合金元素Ti对Mo合金性能及组织结构的影响
成会朝,范景莲,卢明园,刘 涛,田家敏
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:采用粉末冶金方法制备Ti含量为0.3%~1.0%的Mo-Ti合金。通过力学性能实验、光学显微镜观测和SEM分析,对Mo-Ti合金的性能和组织结构进行研究分析。结果表明,在Mo粉中添加TiH2所制备的合金比纯钼金属具有更好的拉伸性能,并且当Ti含量为0.8%时合金的力学性能最好;合金元素Ti除部分固溶到钼基体外,还在晶粒之间和晶粒内部生成(Mo, Ti)xOy弥散相,这些(Mo, Ti)xOy弥散相的生成,一方面净化了晶界氧,使晶粒之间的孔隙减少,同时也阻止晶粒在烧结时的晶粒长大,有利于合金性能的提高;但Ti添加量过多时,会使晶界之间产生过量的(Mo, Ti)xOy质点,使晶粒之间的结合能力减弱,对合金性能产生不利影响。⊙
关键词:Mo-Ti合金;拉伸强度;第二相粒子
中图分类号:TG146.4 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)02-0395-05
Effect of alloyed element Ti on property and microstructure of Mo alloy
CHENG Hui-chao, FAN Jing-lian, LU Ming-yuan, LIU Tao, TIAN Jia-min
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Mo-Ti alloy with 0.3%-1.0%Ti was fabricated by powder metallurgy process. The property and microstructure of Mo-Ti alloy were studied and analyzed through mechanical property test, optical microscope observation and SEM analysis. The result indicates that the property of the alloy by adding TiH2 powder is better than pure Mo. The alloy has the best mechanical property when the additional amount of Ti is 0.8%. The portion of alloyed element Ti solves in the Mo matrix while the others form (Mo, Ti)xOy distributed phase. This kind of dispersion phase absorbs the oxygen in the grain boundary, decreases the number of pores between grains as well as prohibits the growth of the grain that altogether plays a positive role in the enhance of the alloy property. However, over-dose (Mo, Ti)xOy particles could weaken the binding ability of the grains, which would generate negative influence on the property of the alloy.
Key words: Mo-Ti alloy; tensile strength; second phase particles
金属钼具有热膨胀系数低和蒸汽压低,熔点、耐磨性、热导率和高温强度高,以及与多种金属优良的互溶性等特点,因而广泛应用于钢铁工业、电子工业、航空及核能技术、金属压力加工等领域[1-3]。目前,制备钼制品的主要方法有熔炼法和粉末冶金法[4]。但随着现代制品形状的不断复杂化,采用熔炼法制备出钼锭,再后续加工对材料浪费很大,而采用粉末冶金方法不仅可以制备形状复杂的零部件,而且后续加工少,材料利用率高。但是,纯钼金属烧结后若不经后续处理(如形变强化和退火处理),则材料的脆性非常明显,强度也不高[5-6]。但采用粉末冶金方法制备出的制品一般接近最终形状,这些产品很难再进行挤压、锻造、热轧等强化处理来改善塑性,因而,产品的脆性较高,应用受到很大限制。因此,从材质上使钼的性能提高,是扩大粉末冶金方法在钼制品研制与应用的关键。
