DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.01.003
基于CF-EEMD-LSSVR算法的铅冶炼系统温室气体排放的评估与预测
罗曦1,王洪才2,李玉强2
(1. 中南大学 建筑与艺术学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:利用碳足迹理论建立铅冶炼系统生命周期内各工序的投入产出模型,对单位产品温室气体排放进行评估。针对温室气体排放时间序列的非线性,建立1个基于集合经验模态分解法与最小二乘支持向量回归机相结合的预测模型。集合经验模态分解法首先将温室气体排放时间序列分解成一系列相对比较平稳的本征模函数分量,然后利用最小二乘支持向量回归机对各分量分别预测,最后进行叠加求和,将铅冶炼系统温室气体排放量的预测结果与实际结果进行对比。研究结果表明:预测结果与实际结果均方根误差为2.896 1%,所提出的方法可实现铅冶炼系统温室气体排放的精确评估与预测。
关键词:铅冶炼系统;温室气体排放;碳足迹;集合经验模态分解;最小二乘支持向量回归机
中图分类号:TF8 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2018)01-0015-07
Evaluation and prediction of greenhouse gas emission of lead smelting system based on CF-EEMD-LSSVR
LUO Xi1, WANG Hongcai2, LI Yuqiang2
(1. School of Architecture and Art, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Input-output (I-O) model for each step of lead smelting system to evaluate greenhouse gas emission per unit product was established based on carbon footprint (CF) theory. Due to the nonlinear characteristic of greenhouse gas emission data, a prediction model was developed based on the combination of ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and the least square support vector regression (LSSVR).The procedures were as follows: the data of greenhouse gas emission of leads melting system was firstly decomposed into a series of relatively stable intrinsic mode functions (IMF), and then they were separately predicted by LSSVR. The predicted values were compared with the real results. The results show that the root mean square error of the predicted values and the real results is 2.896 1%, which verifies that the proposed method can realize the accurate evaluation and prediction of greenhouse gas emission of lead smelting system.
Key words: lead smelting system; greenhouse gas emission; carbon footprint(CF); ensemble empirical mode decomposition(EEMD); the least square support vector regression(LSSVR)
