
Tribological behavior and wear mechanism of
resin-matrix contact strip against copper with electrical current
TU Chuan-jun(涂川俊), CHEN Zhen-hua(陈振华),
CHEN Ding(陈 鼎), YAN Hong-ge(严红革), HE Feng-yi(何凤亿)
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
Received 8 October 2007; accepted 18 February 2008
Abstract: The resin-matrix pantograph contact strip (RMPCS), which has excellent abrasion resistance with electrical current and friction-reducing function, was developed in view of the traditional contact strips with high maintenance cost, high wear rate with electrical current and severe damage to the copper conducting wire. The characteristics of worn surfaces, cross-section and typical elemental distributions of RMPCS were studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersion spectrometry (EDS). The wear behavior and arc discharge of RMPCS against copper were investigated with self-made electrical wear tester. The results show that the electrical current plays a critical role in determining the wear behavior, and the wear rate of the RMPCS against copper with electrical current is 2.7-5.8 times higher than the value without electrical current. The wear rate of the contact strip increases with the increase of the sliding speed and electrical current density. The main wear mechanism of RMPCS against copper without electrical current is low stress grain abrasive and slightly adhesive wear, while arc erosion wear and oxidation wear are the dominate mechanism with electrical current, which is accompanied by adhesive wear during the process of wear.
Key words: electric contact friction and wear; RMPCS; wear mechanism; arc erosion
1 Introduction
The electric contact friction and wear means that tribological pairs in the electric field have the tribological behavior with electric current. The main characteristic of it is that the wear of tribological pairs is governed by the high electric current[1-4]. A special couple of tribological pairs of the contact strip against copper-quality contact wire of electric railway are made[5-6]. The wear of the contact strip against contact wire with electrical current, which is affected by the machine, friction, chemistry, heat transfer and electric, etc[7-11], is an extremely complicated process and brings about great difficulty for the research. A great deal of study have been done for the electric contact friction and wear. KLAPAS et al demonstrated that the wear of the contact strip against contact wire with electrical current was not only closely affected by the compatibility of different materials of tribological pairs, but also affected by relative sliding speed, current and contact pressure[12]. PRITCHARD et al indicated that the loss of lubricant on the worn surface would lead to high wear rate of the contact strip in rain-water or humid atmosphere[13]. MATSUYAMA proved that the wear mechanism of the contact strip against contact wire with electrical current could be divided into mechanical wear, chemistry wear and electrical wear[8], and this conclusion had been extensively recognized. Based on the wear mechanism of MATSUYAMA, many scholars have engaged in the study of the influence of different load and current on the wear behavior of tribological pairs. KUBO et al considered that the wear of the contact strip with electrical current was the inter superposition of mechanical wear and electrical wear. As the two models were combined, the wear behaviors of tribological pairs with electrical current were different from those without electrical current[7]. HE et al[3] indicated that the increase of worn surface temperature of the copper- matrix contact strip against red copper contact wire with electrical current would make the surface crack expand to a critical value, which would form a special morphology. JIA et al[14] indicated that the wear of tribological pairs was closely related to the change of the surface temperature. The worn structure of tribological pair would be damaged obviously at high temperature, which caused a decrease of peeling resistance perfor-mance on the surface layer, and speeded the phase transformation. All these researches have given the universality rule of the wear of the contact strip against contact wire with electrical current. However, there is few report about the effects of the arc erosion under off-line on the worn surface and wear mechanism of the contact strip against contact wire with electrical current.
Based on the previous investigation[15], RMPCS with excellent abrasion resistance under electrical current, good conductive and friction-reducing function, was produced by the processes of hot rolling, two-step pressing and solidification technology using high temperature modified-resin as binder, and adding electric conductive phase, lubricating phase and intensifier fiber. The effects of sliding time and speed on the wear rate of RMPCS under different electric current were investigated. The effects of the arc erosion under contacting-separating on the wear behavior of RMPCS against copper were analyzed. And the arc erosion process and mechanism of RMPCS against copper were also discussed by theoretical analysis of crack formation of electric contact material[16-17].
