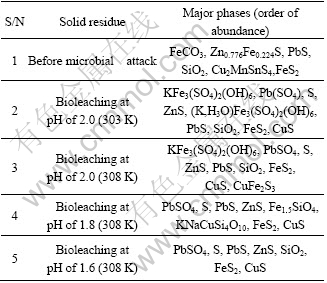
The complete disappearance of siderite in all the solid residues could be due to the high solubility of siderite in aqueous solution, which could lead to complete oxidation of siderite and its transformation and precipitation as secondary iron compounds. Iron oxidation also accounts for the disappearance of all the iron within the sphalerite matrix. Since all the iron within the matrix is oxidized, an un-dissolved and un-oxidized sphalerite ZnS is found in the residue. Lack of jarosite at pH 1.8 and 1.6 confirms the results previously reported by NEMATI et al[46] that jarosite started precipitating at pH values of 1.8, which was towards the lower boundary of the optimal pH range for bacterial growth. DAOUD and KARAMANEV[47] also observed that the optimal pH for the least amount of jarosite was a pH range of 1.6-1.7. Since the combined effects of bacteria-mineral interaction, hydrolysis of ferric iron, and sulphur oxidation lead to an increase in acidity, bioleaching at longer times resulted in reduced pH. The implication of this is that the initial pH at 1.8 could be reduced as indicated by the increase in solution potential, and the decrease in pH would presumably hinder the formation of jarosite.
The morphological features of the ore samples and bioleached residues observed with scanning electron microscope are shown in Fig.18. Bacterial cells were not identified in any of the residues, presumably because they were either covered, encrusted with mineral precipitates, or dead, as SEM observation on dried residues were carried out several days after bioleaching. All the surfaces of the grains was covered and coated with bioleached products and their surface morphologies were differently changed at different pH values during bioleaching. The micrographs generally revealed a semi- porous type of precipitate, which suggested that the precipitates would have less inhibiting effects on the overall mass transfer within the system. However, the precipitates were not perfectly porous, possibly due to the presence of non-porous reaction products (PbSO4 and most likely S0). Critical observation of the precipitates revealed that bioleaching at pH 1.6 transformed most of the bulk ore to residues. This could be attributed to the fact that there was higher microbial dissolution and transformation of the original ore within this pH range. The micrographs of the bioleaching residues at pH of 1.8 and 2.0 revealed that some of the particles were not completely attacked by the microbes. This could explain the lower metal dissolution obtained during the dissolution at these pH values.
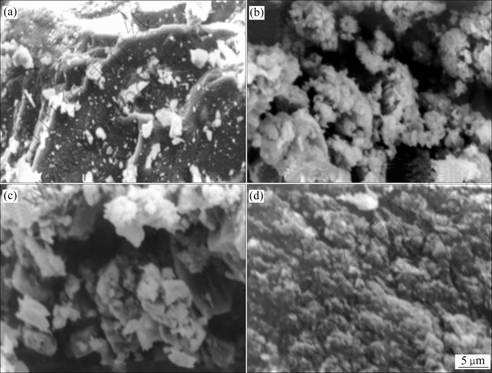
Fig.18 SEM micrographs of ore: (a) Before microbial attack; (b, c, d) After microbial attack at particle size of 75 ?m, stirring speed of 150 r/min, 10% (w/v) pulp density, 12% (v/v) cell addition and pH 2.0 (b), pH 1.8 (c) and pH 1.6 (d)
4 Conclusions
The role of ore mineralogy in optimizing conditions for bioleaching low-grade complex sulphide ore containing high amounts of siderite using mixed cultures of mesophilic microorganisms was studied. Ore mineralogy played major role in understanding the influence of the processing parameters on the bioleaching rates. Optimized parameter values demonstrated that the mixed cultures of mesophiles can extract about two and a half times the amount of zinc than copper over an equivalent period of time.
The optimal zinc, lead and copper dissolutions observed at the particle size fraction of 75 ?m were concluded to be due to the physical influence of particle size chiefly on the mineralogical distribution at this parti- cular particle size. Bioleaching at reduced pH had a positive influence on copper, lead and zinc dissolution, but the effect was greater for copper recovery, possibly due to the absence of jarosite formation. Keeping the ratio of pulp density and volume of inoculum at 5?6 up till 10% (w/v) pulp densities and 12% (v/v) inoculum addition, 89.2% zinc and 36.4% copper can be respectively recovered at optimal parameters of particle size of 75 ?m bioleached at a stirring speed of 150 r/min at pH of 1.6 for 5% and 10% (w/v) pulp density.
