PDP玻璃中金属锌的环境溶出特性
姜鹏飞1,陈海焱1,陈梦君1, 2,蒋冬梅1
(1. 西南科技大学 固体废物处理与资源化教育部重点实验室,四川 绵阳,621010;
2. 清华大学 固体废物处理与环境安全教育部重点实验室,北京,100084)
摘要:通过BCR三步逐级提取法、TCLP程序和DTPA及EDTA生物可利用性提取法,对废弃等离子显示屏玻璃中金属锌的环境溶出特性进行研究。结果表明:废弃PDP玻璃前、后板中Zn的化学形态均以可交换与弱酸溶解态和可还原态为主,前板中可氧化态Zn含量高于残渣态,后板中则残渣态Zn含量高于可氧化态Zn含量。废弃PDP玻璃具有较高的环境浸出毒性,其中,Zn的高浸出毒性主要是由可交换与弱酸溶解态和可还原态决定的,前、后板中这2种形态Zn的浸出量分别占其浸出总量的91.06%和96.79%,而可氧化态和残渣态对其TCLP浸出毒性贡献不大。废弃PDP玻璃中Zn的生物有效提取绝对量较高,其中,后板中Zn的EDTA提取量高达812.17 mg/kg,废弃PDP玻璃潜在的生物可利用性非常高。
关键词:废弃PDP玻璃;TCLP;化学形态;BCR法;生物可利用性
中图分类号:X592 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)04-1589-06
Environment leaching characteristics of metallic Zn in waste PDP glass
JIANG Peng-fei1, CHEN Hai-yan1, CHEN Meng-jun1, 2, JIANG Dong-mei1
(1. Key Laboratory of Solid Waste Treatment and Resource Recycle, Ministry of Education,
Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China;
2. Key Laboratory for Solid Waste Management and Environment Safety,
Ministry of Education, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China)
Abstract: The environment leaching characteristics of metallic Zn in the glass of waste plasma display panel (PDP) were studied using the methods of three-step sequential extraction method (BCR method), toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) and DTPA&EDTA bioavailability extraction procedures. The results show that main chemical forms of Zn in waste PDP (front panel and back panel, FP&BP) are both exchangeable & weak soluble fraction and reducible fraction, the content of oxidizable fraction Zn is higher than that of residual fraction Zn in FP, and the content of BP residual fraction Zn is higher than that of its oxidisable fraction. The waste PDP glass has higher leaching toxicity, which rests with exchangeable &weak acid soluble fraction and reducible fraction. The leaching contents of Zn in FP&BP account for total are 91.06% and 96.79%, respectively, while the oxidizable and residual fractions have little contribution to the TCLP leaching toxicity. The absolute biological extracted effectively quantity of Zn in waste PDP is higher, and the content of EDTA-extractable Zn in BP is 812.17 mg/kg, which displays that waste PDP has higher potential biologic toxicity.