2 Experimental
2.1 Experimental materials
The chemical composition and physical properties of RMPCS material are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of RMPCS material
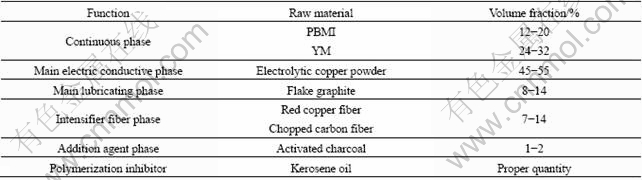
Table 2 Physical properties of RMPCS material

2.2 Preparation process
The preparation process of RMPCS material is shown in Fig.1.
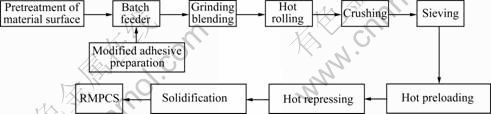
Fig.1 Preparation process of RMPCS material
2.3 Performance measurement of RMPCS against copper
The bulk density of RMPCS was measured by Archimedes method. The Rockwell hardness of RMPCS was accurately measured by HRB sclerometer (HR- 150DT) with the head diameter of 1.587 mm under the load of 980.7 N. The resistivity of RMPCS was measured by a digital intelligent four-probemeter (SZ-82). The impact strength of RMPCS was measured by izod impact test (CBJ-11J). The characteristics of the worn surfaces, cross-section and typical elemental distributions of RMPCS were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JSM-6700F) and energy dispersion spectrometry (Oxford EDS).
The reduction change in thickness and arc discharge of RMPCS against copper were investigated with self-made electrical wear tester. The wear surface was machined with the dimension of 5.0 mm in length in the sliding direction and 20.0 mm in width. The counterpart disk was pure copper, whose surface was thoroughly cleaned with acetone before and after the wear tests. The surface of RMPCS and pure copper were polished by waterproof abrasive paper of 800#. An analog off-line arc trench gap was machined on the surface of the counterpart disk with the dimension of 40.0 mm in length in the sliding direction, 50.0 mm in width and 0.5 mm in thickness. The tail-height of electrical spark was continuously recorded with camera installation. The performance measurement test of RMPCS against copper with and without electrical current was carried out in laboratory environment, in the air at the ambient temperature of (25±2) ℃, with the current density of 105, 195 and 285 A/cm2. The disk was rotated at a sliding speed of 16.7, 25, 33.3 and 41.7 m/s, respectively. The normal load of contact was 50 N. The wear tests were interrupted every 5 min until the sliding time reached 60 min. The schematic of the apparatus is shown in Fig.2.
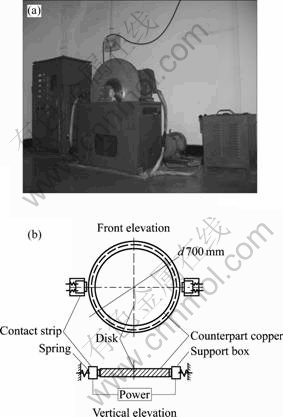
Fig.2 Schematic of self-made apparatus of high speed electrical wear tester
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of electrical current on wear rate of RMPCS
Fig.3 shows the effect of sliding speed and test time on the wear rate of RMPCS under different electric currents. Table 3 gives the test results of RMPCS against copper with and without electrical current.