AcknowledgementThe authors would like to acknowledge the financial support received from the Mellon Postgraduate Mentoring Programme of the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Afria.
References[1] RUBIO A, GARCIA FRUTOS F J. Bioleaching capacity of an extremely thermophilic culture for chalcopyrite materials [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2002, 15: 689-694.
[2] DEVECI H. Effect of particle size and shape of solids on the viability of acidophilic bacteria during mixing in stirred tank reactors [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 71: 385-396.
[3] GOMEZ C, LIMPO J L, DE LUIS A, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F BALLESTER A. Hydrometallurgy of bulk concentrates of Spanish complex sulphides: Chemical and bacterial leaching [J]. Canadian Metallurgy Quarterly, 1997, 26(1): 15-23.
[4] HAN K N, MENG X. Recovery of copper from its sulfides and other sources using halogen reagents and oxidants [J]. Minerals and Metallurgical Processing, 2003, ?20: 160-164.
[5] UBALDINI S, VEGLIO F, BEOLCHINI F, TORO L, ABBRUZZESE C. Gold recovery from a refractory pyrrhotite ore by biooxidation [J]. International Journal of Minerals Processing, 2000, 60: 247-262.
[6] HOLMES D S. Biotechnology in the mining and metal processing industries: Challenges and opportunities [J]. Minerals and Metallurgical Processing, 1998(5): 49-56.
[7] SMITH R W, MISHA M. Mineral bioprocessing: An overview [M]. The Minerals, Metals Materials Society, 1991: 3-26.
[8] ACEVEDO F. Present and future of bioleaching in developing countries [EB/OL]. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 2002, 5(2): http://www.ejbiotechnology.info/content/vol5/issue2/issues/01/5-2i01. pdf.
[9] ANAND P, MODAK J M, NATARAJAN K A. Biobeneficiation of bauxite using Bacillus polymyxa: Calcium and iron removal [J]. International Journal of Minerals Processing, 1996, 48: 51-60.
[10] BRIERLEY C L. Practical role of thermophilic bacteria in bioleaching and biooxidation [C]// International Conference and Workshop Application of Biotechnology to the Mineral Industry. Adelaide: Australian Mineral Foundation, 1993, 2: 1-2.7.
[11] CLARK D A, NORRIS P R. Oxidation of minerals sulphides by thermophilic microorganisms [J]. Minerals Engineering, 1996, 9: 1119- 1125.
[12] ACAR S, BRIERLEY J A, WAN R Y. Conditions for bioleaching a covellite-bearing ore [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2005, 77: 239-246.
[13] GONZALEZ R, GENTINA J C, ACEVEDO F. Attachment behaviour of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans cells to refractory gold concentrate particles [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 1999, 21: 715-718.
[14] GOMEZ C, BLAZQUEZ M L, BALLESTER A. Bioleaching of a Spanish complex sulphide ore bulk concentrate [J]. Minerals Engineering, 1999, 12: 93-106.
[15] THIRD K A, CORD-RUWISCH R, WATLING H R. The role of iron-oxidizing bacteria in stimulation or inhibition of chalcopyrite bioleaching [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 57: 225-233.
[16] NEMATI M, HARRISON S T L. Effect of solid loading on thermophilic bioleaching of sulphide minerals [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2000, 75: 526-532.
[17] NEMATI M, LOWENADLER J, HARRISON S T L. Particle size effects in bioleaching of pyrite by acidophilic thermophile Sulfolobus metallicus (BC) [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2000, 53: 173-179.
[18] DEVECI H. Effect of solids on viability of acidophilic bacteria [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2002, 15: 1181-1189.
[19] DEVECI H, AKCIL A, ALP I. Bioleaching of complex zinc sulphides using mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria: Comparative importance of pH and iron [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 73: 293-303.
[20] HOSSAIN S M, DAS M, BEGUM K M M S, ANANTHARAMAN N. Bioleaching of zinc sulphide(ZnS) ore using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Institution of Engineers (India) Chemical Division, 2004, 85: 7-11.
[21] DAS T, GHOSH M K, CHAUDHURY G R. Assessment of the significant parameters influencing the bio-oxidation and bio- precipitation of iron from industrial leach liquor [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2005, 114: 57-64.
[22] RODRIGUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F, MUNOZ J A. New information on the pyrite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71: 37-46.
[23] RODRIGUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F, MUNOZ J A. New information on the chalcopyrite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71: 47-56.