Key words: waste PDP glass; TCLP; chemical form; BCR method; biological effectiveness
近些年,等离子显示屏(Plasma display panel,PDP)因其具有发光效率好、具有记忆特性、响应时间快、视角大等优点而受到广泛关注,并有逐步取代传统的CRT和LCD的趋势[1]。但随着人们对显示屏大屏幕、薄型化需求的日益增长,PDP更新换代的速度也日益加快,许多未到年限的PDP被过早淘汰,形成了大量的电子垃圾。其中废弃的PDP玻璃因其附加值低,传统的方法又难以实现其资源化而直接被丢弃。此类不合理的电子垃圾处理处置,导致大量的重金属污染物进入自然环境,电子垃圾重金属污染问题也因此成为近年来人们关注的环境问题之一。锌(Zn)是国民建设中最常见的金属之一,其需求量很大。中国是目前世界上最大的锌消耗国,2005年中国的锌消耗量占世界锌消费总量的四分之一,锌消费增长的主要原因是镀锌钢用量的增长。据美国矿务局统计,根据世界上已探明的有色金属储量,锌的使用年限只有23 a[2]。为此,人们都开始日益重视锌的二次使用和循环使用,以满足对金属锌日益增长的需求。目前,亟待处理的废弃玻璃量大、含锌量高,是一种可观的锌二次资源。同时,由于锌等重金属不能被土壤微生物所降解,若随意丢弃可能在土壤中不断积累,一旦过量将具有较大的生物毒性,可能通过食物链对人体健康带来威胁,诸如锌热病等[3]。因此,研究PDP玻璃中锌的环境溶出特性一方面可以为金属锌的资源化再利用提供理论基础,另一方面,也为废弃PDP玻璃的安全、快速、高效处理处置提供科学依据。毒性浸出程序(Toxicity Characteristic leaching procedure,TCLP)通常用来作为评价固体废物是否是危险废物的标准[4]。多级提取法(Sequential extraction procedure,SEP)可以较好地反映重金属的化学形态变化信息,显示重金属的移动性和生物可利用性,该方法也可以间接地评价重金属的环境效应[5-6]。生物可利用性提取法是开展重金属污染风险评价的一种实验研究方法,表征重金属对人体和动物的生物可给性[7]。重金属化学形态的连续提取方法和生物可利用性分析在重金属污染土壤[8-10]、垃圾焚烧飞灰[11-13]、工业废渣[14-15]及河流底泥和沉积物[16-18]等方面已经广泛应用,而关于废弃玻璃中重金属污染特性研究的报道较少。本文作者采用改进的BCR三步逐级提取法、TCLP程序和有机络合提取法研究PDP玻璃中金属锌的化学形态、浸出毒性和生物可给性,综合评价了废弃PDP玻璃的环境溶出特性和环境风险,为PDP玻璃的处理处置与资源化提供科学依据。
1 实验
1.1 样品
实验所用废弃等离子体显示屏(PDP)玻璃由四川长虹集团提供。等离子体显示屏玻璃分为前板玻璃和后板玻璃,其最大的区别在于:后板玻璃一面涂有白色荧光粉,而前板则不含荧光粉。粗碎后的PDP玻璃再用行星球磨机破碎至10 mm以下作为实验样品。废弃PDP玻璃的组成由X线荧光光谱仪(Magix型,荷兰帕纳科公司)测定,结果以氧化物的形式表示,其主要组成(质量分数)如表1所示。实验中所用试剂,如无特别说明,均为分析纯。
1.2 PDP玻璃中锌的化学形态分析
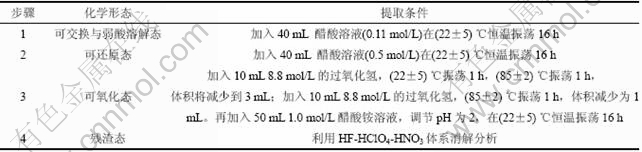
采用欧盟标准委员会(SMT)提出的改进的BCR三步逐级提取法对废弃PDP玻璃中锌的化学形态进行分析。逐级提取步骤如表2所示[19],每次浸取完毕,离心(3 000 r/min)分离30 min,取上清液用孔径0.45 μm的滤膜进行过滤,得到浸取液。用20 mL去离子水洗涤滤饼,离心,弃掉离心液,滤饼进行下一步提取。所得浸取液用原子吸收光谱测试仪(AA-6501,岛津公司)测定Zn浓度。
表1 PDP玻璃组成
Table 1 Chemical composition of PDP glasses %
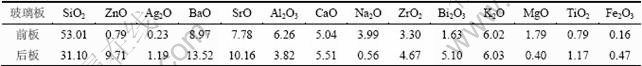
表2 BCR三步逐级提取条件
Table 2 Experiment conditions for sequentially extraction procedure of BCR3
1.3 PDP玻璃中锌的浸出毒性分析
采用美国国家环保局(US EPA)提出的毒性浸出程序(TCLP)[20]分析废弃PDP玻璃中锌的浸出毒性。TCLP实验步骤为:取2 g废弃PDP玻璃样品置于50 mL聚四氟乙烯离心管中,加入40 mL1号浸取液,盖紧瓶盖。在(22±3) ℃,振荡频率为(30±2) r/min条件下,浸取(18±2) h。浸取完毕,用孔径0.45 μm的滤膜进行过滤,所得滤液用原子吸收光谱测试仪(AA-6501,岛津公司)进行分析。