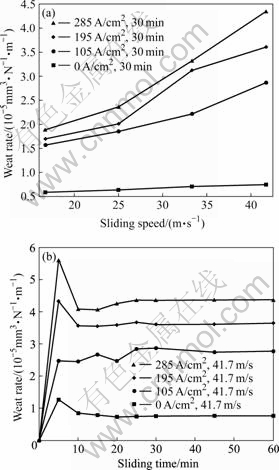
Fig.3 Effect of sliding speed (a) and sliding time (b) on wear rate of RMPCS under different electric currents
As shown in Fig.3(a), the wear rate of RMPCS against copper with electrical current is higher than that without electrical current under the same speed. In air and at ambient temperature, the wear rate of RMPCS increases with the increase of current density. The wear rate of RMPCS against copper with electrical current is 2.7-5.8 times higher than that without electrical current under the same conditions. At a sliding speed of 41.7 m/s and sliding time of 30 min, with the current density of 105, 195 and 285 A/cm2, the wear rates of RMPCS are 2.87×10-5, 3.61×10-5 and 4.35×10-5 mm3/(N?m), respectively. While the wear rate of RMPCS is only 0.75×10-5 mm3/(N?m) without electrical current under the same condition. Moreover, the wear rate of the contact strip increases with the increase of sliding speed and electrical current density. These indicate that the wear behavior of RMPCS against copper is mainly influenced by the existent current. With electrical current, the heat sources[7, 14] of wear surface during the process of wear mainly come from friction heat, arc heat and Joule heat of contact resistance, which obey the Joule’s law. However, the arc heat is mainly produced under electrical current. There are periodically small space between the tribological pairs in separating or contacting course. When the pairs are separated from contact, it results in the increase of contact resistance[18] and a rapid reduction of the electric current in circuit, and instantaneous high voltage is induced between tribological pairs for inductances. When high self-induction voltage break down the air in the contact space, electric spark is produced. The arc heat induced by rotating the closed curve can be given by[7]
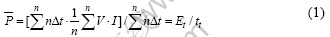
where 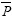 stands for arc heat (W), n stands for the number of arc rotating the closed curve, ?t stands for the maintenance schedule method (s), V stands for instantaneous high self-induction voltage (V), I stands for instantaneous electrical current (A), Et stands for releasing energy of arc rotating the closed curve, and tt stands for total discharge time of arc rotating the closed curve (s). The electric spark, induced in the process between the separating or contacting course, has the characteristic of high density of energy and short duration. Under electrical current, the high temperature induced by arc discharge[19-20] causes the material of contact interface to sequentially experience the cycle process of heating, phase transition of heat decomposition or thermal melting, then degradation reaction of resin-matrix as well as the flow and condensation process of liquid melt metal, which cause serious arc erosion. Simultaneously, the mechanical abrasive wear, induced by the contact pressure, causes the surface layer to transfer and spall. So the wear of the contact strip is intensified, as the energy of the worn surface of RMPCS against copper with electrical current is more than that without electrical current.
stands for arc heat (W), n stands for the number of arc rotating the closed curve, ?t stands for the maintenance schedule method (s), V stands for instantaneous high self-induction voltage (V), I stands for instantaneous electrical current (A), Et stands for releasing energy of arc rotating the closed curve, and tt stands for total discharge time of arc rotating the closed curve (s). The electric spark, induced in the process between the separating or contacting course, has the characteristic of high density of energy and short duration. Under electrical current, the high temperature induced by arc discharge[19-20] causes the material of contact interface to sequentially experience the cycle process of heating, phase transition of heat decomposition or thermal melting, then degradation reaction of resin-matrix as well as the flow and condensation process of liquid melt metal, which cause serious arc erosion. Simultaneously, the mechanical abrasive wear, induced by the contact pressure, causes the surface layer to transfer and spall. So the wear of the contact strip is intensified, as the energy of the worn surface of RMPCS against copper with electrical current is more than that without electrical current.
Fig.3(b) also shows that the wear rate of RMPCS increases rapidly with prolonging time in the initial stage, and then decreases to a steady level, finally the wear rate tends to be stable. Under the same test conditions, the wear rate is maximal at the electrical current density of 285 A/cm2, followed by that at 195 A/cm2, 105 A/cm2 and without electrical current. The main reason is that the contact area with the worn surface of tribological pairs is smaller during the initial stage of wear, thus the wear is larger. With the increase of time, transferring surface films between tribological pairs are formed, which can effectively prevent direct contact of tribological pairs and consequently reduce the wear mass loss of RMPCS.
As shown in Table 3, the worn surface morphologies of RMPCS without electrical current are more integral and smooth than those with electrical current. During the process of wear with electrical current, the tail-height of electrical spark at the sliding speed of 41.7 m/s is higher than that at the sliding speed of 16.7 m/s. The main reason is that the frequency of starting arc increases with the increase of sliding speed. Therefore, a large quantity of heat is produced on the actual contacting area of the part joints through friction, which results in rapid increase in wear mass loss.