目前,添加合金元素使钼合金化是提高钼性能的有效方法之一[7-9]。金属钼是第VIA族、体心立方结构元素,能够与多种元素发生固溶反应。Ti是高熔点元素,它固溶到钼基体后,不仅不降低钼合金的高温性能,而且会使钼的晶格常数发生改变,使钼的脆性降低[10-12]。目前,国外已有一些关于Mo-Ti合金的研究报道,但在国内关于Mo-Ti合金的研究报道很少。本文作者采用粉末冶金方法制备出Mo-Ti合金,研究烧结温度和TiH2添加量对合金力学性能和组织结构的影响。
1 实 验
实验所用Mo粉平均粒度为2.9 μm,氧含量为0.13%,高纯TiH2粉粒度为50 μm。首先,向Mo粉中添加TiH2粉,采用机械球磨分别制备出Ti质量分数分别为0.3%,0.6%,0.8%和1.0%的Mo-Ti混合粉。所有批次粉末均采用相同球磨工艺,图1所示为Mo-Ti球磨粉的SEM像。由图1可以看到,经球磨后,一些颗粒得到细化。将制备出的粉末在300 MPa压力下,采用钢模压制成拉伸试样。压坯先在H2气氛下,于 1 000 ℃预烧2 h,然后,将预烧样在H2保护下进行高温烧结,烧结温度为1 890~1 950 ℃,保温时间均为3 h。
图1 Mo-0.5Ti球磨粉的SEM像
Fig.1 SEM image of Mo-0.5Ti milled-powder
采用LJ-3000A型机械式拉力试验机测定样品拉伸性能。JSM-5600LV型扫描电镜观察粉末形貌和样品断口组织。MeF3A型金相显微镜分析样品相组成。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Mo-Ti合金力学性能
为研究Ti添加量对Mo-Ti合金性能的影响规律,将不同Ti含量的坯体在1 920 ℃烧结3 h,测其抗拉强度。图2所示为Ti含量对钼合金抗拉强度的影响。从图2可以看到,添加少量Ti后,合金的抗拉强度与纯钼金属的相比有较大提高,并且抗拉强度随着Ti添加量的增加而增大。当Ti含量为0.8%时,合金的抗拉强度达到最高,但Ti含量进一步提高时,合金性能又开始下降。金属Ti容易被氧化,TiH2脱氢后生成的Ti除了部分扩散到Mo基体与Mo形成固溶体外,其余将与合金中存在的少量氧或气氛中的氧形成Ti的氧化物。随着TiH2添加量增多,脱氢后形成的Ti含量也增多,固溶进Mo中的Ti含量也增多,从而使合金强度提高。但是,当TiH2含量进一步增多时,也会使合金中Ti的氧化物含量增大,它们过多地存在于晶界之间,会使得晶界的结合强度减弱,从而使合金性能降低。
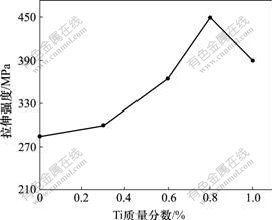
图2 Ti含量对合金抗拉强度影响
Fig.2 Effect of Ti content on tensile strength of Mo alloy
从图2可以看到,当Ti含量为0.8%和1.0%时钼合金的性能最好。为了研究烧结温度对Mo-Ti合金性能的影响规律,将不同烧结温度下制备的Ti含量为0.8%和1.0%的2种钼合金进行性能对比。图3所示为Mo-0.8Ti和Mo-1.0Ti合金在1 890,1 920和1 950 ℃分别烧结3 h后的拉伸强度曲线。从图3可以看 到,在上述温度下烧结,Mo-0.8Ti合金的抗拉强度都高于Mo-1.0Ti合金的抗拉强度,但2种成分合金的抗拉强度都随着烧结温度的升高先增加,然后下降。因此,1 920 ℃是Mo-Ti合金比较理想的烧结温度。

1—Mo-0.8% Ti; 2—Mo-1.0% Ti
图3 烧结温度对Mo-Ti合金抗拉强度的影响
Fig.3 Effects of sintering temperature on tensile-strength of Mo alloy
2.2 组织结构分析
图4所示为Mo-Ti合金断口的SEM像。从图4可以看到,Mo晶粒粒径较小,一般在10~20 μm之 间,但在Mo晶粒和Mo晶界之间有大量的球形颗粒和球形凹坑,并且分布比较均匀。晶粒表面的球形凹坑是球形颗粒粘附在另一晶粒而留下的痕迹。通过对存在于晶粒之间以及晶粒表面的球形颗粒做能谱分析(图5),发现这些颗粒均由Mo,Ti和O元素构成,即为(Mo, Ti)xOy化合物。从能谱分析结果可以发现, (Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒中的氧含量基本在14%左右。 (Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒的形成原因,是由于TiH2脱氢新生成的Ti原子活性很高,同时它又与氧的结合能力很强,这样,就很容易与合金中氧或烧结气氛中的氧发生反应生成Ti的氧化物,而Ti的氧化物在1 800 ℃左右时就会形成液态[13],在高温烧结时它就会与Mo晶体表面活性较强的Mo原子发生如下反应:
TimOn+Mo→(Tim-1, Mo)On+Ti
当反应发生一定时间后形成(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒,在烧结完成降温时,这些(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒为了保持最低能量状态,就以球形状存在晶粒之间。

图4 Mo-Ti合金断口的SEM像