温室气体排放增加导致气候变暖已成为全球共识。我国高度重视温室气体排放问题,并将其作为约束性指标纳入国民经济和社会发展中长期规划[1-2]。随着我国对工业生产企业温室气体排放的控制逐渐严格,铅冶炼工业面临着巨大的温室气体减排压力。然而,温室气体减排的目标实现与路线规划需要对温室气体排放进行科学评估与预测。碳足迹(carbon footprint, CF)用于描述温室气体对气候变化的影响,人们对其有着不同的认识和了解。EIAP(eco-innovation action plan)认为碳足迹是工业过程产生的温室气体转换成CO2等价物[3];POST(Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology)认为碳足迹应该包含3个层面,即碳足迹应该包含生产的直接和间接碳排放、供应过程的直接和间接碳排放、支付过程的直接和间接碳排放[4]。英国Carbon Trust认为碳足迹应是计算产品生命周期内所产生的CO2或温室气体的等价CO2[5];另外,WRI(World Resources Institute)和WBCSD(World Business Council for Sustainable Development)等机构也对碳足迹进行了定义,庞博慧[6]对这些定义进行了总结。碳足迹概念已得到各研究机构的广泛关注,并提出了生命周期法、投入产出法、IPCC法等[7]主要算法。由于传统预测方法的预测精度普遍不高,新的预测理论及方法一直是国内外学者研究的热点。支持向量回归机(support vector regression, SVR)克服了传统神经网络存在的网络结构选择困难、泛化能力差、易陷入局部极小、收敛慢等缺陷,被认为是神经网络的替代方法[8]。最小二乘支持向量回归机(least square support vector regression, LSSVR)计算速度比SVR的计算速度更快[9]。时间序列的非平稳性严重地制约了预测模型的建立和预测精度的提高。目前,降低时间序列非平稳性的方法主要有傅里叶分解法[10]、小波分解法[11]和经验模态分解法(empirical mode decomposition, EMD)[12]。其中,傅里叶分解法得到的子序列在时域内没有分辨率,自适应性差;小波分解法则需要人为预先设定基函数,操作不便,分解结果含有多余信号;EMD具有较高的时频分辨性能,但端点效应和模态混叠现象会降低EMD分解质量。而后有学者提出的集合经验模态分解法(ensemble empirical mode decomposition, EEMD),利用噪声辅助处理方法,通过添加白噪声到信号中弥补EMD算法的缺失尺度[13]。TANG等[14]提出将EEMD与LSSVR组合的预测方法对核能消耗进行了预测,并与单一LSSVR预测模型进行了对比分析,验证了组合预测模型具有更高的预测精度。目前,人们对铅冶炼系统温室气体排放的评估与预测很少,为此,本文作者利用CF,EEMD和LSSVR理论对铅冶炼系统温室气体排放进行评估与预测。
1 铅冶炼系统温室气体排放评估
1.1 铅冶炼系统碳足迹边界
铅冶炼系统整个生命周期可分为配料、粗炼、精炼共3个阶段,每个阶段都需要耗费大量的原料和能源,整个过程会产生大量温室气体排放。本文采用投入产出法(input-output, I-O)分析每个工序单位产品产生的温室气体。基于温室气体的定义,以二氧化碳(CO2)、甲烷(CH4)、氮氧化合物(NOx)为研究对象,分析铅冶炼系统的碳足迹。以水口山法(SKS法)铅冶炼工艺为例,对铅冶炼系统碳足迹边界进行确定。SKS铅冶炼系统是将硫化铅精矿、二次物料、溶剂、烟尘和必要的固体焦炭燃料经过混合并制成颗粒后,从氧气底吹炉的炉顶料仓加入底吹炉,在高温下发生氧化脱硫反应熔炼,产出粗铅、高铅渣及烟气,然后高铅渣被送到鼓风炉并在高温下与溶剂、焦炭等发生还原反应,产生二次粗铅、烟气和铅渣,粗铅铸锭后经过电解精炼用于制造精铅。SKS铅冶炼系统碳足迹研究边界示意图见图1。
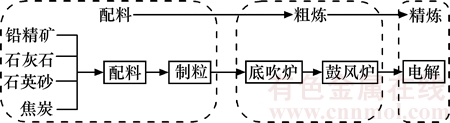