Table 3 Test results of RMPCS against copper
3.2 Worn surfaces and cross-section of RMPCS
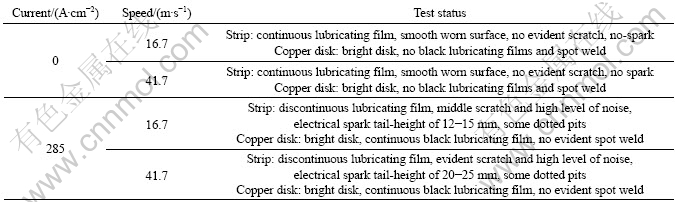
Figs.4 and 5 show the SEM micrographs of the worn surface and cross-section of RMPCS without and with the electrical current density of 285 A/cm2 under the load of 50 N at the sliding speed of 41.7 m/s for 30 min, respectively. The white arrows indicate the sliding direction. The results of EDS analysis on the worn surface with electrical current are listed in Table 4.
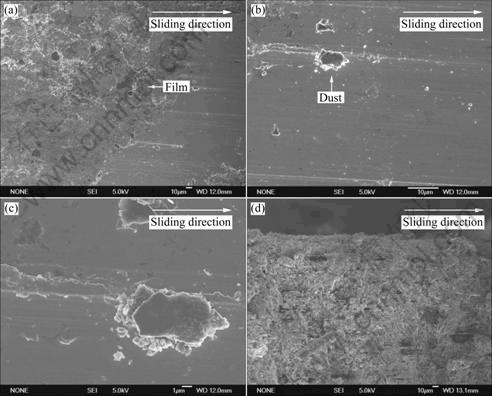
Fig.4 SEM micrographs of worn surface (a, b, c) and cross-section (d) of RMPCS without electrical current
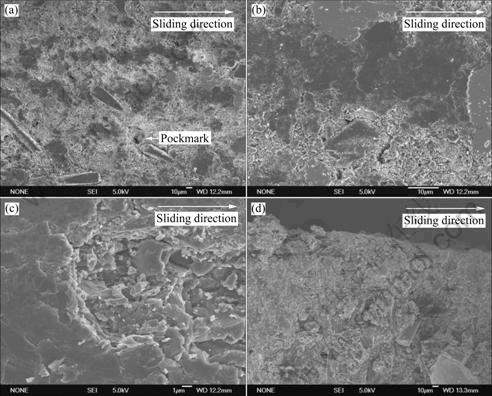
Fig.5 SEM micrographs of worn surface (a, b, c) and cross-section (d) of RMPCS with electrical current density of 285 A/cm2
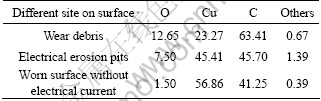
Table 4 EDS analysis results of worn surface with electrical current (mass fraction, %)
As shown in Fig.4, no remarkable spallation on the worn scar surfaces (Figs.4(a)-(c)) of RMPCS is found at high speed without electrical current. The worn surfaces of RMPCS are smooth, dense and there are good interface junctions only with some uniform and micro scars along the sliding direction. Under the external force, the abrasive scraps are produced by crashing and shearing around the contact area during the process of wear (Dust worn zone in Fig.4(b)), and the interaction of tribological pairs mostly shows machining wear. As shown in Fig.5, light and shade stripe and uniformly distributed dotted pits scratch on the worn surfaces (Fig.5(a) and (b)) are presented. At high speed with electrical current, electric spark is induced between the cycling contact or separation of tribological pairs. Resin- matrix of the contact region is thermally decomposed, much small-molecule volatile substance is produced and the low melting point metal is introduced into thermal melting, then different sizes of cyclones (Fig.5(a): Pockmark zone) are formed during the process of condensation, as the temperature of contact strip surface and subsurface sharply increases under the arc heat. The size of arc erosion pits on the worn surface is about 20.5 ?m×30.5 ?m. The surface of RMPCS shows eddy current morphology[21], which leads to electrical arc erosion wear. And oxidation particle is spalled strongly from the worn surface at high temperature. The main reason is that the contact area with the worn surface is ablated rapidly, which leads to thermal decomposition reaction of resins, oxidation reaction of carbon materials as well as thermal melting of metals. The wear behavior results from contact temperature increasing in the course of arc erosion. Adhesive wear and oxidation wear are the main wear mechanisms during the process of wear.