Fig.4 SEM images of fracture sections of Mo-Ti alloy

图5 晶粒表面的球形颗粒能谱分析
Fig.5 EDX analysis of particles of grain boundary
(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒的形成,有利于合金中氧的净化和孔隙的减少。图6所示为样品预烧后的断口面扫描能谱分析结果,可以看到,样品预烧后还有0.7%左右的氧含量。大量的研究结果表明,如果纯钼或钼合金样品在预烧或中温烧结后还有较多的氧含量,那么,烧结时这些氧就极易形成孔隙,导致密度下降[14-15]。
Mo-Ti合金在预烧后仍有0.7%的氧,但在1 920 ℃烧结后的致密度仍高达96.9%以上,这主要是由于 (Mo, Ti)xOy的生成,使钼晶粒上的氧得到净化,这样,在烧结过程中就不会形成孔隙。孔隙减少,会使钼晶粒之间的结合强度增加,从而有利于合金强度的提高。

图6 样品预烧后的断口面扫描能谱分析
Fig.6 EDX analysis of fracture section of presintered specimen
(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒不仅能够影响合金的致密度,而且对合金在烧结过程中的晶粒长大起到阻碍作用。图7~9所示为Mo-0.8%Ti合金在1 890~1 950 ℃烧结后断口的SEM像,并未发现晶粒有明显长大。由于Mo-Ti合金都是沿晶断裂,因此,无法确定在晶粒内部是否也存在(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒。图10所示为Mo-0.8%Ti合金的显微组织,可以看到,在晶界和晶面有一些黑色斑点,尺寸较小的斑点是(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒,其粒径为1~3 μm,因此,可以确定(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒既存在于Mo晶界之间,也存在于晶内。(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒的形成,既起到净化氧、减少孔隙的效果,同时,也阻止了晶粒在烧结过程中的长大,有利于合金性能的提高。但过多数量的(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒夹在Mo晶粒之间,会使得Mo晶粒之间的结合强度减小,因此,当TiH2添加量过多时,除部分Ti固溶到Mo基体外,还有较多的Ti与烧结气氛中的氧发生反应生成氧化物,使晶粒之间生成大量(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒,从而使合金性能下降。
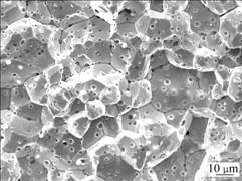
图7 Mo-0.8%Ti合金在1 890 ℃烧结后断口的SEM像
Fig.7 SEM image of fracture section of Mo-0.8%Ti alloy sintered at 1 890 ℃

图8 Mo-0.8%Ti合金在1 920 ℃烧结后断口的SEM像
Fig.8 SME image of fracture section of Mo-0.8%Ti alloy sintered at 1 920 ℃
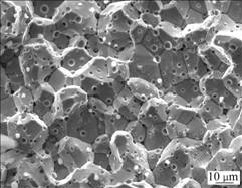
图9 Mo-0.8%Ti合金在1 950 ℃烧结后断口的SEM像
Fig.9 SME image of fracture section of Mo-0.8%Ti alloy sintered at 1 950 ℃

图10 Mo-0.8%Ti合金显微组织
Fig.10 Microstructure of Mo-0.8%Ti alloy
3 结 论
a. 由于Ti可以固溶到Mo基体和净化合金中的氧,向钼中添加少量的Ti元素能够有效地提高合金的抗拉强度,并且当烧结温度为1 920 ℃、Ti添加量为0.8%时,合金的拉伸强度最大。
b. Ti元素的加入,使Mo-Ti合金生成(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒,这些颗粒既减少了孔隙的生成,同时也有效地阻止了晶粒在烧结过程中的晶粒长大,对合金性能的提高产生有利影响。但当Ti添加量过多时,会使Mo晶粒之间产生过量的(Mo, Ti)xOy颗粒,使晶界的结合强度变小,从而又对合金性能产生不利影响。
参考文献:
[1] 张久兴, 刘燕琴, 刘丹敏, 等. 微量La2O3对钼的韧化作用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(1): 13-17.