1.4 PDP玻璃中锌的生物可利用性分析
分别采用DTPA与EDTA 2种有机络合物作为提取剂对废弃PDP玻璃进行提取,分析金属锌的生物可利用性。DTPA提取法[21]步骤为:取10 g废弃PDP玻璃置于50 mL聚四氟乙烯离心管中,加入20 mL 0.005 mol/L DTPA与0.01 mol/L CaCl2的混合溶液(调节溶液的pH到7.3),盖紧离心管口,于往复式振荡器上振荡2 h。3 000 r/min离心20 min后取上清液,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤,用原子吸收光谱仪进行测定。EDTA提取法[22]条件如下:取2 g废弃PDP玻璃于50 mL聚四氟乙烯离心管,加入20 mL 0.05 mol/L EDTA溶液,此溶液用氨水(Ammonia solution)调节pH至7.0,振荡1 h。以3 000 r/min离心20 min后取上清液,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤,用原子吸收光谱仪测定Zn的含量。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 化学形态分析
重金属的毒性不仅与其金属总量有关,而且很大程度是由其化学形态分布决定,不同化学形态产生不同的环境效应,直接影响重金属的环境毒性、迁移及转化过程。根据改进的BCR三步逐级提取法,可交换与弱酸溶解态主要是可交换吸附的离子和碳酸结合的形态,在中性或弱酸性条件可释放进入水体和土壤,最容易对环境造成影响,对水体和生物可能具有直接的危害。可还原态主要是与无定形的铁锰氧化物和水化氧化物结合形态,在还原条件下易释放。可氧化态主要是与有机质和硫化物结合的形态,难溶于水,在强氧化条件下可以分解。残渣态是环境中最稳定的一种形态,对环境比较安全。采用改进的BCR三步逐级提取法对废弃PDP玻璃进行逐级提取,各化学形态中Zn含量(质量浓度)如下表3所示。
表3 废弃PDP玻璃中各化学形态Zn含量
Table 3 Zn content of each chemical form in waste PDP glasses mg/L
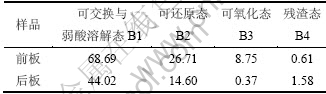
为了更好地了解废弃PDP中Zn不同化学形态的分布特征,将其不同化学形态所占总量的比例作图,4种化学形态分布如图1所示。结合表3和图1可知,BCR三步法逐级提取PDP玻璃前、后板,Zn在可交换与弱酸溶解态的溶出质量浓度分别为68.69 mg/L和44.02 mg/L,分别占前、后板锌总量的65.56%和72.68%,可还原态Zn前、后板溶出质量浓度分别为26.17 mg/L和14.60 mg/L,分别占各自锌总量的25.5%和24.11%。前板的可氧化态Zn的浸出质量浓度为8.75 mg/L,约占锌总量的8.35%,而只有0.59%的Zn存在于残渣态中。后板中残渣态Zn含量占2.61%,可氧化态中Zn含量最少,为0.60%。这表明,从废弃PDP玻璃中Zn的绝对和相对含量来看,因其主要以可交换与弱酸溶解态和可还原态的形式存在,在环境中稳定性较差,容易浸出,具有较大的环境风险。
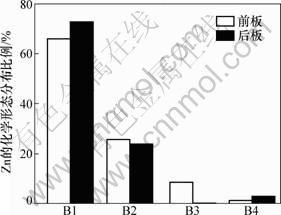
图1 废弃PDP玻璃中Zn的化学形态分布
Fig.1 Fractions of metallic Zn in waste PDP glasses
2.2 化学形态与浸出毒性关系分析
TCLP实验结果显示实验样品PDP玻璃前、后板中Zn均具有较高的浸出质量浓度,分别是215.03 mg/L和108.64 mg/L。
为了分析废弃PDP玻璃中Zn的浸出毒性与其化学形态分布的关系,分别对废弃PDP玻璃前、后板经逐级抽提后的残渣用TCLP鉴定其Zn的浸出毒性(各级残渣的浸出毒性鉴别分别记作FII,FIII,FIV)。如将PDP进行可还原态提取后,用TCLP鉴定Zn的浸出毒性,此次毒性浸出操作记作FIII。所得数据如表4所示。
表4 废弃PDP玻璃及逐级提取后残渣中Zn的TCLP浸出质量浓度
Table 4 Zn leaching concentrations from waste PDP glasses and corresponding residues after TCLP mg/L
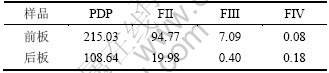
由表4可知,PDP玻璃前、后板中Zn的TCLP浸出浓度均最高,然后随着逐级提取的进行而依次减小,废弃PDP玻璃前、后板中Zn的TCLP浸出质量浓度顺序相同,从大到小依次为:原PDP玻璃、可交换与弱酸溶解态、可还原态、可氧化态。