[24] RODRIGUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F, MUNOZ J A. New information on the sphalerite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71: 57-66.
[25] SAMPSON M I, VAN DER MERWE J W, HARVEY T J, BATH M D. Testing the ability of a low grade sphalerite concentrate to achieve autothermality during biooxidation heap leaching [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18: 427-437.
[26] AKCIL A, CIFTCI H, DEVECI H. Role and contribution of pure and mixed cultures of mesophiles in bioleaching of a pyritic chalcopyrite concentrate [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20: 310-318.
[27] DONATI E, CURUTCHET G, POGLIANI C, TEDESCO P. Bioleaching of covellite using pure and mixed cultures of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Thiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Process Biochemistry, 1996, 31: 129-134.
[28] GIAVENO A, DONATI E. Bioleaching of heazelwoodite by Thiobacillus spp [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2001, 36: 955- 962.
[29] FALCO L, POGLIANI C, CURUTCHET G, DONATI E. A comparison of bioleaching of covellite using pure cultures of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans or a mixed culture of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71: 31-36.
[30] OLUBAMBI P A, NDLOVU S, POTGIETER J H, BORODE J O. Influence of applied mineralogy in developing optimal hydrometallurgical processing route for complex sulphide ores [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2006, 27: 143-158.
[31] TORRES F, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F, BALLESTER A, MIER J L. The bioleaching of different sulfide concentrates using thermophilic bacteria [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1995, 26: 1995-455.
[32] MAKITA M, ESPER?N M, PEREYRA B, L?PEZ A, ORRANTIA E. Reduction of arsenic content in a complex galena concentrate by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [EB/OL]. BioMed Central(BMC) Biotechnology, 2004. http: //www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6750/4/ 22.
[33] OLUBAMBI P A, NDLOVU S, POTGIETER J H, BORODE J O. Effects of ore mineralogy on the microbial leaching of low-grade complex sulphide ores [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 86: 96-104.
[34] SHI S Y, FANG Z H, NI J R. Comparative study on the bioleaching of zinc sulphides [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41: 438-446.
[35] ROSSI G. The design of bioreactors [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59: 217-231.
[36] TIPRE D R, DAVE S R. Bioleaching process for Cu-Pb-Zn bulk concentrate at high pulp density [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 75: 37-43.
[37] BAILLEY A D, HANSFORD G S. Factors affecting bio-oxidation of sulfide minerals at high concentration of solids—A review [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1993, 42: 1164-1174
[38] ACEVEDO F, GENTINA J C, VALENCIA P. Optimization of pulp density and particle size in the biooxidation of a pyritic gold concentrate by Sulfolobus metallicus [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2004, 20: 865-869.
[39] QIU M, XIONG S, ZHANG W, WANG G. A comparison of bioleaching of chalcopyrite using pure culture or a mixed culture [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18: 987-990.
[40] BHATTI T M, BIGHAM J M, CARLSON L, TUOVINEN O H. Mineral products of pyrrhotite oxidation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59: 1984-1990.
[41] APEL A W, DUGAN R P. Hydrogen ion utilization by iron grown Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [M]// MURR E L, TORMA A E, BRIERLEY A J, eds. Metallurgical Applications of Bacterial Leaching and Related Microbiological Phenomena. New York: Academic Press, 1978: 45-58.
[42] KEELING S E, PALMER M L, CARACATSANIS F C, JOHNSON J A, WATLING H R. Leaching of chalcopyrite and sphalerite using bacteria enriched from a spent chalcocite heap [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18: 1289-1296.
[43] MAZUELOS A, PALENCIA I, ROMERO R, RODRIGUEZ G, CARRANZA F. Ferric iron production in packed bed bioreactors: Influence of pH, temperature, particle size, bacterial support material and type of air distributor [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2001, 14: 507-514.
[44] POGLIANI C, DONATI E. Immobilisation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: Importance of jarosite precipitation [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2000, 35: 997-1004
[45] PACHOLEWSKA M. Bioleaching of galena flotation concentrates [J]. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing, 2004, 38: 281- 290
[46] NEMATI M, HARRISON S T L, HANSFORD G S, WEBB C. Biological oxidation of ferrous sulphate by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: A review on the kinetic aspects [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 1998, 1: 171-190.
[47] DAOUD J, KARAMANEV D. Formation of jarosite during Fe2+ oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2006, 19: 960-967.
Corresponding author: P. A. OLUBAMBI; Tel: +27117177597, Fax: +27117177591 E-mail: polubambi@yahoo.com