图1 SKS铅冶炼系统碳足迹研究边界示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of CF research boundary for SKS lead smelting system
1.2 铅冶炼系统碳足迹模型
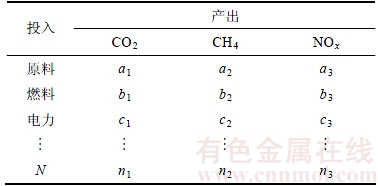
铅冶炼系统各工序中物质、元素的质量是守恒的,在各工序内运用I-O法分析工序内单位产品产生的温室气体(CO2、CH4和NOx),计算铅冶炼系统整个生命周期内的碳足迹。根据如图2所示的投入产出模型和表1所示的各工序投入和产出,可得到下列变量矩阵形式。
投入项:
 (1)
(1)
温室气体排放因子:
 (2)
(2)
CO2当量排放量:
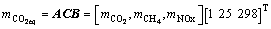 (3)
(3)
式中:mCO2为CO2排放量;mCH4为CH4排放量;mNOx为NOx排放量;B=[1, 25, 298]为CO2当量因子,是在特定长度的评估期内,某温室气体相对相同质量CO2的暖化能力,即CO2当量因子为1,CH4的CO2当量因子为25,N2O的CO2当量因子为298[15]。
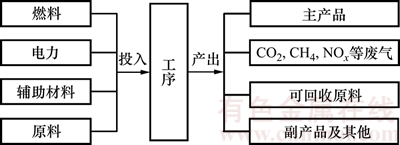
图2 SKS铅冶炼系统投入产出模型
Fig. 2 I-O model of SKS lead smelting system
表1 SKS铅冶炼系统碳足迹投入和产出
Table 1 CF I-O of SKS lead smelting system kg
1.3 实际铅冶炼系统碳足迹计算
选取企业A作为分析案例。综合中国实际铅生产情况,根据“IPCC国家温室气体清单指南”,得到铅冶炼过程所需原料及能源的温室气体排放因子,见表2。
根据企业A能源平衡表,可知该企业当年共配料17.41万t,原材料精矿粉消耗量为15.74万t,石灰石0.58万t,基于上述计算方法,对配料进行物流与投入产出进行分析,将其转化为单位制粒矿I-O表,如表3所示。从表3可看出:1 t制粒矿的mCO2eq为458.65 kg,其中动力煤产生的mCO2eq最大,为373.84 kg,占配料工序mCO2eq的81.51%,电力、蒸汽、热水的mCO2eq分别为66.83,8.32和9.66 kg。从温室气体种类来计算,配料工序中,CO2的mCO2eq为249.11 kg,占54.31%;CH4的mCO2eq为0.94 kg,占0.20%;NOx的mCO2eq为208.60 kg,占45.48%。
粗炼工序I-O表见表4。从表4可见:1 t粗铅的mCO2eq为3 002.39 kg,其中焦炭产生的mCO2eq最大,为2 225.56 kg,占粗炼工序m(CO2eq)的74.12%;动力煤、烟煤、石灰石、电力、蒸汽、热水的mCO2eq分别为279.64,408.96,9.92,51.28,3.25和3.78 kg。从温室气体种类来计算,在粗炼工序中,CO2的mCO2eq为2 156.81 kg,占71.83%;CH4的mCO2eq为2.15 kg,占0.08%;NOx的mCO2eq为208.89 kg,占28.09%。
精炼工序I-O表见表5。从表5可见:1 t精铅的mCO2eq为245.30 kg,其中煤气产生的mCO2eq最大,为151.14 kg,占精炼工序mCO2eq的61.61%,电力、蒸汽、热水的mCO2eq分别为75.68,10.92和7.56 kg。从温室气体种类来计算,在精炼工序中,CO2的mCO2eq为178.24 kg,占72.66%;CH4的mCO2eq为1.50 kg,占0.61%;NOx的mCO2eq为65.56 kg,占26.73%。
企业A铅冶炼系统中各工序单位产品产生的mCO2eq见表6。从表6可见粗炼工序单位产品的mCO2eq远比其他工序的高,这是因为粗炼过程能耗大,且焦炭、动力煤、烟煤等耗能类型对应的mCO2eq较大,而配料工序和精炼工序能耗较小,mCO2eq较小。从能源类型分析,焦炭、煤气、动力煤、烟煤是铅生产过程中mCO2eq的主要贡献者。
2 铅冶炼系统温室气体排放预测
2.1 EEMD-LSSVR预测模型的建立