将原废弃PDP玻璃中Zn的TCLP浸出浓度减去逐级抽提第1步后残渣的浸出质量浓度,得到可交换与弱酸溶解态所对应的TCLP浸出质量浓度,再将逐级抽提第1步后残渣的浸出质量浓度减去逐级抽提第2步后残渣的浸出质量浓度,得到可还原态所对应的TCLP浸出质量浓度,这样依次得到废弃PDP玻璃前、后板Zn的可交换与弱酸溶解态(F1)、可还原态(F2)、可氧化态(F3)所对应的TCLP浸出质量浓度,而残渣态(F4)所对应的TCLP浸出质量浓度即废弃PDP玻璃经过第3步逐级抽提后的TCLP浸出质量浓度,结果如表5所示。
表5 废弃PDP玻璃Zn及Zn各化学形态的TCLP浸出质量浓度
Table 5 TCLP leaching concentrations of Zn contained in waste PDP glasses and TCLP leaching concentrations each fraction of Zn mg/L
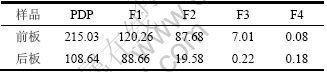
表5所示为废弃PDP玻璃所含Zn及其各化学形态TCLP浸出浓度的绝对值。各化学形态所对应的TCLP浸出浓度占相应废弃PDP玻璃的TCLP浸出质量浓度的比例如表6所示。
由表6可知,废弃PDP玻璃中Zn的浸出毒性主要来自于其可交换与弱酸溶解态(前板为55.93%,后板为81.61%)、可还原态(前板为40.76%,后板为19.98%),而可氧化态和残渣态对其浸出毒性的贡献不大,基本可以忽略。也就是说,在TCLP浸出毒性实验中,废弃PDP玻璃中Zn的可交换与弱酸溶解态、可还原态都可能进入溶液,对环境危害较大,而可氧化态和残渣态则比较稳定,很难进入溶液,对环境相对安全。
表6 Zn各化学形态TCLP浸出浓度分布
Table 6 Distribution of TCLP leaching concentrations from Zn Fractions %

2.3 生物可利用性分析
生物有效态的Zn指能够被生物有效利用的部分。Van der Hock等[23]研究显示DTPA和EDTA提取金属元素与小麦根和茎叶吸收金属含量有着显著的联系。Jegadeesan等[24]也通过对燃煤飞灰的提取实验发现EDTA和DTPA提取可以用来金属元素的潜在生物可利用性,并提倡推广到其他固体废物的管理方案中。DTPA和EDTA实验分别提取废弃PDP玻璃前、后板中的生物有效态Zn,结果如表7所示。
表7 废弃PDP玻璃中DTPA和EDTA可提取的生物有效态Zn
Table 7 DTPA- and EDTA-extractable Zn in waste PDP glasses mg/kg
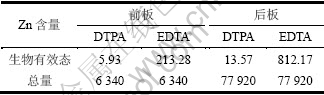
由表7可知,DTPA可提取Zn含量明显低于EDTA可提取Zn含量,主要的原因是不同提取剂本身的性质不同[25]。与PDP玻璃前、后板中Zn总量相比,其DTPA 可提取的生物有效态含量均较少,前、后板中分别为总量的0.09%和0.02%,EDTA可提取生物有效态含量相对较高,前板中约为3.36%和后板中约为1.04%。从DTPA 和 EDTA 可提取的生物有效态Zn含量的绝对值来看,前、后板数值均很高。如后板的EDTA可提取的生物有效态Zn的含量高达812.17 mg/kg。这表明:如果废弃PDP玻璃中的锌进入环境后,极有可能在植物体内富集。总的来看,废弃PDP玻璃中的生物有效态Zn的含量都很高。
3 结论
(1) 虽然PDP玻璃前、后板中Zn的化学形态有些区别,前板中Zn含量从高到低的顺序为:可交换与弱酸溶解态、可还原态、可氧化态、残渣态;后板中Zn含量从高到低的顺序为:可交换与弱酸溶解态、可还原态、残渣态、可氧化态,但均主要以可交换与弱酸溶解态和可还原态的形式存在,在环境中稳定性较差,容易浸出,具有较大的环境风险。
(2) 废弃PDP玻璃具有较高的浸出质量浓度,前、后板浸出质量浓度分别为215.03 mg/L和108.64 mg/L,Zn的高浸出毒性主要是由可交换与弱酸溶解态和可还原态Zn决定的,前、后板中其含量分别占各自Zn总量的91.06%和96.79%,而可氧化态和残渣态对其TCLP浸出毒性贡献不大。
(3) 尽管EDTA和DTPA可提取Zn含量相对于废弃PDP玻璃中Zn总量较低,最高值为前板的EDTA提取量,为3.36%,最低值为后板的DTPA提取量,为0.02%,但其绝对提取量非常高,如PDP玻璃后板中Zn的EDTA提取量就高达812.17 mg/kg,表明废弃PDP玻璃潜在的生物可利用性很高,很容易在植物体内富集。
参考文献:
[1] 郑姚生, 李俊涛, 汤勇明, 等. 等离子体显示器的现状与发展[J]. 真空, 2000, 10(5): 1-5.
ZHENG Yao-sheng, LI Jun-tao, TANG Yong-ming, et al. Development of plasma display panel[J]. Vacuum, 2000, 10(5): 1-5.