It can be seen in Fig.4(d) and Fig.5(d) that RMPCS possesses a homogeneously dense structure at the high speed without electrical current. Particle chaos arrangement starch and agglomeration-free zone are found on the cross-section, which shows good dispersive and no obvious preferred orientation. The average grain size of friction deformed layer is less than 10 ?m. No obvious plastic deformation can be observed in the cross- section. The interface between the matrix and other phases is well bonded. The microstructure of cross sections for the specimens at high speed with electrical current is smooth, dense and uniform, and the average grain size of friction deformed layer is about 10 ?m. No cross cracks and obvious porosities are presented. These indicate that the wear mechanism is mainly surface part spilling at high speed with electrical current.
As shown in Table 4, the oxygen contents of the electrical erosion pits and wear debris increase with the increase of contacting temperature and testing time, achieving about 12.65% and 7.50% respectively. The EDS analysis results of the worn surface with and without electrical current indicate that the worn surface of RMPCS may be oxidized during the process of wear with electrical current. And the different heat sources caused by electric arc, contact resistance and friction at high speed with large current lead to the oxidation of copper and formation of oxide particles. The result shows that the content of elemental Cu is decreased while the content of elemental O increases.
3.3 Wear mechanism of RMPCS against copper
RMPCS against copper presents different wear mechanisms with or without electrical current. The continuous surface films, which are grown up between the worn surfaces of RMPCS against copper, mainly come from the flake graphite and dielectric oxide of copper during the process of wear without electrical current. Therefore, the surface films are damaged before resin-matrix fails, which can effectively prevent the direct contact of worn surface during the process of wear. As time prolongs, the continuous lubricating film forms on the worn surface. The dynamic equilibrium of self-lubricating film is kept due to the balance of squeezing out and restricting of solid lubricant. So the main wear mechanism of RMPCS against copper without electrical current is low stress grain abrasive and slightly adhesive wear. The electrical arc caused by the off-line between tribological pairs is serious during the process of wear with electric current, which results in abundant heat of the electrical arc, especially at higher current density. The contact regions may thermally decompose and oxidize, then present the characteristic of oxidation wear under the instantaneous high temperature, which is caused by electric arc, contact resistance and friction at high speed with high electrical current. As the temperature of contact strip surface and subsurface sharply increases under the arc heat, cyclones of different sizes are formed in the process of condensation. Therefore, the main wear mechanism of RMPCS against copper with electrical current is intersecting of arc erosion wear and oxidation wear, which is accompanied by adhesive wear during the process of wear.
4 Conclusions
1) The wear behavior of RMPCS against copper is mainly influenced by the existent current. The wear rate of the contact strip increases with the increase of sliding speed and electrical current density. The wear rate of RMPCS against copper with electrical current is 2.7-5.8 times higher than that without electrical current under the same test conditions.
2) During the process of wear with electrical current, the tail-height of electrical spark at the sliding speed of 41.7 m/s is higher than that at the sliding speed of 16.7 m/s.
3) The main wear mechanism of RMPCS against copper without electrical current is low stress grain abrasive and slightly adhesive wear. While the main wear mechanism of RMPCS against copper with electrical current is the intersecting of arc erosion wear and oxidation wear, which is accompanied by adhesive wear during the electrical wearing processes.
4) The localized worn surface of the contact strip forms the circinate pits and presents the characteristic of arc erosion wear by arc heat induced in the separating or contacting course.
References
[1] HE D H, MANORY R, SINKIS H. A sliding wear tester for overhead wires and current collectors in light rail systems [J]. Wear, 2000, 239(1): 10-20.