传统方法的温室气体监测都是通过工作人员对仪器设备仪表进行定期检测,这样不利于对实际生产中排放的温室气体进行监控。通过研究碳足迹预测可以把握温室气体排放趋势,对于指导实际生产具有重要意义。铅冶炼系统温室气体排放时间序列具有非稳态性、非线性的特性,只采用一般的预测方法难以取得较高的预测精度。基于EEMD降低时间序列非稳态性的优势以及LSSVR模型预测非线性系统的良好性能,本文建立一个基于EEMD-LSSVR组合的模型,以预测铅冶炼系统温室气体排放,其建模流程如图3所示。
表2 SKS铅冶炼系统所需原料及能源的温室气体排放因子
Table 2 Greenhouse gas emission factors of material and energy of SKS lead smelting system
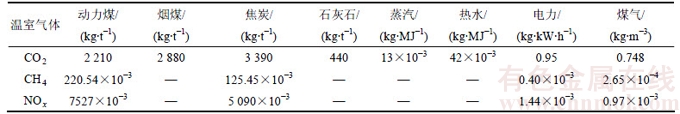
表3 配料工序的单位产品温室气体排放质量的I-O评估
Table 3 I-O assessment of greenhouse gas emission quality per product in batching process kg
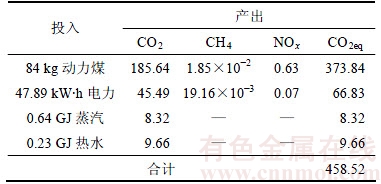
表4 粗炼工序的单位产品温室气体排放质量的I-O评估
Table 4 I-O assessment of greenhouse gas emission quality per product in smelting process kg
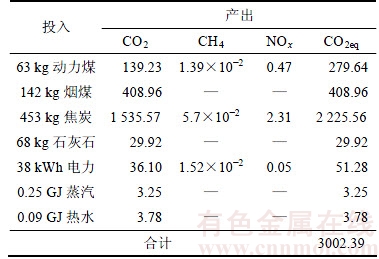
表5 精炼工序的单位产品温室气体排放质量的I-O评估
Table 5 I-O assessment of greenhouse gas emission quality per product in refining process kg
表6 企业A铅冶炼系统的单位产品温室气体排放质量
Table 6 Greenhouse gas emission quality per product for lead smelting system of enterprise A
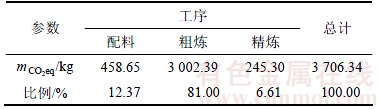
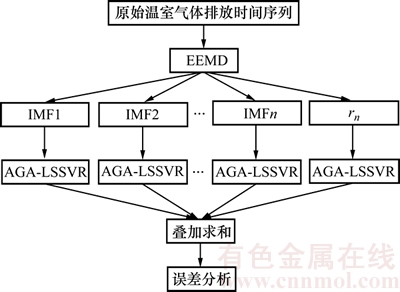
图3 EEMD-LSSVR预测模型
Fig. 3 EEMD-LSSVR prediction model
1) 对原始的风功率时间序列{x(t)}进行EEMD分解,得到不同时间尺度的n个本征模函数(intrinsic mode function, IMF)分量和1个残差余项rn[16-18]。
2) 针对每个IMF分量和残差余项rn,分别建立各自的LSSVR模型并进行预测。
3) LSSVR预测精度与正则化参数γ和径向基核函数宽度参数σ2密切相关,利用自适应遗传算法(adaptive genetic algorithm, AGA)优化γ和σ2[19-20],得到全部LSSVR模型的预测值。
4) 叠加不同尺度下温室气体排放预测值,将其作为最终的温室气体排放预测值。
5) 分析均方根误差(root mean square error, RMSE)。
2.2 EEMD-LSSVR预测模型的应用
图4所示为企业A在一段时间内通过实际污染物排放测试设备(包括Horiba MEXA-720 和HoribaMEXA-554JU)测出的铅生产过程的碳足迹时间序列,可以看出碳足迹时间序列的不稳定性,它主要是铅冶炼原料成分不同、生产过程不稳定性、系统非线性等因素所致。
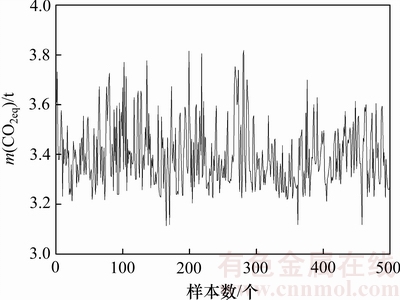
图4 企业A铅冶炼系统的单位产品温室气体排放的实测时间序列
Fig. 4 Test data of greenhouse gas emission per product of lead smelting system in enterprise A
为了得到更好的预测效果,首先对时间序列进行EEMD分解,得到7个IMF分量和1个剩余分量rn,如图5所示。从图5可以看出:IMF1和IMF2波动明显较大,比较复杂。由于径向基核函数是局部核函数,有较强的局部自适应能力,学习能力较强,通过调整核参数,就能够很好地模拟相应的信号,所以,对于IMF1和IMF2选用径向基核函数。IMF3~IMF7和rn相对来说波动不是很大。由于线性核是一种全局性核函数,有着较强的外推能力,适用于对变化比较平缓的信号进行建模,所以,对于IMF3~IMF7和rn选用线性核函数。