[2] 孔明, 王晔. 中国再生锌工业[J]. 有色金属, 2010(5): 51-55.
KONG Ming, WANG Ye. China secondary zinc production[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2010(5): 51-55.
[3] 朱贤英. 论有毒重金属污染对人体健康的危害及饮水安全[J].湖北教育学院学报, 2006, 23(2): 12-18.
ZHU Xian-ying. Heavy metal pollutions harm to our health & the safe of drinking water[J]. Journal of Hubei University of Education, 2006, 23(2): 12-18.
[4] Jang, Y C, Townsend T G. Leaching of lead from computer printed wire board and cathode ray tubes by municipal solid waste landfill leachates[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2003, 37: 4778-4784.
[5] Lambi E, Zhao F J, Zhang G, et al. Insitufixation of metals in soils using bauxite residue chemical assessment[J]. Environ Pollut, 2002, 118(3): 435-443.
[6] Papassiopi N, Konionyianni A, Vanuanidou K, et al. Assessment of chromium biostabilization in contaminated soils using standard leaching and sequential extraction techniques[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2009, 407(2): 925-936.
[7] Kin J Y, Kim K W, Lee J U, et al. Assessment of As and heavy metal contamination in the vicinity of Duckum Au-Agmine[J]. Korea Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2002, 24(3): 215-227.
[8] Davis A, Ruby M V, Bergstorm P D. The bioavailability of arsenic and lead in soils from the Butte, Montana mining distriit[J]. Environ Scie Technol, 1992, 23(3): 461-468.
[9] 雷鸣, 廖柏寒, 秦普丰, 等. 矿区污染土壤Pb、Cd、Cu的形态分布及其生物活性的研究[J]. 生态环境, 2007, 16(3): 807-811.
LEI Ming, LIAO Bo-han, QIN Pu-feng, et al. Fraction distributions and availability of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn in contaminated soils around mine[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2007, 16(3): 807-811.
[10] 何品晶, 章骅, 王正达, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰的污染特性[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 31(8): 972-976.
HE Pin-jing, ZHANG Hua, WANG Zheng-da, et al. Pollution characteristics of air pollution control residues from municipal solid waste incineration plant[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2003, 31(8): 972-976.