[2] ZHAO H, BARBER G C, LIU J. Friction and wear in high speed sliding with and without electrical current [J]. Wear, 2001, 249(5/6): 409-414.
[3] HE D H, MANORY R, GRADY N. Wear of railway contact wires against current collector materials [J]. Wear, 1998, 215(1/2): 146-155.
[4] TU Chuan-jun, CHEN Zhen-hua, CHEN Gang, YAN Hong-ge, XIA Jin-tong, LIU Jun. Current status and development of carbonic system pantograph strip for electric locomotive [J]. Carbon Techniques, 2007, 26(4): 23-29. (in Chinese)
[5] AZEVEDO C R F, SINATORA A. Failure analysis of a railway copper contact strip [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2004, 11(6): 829-841.
[6] JIA S G, LIU P, REN F Z, TIAN B H, ZHENG M S, ZHOU G S. Sliding wear behavior of copper alloy contact wire against copper-based strip for high-speed electrified railways [J]. Wear, 2007, 262(8): 772-777.
[7] KUBO S, KATO K. Effect of arc discharge on wear rate of Cu-impregnated carbon contact strip in unlubricated sliding against Cu trolley under electric current [J]. Wear, 1998, 216(2): 172-178.
[8] MATSUYAMA S. Electric contact tribological behavior of pantograph [J]. Toyo Denki Giho, 1995, 91: 52-60.
[9] FENG Y, ZHANG M, XU Y. Effect of the electric current on the friction and wear properties of the CNT-Ag-G composites [J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(13): 2685-2692.
[10] NAGASAWA H, KATO K. Wear mechanism of copper alloy wire sliding against iron-base contact strip under electric current [J]. Wear, 1998, 216(2): 179-183.
[11] BOUCHOUCHA A, CHEKROUD S, PAULMIER D. Influence of the electrical sliding speed on friction and wear processes in an electrical contact copper-stainless steel [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2004, 223(4): 330-342.
[12] KLAPAS D, HACKAM R. Wear in a simulated power collection system for railways [J]. Electric Contacts Colloquium Digest, 1979, 13: 81-83.
[13] PRITCHARD C, WILLIAMSON P K. The laboratory simulation of pantograph wear [J]. Electric Contacts Colloquium Digest, 1979, 13: 91-93.
[14] JIA S G, LIU P, REN F Z, TIAN B H, ZHENG M S, ZHOU G S. Wear behavior of Cu-Ag-Cr alloy wire under electrical sliding [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 398(1/2): 262-267.
[15] CHEN Z H, TENG J, CHEN G, FU D F, YAN H G. Effect of the silicon content and thermomechanical treatment on the dry sliding wear behavior of spray-deposited Al-Si/SiCp composites [J]. Wear, 2007, 262(3/4): 362-368.
[16] KANG S, BRECHER C. Cracking mechanisms in AgSnO2 contact materials and their role in the erosion process [J]. IEEE Trans on CHMT, 1989, 12(1): 32-38.
[17] GUO Feng-yi, MIAO Sheng-zhang, YANG Wei, ZHAO Ran. The effect of electrical arc force on arc erosion morphology features of contact surfaces [J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University, 1999, 18(2): 140-143. (in Chinese)
[18] HOLM R. Electric contact theory and application [M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1967.
[19] HE D H, MANORY R. A novel electrical contact material with improved self-lubrication for railway current collectors [J]. Wear, 2001, 249(7): 626-636.
[20] LU C T, BRYANT M D. Thermoelastic evolution of contact area and mound temperatures in carbon graphite electrical contact [J]. Wear, 1994, 174(1/2): 137-146.
[21] YAMAGUCHI T, IWAI Y, INAGAKI S, UEDA M. A method for detecting bearing wear in a drain pump utilizing an eddy-current displacement sensor [J]. Measurement, 2003, 33(3): 205-211.
Foundation item: Project (06FJ3041) supported by the Key Laboratory Open Foundation of Hunan Province, China
Corresponding author: CHEN Zhen-hua, Tel: +86-731-8821648; E-mail: tcj122@yahoo.com.cn
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)