ZHANG Jiu-xing, LIU Yan-qin, LIU Dan-min, et al. Toughness of La2O3-doped Mo alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(1): 13-17.
[2] Zheng J H, Bogaerts W F, Vancoillie I, et al. Initial corrosion evaluation of molybdenum based alloys for the NET divertor design[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 1991, 18: 179-183.
[3] 向铁根. 钼冶金[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2002: 5.
XIANG Tie-gen. Molybdenum metallurgy[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2002: 5.
[4] Sharma I G, Chakraborty S P, Suri Α K. Preparation of TZM alloy by aluminothermic smelting and its characterization[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 393: 122-128.
[5] Mrotzek T, Hoffmann A, Martin U. Hardening mechanisms and recrystallization behaviour of several molybdenum alloys[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2006, 24: 298-305.
[6] Cockeram B V. The mechanical properties and fracture mechanisms of wrought low carbon arc cast (LCAC), molybdenum-0.5pct titanium-0.1pct zirconium (TZM), and oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) molybdenum flat products[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2006, 418: 120-136.
[7] Hiroaki K, Yuji K, Tamaki S, et al. Development of Mo alloys with improved resistance to embrittlement by recrystallization and irradiation[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1996, 223/227: 557-564.
[8] Cockeram B V. Measuring the fracture toughness of molybdenum-0.5 pet titanium-0.1 pet zirconium and oxide dispersion-strengthened molybdenum alloys using standard and subsized bend specimens[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33A: 3685-3707.
[9] Scibetta M, Chaouadi R, Puzzolante J L. Analysis of tensile and fracture toughness results on irradiated molybdenum alloys, TZM and Mo-5%Re[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2000, 283/287: 455-460.
[10] Fumio M, Kensuke S. Mechanical properties and neutron-irradiation effects in the welds of molybdenum and its alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1991, 179/181: 592-595.
[11] Takeshi I, Yutaka H, Masahiro N, et al. Effects of Ti addition on carbon diffusion in molybdenum[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 414: 82-87.
[12] SHI Hui-Ji, Christophe K, Guy P. High temperature isothermal and thermomechanical fatigue on a molybdenum-based alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 247(1/2): 180-186.
[13] Myoung K Y, Yutaka H, Hiroaki K, et al. Recrystallization of TiC dispersion Mo-alloy[J]. Int J of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 1996, 14: 355-364.
[14] Takanori K, Yutaka H, Seiji N, et al. Effects of sintering conditions on the properties of sintered molybdenum[C]//Kwang Y E. 2006 Powder Metallurgy World Congress. Busan: Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute, 2006, Part(Ⅱ): 1153-1154.
[15] Calderon H A, KostorzG G. Microstructure and plasticity of two molybdenum-base alloys (TZM)[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1993, 160(2): 189-199.
收稿日期:2008-02-25;修回日期:2008-06-02
基金项目:教育部新世纪人才计划基金资助项目(NCET-05-0693);国家军工配套项目(JPPT-115-2-662)
通信作者: 范景莲(1967-),女,湖南澧县人,教授,博士生导师,从事难熔金属与硬质合金研究;电话:0731-8836652;E-mail: nanotung@mail.pmworld.cn