[11] 薛军, 王伟, 汪群慧. 传统酸浸和微波酸浸处理飞灰重金属的效果及重金属的形态变化特征[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(2): 535-539.
XUE Jun, WANG Wei, WANG Qun-hui. Traditional and microwave acid extraction of heavy metals from MSWI fly ash and their redistribution of fractions[J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(2): 535-539.
[12] Huang S J, Chang C Y, Mui D T, et al. Sequential extraction for evaluating the leaching behavior of selected elements in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2007, 149: 180-188.
[13] 郭朝晖, 程义, 柴立元, 等. 有色冶炼废渣的矿物学特征与环境活性[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(6): 1100-1105.
GUO Chao-hui, CHEN Yi, CHAI Li-yuan, et al. Mineralogical characteristics and environmental availability of non-ferrous slag[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(6): 1100-1105.
[14] 张清敏, 胡国臣, 王忠, 等. 粉煤灰中重金属Pb, Cd的有效态研究[J]. 农业环境保护, 2000, 19(6): 350-351.
ZHANG Qing-min, HU Guo-chen, WANG Zhong, et al. Study on availability of Pb, Cd in pulverous coal ash[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2000, 19(6): 350-351.
[15] Martin R, Sanchez D M, Gutierrez A M. Sequential extract ion of U,Th, Ce, La and some heavy metals in sediments from Ortigas river, Spain[J]. Talanta, 1998, 46: 1115-1121.
[16] 朱萍, 李晓晨, 马海涛, 等. 污泥中重金属形态分布与可浸出性的相关性研究[J]. 河海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 35(2): 121-124.
ZHU Ping, LI Xiao-chen, MA Hai-tao, et al. Correlation between chemical forms and leachability of heavy metals in sludge samples[J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2007, 35(2): 121-124.
[17] Davidson C M, Duncan A L, Litt lejohn D, et al. Acritical evaluation of the three-stage BCR sequential extraction procedure to assess the potential mobility and toxicity of heavy metals in industrially contaminated land[J]. Analyt ica Chimica Acta, 1998, 363: 45-55.
[18] 千娜, 金章东, 姚拓. 太湖梅梁湾沉积物中重金属的赋存相态及对污染历史的示踪[J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(4): 397-406.
QIAN Na, JIN Zhang-dong, YAO Tuo. Chemical fractions of heavy metals of sediments in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu and tracing for its pollution history[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2007, 19(4): 397-406.
[19] Pueyo M, Mateu J, Rigol A, et al. Use of the modified BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure for the study of trace element dynamics in contaminated soils[J]. Environ Pollut, 2008, 152: 330-341.
[20] EPA U S. Test methods for evaluating solid waste[M]. Washington DC: Office of Solid Waste, 1996: 846-847.
[21] Lindsay W L, Norvell W A. Development of a DTPA Soil Test for Zinc, Iron, Manganese, and Copper[J]. Soil Science Societyof AmericaJournal, 1978, 42: 421-428.
[22] Wear J I, Evans C E. Relationship of zinc uptake by corn and sorghum to soil zinc measured by three extractants[J]. Soil Science Societyof AmericaJournal, 1968, 32: 543-546.
[23] van der Hock E E, Bonouvrie P A, Comans R N J. Sorption of As and Se on mineral components of fly ahs: Relevance for leaching processes[J]. Appl Geochem, 1994, 9: 403-412.
[24] Jegadeesan G, Al-Abed S R, Patricio P. Influence of trace metal distribution on its leach ability from coal fly ash[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87: 1887-1893.
[25] Gupta A K, Sinha S. Assessment of single extraction methods for the prediction of bioavailability of metals to Brassica juncea L. Czern. (var. Vaibhav) grown on tannery waste contaminated soil[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2007, 14: 144-150.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2011-06-14;修回日期:2011-09-20
基金项目:四川省教育厅青年基金资助项目(10ZB012);清华大学固体废物处理与环境安全教育部重点实验室开放基金资助项目(SWMES2010-09)
通信作者:陈海焱(1964-),男,四川简阳人,教授,从事固体废弃物处理处置与资源化研究;电话:13808111780;E-mail:chenhai-yan@163.com