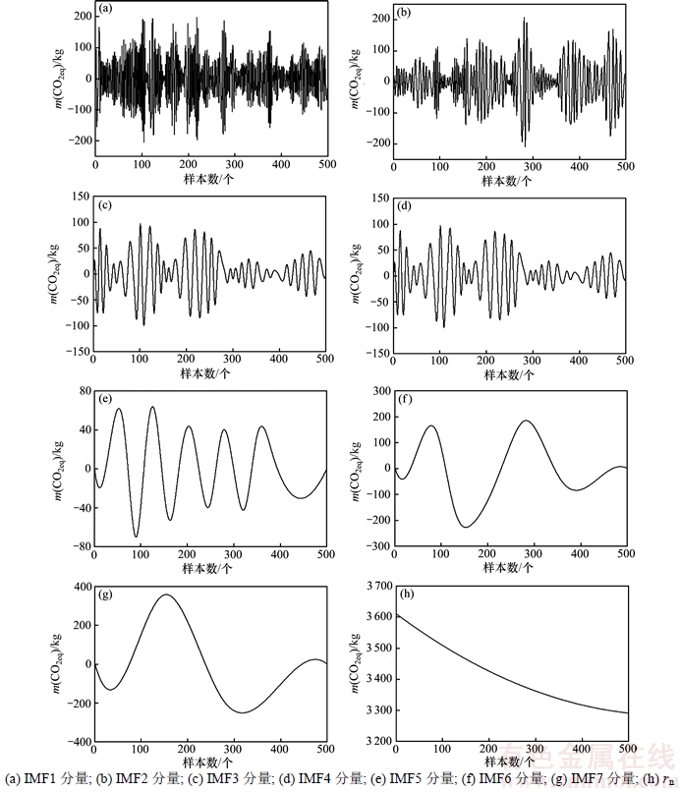
图5 单位产品温室气体排放时间序列的EEMD分解
Fig. 5 EEMD decomposition of greenhouse gas emission data per product
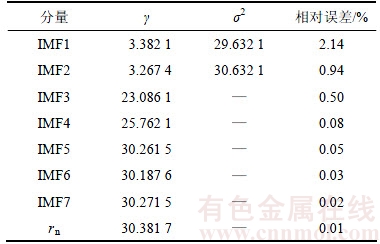
利用AGA算法优化LSSVR模型参数时,对LSSVR模型中γ和σ2进行二进制编码,产生随机初始化种群,其中种群规模为50,染色体长度为20(γ和σ2编码长度均为10),γ的范围为(0.1, 100),σ2的范围为(0.01, 40);然后,构造各染色体的适应度函数,计算适应度是否达到期望或满足最大迭代次数。若满足条件,则停止计算,输出优化参数。这里将最大迭代步数设置为500。图6所示为AGA寻找LSSVR最佳参数时的适应度进化曲线。通过AGA算法优化,最终得到的各个分量的LSSVR预测模型中γ和σ2的最优值以及误差如表7所示。从表7可以看出:第1个高频分量波动大,因而相对误差较大,而其余各个分量的预测效果较好。
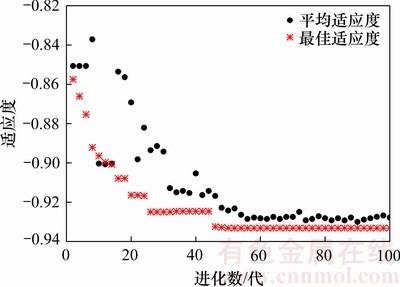
图6 AGA寻找LSSVR最佳参数的适应度曲线
Fig. 6 Fitness curves for LSSVR parameters optimized by AGA
表7 LSSVR参数取值以及预测相对误差
Table 7 LSSVR parameters value and prediction error
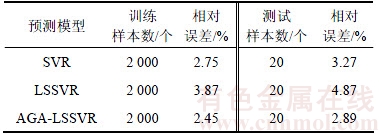
为了验证本文所采用模型的优越性,分别采用SVR,LSSVR和AGA-LSSVR这3种模型对铅冶炼温室气体排放进行预测,比较其效果。采用3种模型分别进行预测,得到的预测曲线如图7所示,预测误差如表8所示。从表8可见:SVR,LSSVR和AGA-LSSVR对训练样本的温室气体排放预测均方根误差分别为2.75%,3.87%和2.45%,对测试样本的温室气体排放预测均方根误差分别为3.27%,4.87%和2.89%。可见AGA-LSSVR对铅生产过程各工序预测精度最高,SVR的预测精度要比LSSVR的精度高。LSSVR与SVR相比虽然提高了运算速度,但LSSVR求解的是线性方程,方程解满足极值条件,但不能保证全局最优解。
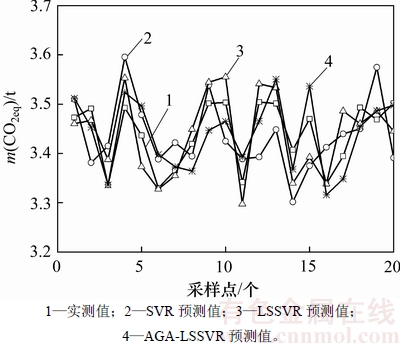
图7 单位产品温室气体排放实测值与预测值对比
Fig. 7 Comparison between measured and predicted value of greenhouse gas emission
表8 SVR,LSSVR和AGA-LSSVR对温室气体排放预测精度对比
Table 8 Prediction performance comparison of greenhouse gas emission between SVR,LSSVR and AGA-LSSVR
3 结论
1) 利用投入产出法建立了铅冶炼过程生命周期内各工序(配料工序、粗炼工序、精炼工序)的CF模型,计算了铅冶炼过程的CO2当量排放量,发现粗炼工序单位产品的m(CO2eq)远比其他工序的高。
2) EEMD分解温室气体排放时间序列可以有效地提高预测时间序列的规律性和平稳性。利用AGA-LSSVR组合模型可以有效地预测铅冶炼系统温室气体排放的变化,对训练样本和测试样本的温室气体排放预测均方根误差可分别达2.45%和2.89%。
参考文献:
[1] OU X M, YAN X X, ZHANG X L. Life-cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions for electricity generation and supply[J]. Applied Energy, 2011, 88(1): 289-297.
[2] 蒋继穆. 我国铅锌冶炼现状与持续发展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(1): 52-62.
JIANG Jimo. Status and sustainable development of lead and zinc smelting industry in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(1): 52-62.
[3] Eco-innovation Action Plan (ETAP). The carbon trust helps UK businesses reduce their environmental impact[R]. UK: Press Release, 2007: 80-90.
[4] Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology (POST). Carbon footprint of electricity generation[R]. London, UK: Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology, 2006: 110-113.
[5] Carbon Trust. Carbon footprint measurement methodology[R]. London, 2007: 55-60.
[6] 庞博慧. 基于碳足迹理论的水电枢纽工程能耗分析研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学建筑工程学院, 2014: 9-11.
PANG Bohui. Energy consumption analysis of hydropower projects based on carbon footprint theory[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University. School of Architecture and Engineering, 2014: 9-11.
[7] 王微, 林剑艺, 崔胜辉, 等. 碳足迹分析方法研究综述[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2010, 33(7): 77-84.
WANG Wei, LIN Jianyi, CUI Shenghui, et al. An overview of carbon footprint analysis[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 33(7): 77-84.
[8] ACHARYA U R, NG E Y K, TAN J, et al. Thermography based breast cancer detection using texture features and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2012, 36(3): 1503-1510.
[9] QU J, ZUO M J. An LSSVR-based algorithm for online system condition prognostics[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(5): 6089-6102.
[10] 桑丙玉, 王德顺, 杨波, 等. 平滑新能源输出波动的储能优化配置方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(22): 3700-3706.
SANG Bingyu, WANG Deshun, YANG Bo, et al. Optimal allocation of energy storage system for smoothing the output fluctuations of new energy[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(22): 3700-3706.
[11] MONFARED M, RASTEGAR H, KOJABADI H M. A new strategy for wind speed forecasting using artificial intelligent methods[J]. Renewable Energy, 2009, 34(5): 845-848.
[12] LEI Yaguo, LIN Jing, HE Zhengjia, et al. A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 35(1/2): 108-126.
[13] ZHANG Xiaoyuan, ZHOU Jianzhong. Multi-fault diagnosis for rolling element bearings based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and optimized support vector machines[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 44(1/2): 127-140.
[14] TANG Ling, YU Lean, WANG Shuai, et al. A novel hybrid ensemble learning paradigm for nuclear energy consumption forecasting[J]. 2012, 93: 432-443.
[15] 高成康, 陈杉, 陈胜, 等. 中国典型钢铁联合企业的碳足迹分析[J]. 钢铁, 2015, 50(3): 1-8.
GAO Chengkang, CHEN Shan, CHEN Sheng, et al. Carbon footprint analysis of typical chinese iron and steel enterprises[J]. Iron & Steel, 2015, 50(3): 1-8.
[16] LEI Yaguo, HE Zhengjia, ZI Yangyang. Application of the EEMD method to rotor fault diagnosis of rotating machinery[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2009, 23(4): 1327-1338.
[17] LEI Yaguo, HE Zhengjia, ZI Yangyang. EEMD method and WNN for fault diagnosis of locomotive roller bearings[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(6): 7334-7341.
[18] WANG Tong, ZHANG Mingcai, YU Qihao, et al. Comparing the applications of EMD and EEMD on time & ndash; frequency analysis of seismic signal[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2012, 83(6): 29-34.
[19] CHAKRA N C C, SARAF D N. History matching of petroleum reservoirs employing adaptive genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2015, 6(4): 653-674.
[20] 魏立新, 李兴强, 李莹, 等. 基于改进自适应遗传算法的冷连轧轧制规程优化设计[J]. 机械工程学报, 2010, 46(16): 136-141.
WEI Lixin, LI Xingqiang, LI Ying, et al. Optimization of tandem cold rolling schedule based on improved adaptive genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(16): 136-141.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2017-04-13;修回日期:2017-07-18
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51478470) (Project(51478470) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:罗曦,博士,讲师,硕士生导师,从事低碳城市规划、能源规划研究;E-mail: 41693131@qq.com